The Cerebellum And Parkinsonian Akinesia/rigidity
Parkinsons disease is not a homogenous disease and has two predominant forms: akinesia and rigidity and prominent resting tremor . Akinesia can be defined as a delay or a failure in movement initiation , particularly for self-initiated movements. Functional neuroimaging studies using PET or blood oxygen leveldependent functional MRI frequently demonstrated increased activation in the cerebellum in patients with Parkinsons disease during performance of various upper limb movements . For example, during externally or internally timed simple finger movements , motor timing , complex sequential movements , bimanual two-hand coordinated tasks or two different motor tasks simultaneously , patients with Parkinsons disease OFF medication showed hyperactivation in the cerebellum.
Brain areas more activated in patients with Parkinsons disease than in normal subjects during automatic execution of sequential movements. Modified from, with permission from Oxford University Press.
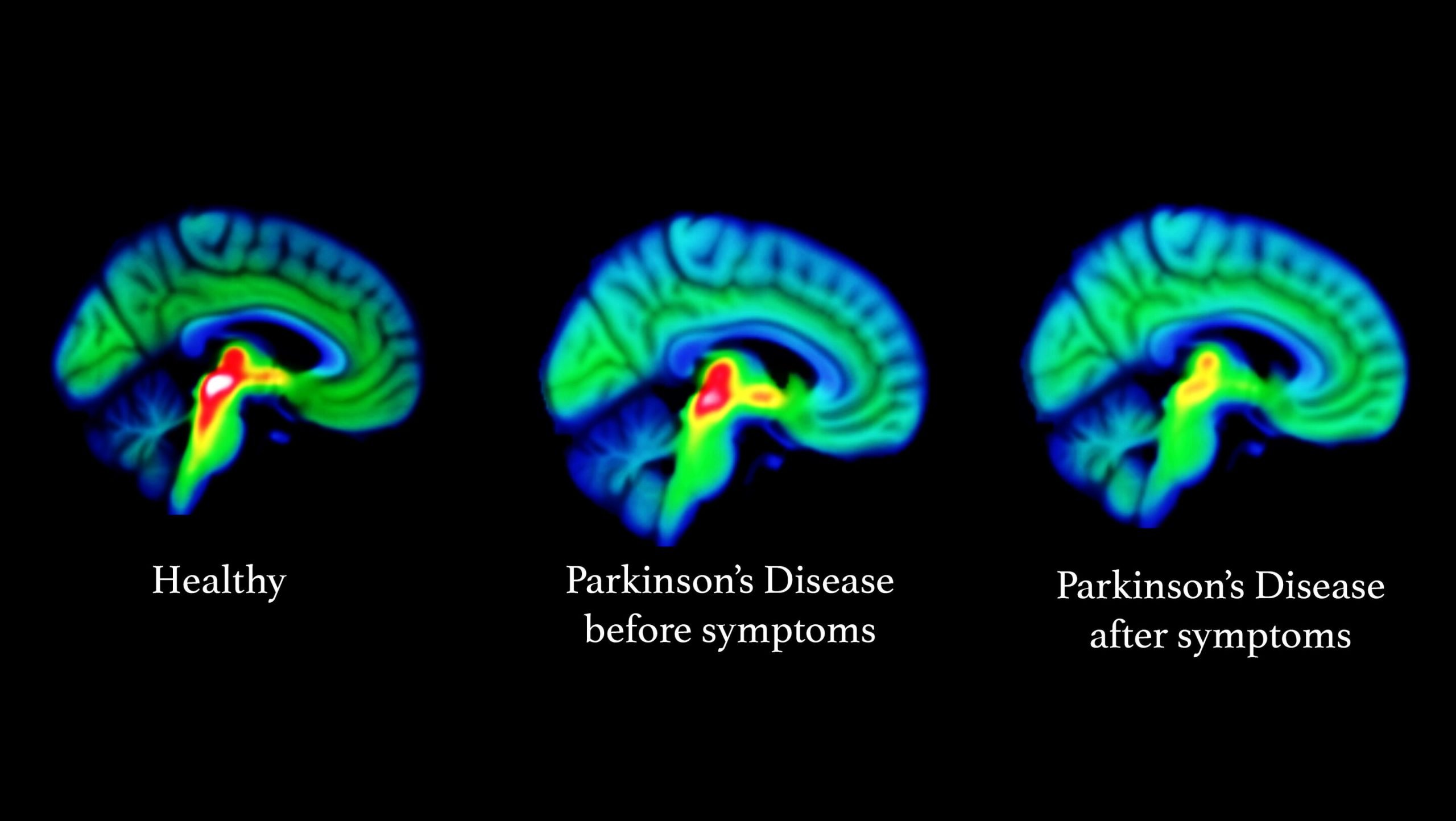
The neurodegenerative process in Parkinsons disease begins several years before the onset of any clinical symptoms . The motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease usually present after 70% of dopaminergic neurons have degenerated . Presumably, the compensatory effect in the cerebellum and other brain regions accounts for delaying the onset of motor symptoms and preserving relatively normal function.
What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinson’s is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
Surgical Treatment For Parkinsons
This is advised when the disease progresses and the medications are no longer controlling the symptoms of PD adequately.
- As the disease progresses, Levodopa still works, but the brains response to the medication becomes less predictable. Levodopa may take longer to kick in and may wear off earlier, requiring patients to take medication more frequently during the day. Higher doses of levodopa are associated with abnormal involuntary movements, known as dyskinesias . Unpredictable medication effect results in OFF time when patients feel stiff, rigid, stuck, frozen, slow, or fatigued, compared to ON time when movements are smooth and closer to normal.
- Treatment options as the disease progresses include taking levodopa more frequently; making the medication last longer by adding medications to reduce the metabolism of levodopa, or dopamine adding or changing to long-acting forms of levodopa , or adding or changing to long-acting forms of dopamine agonist . Amantadine can be added to reduce dyskinesia. As these options are being considered and implemented, its time to consider deep brain stimulation surgery .
- Deep brain stimulation surgery is FDA-approved for the treatment of motor complications in Parkinsons disease and is not experimental. DBS is not a last-resort treatment. It has been shown that DBS is more beneficial when performed earlier in the course of the disease compared to waiting for disability.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Cause Back Pain
How Do Symptoms Progress And What Is The Outlook
The symptoms of PD tend to become gradually worse over time. However, the speed of progression varies greatly from person to person. When symptoms first begin, you may not need treatment when symptoms are relatively mild.
Most people with PD can expect to have some time of relatively mild symptoms. Then, when the symptoms become worse, they can expect several years of good or reasonable control of the symptoms with medication. But everyone is different and it is difficult to predict for an individual how quickly the disease will progress. Some people may only be slightly disabled 20 years after PD first begins, whereas others may be very disabled after 10 years.
Research into PD is active. For example, one main aim of research is to find medicines that prevent the damage to the affected cells, rather than just treating the symptoms, which is the main value of treatment at present. Further research on these chemicals continues. Research is underway using stem cell therapy to help treat PD. Other researchers are looking at alpha synuclein, a protein that gathers around the junction between nerve cells and is thought to affect the way messages are conducted between the brain and the nerves controlling movement.
Further reading and references
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Don’t Miss: Should Someone With Parkinson’s Drive
The Cerebellum And Dyskinesia
Chronic dopamine replacement therapy in patients with Parkinsons disease is commonly complicated by involuntary movements known as levodopa-induced dyskinesia . The neural mechanisms of levodopa-induced dyskinesia are still partially obscure, but levodopa-induced dyskinesia has been considered to be the consequence of an abnormal activity pattern in the striato-thalamo-cortical loops, which in turn induces the excessive disinhibition of thalamocortical neurons and overactivation of cortical motor areas . Recent studies suggested that the cerebello-thalamo-cortical circuit also contributes to the development of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus, the surgical procedures that alleviate levodopa-induced dyskinesia , was reported to modulate neural activity or metabolism in the cerebellum . In a PET study on patients with advanced Parkinsons disease undergoing stereotactic pallidal surgery , the level of binding potential of cerebellar sigma receptors did not correlate with the Hoehn and Yahr stages, or Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale, but a positive correlation was seen between the binding potential and the preoperative levodopa-induced dyskinesia severity score, giving evidence that the cerebellum may be involved in the genesis of dyskinesia.
Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
These common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease often begin gradually and progress over time:
- Shaking or tremor
- Poor posture
- Slowing of body movements
As the disease continues to progress, additional symptoms can occur such as slurred or soft speech, trouble chewing and/or swallowing, memory loss, constipation, trouble sleeping, loss of bladder control, anxiety, depression, inability to regulate body temperature, sexual dysfunction, decreased ability to smell, restless legs and muscle cramps.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Cause Dementia
How Is Parkinson Disease Treated
Parkinson disease can’t be cured. But there are different therapies that can help control symptoms. Many of the medicines used to treat Parkinson disease help to offset the loss of the chemical dopamine in the brain. Most of these medicines help manage symptoms quite successfully.
A procedure called deep brain stimulation may also be used to treat Parkinson disease. It sends electrical impulses into the brain to help control tremors and twitching movements. Some people may need surgery to manage Parkinson disease symptoms. Surgery may involve destroying small areas of brain tissue responsible for the symptoms. However, these surgeries are rarely done since deep brain stimulation is now available.
Alzheimer’s And Dementia: Which Areas Of The Brain Are Affected
The human brain is made of billions of specialized cells designed to process and transmit information. When these cells lose their ability to function properly, vital communication between neurons is impaired or completely interrupted.
Dementia and Alzheimers disease disrupt neurons and cause damage to many areas of the brain, leading to a wide array of progressive symptoms. If you suspect dementia or Alzheimers in a loved one, it is important to find a neurologist to diagnose the cause of these cognitive and behavioral changes.
Before identifying the specific brain changes and the areas of the brain which are affected by Alzheimer’s, its important to define neurology terms to better understand this disease.
Don’t Miss: Do Parkinson’s Tremors Get Worse With Stress
Some Other General Points
Stay as active as possible. Exercise regularly as much as you are able. This may not be possible when the condition is more advanced. However, it is something to consider when symptoms are not too bad. You may walk more slowly than before but a daily walk is good exercise and may help to loosen up stiff muscles. Well-meaning relatives or friends may tell you to rest and take things easy. However, as much as possible and for as long as possible, resist the temptation for others to do things for you just because it may be quicker.
Constipation is common in people with PD. Help to reduce the chance of this by having lots to drink and eat plenty of vegetables, fruit, and foods high in fibre. Exercise can also improve constipation. Sometimes laxatives may be needed to treat constipation.
Some medicines taken for other conditions can interfere with dopamine and make PD worse. These may be prescribed for such things as mental illness, sickness, vertigo and dizziness. Check with your doctor if you are unsure about any medicines that you take.
Driving. If you are a driver you should tell the DVLA and your insurance company if you develop PD. Your insurance may be invalid if you do not. Depending on the severity of symptoms and the medicines that you are taking, you may still be allowed to drive following a medical assessment.
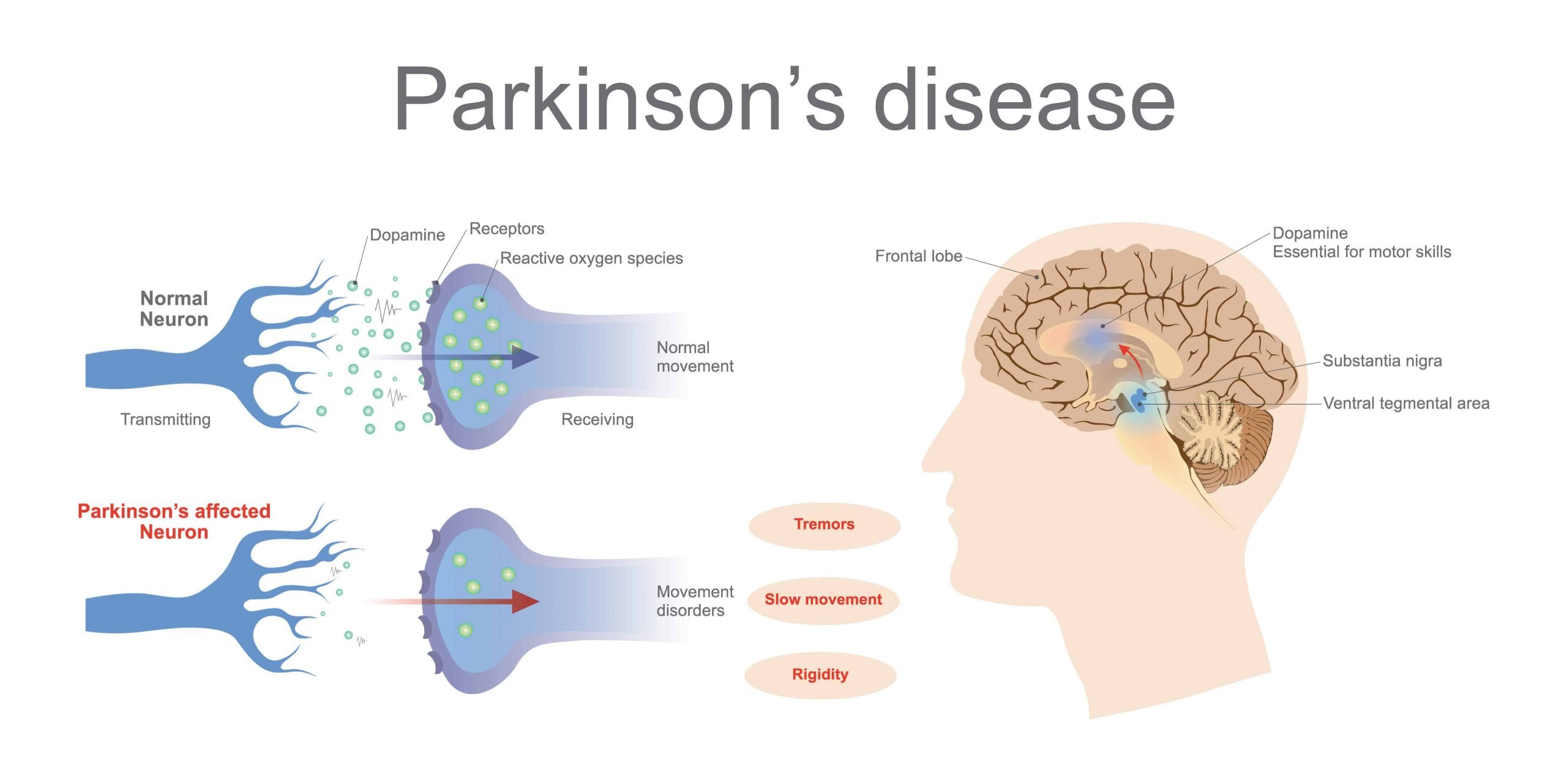
The Substantia Nigra And Movement
The reason that Parkinsons causes movement symptoms is that the substantia nigra makes up part of the circuitry, called the basal ganglia, that the brain uses to turn thought about movement into action.
The structures of the basal ganglia.
The substantia nigra is the master regulator of the circuit, it mainly communicates using the chemical dopamine, but other chemical transmitters are also used to communicate between other areas of the basal ganglia.
The balance of signals being sent between these structures allows us to control movement. But as Parkinsons progresses, and the dopamine-producing brain cells in the substantia nigra are lost, movement symptoms appear. Without enough dopamine, it becomes harder to start and maintain movements, which leads to symptoms such as slowness of movement, rigidity and freezing. And an imbalance of signals in the basal ganglia means people with Parkinsons can experience what is known as a resting tremor.
But while this is the description of Parkinsons you may find in most textbooks, it is now recognised that changes are not limited to the substantia nigra and basal ganglia.
Read Also: What Is Rigidity In Parkinson’s Disease
What Part Of The Brain Does Parkinsons Affect
There are several parts of the brain that Parkinsons disease affects. There are three areas of the brain that most affected.
- The subthalamic nucleus a nerve center near the substantia nigra; is responsible for parts of motor control .
- The globus pallidus another nerve center responsible for movement, balance, and walking.
- The basal ganglia a group of structures inside the brain that help to provide coordination and movement. The basal ganglia are known as a movement circuit, and lack of chemicals here can cause parts of this circuit to become unsynchronized.
The most affected area of the brain is an area within the basal ganglia called the substantia nigra. The substantia nigra is located near the brainstem, the region of the brain that calculates and initiates movements. This area contains neurons that are sensitive to a neurotransmitter called dopamine. In PD, these neurons start to degenerate over time and become less sensitive to dopamine.
What Is The Difference Between Dementia And Alzheimers Disease
Dementia is not a specific disease, but an umbrella term that describes an array of cognitive symptoms which impair an individuals ability to perform everyday tasks and live independently. Alzheimers disease is one type of dementia.
Some of the signs of dementia include1:
- Reduced ability to focus
- Changes in language and communication
- Impaired judgment and reasoning
Some other types of dementia with unique causes and diagnostic markers are1:
- Frontotemporal dementia
- Dementia related to Parkinsons disease
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Mixed dementia
You May Like: Do People Die From Parkinson’s Disease
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal; and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
The Cerebral Network Underlying Parkinsons Tremor
The occurrence of resting tremor in PD is probably related to the death of SNc dopamine-containing cells. PD tremor mainly involves dysfunctions in the system formed by the motor cortex, cerebellum, thalamus, and basal ganglia. Patients with tremor-dominant PD show an increased functional connectivity between BG and the cerebello-thalamo-cortical circuit. This evidence suggests that PD tremor may result from a pathological interaction between BG and the cerebello-thalamo-cortical circuit . However, the specific mechanisms underlying such pathological interaction are still widely debated.
Support for our corticalsubcortical circuit hypothesis underlying tremor comes also from analysis of the tremor-related activity in the areas considered in . Overall, on the methodological side this analysis shows how a system-level perspective is needed to disentangle the complex involvement of different neural circuits in the production of PD tremor.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Face
New Approaches For Monitoring And Treating Pd
The system-level view of PD features has a high potential for the development of innovative procedures for monitoring and treating PD. We show this by illustrating some of these possibilities. Regarding monitoring, one of the biggest future challenges for imaging techniques applied to PD is to integrate their results to identify the mechanisms that might be targeted with drugs and other interventions.,,
By disentangling the multifaceted mechanisms underlying PD symptoms, the system view of PD proposed here, operationalized into dynamical system-level models integrating multi-source data, could lead to a systematic data-driven improvement of therapies., We support this possibility by referring to some relevant treatment techniques. DBS and transcranial magnetic stimulation have been used with various brain targets, in particular sites involving areas of the BGCtxCer system and not only BG. Indeed, several experiments support the idea that DBS preferentially modulates remote structures rather than local circuits since fibers of passage are more excitable than local cell bodies at the site of stimulation. The analysis of the corticalsubcortical circuits discussed above, possibly supported by computational models integrating multiple data sources, could represent a necessary step to better understand the mechanisms underlying DBS/TMS effects and so to identify possible new targets within the BGCtxCer system.
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Treated
If a doctor thinks a person has Parkinson’s disease, there’s reason for hope. Medicine can be used to eliminate or improve the symptoms, like the body tremors. And some experts think that a cure may be found soon.
For now, a medicine called levodopa is often given to people who have Parkinson’s disease. Called “L-dopa,” this medicine increases the amount of dopamine in the body and has been shown to improve a person’s ability to walk and move around. Other drugs also help decrease and manage the symptoms by affecting dopamine levels. In some cases, surgery may be needed to treat it. The person would get anesthesia, a special kind of medicine to prevent pain during the operation.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Disease Deadly
The Cerebellum And Non
Many non-motor symptoms, including sensory, autonomic, cognitive and behavioural problems, coexist with the motor signs in Parkinsons disease . Non-motor symptoms exist in up to 60% of patients , and can be primary complaints in Parkinsons disease . Cognitive impairment is common in patients with Parkinsons disease . Hypometabolism in the prefrontal, parietal, temporal and mesolimbic regions was correlated with cognitive impairment in Parkinsons disease . With fluorodeoxyglucose PET and spatial covariance analysis, identified a significant covariance pattern that correlated with cognitive performance, particularly involving executive functioning in Parkinsons disease. This Parkinsons diseaserelated cognitive pattern is characterized by metabolic reductions in frontal and parietal association areas, and increases in the cerebellar vermis and dentate nuclei . Parkinsons diseaserelated cognitive pattern expression increased with worsening of cognitive impairment , but is not correlated with the decline of striatal dopaminergic function . Therefore, the hypermetabolism in the cerebellum might also be a compensatory effort to maintain cognitive function in Parkinsons disease.
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Speech
