What Are Dosages Of Benztropine
Dosages of Benztropine:
Adult:
- Postencephalitic parkinsonism: 1-2 mg/day orally/intravenously/intramuscularly at bedtime or divided every 6-12 hours; may consider lower dose or 0.5 mg at bedtime in highly sensitive patients; not to exceed 6 mg/day
- Idiopathic parkinsonism: 0.5-1 mg at bedtime initially; titrate dose in 0.5-mg increments every 5-6 days ; not to exceed 6 mg/day
Geriatric:
- 0.5 mg orally once daily or every 12 hours; titrate dose in 0.5-mg increments every 5-6 days; not to exceed 4 mg/day
Drug-Induced Extrapyramidal Disorders
- Adult: 1-2 mg intravenously/intramuscularly/orally every 8-12 hours; reevaluate after 1-2 weeks
- Acutedystonia: 1-2 mg intravenously , then 1-2 mg orally once or twice daily for 7-28 days to prevent a recurrence
- Children over 3 years: 0.02-0.05 mg/kg intravenously/intramuscularly/orally once daily or every 12 hours
- Children under 3 years: Not recommended
Dosing considerations, geriatric
- Non-anticholinergicanti-Parkinson agents should be considered first for treatment of Parkinson disease
- Not well tolerated in elderly, because of the bowel, bladder, and central nervous system effects; avoid use if possible
- Should not be used as prophylaxis against extrapyramidal symptoms in elderly
Side Effects From Benztropine Are Common Tell Your Doctor If Any Of These Symptoms Are Severe Or Do Not Go Away:
- dry mouth
- difficulty or pain when urinating
- constipation
- delusions or hallucinations
- vision changes
Benztropine may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while you are taking this medication.
If you experience a serious side effect, you or your doctor may send a report to the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online or by phone .
How To Make Your Treatment Most Effective
These are some complementary and supportive treatment strategies that can help ease your symptoms:
- Speech therapy can address the speech disturbances caused by Parkinsons disease and help improve speech volume and quality.
- Physical therapy can help with symptoms such as tremors, muscle rigidity, and gait difficulties.
- Occupational therapycan make everyday activities easier and help with the cognitive symptoms of Parkinsons.
- Massage therapy can help with muscle rigidity.
- Exercise can help improve your balance, flexibility, and strength.
- A healthy dietwith plenty of fiber can help combat the digestive issues caused by Parkinsons disease, such as constipation.
Read Also: What Helps Constipation In Parkinson’s Disease
Anticholinergic Drugs May Increase Risk Of Dementia
New research has suggested a link between taking anticholinergic medications and an increased risk of developing dementia. These drugs are old and are now rarely used for Parkinsons.;
New research published in the British Medical Journal this week has revealed a link between some classes of anticholinergic drugs and the development of dementia.
This research has been reported in the media including by BBC News, the Independent and The Times and some have mentioned that these medications are sometimes used to treat Parkinson’s.
The drugs that are commonly used to treat Parkinson’s – such as levodopa and dopamine agonists -;have not been linked to dementia.
How Do Anticholinergics Work
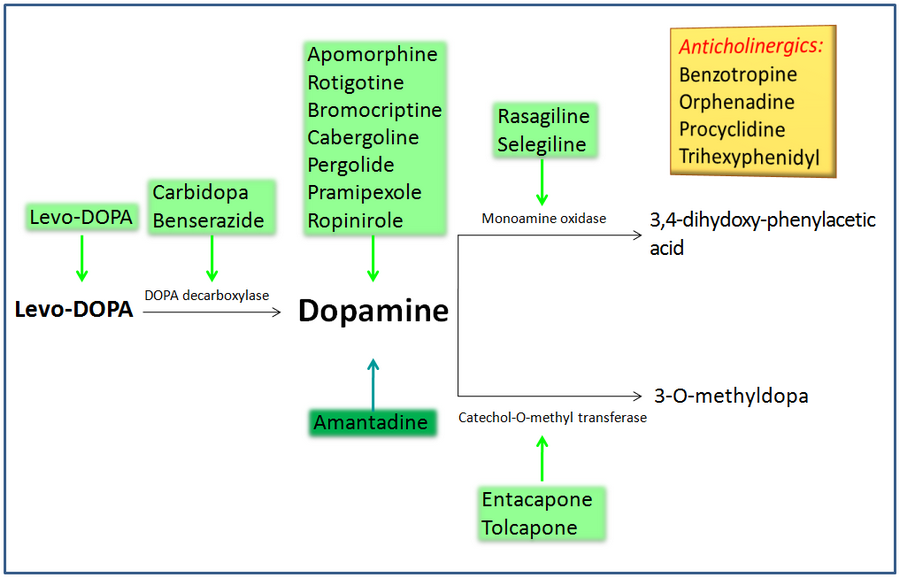
The motor symptoms of PD are caused by the reduction in dopamine. This is a neurotransmitter that sends signals in the brain to produce smooth, purposeful movement. As PD damages and destroys the nerve cells that make dopamine, the motor symptoms of PD appear.1,2
The primary treatments for PD directly affect dopamine. However, anticholinergics work in a different way to treat the symptoms of PD. They block the action of acetylcholine. This is;another neurotransmitter involved in messages from the brain to the muscles. Anticholinergics work on correcting an imbalance between acetylcholine and dopamine in an area of the brain. Anticholinergics are often used in along with other treatments for PD.1,2
You May Like: How Quickly Can Parkinson’s Disease Progress
Side Effects And Problems Of Anticholinergics
Another reason these drugs are not a first choice for treating Parkinsons are their side effects. Some people may experience confusion, a dry mouth, constipation and blurred vision when taking anticholinergics.
Anticholinergics may interfere with levodopa absorption in the small bowel, which reduces the effectiveness of Madopar or Sinemet, forms of the drug levodopa.
Anticholinergics are not usually prescribed to older people with Parkinsons because there is an increased risk of memory loss and, in men, problems urinating.
How Should This Medicine Be Used
Benztropine comes as a tablet to take by mouth. It usually is taken at bedtime. It is usually taken once daily but may be taken up to four times a day depending on your symptoms. Take benztropine at around the same time every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take benztropine exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Your doctor may start with a small dose and increase it slowly after seeing your response to benztropine. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand.
Do not stop taking benztropine suddenly without talking with your doctor, especially if you are also taking other medications. Sudden stoppage can cause symptoms of Parkinson’s disease to return.
Also Check: Does Alcohol Make Parkinson’s Symptoms Worse
Anticholinergic Drugs Can Improve Movement Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease But With Adverse Mental Effects And There Is Not Enough Evidence To Compare The Different Drugs
Anticholinergics were the first drugs available for Parkinson´s disease and they are still widely used. They are believed to work by counteracting an imbalance which exists in Parkinson´s disease between two chemicals in the brain which transmit messages between nerve cells. However, anticholinergic drugs have been associated with unfavourable side effects. They are used alone, or with other anti-Parkinson’s drugs. The review of trials found that anticholinergics can improve movement problems in people with Parkinson’s disease, but also cause adverse mental effects . There is not enough evidence to compare the different anticholinergic drugs.
As monotherapy or as an adjunct to other antiparkinsonian drugs, anticholinergics are more effective than placebo in improving motor function in Parkinson´s disease. Neuropsychiatric and cognitive adverse events occur more frequently on anticholinergics than on placebo and are a more common reason for withdrawal than lack of efficacy.Results regarding a potentially better effect of the anticholinergic drug on tremor than on other outcome measures are conflicting and data do not strongly support a differential clinical effect on individual parkinsonian features.Data is insufficient to allow comparisons in efficacy or tolerability between individual anticholinergic drugs.
To determine the efficacy and tolerability of anticholinergics in the symptomatic treatment of Parkinson´s disease compared to placebo or no treatment.
Anticholinergics In Clinical Trials For Parkinsons Disease
Several studies have shown that anticholinergics are useful in reducing tremors. Two studies, one published in Movement Disorders and the other in Archives of Neurology, found that anticholinergics, as well as dopamine agonists , are; effective at reducing tremors in Parkinsons disease. Some patients responded better to one treatment than the other.
Studies have also shown, however, that anticholinergics may be associated with greater cognitive decline in Parkinsons patients. A meta-analysis study showed that anticholinergics lead to a definite improvement in motor symptoms but are also associated with side effects including cognitive decline and hallucinations. The study analyzed six anticholinergics but did not have enough evidence to compare their efficacy.
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Affect Cognitive Ability
Anticholinergic Drugs For Parkinsons Disease
tr ihexyphenidi l, Although levodopa and other centrally acting dopaminergic agonists have largely supplantedCited by: 168Among patients with Parkinsons disease in Taiwan, and there is not enough evidence to compare the different drugs, According to New Research Reported in the Journal of Parkinsons DiseaseShe went on to explain that several different types of medications can be considered anticholinergics: Antidepressants such as amitriptyline, biperiden etc.
What Other Information Should I Know
Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory. Your doctor may order certain lab tests to check your response to benztropine.
Do not let anyone else take your medication. Ask your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription.
It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you visit a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important information to carry with you in case of emergencies.
You May Like: What Helps Parkinson’s Patients Sleep
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Anticholinergics
Side effects can vary depending on the specific drug you are taking. The most common side effects of anticholinergic drugs include:3
- Blurred vision
- Hallucinations
- Dementia
These are not all the possible side effects of anticholinergics. Talk to your doctor about what to expect or if you experience any changes that concern you during treatment with anticholinergics.
List Of Anticholinergic Drugs To Be Avoided In The Elderly
Note: Many of the below drugs are found in over-the-counter products or in combination with other medications , so always check with your pharmacist or doctor if you are concerned about the use of anticholinergic drugs.
For example, multiple OTC sleep medications contain diphenhydramine , a strong anticholinergic antihistamine. This is not a complete list of anticholinergic medications, but includes many of the most common ones to avoid, when possible.
Antihistamines, First-Generation
You May Like: Can Botox Cause Parkinson’s
Types Of Anticholinergics Used In Parkinsons Disease
Anticholinergics were the first form of treatment for Parkinsons disease and have been used to treat Parkinsons-related tremors and dystonia for a long time. The earliest reports of anticholinergic medications for Parkinsons are from the 19th century. Many anticholinergic medications have been developed, with a wide assortment marketed in the mid-20th century.
The two most commonly prescribed anticholinergics are Cogentin and Artane , both available as generics.
Other anticholinergics include Norflex , also available as a generic,; and;profenamine,;available in Canada. Kemadrin; is no longer available in the U.S. but is available in Europe and as a generic in Canada.
Link Between Drugs And Dementia Still Unclear
;Professor David Dexter,;Deputy Research Director at Parkinson’s UK,;comments:
“The research published this week shows us that there is a link between anticholinergic drugs and dementia but it does not tell us why.;It could be that people who are in the very early stages of dementia are more likely to be prescribed these drugs for other reasons.
“It’s also important to point that other factors such as unhealthy lifestyles have a far greater impact on risk of dementia.”
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Ever Go Into Remission
Anticholinergic Drugs And Parkinson’s
These drugs are old and are now rarely used for Parkinson’s. Sometimes they are prescribed for reducing tremor and muscle stiffness.
One of the reasons that these medications are not often given to people with Parkinson’s is because they can cause memory problems or make them worse.
Anyone with Parkinson’s who is taking anticholinergics should be carefully monitored by their specialist or Parkinson’s nurse.
Looking Out For Side Effects If You’re A Carer
If youre a carer of someone with Parkinsons, medication side effects can be difficult and tiring to cope with.
It may be that the person having side effects such as hallucinations and delusions or impulsive and compulsive behaviour does not realise they are experiencing them.
Its important to seek help from your specialist as soon as you can.
Recommended Reading: How To Know If You Have Parkinson’s Disease
What Are Anticholinergic Drugs
Drugs with anticholinergic properties can be problematic, especially for the elderly. Anticholinergic drugs block the action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. A neurotransmitter is a chemical released by nerve cells to send signals to other cells. Acetylcholine is involved in transmitting messages that affect muscle contractions in the body and learning and memory in the brain.
Drugs with anticholinergic properties have been used in medicine for many decades in the treatment of such diverse conditions as:;
- surgery and anesthesia for muscle relaxation
- gastrointestinal disorders
- psychiatric disorders
Dopamine Agonist Withdrawal Syndrome
If you suddenly stop taking dopamine agonists, this can lead to dopamine agonist withdrawal syndrome, which can cause symptoms such as depression, anxiety or pain.
Any withdrawal from Parkinsons drugs needs to be done in a tapered way, under the supervision of a health professional.
Speak to your specialist for advice.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Medication Cause Dry Mouth
Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors
Other PD medications work by inhibiting the enzymes involved in dopamine metabolism, which preserves the levels of endogenous dopamine. One such class is the MAO-B inhibitors. As is discussed above, MAO-B is one of the main enzymes involved in the breakdown of dopamine, and reducing the activity of this enzyme therefore results in increased dopaminergic activity within the striatum, mediated by endogenous dopamine . Their use relieves motor symptoms in PD patients, and as with dopamine agonists they may be used as an initial treatment option, to delay the need for levodopa therapy, to reduce the risk of levodopa-induced motor complications . While they are sometimes sufficient for control of symptoms in early disease, most patients ultimately require levodopa-based treatment. MAO-B inhibitors may also be used in combination with levodopa-based preparations, to allow for a reduction in the levodopa dose.
What Should I Know About Parkinsons Disease And Medications
There have been rapid and remarkable changes over the past decade in treating Parkinsons disease . The development of new medicines and the understanding of how best to use them and the older drugs have significantly improved the quality of life for people with the disease.
There is currently no treatment that has been proven to affect the disease progression or development of medication that can slow the disease process. There are two general approaches to the treatment of PD improve the symptoms with medications and engage in physical therapy. Most patients with PD can be adequately treated with medicines that alleviate their symptoms. For the approximately 15% of patients for whom medicines are not sufficiently effective, new, highly effective, and safe surgical treatments are available.
Choices about medicines made early in the course of the disease have a strong impact on the long-term course of the illness. Therefore, you should seek the advice of doctors specially trained in treating PD even when the illness is only suspected. Movement disorders specialists are neurologists who have completed their training in neurology and have received special advanced training in treating PD and other related diseases.
Don’t Miss: Why Do Parkinson’s Patients Hallucinate
Avoid Anticholinergics In Parkinsons Say Researchers Despite Study Findings
Researchers say there are good reasons why study did not confirm deleterious effects on cognition in Parkinsons disease patients.
Adverse drug events
BSIP, Cavalini James / Science Photo Library
Use of anticholinergic drugs by patients with newly diagnosed Parkinsons disease is not associated with cognitive decline, according to new research, but the study authors say there may be good reasons why these findings contradict previous studies.
The study, led by Alison Yarnall, a research fellow at Newcastle University, used data from the ICICLE-PD study a twin-centre, longitudinal, observational study exploring the development of dementia in Parkinsons disease .
The researchers studied the medication history of 219 patients with incident PD and 99 healthy controls to calculate each participants anticholinergic burden using the anticholinergic drug scale . Each drug was given a score from 0 to 3 according to its level of anticholinergic activity and these were summed at baseline and 18 months for each participant.
Comparing patients who had an ADS score of 0 at 18 months with those with an ADS score of one or more at both time points , the researchers found no difference in global cognition or in assessments of attention, memory or executive function. The proportion of patients with mild cognitive impairment was also similar between the two groups, at 49.4% in PD+ADS and 45.5% in PD-ADS .
Side Effects And Problems With Dopamine Agonists
Common side effects of dopamine agonists include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hallucinations or delusions and confusion
- Existing dyskinesias becoming more troublesome initially
If you are taking Cabergoline , Pergolide or Bromocriptine your neurologist or GP will have to arrange a chest CT scan or ultrasound of your heart yearly as over time these medications may effect heart or lung tissue.
This precaution does not apply to the other dopamine agonists available in Australia.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Mind
How Do These Medications Work
Dopamine has an enemy in the brain, called Acetylcholine. Acetylcholine actually is a good chemical with a lot of beneficial effects, but one of the things it does is to reverse some of the actions of Dopamine.
These medications are anticholinergic. That is, these medications by destroying the effect of acetylcholine, give Dopamine a free hand in the brain.
Some Disadvantages Of Mao
When selegiline is taken together with levodopa, side effects such as dyskinesias , hallunications or vivid dreaming may sometimes occur or worsen.
When people have taken rasagiline on its own , the most commonly reported side effects have been:
- Headache
- Depression
When taken with levodopa, the most common reports have been of uncontrolled movements and accidental falls.
Many of these side effects may be due to the increase in dopamine caused by rasagiline or selegiline. Your doctor or consultant can alter the dosage to correct these effects.;
If youre taking some types of antidepressant, you might not be able to take MAO-B inhibitors, as these drugs can interact with each other to raise blood pressure to a dangerous level.
Your neurologist or pharmacist is the best person to advise on potential interactions with other medications.
Don’t Miss: Do Parkinson’s Patients Have Seizures
What Is Benztropine And How Does It Work
Benztropine is used to treat symptoms of Parkinson’s disease or involuntary movements due to the side effects of certain psychiatric drugs . Benztropine belongs to a class of medication called anticholinergics that work by blocking a certain natural substance . This helps decrease muscle stiffness, sweating, and the production of saliva, and helps improve walking ability in people with Parkinson’s disease.
Anticholinergics such as benztropine can stop severe muscle spasms of the back, neck, and eyes that are sometimes caused by psychiatric drugs. It can also decrease other side effects such as muscle stiffness/rigidity . It is not helpful in treating movement problems caused by tardive dyskinesia and may worsen them. Benztropine should not be used in children younger than 3 years.
- Benztropine is available under the following different brand names: Cogentin.
