Negative Impact Of Severity Of Pain On Mood Social Life And General Activity In Parkinson’s Disease

This case control study designed for clinicians and rehabilitation specialists to effectively identify pain from the patient’s point of view determined that PD patients had significantly higher pain severity scores compared to controls. PD patients with depressive symptoms had significantly higher pain severity and pain interference scores than controls without depressive symptoms. PD patients reported greater scores on Global BPI pain interference and all components of the pain interference subscale. Therefore, PD and depression seem to be correlated with higher perceived pain, severity and interference. A report on this study, by Jose Marques Lopes, PhD., was published in Parkinson’s News Today, September 21, 2018.
Revisiting Pain In Pdthe 50 Shades Of Pain Experienced By Parkinsons Patients
Pain is a quality of life issue for people with Parkinson’s disease and can be under treated by doctors who may assume that is worsens as the disease progresses, although for some pain is an initial symptom of PD. This article helps focus your physician’s attention in the right direction to accurately diagnose your pain.
Pain Management In Patients With Parkinsons Disease: Challenges And Solutions
This review focuses on the diagnosis and management of Parkinson-related pain. It reviews the incidence and prevalence of PD, general pain and PD-related pain, the pathophysiological pathways of pain in PD, physiological pathways of pain relief, measurements of pain, clinical diagnosis of PD-related pain, and treatment strategies.
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinson’s disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didn’t exercise or didn’t start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinson’s, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments — whether medicines or deep brain stimulation — are optimal; and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Improve the quality of your sleep.
Pain Is An Unfortunately Common Problem In Parkinsons Disease

Of course, pain is common in the general population, especially among older people. A recent American study found that pain affected about twice as many people with Parkinson’s Disease than those of the same age and gender without PD. About 50% of Parkinson’s Disease patients in that study suffered from painful disorders. Men and women seem to be about equally affected. A very well described scenario is the patient who is followed for a painful frozen shoulder for a year or so before a tremor develops leading to a diagnosis of PD. Pain clearly plays a major role in quality of life. Everyone with chronic pain enjoys life less, leading to a vicious cycle in which pain causes depression or isolation which in turn leads to more pain.
Parkinson patients suffer from the same pain problems that other people have, often amplified by the motor dysfunction, but they also have additional pain problems which are unique to PD.
One recent review classified the types of pain Parkinson’s Disease patients have into: musculoskeletal, in which the pain results from problems with the muscles , bones or joints; dystonic, which is due to abnormal muscle contractions caused by the Parkinson’s Disease or the medications used to treat it; radicular pain, which is feels like the pain caused by pinched nerves; central pain, which is presumed due to abnormalities in the brain, and is a continuously present pain that cannot be explained otherwise; and discomfort related to an unpleasant urge to move.
Opening The Medicine Box In The Mind: The Psychology Of Pain
In this 50-minute lecture, Beth Darnall, PhD explains how our experience of pain goes beyond the physical sensation of pain. It has emotional and psychological components that affect our ability to treat pain. She cites research to demonstrate that and shares 13 specific tips to reduce the experience of pain and increase treatment effectiveness. Audience questions follow the lecture.
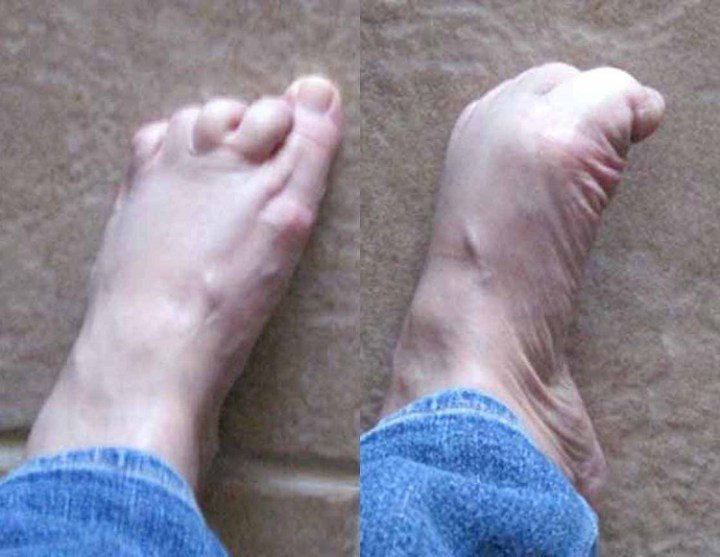
Foot Problems As An Early Sign Of Pd: Oh What A Drag It Is
Search on the internet for . Surprisingly, you will not find foot drag on most of the lists. Yet, Ali Samil, in the chapter “Cardinal Features of Early Parkinson’s Disease,” in the book “Parkinson’s Disease: Diagnosis and Clinical Management,” lists foot drag as an important early symptom.
I have been dealing with foot drag for a few years — that squeak of the sneaker on the kitchen floor when the foot drag catches, scuff marks left behind. While at a professional conference, the foot drag caught the top edge of a stair just as I was headed down, and down I went, grasping the handrail to rescue an awful fall. Recently, it has been much worse, and oh, what a drag it is now.
Reflecting on it, it seems almost impossible that I could seriously hurt my foot walking on a flat, carpeted surface with no obstacles in the way. But that is exactly what happened. Walking barefoot on a carpeted floor, my foot dragged, and then my big toe jammed into the carpet — HARD! I screamed, tears flowed, and I fell to the floor weeping from the pain. The toe turned a nice purple shortly thereafter, but luckily nothing was broken. I don’t walk barefoot anywhere now, except for a few steps in and out of the shower.
I am surprised that there is not more mention of foot drag in the lists of early PD symptoms. If it is a cardinal early symptom, then both patients and care providers should be given the heads up , along with some guidelines on how to adjust.
***
Lower Back Pain And Back Of The Neck Pain Are Most Common
Pain occurs for a number of reasons and it’s not always clear what the cause is, making it difficult to figure out how best to treat it. I believe that most common pain problems in Parkinson’s Disease are the same as in the general population, but amplified. Low back pain and back of the neck pain are probably the most common pain conditions in PD. The reason Parkinson’s Disease patients have so many problems with their low back and their neck is their posture. Parkinson’s Disease causes a stooped posture. Some of this happens with age anyway, particularly in women after menopause when their bones soften, but is always worse from the PD. All Parkinson’s Disease patients have some degree of stooped posture and many also tilt to one side. Because of the stooped posture, the muscles in the lower back have to pull much harder to keep the spine upright.
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinson’s disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable – reducing symptoms during “on” periods and no longer controlling symptoms during “off” periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they can’t. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinson’s disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare team’s efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinson’s disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein – glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF – to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
How To Deal With The 6 Common Causes Of Leg Pain In Pd
Severe leg pain is a common complaint from people with PD. Lately, it is understood that central pain is common to Parkinson’s disease, and can even be the first sign of PD, usually bilaterally. This blog post lists six causes of lower limb pain, and the importance of treating it. Treatments depend on properly identifying the source of pain. Some treatment suggestions are included.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinson’s disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Whats The Difference Between Dystonia And Dyskinesia

Both dystonia and dyskinesia affect your muscles and joints; however, there are distinct differences between them that require unique treatments. Dystonia is a movement disorder that can occur with or without a Parkinson’s diagnosis, while dyskinesia is often a side effect people experience as a result of taking Parkinson’s medications. Though both involve similar abnormal movements of the arms, legs, neck, and face, dystonia is characterized by more sustained muscle contractions and pain.
Strengthening Exercises Or Stretching May Be Helpful
Imagine that the spine is like a telephone pole or the mast of a sailboat. If the pole is not exactly upright, even a slight tilt requires a great force to keep it from tilting further and falling. In the human body, this means that the lower back muscles are under great stress. It also means that the tension on the back bones is much increased as well. This worsens whatever problems, like arthritis, that are already present. The same process applies to the neck, although the forces are less great. Strengthening exercises or stretching may be helpful. Almost everyone over the age of 60 has arthritis in their spine. Luckily most don’t have pain from it, but those who do will have it worsened by the spine curvature caused by the PD.
PD patients also frequently have an aching discomfort in their muscles, particularly in the thighs and shoulders. I think this is due to the rigidity, or stiffness, that is part of the Parkinson’s Disease syndrome, but I’ve seen many patients with this pain and no apparent stiffness on examination, hence not explained. It is common and it often, but not always, responds to alterations of the usual Parkinson’s Disease medications for movement. Exercise and stretching may be helpful as well and should always be tried first before increasing medications.
Pain is a challenge in PD. We can’t measure it and often cannot find its cause. It is, however, often treatable, and reducing pain improves quality of life.
Leg Cramps In Seniors A Seriously Painful Experience Ceci
Leg cramps in seniors tend to increase in frequency with aging. They are usually quite painful involuntary contraction of a muscle or a group of muscles in the thighs, calves or feet. If this contraction occurs for longer than a few seconds, it moves from being a muscle in spasm to a leg cramp. This article discusses the causes, symptoms, tips for relief and preventive measures for leg cramps in seniors.
Leg cramps are quite common but generally come as a shock to an aging senior the first time they occur and can throw them into a panic. This article seeks to educate the aging senior about this unexpected occurrence.
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinson’s disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms; others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Treatment Depends On Properly Identifying The Type

If pain is bilateral always assume it is central pain; pain due to PD. In my experience Azilect works great for this type of pain. Other medications which can be employed for this pain as well.
Massage therapy works for all types of leg pain-my favorite therapy but can be costly. Water therapy may also work for all types except central pain. Physical therapy can alleviate dystonia pain, as well as musculoskeletal and radicular pain.
If pain is due to dystonia related to levodopa intake, find out when it occurs—end of dose or at peak dose. Typically adjusting medication doses will resolve problem. However, if dystonia is an initial symptom of PD, initiating treatment with levodopa will resolve. If medication adjustment does not work well for levodopa induced dystonia, another treatment option is DBS . Pain due to dystonia independent of cause can also respond well to Botox injections, as well as centrally acting muscle relaxants. To avoid and alleviate pain caused by stiff muscles, a great treatment option is activity in the form of stretching exercises—any number of activities will do such as tai-chi or yoga. For me when I start having radicular pain shooting down my leg it is time to up my levodopa dosage.
If you are having leg pain make sure to discuss it with your physician.
Pain In Parkinsons Disease: A Spotlight On Women
This 2-page interview with neurologist, Dr. Jori E. Fleisher, discusses pain in Parkinson’s disease with some interesting statistics about women and pain. Dr. Fleisher outlines the 4 primary types of pain in PD, how depression interferes with pain management, the role of exercise and medications in pain management as well as alternative therapies.
What Should I Expect At A Podiatry Appointment
It is a good idea to try to make appointments at a time of day when you are least likely to experience tremor or other involuntary movements as the podiatrist may need to use sharp instruments. It may also be helpful if your carer is with you for the first appointment so that they understand how they can help you between appointments.
The initial appointment will last around 30 minutes, although this will vary depending on where you live. Additional assessment and treatment sessions will normally take between 20-30 minutes.
The podiatrist will take a full medical history, including your Parkinson’s and any other health problems, as these can affect your feet. They will need to know what medications you take so make sure you take a list of medications with you.
They will assess your feet, including the condition of your skin and nails, circulation and nerves. They will also watch the way you walk and the position and movement of your feet .
The podiatrist will then suggest a care plan including treatment of any immediate problems, future appointments and day-to-day care such as nail cutting, exercise and the use of creams.
In some countries home visits may be arranged if mobility is very limited.
Second Type Of Leg Pain Is Caused By Dystonia
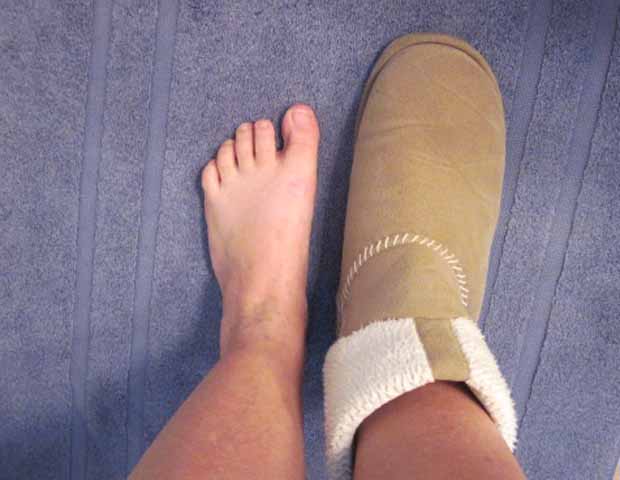
When related to levodopa, it usually occurs as a wearing off but can also occur at peak dose. In most cases this leg pain is unilateral and has direct correlation to medication intake. When pain is due to dystonia, it is more common in early morning. This type of leg pain is usually accompanied by toes curling and foot abnormally posturing.
Can Leg Cramps Be A Sign Of Something Serious

In most cases, foot cramps are not serious and are rarely amedical emergency. But sometimes, theycan be a sign of an underlying medical condition which would need treatment. If you are experiencing regular cramps inyour hands or feet, consult your doctor. It is really important to get an accurate diagnosis.
If you are having other problems with your foot as well, visit the foot pain diagnosis section for help working out what may be causing your problem and what you can do about it.
Treatment For Dystonia In Parkinsons Disease
The exact relationship between PD and dystonia remains unknown, which makes treatment challenging. The Parkinson’s Foundation recommends tracking when dystonia symptoms occur in relation to taking levodopa, the most commonly prescribed medication for PD. If dystonia occurs when levodopa levels are low, such as upon waking in the morning, then your doctor may recommend adjusting the timing or dosage of your medication.
If dystonia occurs even when levodopa has achieved peak levels in your body, then your doctor may recommend injections of botulinum toxin to the affected muscles. Botulinum toxin relaxes muscles and makes it difficult for them to contract, even involuntarily. The injections are repeated every few weeks.
Deep brain stimulation also has shown promise for relieving dystonia in Parkinson’s disease . However, sometimes DBS can trigger a dystonia, such as eyelid twitching, so this treatment usually is reserved as a last resort.
As a symptom of Parkinson’s disease, dystonia can inhibit you from pursuing physical activities you enjoy. But exercise and physical activity are powerful tools in managing PD. Work with your doctor to find medications that improve dystonia symptoms and keep you as mobile as possible. Staying active can help you maintain a high quality of life when living with PD.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Decreased facial expressions: You may not smile or blink as often as the disease worsens; your face lacks expression.
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
How Do I Prevent Falls From Common Hazards
- Floors: Remove all loose wires, cords, and throw rugs. Minimize clutter. Make sure rugs are anchored and smooth. Keep furniture in its usual place.
- Bathroom: Install grab bars and non-skid tape in the tub or shower. Use non-skid bath mats on the floor or install wall-to-wall carpeting.
- Lighting: Make sure halls, stairways, and entrances are well-lit. Install a night light in your bathroom or hallway and staircase. Turn lights on if you get up in the middle of the night. Make sure lamps or light switches are within reach of the bed if you have to get up during the night.
- Kitchen: Install non-skid rubber mats near the sink and stove. Clean spills immediately.
- Stairs: Make sure treads, rails, and rugs are secure. Install a rail on both sides of the stairs. If stairs are a threat, it might be helpful to arrange most of your activities on the lower level to reduce the number of times you must climb the stairs.
- Entrances and doorways: Install metal handles on the walls adjacent to the doorknobs of all doors to make it more secure as you travel through the doorway.
Fourth Type Of Leg Pain Is Radicular Pain

In this case, the pain is caused by compression of nerves in lumbar area which results in weakness, numbness and tingling, and loss of reflexes from buttocks to foot in a distribution of a nerve. It can be acute or chronic, and can be worse with standing and sitting, or better with laying down. Of note: in my experience many patients including myself have these symptoms not because of physically herniated disc but rather by the stretching of a nerve in the canal as it exists due to severe musculoskeletal rigidity and abnormal posturing.
The Gastrointestinal Tract And Parkinsons
As promised in a previous blog, I now return to the topic of the gastrointestinal tract and Parkinson’s disease . As most of you know, GI symptoms are very common in PD. We will discuss what those symptoms are, why they occur, and the current research that links what is happening in the gut to theories as to why PD occurs at all. Many of you have suggested gut-related topics for this blog including a discussion of symptoms such as bloating and constipation, and a discussion of the use of probiotics in PD. I will address these issues as well. Submit additional topics that you would like to read about here.
GI symptoms can be among the most bothersome of the non-motor symptoms of PD. Constipation is the most common of these symptoms, affecting 80-90% of people with PD. APDA has a helpful brochure with practical tips to prevent and treat constipation in PD.
GI pathology in Parkinson’s disease however, can involve the entire GI tract and includes sialorrhea and dysphagia . In addition, delayed gastric emptying, in which the digestive contents are held up in the stomach and do not move normally into the small intestine, can cause sensations of nausea and bloating.
The gut has its own nervous system
The gut as a biomarker
Entry to the brain
How do Lewy bodies propagate?
Parkinsons Disease: Recognizing Symptoms
Parkinson’s is a progressive neurological disease. People with Parkinson’s experience various physical, cognitive, and psychological symptoms. Often, the early symptoms of Parkinson’s are so subtle that the disease goes unnoticed for years. As the disease progresses, a lack of motor skills becomes more apparent. This is followed by cognitive impairments, including trouble following directions and loss of thought.
Doctors look for early evidence of non-motor or pre-motor symptoms long before motor symptoms appear. According to neurologist Dr. Lawrence Severt, the following non-motor symptoms may be early indicators of Parkinson’s:
- a diminished sense of smell
- a long history of constipation
- REM-sleep behavior disorder
- a history of anxiety and depression
Other non-motor symptoms may include:
- speaking in a low-volume voice
- changes in speech
- low blood pressure when standing
- painful foot cramps
First Type Of Leg Pain Is Central Pain
This pain is described as constant burning sensation with occasional burst of sharp pain. As it was in my case, this pain is commonly exacerbated by cold and by light touch. I could not stand the sheets to touch my skin and being in a cold room sent my pain through the roof. This type is usually bilateral but it may start on the side where other Parkinson’s symptoms begin. For me, it was the leg where my rest tremor began.
Want More Practical Articles Like This
Much more can be found in our Every Victory Counts® manual. It’s packed with up-to-date information about everything Parkinson’s, plus an expanded worksheets and resources section to help you put what you’ve learned into action. Request your copy of the Every Victory Counts manual by clicking the button below.
Thank you to our 2020 Peak Partners, Amneal and Kyowa Kirin, with special support from Adamas, for helping us make printing, distributing, and shipping the Every Victory Counts manual for free possible.
Additional Ways To Stop Foot Cramping
Aside from the strategies mentioned with each cause of foot cramping above, there are several other things you can do for foot cramps. Massaging your feet, especially in the middle of a cramp, can help. If you are in pain, try taking an over-the-counter pain reliever. Cool or hot compresses can also relieve muscle pain.
In a recent study at Brigham Young University, researchers found that pickle juice was effective at stopping exercise-induced cramps once they started.20Scientists aren’t sure why this worked, but they think it may have something to do with muscle fatigue.
Tips To Relieve Leg Cramps In Seniors
Leg cramps are painful, and when they do occur, the immediate desire of the affected is to find relief. It is unhelpful if you do not know what to do as this will continue to prolong the pain. Lying down or sitting down will not provide any relief.
Stretch. Despite your aversion to doing so, straighten your leg and then flex it several times. Pull your toes towards your shin to stretch the muscles.
Massage the muscles. Use your hands to gently massage the muscles. Sometimes you may find this difficult to do because of the pain.
Stand Up. Press your feet against the floor as forcefully as you can. You might not have success doing this the first time, but persist until you can do it. It will provide some relief.
Begin to Walk. While you are walking around the round ensure that you periodically wiggle your leg. Also, try to walk on your heels for some time to activate the muscles opposite your calf
Apply heat or cold to the affected area if possible. To apply heat use a heating pad or apply cold by wrapping a bag of ice in a towel.
Take Over-the-Counter Pain killers if you continue to experience soreness after cramping has subsided.
Finally, take some time to evaluate what could have triggered the event so that you try to manage future events.
Ways To Prevent Leg Cramps In Seniors
Because most leg cramps occur while in bed at night, it is helpful to find ways to prevent or reduce leg cramps in seniors and the elderly.
Here are a few ways to prevent nocturnal muscle cramps:
- Drink plenty of fluids during the day to avoid being dehydrated. Drink 6-8 cups of preferably non-caffeinated liquids each day
- During the day, always wear supportive footwear that is not tight during the day especially if you have flat feet.
- Stretch your legs, especially your calves and hamstrings before going to bed. Regular daily stretching may also help prevent nocturnal leg cramps
- Sleep with loose, untucked sheets and comforters to keep feet unconstricted and pointed upward
- Change your sleeping position if you consistently find that one position triggers nocturnal clamping.
- Use pillows to elevate or wedge your legs to make your sleeping position more comfortable. Leg elevation pillows have proved beneficial to improving blood circulation in the legs and providing relief during the night when leg cramps in seniors largely occur as they age. Check a previous article on this website for detailed review of several leg elevation pillows and how to go about choosing the right one for you – Leg Cramps in Seniors. The Best Leg Pillows for Night Relief.
