What Is Parkinsons Disease Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
The causes and symptoms of Parkinson’s disease can vary from person to person. While there is no cure, there are medications and treatments to help manage the condition.
Parkinson’s disease is a movement disorder that happens when nerve cells in a certain part of the brain are no longer making the chemical dopamine.
The condition is also sometimes known as paralysis agitans or shaking palsy.
The Parkinson’s Foundation estimates that 60,000 Americans are diagnosed with Parkinson’s every year. However, the true number of people who develop the disease may be much higher.
The Evolution Of Critical Symptoms Involved In Diagnostic Procedures Of Pd
- Diagnostic criteria: presence of bradykinesia and at least one of the following symptoms: muscular rigidity, 4–6 Hz rest tremor and postural instability
- Exclusion criteria: history of repeated strokes or head injury, encephalitis, early severe autonomic involvement or dementia, Babinski sign, negative response to levodopa treatment and MPTP exposure
- Supportive criteria : unilateral onset, rest tremor, progressive course, persistent asymmetry, excellent response to dopaminergic therapy, levodopa-induced dyskinesia, positive levodopa response five years or more and clinical course of ten years or more
What Are The Risk Factors Of Developing Dementia After Parkinsons Disease
Certain patients with Parkinson’s disease are at higher risk of developing dementia than others. Some of the vital risk factors for developing dementia after Parkinson’s disease may include older age, severity of symptoms and presence of mild cognitive impairment. Other additional symptoms which act as risk factor for developing into full fledged dementia include-
- Excessive sleepiness in the daytime.
- Presence of hallucination in the absence of other dementia related symptoms.
- Presence of postural instability and gait which include freezing that occurs suddenly, difficulty in initiating movement and problems with balancing and frequent falling.
Correlation Between Symptoms And Pathologic Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Braak et al. have proposed that PD is a synucleinopathy with 6 neuropathologic stages . It is believed that the pathologic changes in PD begin years before motor symptoms appear. Table 1 summarizes the 6 pathologic stages proposed by Braak and colleagues.
Table 1 Pathologic Stages of Parkinsons disease Proposed by Braak et al.
Stage 1 Medulla oblongata and olfactory bulb lesions in dorsal nucleus of cranial nerves IX and X, intermediate reticular formation, olfactory bulb, and anterior olfactory nucleus
Stage 2 Pontine tegmentum pathology of stage 1 plus lesions in caudal raphe nuclei, gigantocellular reticular nucleus, and ceruleus-subceruleus complex
Stage 3 Midbrain pathology of stage 2 plus lesions in pars compacta of substantia nigra
Stage 4 Basal prosencephalon and mesocortex pathology of stage 3 plus prosencephalic lesions, anteromedial temporal mesocortex, and allocortex
Stage 5 Neocortex pathology of stage 4 plus lesions in prefrontal cortex and sensory association neocortical areas
Stage 6 Neocortex pathology of stage 5 plus lesions in first-order sensory association areas, premotor cortex, and even primary sensory and motor cortices
One Of The Most Difficult Neurological Disorder Symptoms Of Parkinsons
Why might this be important to families challenged by PD? Because the biggest source of conflict in families occurs when loved ones fail to recognize that a person with brain changes is not the same person who existed at an earlier time in life. Human beings greatly value continuity in personality but by expecting the person to be the same as they once were, loved ones are unfair to the person with brain insult. This person could no more return to an earlier personality state than he or she can will away tremors or rigidity. Energy expended in any way other than coming to terms with this “new” person is fruitless. There is actually some fascinating research in this area and it is likely to be a topic for a great deal more discussion in future blogs.
Because of the greater likelihood for executive dysfunction and dementia, personality change is easier to see among individuals with more advanced PD. Motivation is frequently affected, resulting in apathy that diminishes how actively an individual interacts with other people and with the world . Thinking or cognition changes can cause the person to process information more slowly and with less focus and concentration . A previously methodical, consistent individual often becomes increasingly chaotic in their response to their environment . One easily becomes less interested and hopeful about the future .
Continue Learning About Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms & Warning Signs
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a person’s symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinson’s disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinson’s disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinson’s, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinson’s disease medication; in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Pain Is A Common But Overlooked Problem In Parkinsons Disease
Pain is an often overlooked non-motor symptom of Parkinson’s disease . Studies show that between 40-80% of people with PD report pain, which is likely why it is often suggested as a topic for this blog.
One of the reasons why the topic of pain and PD is difficult to address is that it is sometimes tough to discern whether a particular pain is due to PD or not. Chronic pain is such a common symptom among the general population, and people with PD are not immune to common problems as well. However, there are aspects of PD that may exacerbate the pain experienced from a common problem. In addition, there are particular types of pain that may be unique to people with PD.
Brain Imaging And Other Tools To Aid Diagnosis Of Parkinsons

In addition to taking a history and performing a detailed neurologic examination, physicians sometimes use brain imaging to help support a particular diagnosis. However, these studies have their limitations in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and are typically used only in select patients. Brain imaging is not routinely performed by neurologists or movement disorder specialists when they are considering a diagnosis, especially if the person’s symptoms strongly suggest to the physician that idiopathic Parkinson’s disease is the correct diagnosis.
Helping diagnose Parkinson’s with DaTscan and other tests
Rather, use of imaging is most helpful when the diagnosis is uncertain, or when physicians are looking for changes in the brain that are more typical of one of several Parkinsonian syndromes and other conditions that can mimic Parkinson’s. Imaging studies to evaluate Parkinson’s disease and Parkinsonian syndromes include magnetic resonance imaging , which examines the structure of the brain, and DaTscan, an imaging test approved by the Food and Drug Administration to detect the dopamine function in the brain. A DaTscan may help differentiate idiopathic Parkinson’s disease from certain other neurologic disorders. Most physicians’ offices will have access to MRI; however, DaTscan imaging may only be available at larger hospitals or medical centers.
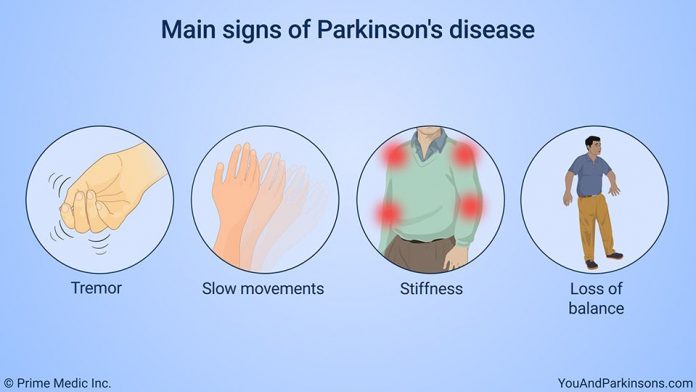
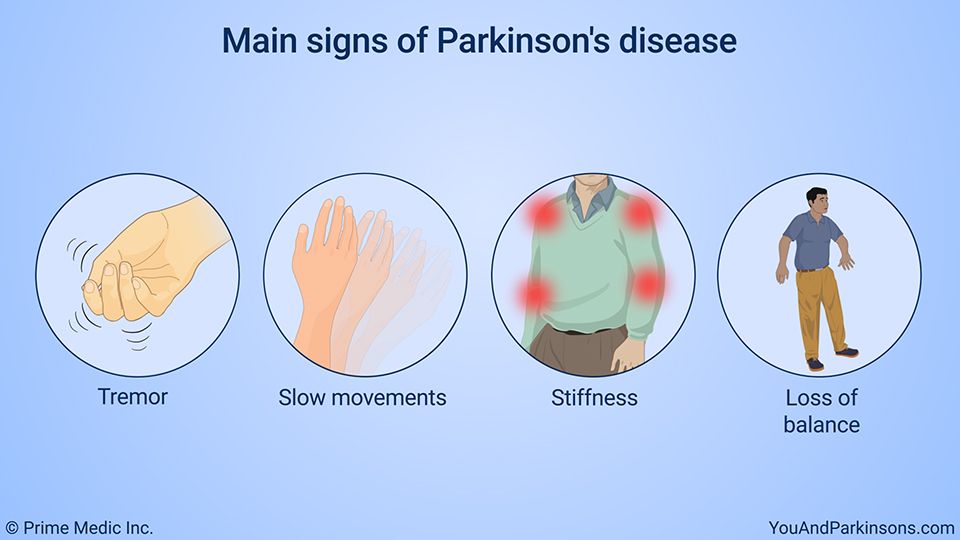
What Are The Primary Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
There are four primary motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability . Observing two or more of these symptoms is the main way that physicians diagnose Parkinson’s.
It is important to know that not all of these symptoms must be present for a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease to be considered. In fact, younger people may only notice one or two of these motor symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease. Not everyone with Parkinson’s disease has a tremor, nor is a tremor proof of Parkinson’s. If you suspect Parkinson’s, see a neurologist or movement disorders specialist.
Tremors
Read more about Parkinson’s tremors
Rigidity
Bradykinesia
mask-like expression of the face
Postural Instability
Walking or Gait Difficulties
Dystonia
Vocal Symptoms
Neuroimaging In The Diagnosis Of Early Parkinsons Disease
PD is a clinical diagnosis; in typical cases, no laboratory test or neuroimaging is necessary. However, when the history or clinical findings are atypical, MRI may be helpful. Over the last 2 decades, functional neuroimaging of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway with PET and single photon emission computed tomography has been refined as a tool in quantifying functional dopaminergic terminals in the striatum .
Functional neuroimaging is still used only experimentally and not for the routine diagnosis of early PD or assessment of disease progression. Both SPECT and PET have been used in therapeutic trials that include disease progression as an outcome measure . However, drug-induced changes in radiotracer binding might undermine the reliability of imaging studies of disease progression . For this reason, there is much controversy about the interpretation of the neuroimaging findings of those trials .
What Is Parkinsonism Is It Different From Parkinsons
Parkinson’s disease is the most common cause of parkinsonism, a category of neurological diseases that cause slowed movement.
No quick or easy diagnostic tests exist for Parkinson’s disease, so a patient may receive an initial diagnosis of parkinsonism without a more specific condition being confirmed.
Classic Parkinson’s disease — referred to as idiopathic because it has no known cause — is the most common and most treatable parkinsonism.
About 15 percent of people with parkinsonism have atypical variants, which are also known as Parkinson’s plus syndromes.
What Causes Sudden Chills And Shaking Without Fever

Body chills are commonly caused by cold external temperatures, or changing internal temperatures, such as when you have a fever . When you have chills without a fever , causes may include low blood sugar, anxiety or fear, or intense physical exercise.
You might be interested: Sponge bath for elderly
Research And Statistics: Who Has Parkinsons Disease
According to the Parkinson’s Foundation, nearly 1 million people in the United States are living with the disease. More than 10 million people worldwide have Parkinson’s.
About 4 percent of people with Parkinson’s are diagnosed before age 50.
Men are 1.5 times more likely to develop the disease than women.
Cardinal Motor Features Of Early Parkinsons Disease
Tremor
Tremor is the most common presenting sign of early PD . Approximately 70% of patients notice tremor as the first symptom . Onset of tremor is usually in one hand; it may later involve the contralateral upper limb or ipsilateral lower limb. Typically, the tremor is a 3- to 5-Hz rhythmic “pill-rolling” movement of the thumb and index finger while the hand is at rest. There may be abduction and adduction of the thumb or flexion and extension of the wrist or of the metacarpophalangeal joints. The tremor may also extend to the forearm with pronation/ supination or even to the elbow and upper arm.
During early disease, tremor is often intermittent and is evident only under stress. Tremor is worsened by anxiety, fatigue, and sleep deprivation. It diminishes with voluntary activity but may reappear with static posture and is absent during sleep. Resting tremor is enhanced by mental task performance, such as “serial 7” subtractions, and by motor task performance in a different body part. The hand tremor may also be enhanced during ambulation. Compared with essential tremor, the resting tremor of PD is generally less likely to be exacerbated by caffeine or improved with alcohol.
Rigidity
Bradykinesia
Generalized bradykinesia is rated by the overall slowing of all body parts, including an evaluation of how easily the patient stands from a seated position with or without pushing off the arm rests and of the patient’s speed of ambulation.
Postural Instability and Gait Disturbance
What Are The Cardinal Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the motor abilities of a patient. The cardinal signs of Parkinson’s disease are normally related to the motor functions which may be voluntary or involuntary in nature. Such symptoms usually start on the one side of the body which are initially mild, and progresses over the period of time. The cardinal signs include-
Tremors: Tremors originating in fingers, hands, feet, arms, jaw, legs or head. Such tremors are seen to occur most often while the patient is resting. These tremors may worsen when the patient gets excited, stressed, or tired.
Rigidity in Limbs: A pattern of stiffness or rigidity is seen in the limbs and trunk, which may increase in case of movement. Such rigidity may produce muscle aches and pain.
Loss of Fine Motor Skills: Loss of fine motor skills may lead to cramped handwriting which may be difficult to read. Such condition is called micrographia. Patient may also find it difficult to eat.
Loss of Movement: Progressive slowness of voluntary movement which may result in difficulty to initiate movement and to even complete a movement gradually.
Loss of Reflexes: Impairment or loss of reflexes to adjust the posture and maintain balance is also cardinal signs of Parkinson’s disease.
How Long Can You Have Parkinson’s Without Knowing

When they compared the daily functioning of people who were later diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with those who were not, the researchers found that from seven years before diagnosis onward, people who later were diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease more often had problems in instrumental daily activities.
What Doctors Look For When Diagnosing Parkinsons
Certain physical signs and symptoms — noticed by the patient or his or her loved ones — are usually what prompt a person to see the doctor. These are the symptoms most often noticed by patients or their families:
-
Shaking or tremor: Called resting tremor, a trembling of a hand or foot that happens when the patient is at rest and typically stops when he or she is active or moving
-
Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement in the limbs, face, walking or overall body
-
Rigidity: Stiffness in the arms, legs or trunk
-
Posture instability: Trouble with balance and possible falls
Once the patient is at the doctor’s office, the physician:
-
Takes a medical history and does a physical examination.
-
Asks about current and past medications. Some medications may cause symptoms that mimic Parkinson’s disease.
-
Performs a neurological examination, testing agility, muscle tone, gait and balance.
What Are The Risk Factors For Parkinsons Disease
Risk factors for Parkinson’s disease include:
Genetics
People with a first-degree relative with Parkinson’s are at an increased risk for the disease — possibly as much as 9 percent greater.
Fifteen to 25 percent of people with Parkinson’s have a known relative with the disease, but a condition called familial Parkinson’s, which has a known genetic link, is relatively rare.
Age
The average age of onset is 60 years, and the incidence rises with advancing age. About 10 percent of people have “early-onset” or “young-onset” disease, which begins before age 50.
Gender
Parkinson’s affects about 50 percent more men than women, for unknown reasons.
Pesticide Exposure
Exposure to some pesticides has been shown to raise the risk of developing Parkinson’s.
Problematic chemicals include organochlorine pesticides like DDT, dieldrin, and chlordane. Rotenone and permethrin have also been implicated.
Fungicide and Herbicide Exposure
Exposure to the fungicide maneb or the herbicides 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid , paraquat, or Agent Orange may raise the risk of Parkinson’s.
The U.S. Veterans Health Administration considers Parkinson’s to be a possible service-related illness if the person was exposed to significant amounts of Agent Orange.
Head Injuries
Head injuries may contribute to the development of Parkinson’s in some people.
Coffee and Smoking
People who drink coffee or smoke tobacco have been found to have a lower risk of Parkinson’s disease, for reasons that remain unclear.
The Differential Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
The clinical diagnosis of PD relies heavily on history, neurologic examination, and improvement of motor signs with dopaminergic therapy . The differential diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes is extensive . It includes normal aging, essential tremor, drug-induced parkinsonism, the Parkinson-plus syndromes , vascular parkinsonism, normal-pressure hydrocephalus, and other less common diseases . Attention to distinct patterns of symptoms and signs and the time course of the disease can help to improve diagnostic accuracy .
Normal Aging
There is little agreement on a definition of normal aging . Slowness of movement, stooped posture, stiffness, and postural instability are common in the elderly . Comorbid conditions such as arthritis can also contribute to reduced mobility and stiffness. Asymmetric motor signs and a more accelerated rate of symptom progression are more suggestive of PD. If the level of suspicion for PD is high enough, a trial of levodopa may be the only way to establish significant and sustained response to dopaminergic therapy and hence the clinical diagnosis of PD.
Essential Tremor
Drug-Induced Parkinsonism
Drug-induced parkinsonism usually occurs after exposure to neuroleptics. Antiemetic and promotility agents , reserpine , tetrabenazine , and even some calcium channel blockers can cause parkinsonism. The symptoms are symmetric, and drug-induced parkinsonism resolves when the offending drug is stopped, although resolution may require weeks to months.
Parkinsons Disease Symptoms 4 Cardinal Signs

The article Parkinson’s disease early symptoms described a variety of signs that might be indicative of oncoming or early Parkinson’s. Given that many of the signs could be due to a variety of completely unrelated conditions, a more structured and formal classification is required to differentiate Parkinson’s from other diseases. This can be achieved by grouping the symptoms into primary motor related symptoms , associated symptoms and neuropsychiatric dysfunction.
This article explains the 4 primary motor symptoms for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis, which includes:
What Diseases Can Be Mistaken For Parkinson’s This is the list of different diseases that may be mistaken with Parkinson’s disease:
- Progressive supranuclear palsy.
Alzheimer’s disease and primary lateral sclerosis can also be mistaken for Parkinson’s disease. Other similar conditions include essential tremor, dystonic tremor, vascular Parkinsonism, and drug-induced Parkinsonism.
One may also ask, what are the four cardinal signs of Parkinson’s disease? Cardinal symptoms. Four symptoms are considered cardinal in PD: bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity, and postural instability also referred to as parkinsonism. Tremor is the most apparent and well-known symptom.
Moreover, what is similar to Parkinsons?
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: An Atypical Parkinsonian Syndrome. Progressive supranuclear palsy is not Parkinson’s disease , but is a Parkinsonian-like syndrome. PSP is a rare brain disorder that causes serious and progressive problems with gait and balance, as well as eye movement and thinking problems.
Does stress cause Parkinson’s disease?
Research suggests that stressful life events may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease. In addition, animal studies indicate that stress damages dopamine cells, resulting in more severe parkinsonian symptoms. In humans, acute stress can worsen motor symptoms, including bradykinesia, freezing, and tremor.
Causes And Risk Factors Of Parkinsons Disease
Most cases of Parkinson’s disease are idiopathic, meaning the cause is unclear.
It’s widely believed that a person with Parkinson’s may have been genetically vulnerable to the disease, and that one or more unknown factors in the environment eventually triggered the disease.
Most of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease come from the loss of neurons in an area of your brain called the substantia nigra.
Normally, the neurons in this part of the brain make the chemical messenger dopamine, which allows communication with another area of the brain, the corpus striatum.
This communication helps produce smooth, purposeful movement. When the neurons in the substantia nigra die, the resulting loss of communication leads to the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s.
Although the cause of this cell death is unknown, many researchers believe that the cells are killed by clumped proteins called Lewy bodies.
Cardinal Features Of Early Parkinsons Disease
The term parkinsonism has evolved over time to refer to the constellation of signs in the clinical entity described by James Parkinson in 1817 . The 3 cardinal signs include resting tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia. However, there are no specific criteria for the use of this term. For instance, does the presence of any of the core features alone constitute parkinsonism? Or is a threshold of motor signs needed before a patient would be labeled as having parkinsonism?
Parkinson’s disease , the most common cause of parkinsonism , has a more specific definition, with gradations of diagnostic certainty . The definitive diagnosis of PD requires autopsy; however more rigorous clinical diagnostic criteria have emerged over the last 2 decades . The motor signs of early PD are usually asymmetric, and symptomatic improvement with dopaminergic drugs is significant and sustained. Familial parkinsonism and familial PD are entities that may follow an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Clinical Features Epidemiology And Etiology

The four cardinal features of Parkinson disease are tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Parkinsonism is a non-specific term used to describe a constellation of signs on physical examination similar to those seen in Parkinson disease. Parkinson disease is defined as asymmetric Parkinsonism with no known cause, characterized by most of the four cardinal features, and responsive to anti-Parkinson medications . The diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease have become more rigorous with gradations of diagnostic certainty. Any one of resting tremor, rigidity, or bradykinesia would suggest clinically possible Parkinson disease. Any two of the four cardinal signs would suggest clinically probable Parkinson…
Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease Jump to navigationJump to searchWilliam Richard Gowers
Signs and symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are varied. Parkinson’s disease affects movement, producing motor symptoms. Non-motor symptoms, which include dysautonomia, cognitive and neurobehavioral problems, and sensory and sleep difficulties, are also common. When other diseases mimic Parkinson’s disease, they are categorized as parkinsonism.
Is Teeth Chattering A Sign Of Parkinson’s 4.3/5Parkinson’steeth chatter
The two conditions have key differences to look for: Essential tremor doesn’t cause associated health problems, while Parkinson’s carries other symptoms, such as stooped posture and balance problems. Essential tremor may affect the voice box, but Parkinson’s does not.
Also Know, what are the very early signs of Parkinson’s disease?
- cramped handwriting or other writing changes.
- tremor, especially in finger, hand or foot.
- uncontrollable movements during sleep.
- limb stiffness or slow movement
- voice changes.
- rigid facial expression or masking.
- stooped posture.
Regarding this, is pill rolling always a sign of Parkinson’s?
A pill rolling tremor is the most common tremor associated with Parkinson’s disease, a nervous system disorder that affects movement. It’s usually one of the earliest symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
What causes jaw trembling?
Essential tremor is the involuntary shaking or trembling of part of the body. It usually affects the hands and head, but it can also cause trembling in the jaw, feet, tongue, and face.These include:
New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.’s Parkinson’s Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But that’s now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
Parkinsons Disease And Physical Therapy

It is estimated that more than 10 million people worldwide have been diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. This disease is defined as “A chronic progressive neurological disorder caused by the lack of dopamine production in the brain.” The average duration of Parkinson’s disease is between 10-13 years with direct and indirect costs equating to more than 25 billion dollars each year for the U.S. alone.
Painful Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Pain can sometimes be an early symptom of PD. For example, a person may complain of a painful shoulder and be diagnosed with an orthopedic condition such as a frozen shoulder, only to develop a rest tremor on that side at a later point. The painful shoulder was in fact not a frozen shoulder after all, but rather pain due to the rigidity of PD. Now of course, sometimes a frozen shoulder is really just a frozen shoulder, so there’s no need to jump to conclusions when you are experiencing pain. Not every ache and pain is a sign of PD, but it is important for you to educate yourself, be aware of the possible connections, and be proactive about seeking medical attention for any notable pain you are experiencing.
If you have PD and develop pain, it is important to first bring this to the attention of your doctor. The pain may be related to your PD, or the pain may be due to a common problem such as arthritis which is exacerbated by your PD. However, in some cases, it may be a symptom of a more serious medical problem. So do not assume that the pain is related to your PD before getting an appropriate medical workup.
Black Americans And Parkinsons Disease
Most research suggests that Parkinson’s disease is more likely to affect whites and Hispanics.
But, some studies have shown that Black patients may be less likely to receive proper care for the disease.
A review published in 2018 in Neurology found there are racial disparities when it comes to managing Parkinson’s disease.
Researchers identified one study that showed Black patients were 4 times less likely than whites to be started on treatment for Parkinson’s.
Another study found an average seven-year delay in diagnosis among Black patients.
Theories About What Causes Parkinsons
The cause of Parkinson’s disease is still unknown, although there is some evidence for the role of genetics, environmental factors, or a combination of both. It is also possible that there may be more than one cause of the disease. Scientists generally believe that both genetics and environment interact to cause Parkinson’s disease in most people who have it.
Currently, there is an enormous amount of research directed at producing more answers about what causes Parkinson’s disease and how it might be prevented or cured. When physicians diagnose Parkinson’s, they often describe it as idiopathic . This simply means that the cause of the disease is not known.
Can High Blood Pressure Cause Shaking

High Blood Pressure , Loss Of Coordination, Shaking And Shaking Hands Or Tremor . Your symptoms and signs match a wide variety of different medical conditions, including high blood pressure or a disorder of your muscles. If you have had an emotionally traumatic experience, an acute stress reaction is another possibility.
You might be interested: Normal blood pressure range for elderly
Treating Parkinsons Disease With Lsvt
Parkinson’s disease is one of the most complicated diagnoses that Physical Therapists and Occupational Therapists treat due to its wide variety of clinical presentations and lack of standardization of care.
The typical approach is to treat each impairment individually, but this can be a slow process with seemingly endless visits. This approach can make documentation for reimbursement difficult, since it requires treatment of multiple body parts and systems on a long-term basis.
In this article, we will discuss an evidence-based practice called Lee Silverman Voice Treatment BIG Therapy for Parkinson’s disease. We will review the motor signs of PD and take an in-depth look at how LSVT BIG could boost your patient outcomes and replace your typical treatment techniques for PD.
How Parkinson’s affects the motor system
As a review, there are four cardinal signs of Parkinson’s disease that affect the motor system:
Intro to LSVT BIG for Parkinson’s
The treatment focuses on big amplitude of movement to compensate for the hypokinesia associated with PD. That means all exercises are performed with the largest possible motion, hence the name “BIG.” The high-intensity exercise helps improve neuroplasticity of movement.
Typical LSVT BIG sessions
Evidence-based outcomes for LSVT
References
Characteristics Of Parkinsons Disease
The four Cardinal signs of Parkinson’s Disease include:
Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
The motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease refer to those that affect the body’s movement.
Motor symptoms are grouped into primary motor symptoms and secondary motor symptoms. Primary motor symptoms are important for the diagnosis of the disease. In addition, there are non-motor symptoms associated with the disease.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed

There are no particularly specific tests that confirm the presence of Parkinson’s disease. Once the patience comes with the symptoms, the doctor usually takes the physical history of the patient. His way of walking and level of cognition is assessed. The doctor then may ask the patient to go for certain tests like-
Blood Test- The blood test is usually done in order to rule out any other condition responsible for the symptoms of motor instability. Such conditions may include liver damage or abnormal thyroid level.
MRI and CT Scans- The patient may be asked to go for a CT or MRI scans to diagnose the presence of brain tumor or stroke. The MRI or CT scan results with Parkinson’s disease are usually normal.
Pet Scan- PET scan may help in the detection of low levels of dopamine in the brain at times. PET scans are highly specialized imaging technique which uses substances which are radioactive in nature to create three dimensional images of the substances in the body.
Also Read:
Environmental Factors And Exposures
Exposure to pesticides and a history of head injury have each been linked with PD, but the risks are modest. Never having smoked cigarettes, and never drinking caffeinated beverages, are also associated with small increases in risk of developing PD.
Low concentrations of urate in the blood is associated with an increased risk of PD.
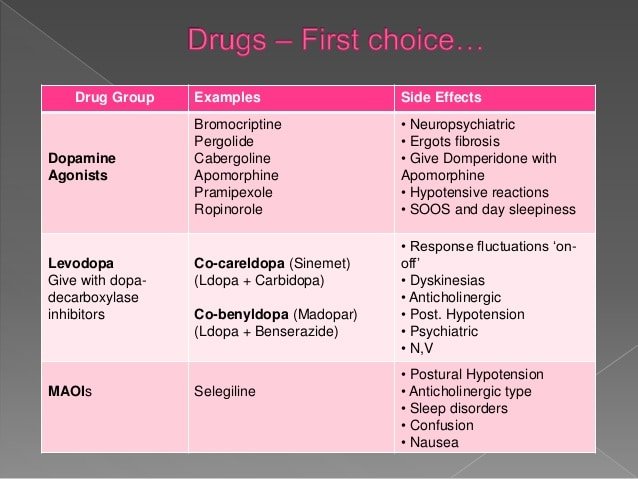
Drug-induced parkinsonism
Different medical drugs have been implicated in cases of parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism is normally reversible by stopping the offending agent. Drugs include: