Using Amphetamines May Increase Risk Of Parkinson’s Disease Study Suggests

- Date:
- American Academy of Neurology
- Summary:
- New research shows people who have used amphetamines such as benzedrine and dexedrine appear to be at an increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
New research shows people who have used amphetamines such as benzedrine and dexedrine appear to be at an increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, according to a study released February 22 that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 63rd Annual Meeting in Honolulu April 9 to April 16, 2011.
Benzedrine and Dexedrine are amphetamines often prescribed to increase wakefulness and focus for people with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and narcolepsy, a disorder that can cause excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden attacks of sleep. They are also used to treat traumatic brain injuries.
The study involved 66,348 people in northern California who had participated in the Multiphasic Health Checkup Cohort Exam between 1964 and 1973 and were evaluated again in 1995. The average age of the participants at the start of the study was 36 years old. Of the participants, 1,154 people had been diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease by the end of the study.
Exposure to amphetamines was determined by two questions: one on the use of drugs for weight loss and a second question on whether people often used Benzedrine or Dexedrine. Amphetamines were among the drugs commonly used for weight loss when this information was collected.
Story Source:
Adhd Drugs Associated With A Dramatic Increased Risk For Parkinsons
Estimates indicate that approximately 11% of school-aged children in United States have attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder . Further, approximately 2/3 of these children are currently being medicated for this diagnosis. The most common medications are essentially stimulants like amphetamines or methylphenidates, including drugs like Adderall and Ritalin.
The areas of the brain that are potentially damaged or disrupted by these medications include the basal ganglia, brain structures that are involved in coordinated movement. The other area that is potentially involved is the cerebellum, which also plays a role in movement.
In a recent study published in Neuropsychopharmacology, researchers from the University of Utah attempted to determine if children with ADHD had an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease or other issues related to damage to the areas of the brain described above. Further, they wanted to determine if in fact being treated for ADHD might increase risk for Parkinson’s down the line.
The research involved the review of more than 11 million individuals and ultimately arrived at a cohort of around 32,000 individuals who had a history of being diagnosed with ADHD. These subjects were at least 20 years of age in 2011 and of them, approximate 5,000 had been treated with stimulant medications, again for ADHD. These subjects were compared to approximately 160,000 individuals in whom there was no history of ADHD.
Related Topics
Discuss The Latest Research In The Parkinsons Disease News Forums
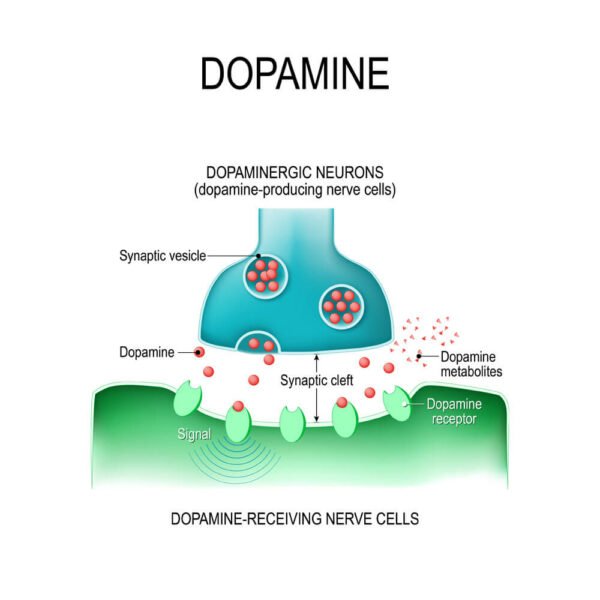
Parkinson’s disease is also characterized by a lack of dopamine, a consequence of the progressive degeneration and death of nerve cells that produce this neurotransmitter — the so-called dopaminergic neurons.
Treatment for ADHD includes the use of therapeutic stimulants that increase the amount of dopamine in the brain, such as amphetamine, methylphenidate and dexmethylphenidate.
The long-term impact of ADHD, its treatment and the risk of developing brain diseases such as Parkinson’s is largely unknown.
Researchers at the University of Utah performed a retrospective analysis of the Utah Population Database , which contains the medical records of more than 11 million people who have lived in the state.
They analyzed data from people born between 1950 and 1992, who were at least 20 years old by the end of 2011 and had no prior diagnosis of Parkinson’s or Parkinson’s-like diseases.
In total, their analysis included 31,769 patients who were diagnosed with ADHD, 4,960 of whom were prescribed stimulant medications — 2,716 received amphetamine salts , 1,941 were treated with methylphenidate and 303 receiving both therapies.
As controls, they included 158,790 non-ADHD individuals, matched for gender and age with the ADHD group.
Researchers found that ADHD patients had more than twice the risk of developing Parkinson’s and Parkinson’s-like diseases.
Pretreatment With Lower Psychostimulant Doses Is Neuroprotective
If you are psychostimulant-naive and are thinking about initiating psychostimulant therapy to control inattentive symptoms of ADHD, start at the lowest possible dose and titrate upward slowly. Recent evidence has emerged that pretreatment with low-dose AMP and METH in young animals ameliorates the neurotoxicity of future high dose challenge with these drugs . Lower doses may give the brain time develop an adequate defense against future insults.
Adhd Diagnosis Could Increase Risk For Parkinsons Study Suggests

People diagnosed with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder , usually detected at an early age in hyperactive children, may have an increased risk of developing Parkinson’s and Parkinson’s-like diseases, a new study suggests.
“Parkinson’s disease is commonly thought of as a neurodegenerative disease associated with aging,” Glen Hanson, PhD, professor at the University of Utah Health and the study’s lead author, said in a press release. “This may be the first time where a childhood disease and its treatment may be linked to a geriatric expression of neurodegenerative disorder.”
The study, “Increased Risk of Diseases of the Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum in Patients with a History of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder,” was published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology.
ADHD is estimated to affect approximately 11% of children ages 4-7 in the United States, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
ADHD, characterized by hyperactivity and attention impairments that may interfere with the child’s development, is linked with a deregulated release of the neurotransmitter dopamine, a key signaling molecule that regulates brain cell activity and function.
A Critical Reappraisal Of The Worst Drugs In Parkinsons Disease
What are the worst drugs for Parkinson’s disease patients? Couldn’t a simple list be assembled and disseminated to the Parkinson community? Recently Ed Steinmetz, an experienced neurologist in Ft. Meyers, FL pointed out to me, a list approach published in the Public Citizen Newsletter . The approach was to list every drug associated with a single confirmed or unconfirmed symptom of Parkinson’s disease or parkinsonism. Parkinson’s disease is defined as a neurodegenerative syndrome , whereas parkinsonism encompasses a wider net of drug induced and other potential causes. In parkinsonism symptoms are similar to Parkinson’s disease, but patients do not have Parkinson’s disease. Patients and family members confronted with a simple “drug list” approach may falsely conclude that most medicines are bad for Parkinson’s disease, and that any medicine may cause parkinsonism. This concept is in general, incorrect. Although the approach is well-meaning, it is in need of a major revision, as Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism are too complex to summarize by simple lists. In this month’s column I will try to summarize the key information that patients and family members need to know about the “worst pills,” for Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism.
A Florida Parkinson’s Treatment Blog by Michael S. Okun, M.D.
UF Center for Movement Disorders & Neurorestoration, Gainesville FL
Using Amphetamines May Increase Risk Of Parkinsons Disease
The American Academy of Neurology, an association of more than 22,500 neurologists and neuroscience professionals, is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.For more information about the American Academy of Neurology and its upcoming Annual Meeting, visit http://www.aan.com.
New Research Finds Link Between Adhd And Parkinson Disease Kelly Davio
Researchers from the University of Utah explain that patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder were more than twice as likely to develop early-onset Parkinson disease or a related basal ganglia and cerebellum disease than peers who do not have ADHD. Among patients with more severe disease who are prescribed stimulant medications to control their ADHD, the risk was 6- to 8-fold higher.
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder affects approximately 11% of children in the United States, and some previous research has suggested that that exposure to stimulants commonly used to treat the disorder can result in persistent basal ganglia dopaminergic deficits. Now, new research shows that patients with ADHD have an increased risk of developing Parkinson disease and related basal ganglia and cerebellum diseases, and patients treated with stimulants have an even greater risk.
In a paper today in Neuropsychopharmacology, researchers from the University of Utah explain that patients with ADHD were more than twice as likely to develop early-onset PD or a BGC disease than peers who do not have ADHD. Among patients with more severe disease who are prescribed stimulant medications to control their ADHD, the risk was 6- to 8-fold higher.
In the ADHD cohort, the rate of incident BGC diseases was 0.52%, compared with 0.19% in the non-ADHD cohort, and the age of disease onset was slightly younger among patients with ADHD than in those without ADHD .
Differences In Structure And Uses Similarities In Effects

Modafinil has a unique structure and is not a stimulant like Adderall, but it does have stimulant-like effects and improves alertness, enhances thinking and perception, in addition to helping to keep people awake. Experts aren’t exactly sure how it works, although they have elucidated that it enhances several chemicals and neurotransmitters in the brain including dopamine, serotonin, histamine, glutamate, and GABA. Although studies have not shown any significant withdrawal effects, any drug that provides stimulant effects to the brain enforces drug taking to some extent and carries the potential for dependence which could lead to withdrawal symptoms. Anecdotally people have reported significantly reduced energy, lack of motivation, and depression following discontinuation of Provigil. Modafinil should always be tapered on drug discontinuation if it has been used for a long period of time.
Modafinil was first approved by the FDA in 1998 to treat narcolepsy, and is also used to treat excessive sleepiness caused by obstructive sleep apnea or shift work. Off-label it has been used to help people with Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple Sclerosis stay alert, and has been favored by students, executives, and the military as a way to combat sleep deprivation and fatigue. Even though it is not approved for ADHD, it is often used and at least one study has suggested it helps reduce symptoms of impulsivity in those with ADHD.
Adhd & Pd: The Basal Ganglia And Cerebellum Connection
All Science News articles summarize a research study and are not an official opinion, endorsement or position of the Parkinson’s Foundation’s.
Two parts within our brain require healthy dopamine regulation and transmission to do their jobs:
- The basal ganglia: messengers that sort out information for the spinal cord and cerebellum and are associated with various functions, including motor control, motor learning, executive functions and behaviors, and emotions.
- The cerebellum: involved in movement and coordination, walking, posture, reflexes, and eye and head movement; it also sends instructions to our muscles that adjusts our posture and keeps our bodies moving smoothly.
Adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder have been shown to have damaged dopamine neurons in the basil ganglia, and, commonly have cerebellar abnormalities, much like people with Parkinson’s disease . So, are ADHD and PD somehow connected? Perhaps.
A recently published study in the journal, Neuropsychopharmacology, sought to determine if having ADHD and/or its treatment, increases the risk of having basal ganglia and cerebellar diseases. In this 20-year follow-up retrospective cohort study, a total of 190,586 patient records from Utah were examined. People with no prior PD diagnosis or symptoms, no basal ganglia/cerebellar disease and those with a history of substance abuse were excluded from participating in the study.
Results
In terms of comparing people with ADHD to non-ADHD, :
Learn More
Stimulant Adhd Medications And Your Circulatory System
All stimulants can impact your circulatory system in a few ways. They can make your heartbeat faster, increase your blood pressure, and constrict your blood vessels. You should avoid drinking alcohol when you take stimulant ADHD medications, as this can increase your likelihood of developing heart problems.
In a small number of extreme cases, people who take stimulant ADHD medications may experience a stroke or heart attack. Seek medical help immediately if you start to feel chest pain. People with pre-existing heart conditions can experience sudden death after taking stimulant ADHD medications.
Stimulant Adhd Medications And Your Respiratory System
Respiratory side effects from stimulant ADHD medications can be related to your respiratory and circulatory system. In some cases, patients might have trouble breathing or notice their fingers and toes turning blue because their bodies are not circulating enough oxygen. Call your doctor or go to the nearest emergency room immediately for treatment.
Stimulant Adhd Medications And Your Digestive System
Stimulant ADHD medications increase how much glucose gets released into your system, which can cause all sorts of digestive issues. You might lose your appetite, resulting in unexpected and unwanted weight loss. This can be especially harmful to children who are still growing. Adults usually only experience weight loss temporarily, and they regain their appetite soon after their body adjusts to the medication.
Some digestive issues people who take stimulant ADHD medications might experience include the following:
- Nausea
Adderall Neurotoxicity: How To Protect Your Brain
Oxidopamine – A toxic oxidation product of dopamine
Although Adderall confers clear clinical benefits in patients with ADHD, Adderall neurotoxicity is well-documented. Specifically, Adderall is neurotoxic to the dopaminergic system. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that regulates reward, pleasure, motivation, and muscular tone.
Adderall improves attention by eliciting dopamine and norepinephrine release. Dopamine may auto-oxidize to form 6-hydroxydopamine which can damage dopaminergic neurons.
Dopaminergic neurons are particularly sensitive to oxidative stress18 due in part to their high metabolic rate. Parkinson’s disease is caused by the death of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Methamphetamine use is considered a risk factor for the development of Parkinson’s disease.
How Adhd Medication Impacts Your Nervous System
People with ADHD can get bored extra fast when working on something that isn’t interesting. Therefore, many students with ADHD struggle to do homework or pay attention in class. However, that doesn’t mean that people with ADHD are doomed to struggle. Often, people with ADHD have highly successful careers working in fast-paced, high-intensity environments.
Even when someone with ADHD has found a passion for something, they can still struggle with certain aspects of their lives. The primary reason for taking drugs such as Adderall, Vyvanse, and Ritalin is to balance the body’s central nervous system. Positive effects of these drugs include feeling more alert during the day, having more impulse control, and being able to concentrate on important tasks.
Adderall Statistics & Use In The United States
Close to 50 million prescription stimulant drugs like Adderall were dispensed in 2011 to treat symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, or ADHD.
This represents an almost 40 percent rise in these prescriptions since 2007, the Drug Enforcement Agency states. ADHD is one of the most common childhood neurobiological disorders. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that as of July 2015, almost 10 percent, or close to 6 million, American children between the ages of 4 and 17 had been diagnosed with ADHD at some point in their lifetimes.
The risk of developing a stimulant addiction with prescription drugs, such as Adderall, is becoming more prevalent in the U.S. At American Addiction Centers we understands the dangers of prescription drug abuse and we are here to help. For more information about addiction and treatment options, call us at to speak confidentially with an admissions navigator for help getting access to our successful substance abuse programs.
AAC is in-network with many insurance providers. Addiction treatment can be free depending on your policy.
Learn More and Verify Your Insurance with AAC
A study at the University of Kentucky found that 30 percent of its students had abused an ADHD stimulant drug like Adderall at some point as a possible “study enhancer,” CNN reports.
Stimulant drugs like Adderall are addictive and using them recreationally may increase the chances of developing a psychological and physical dependence on them.
Adhd Tied To Raised Risk Of Early Parkinson’s
HealthDay Reporter
WEDNESDAY, Sept. 12, 2018 — People with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder may be more than twice as likely to develop an early onset form of Parkinson’s, new research warns.
What’s more, among “those ADHD patients who had a record of being treated with amphetamine-like drugs — especially Ritalin — the risk dramatically increased, to between eight- to nine-fold,” said senior study author Glen Hanson.
But his team did not prove that ADHD or its medications actually caused Parkinson’s risk to rise, and one ADHD expert noted that the absolute risk of developing Parkinson’s remains very small.
For the study, researchers analyzed nearly 200,000 Utah residents. All had been born between 1950 and 1992, with Parkinson’s onset tracked up until the age of 60.
Prior to any Parkinson’s diagnosis, roughly 32,000 had been diagnosed with ADHD.
Hanson, a professor of pharmacology and toxicology at the University of Utah, said that ADHD patients were found to be “2.4 times more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease-like disorders prior to the age of 50 to 60 years,” compared with those with no history of ADHD. That finding held up even after accounting for a number of influential factors, including smoking, drug and alcohol abuse, and other psychiatric disorders.
“Although we cannot accurately say how much time elapsed between ADHD and Parkinson’s-like disorder diagnosis, it was probably between 20 to 50 years,” he said.
Neuropsychopharmacology
Methylphenidate Use For Fatigue In Parkinsons Non-Motor Symptoms
Methylphenidate , better known by its brand name, Ritalin, is popular for its use in the treatment of children with ADHD. It was FDA approved in the 1950s and became increasingly prescribed in the 1990s. MP has since been used for other disorders, including narcolepsy, refractory depression and fatigue caused by medical and neurological disorders.
Fatigue in Parkinson’s is a common problem encountered by one-third to one-half of people with the disease. Parkinson’s fatigue is often unrelated to the disease severity and overall motoric disability. Medications used to treat the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s typically do not improve fatigue, and treatment specific to fatigue is lacking.
MP is a psychostimulant which has seen an increase in off-label use to treat Parkinson’s fatigue. MP works by decreasing the reuptake of neurotransmitters, like dopamine and norepinephrine, thus making them available longer in the synaptic cleft where the chemicals can act on the receiving brain cells.
Based on their clinical experience, many physicians are recommending that patients try MP for Parkinson’s fatigue, especially when quality of life is greatly impacted.
MP is an old drug that may have newer uses; it may have potential to help people with Parkinson’s. As with all medications, discuss the risks and benefits of MP with your neurologist and other healthcare team members before deciding if it is right for you.
Should I Get Treatment For Adderral Addiction
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Nemo enim ipsam voluptatem quia voluptas sit aspernatur aut odit aut fugit, sed quia consequuntur magni dolores eos qui ratione voluptatem sequi nesciunt. Neque porro quisquam est, qui dolorem ipsum quia dolor sit amet, consectetur, adipisci velit, sed quia non numquam eius modi tempora incidunt ut labore et dolore magnam aliquam quaerat voluptatem. Ut enim ad minima veniam, quis nostrum exercitationem ullam corporis suscipit laboriosam, nisi ut aliquid ex ea commodi consequatur? Quis autem vel eum iure reprehenderit qui in ea voluptate velit esse quam nihil molestiae consequatur, vel illum qui dolorem eum fugiat quo voluptas nulla pariatur?
Amphetamine Use May Increase Parkinsons Risk July 15th, 2011 by Mike
In April 2011, the American Academy of Neurology had a big annual meeting in Hawaii to discuss the state of their field and recent findings. Among those discussion items was a 38-year study on amphetamine users; one of the first to offer observations about the long-term impact of amphetamine use.
How Extended Adderall Use Affects The Brain
Stimulants increase concentration and energy levels while decreasing the need for sleep and suppressing the appetite. Adderall increases the activity of several neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and especially dopamine. Over time, the changes in dopamine activity can impact our brain’s reward center, and alter our ability to experience pleasure without the chemical support of continued amphetamine use.. The more often Adderall is taken, the more ingrained these changes become. A tolerance to the drug may form, and more Adderall may be needed at each dose in order to feel the same desired effects.
As Adderall leaves the bloodstream, withdrawal symptoms and drug cravings may occur, indicating a physical and emotional dependence on the drug. The way in which Adderall is abused, along with the amount and duration of abuse can affect the dependence level to the drug. Crushing the pills and then injecting or snorting them, for example, sends the drug into the brain more rapidly than ingesting them whole and having them enter the bloodstream via the digestive tract. As a result, injecting or snorting the crushed pills increases the chances for a life-threatening overdose and the potential for addiction. Addiction is a disease that affects each person individually, and environmental and biological factors may also play a role in its onset.
Overcoming The Consequences Of Adderall Use
Many of these conditions can be reversed by stopping Adderall usage, though some of them result in permanent damage or even death. An Adderall addiction treatment center can provide you with the guidance and medical attention to properly address your underlying issues and provide you with the treatment you need in a safe environment to fully recover and best address your diagnoses in a healthy way. It is very important, however, to note that regular prescribed usage of Adderall for the treatment of ADHD or narcolepsy is usually safe and does not usually result in significant medical or psychiatric consequences; in fact, research shows that the risk of consequences like developing a substance use disorder from untreated ADHD is higher than the risks of regular prescribed Adderall usage.
If you believe that you or a loved one are abusing—or are addicted to—Adderall, please contact one of our caring advisors today for more information about how we can help.
Adhd Doubles Risk Of Early Onset Parkinsons
Investigators at the University of Utah Health have released some interesting, if not disturbing new findings: attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder patients have a greater risk of developing Parkinson’s and Parkinson-like diseases than individuals with no ADHD history. The results from the new study were released in Neuropsychopharmacology through an article titled “Increased risk of diseases of the basal ganglia and cerebellum in patients with a history of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.”
This new data is significant as 11% of children nationwide have been diagnosed with ADHD. Moreover, the long-term health effects of having ADHD and of common ADHD medications remains understudied.
“Parkinson’s disease is commonly thought of as a neurodegenerative disease associated with aging,” explains senior study investigator Glen Hanson, D.D.S., Ph.D., professor of pharmacology and toxicology in the School of Dentistry at U of U Health. “This may be the first time where a childhood disease and its treatment may be linked to a geriatric expression of a neurodegenerative disorder.”
However, the authors did caution that patients with a more severe type of ADHD may inherently be at an increased risk of motor neuron diseases like Parkinson’s, and the results may or may not be a direct result of the stimulant medication. Future studies are needed to reach a more definitive conclusion.
Various Kinds Of Stimulant Adhd Medications
Stimulant medications, like Adderall, Vyvanse, and Ritalin are the most commonly used treatments for ADHD. They can decrease your ability to get distracted and help you focus by increasing certain brain chemicals. Many people notice improvements within one to two hours of taking a stimulant for ADHD.
Stimulant ADHD medications use one of two first-line molecules—methylphenidate and dextro-amphetamine. Both types of stimulants can be habit-forming when taken incorrectly, so they should always be taken under the guidance of a licensed doctor. They have similar side effects.
What Happens In The Vagus Nerve: The Pd Gut

The gut-brain relationship is real. Stomach or intestinal distress can lead to anxiety or depression. However, those gut-brain connections go much further: evidence from recent studies strongly suggest a link between the gut and Parkinson’s disease .
In the PD research field, the Braak Hypothesis states that the earliest signs of Parkinson’s are found in the enteric nervous system . This theory is supported by evidence that in PD, non-motor symptoms, such as constipation, may appear before motor symptoms. Braak hypothesized that abnormal alpha-synuclein can spread from the gut via the vagus nerve to the midbrain, where it selectively kills dopamine neurons.
Get to Know the Brain
Alpha-synuclein: a protein found in the brain, central to Parkinson’s.
Central Nervous System:controls most functions of the body and mind. Consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
Prion: a protein that can harm a normal protein, causing damage to healthy brain cells. Some scientists believe alpha-synuclein can become a prion and lead to Lewy body clumps, the hallmark of PD.
Vagus Nerve: a nerve that connects the brain to the gut. Regulates organ functions, such as digestion, heart rate, respiratory rate, coughing, sneezing and swallowing.
ResultsIn normal mice:
In the mice with no alpha-synuclein:
- Injecting abnormal alpha-synuclein into their gut successfully made it into the brain, but nothing happened. Since there was no normal alpha-synuclein, it was not able to start the clumping.
Benefits Of Adderall In Patients With Adhd
The benefits of Adderall in certain patients cannot be dismissed despite these safety concerns.
An MRI-based neuroimaging study provided tentative evidence that therapeutic doses of psychostimulants in patients with ADHD rescues alterations in brain structure compared with unmedicated subjects3, which may underlie the clinical benefits of psychostimulants in this patient population.
It remains possible that amphetamine exerts neurotrophic effects in individuals with ADHD by facilitating normal brain development and enhancing reward saliency while also at the same time adversely affecting the dopaminergic system. Elevations in intracellular dopamine concentrations outside of vesicular storage likely promotes the formation of 6-hydroxydopamine . 6-OHDA or oxidopamine is a potent neurotoxin which selectively destroys dopaminergic neurons and is employed in animal models to emulate methamphetamine abuse and Parkinson’s disease.
These biochemical events likely underlie Adderall neurotoxicity.
Heres The Excerpt From Physicians Weekly
Amphetamine Use May Increase Parkinson’s Risk
The Particulars: Amphetamines were once recommended for treating patients with Parkinson’s disease. Recent studies, however, have suggested that this class of drugs may be linked to a higher risk of developing Parkinson’s.
Data Breakdown: Researchers conducted an analysis in 66,438 individuals who did not have Parkinson’s disease at baseline and collected information on exposure to amphetamines. Through a mean follow-up of 38.8 years, 1,154 patients received a Parkinson’s diagnosis. The average age at baseline was 36, and the average age at diagnosis was 70. Individuals who reported often taking amphetamine sulfate or dextroamphetamine sulfate had a 56% greater risk of having a Parkinson’s diagnosis decades later. The magnitude of the relationship was similar for both men and women. Participants who reported taking weight-loss medication at baseline did not have an elevated risk for Parkinson’s disease through follow-up .
Take Home Pearls: The use of amphetamines appears to be associated with an elevated risk for developing Parkinson’s disease later in life. Considering the wide population exposure to both legal and illegal amphetamines, more studies are needed to address this association.
I’ve expected this for years since they plug into the basal ganglia. Also explains why cigarette smokers don’t get Parkinson’s . Dextroamphetamine forces the dopamine out of the cell.
Alternative Adhd Medications To Consider
Adderall is the most common prescription used to treat ADHD, but it is not the only one. There are two primary types of medications used for ADHD—stimulant and non-stimulant. These have the same purpose of helping you focus and feel calm. Tell your doctor about all your current medications and existing conditions so they can determine which one will likely work best for you.
Introduction: Adhd And Psychostimulants
The center for disease control has estimated that over five million children have been diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in the United States alone. Psychostimulants, including amphetamine salts, are the most widely-prescribed medications for the treatment of ADHD.
State-based Prevalence Data of ADHD Diagnosis : Children EVER diagnosed with ADHD19
Despite considerable research in animal models and in vitro, the likelihood of irreversible Adderall neurotoxicity to dopaminergic neurons at therapeutic dosages in humans remains controversial and poorly characterized. Physicians have a responsibility to disclose the long-term risks of medications so that patients can make informed decisions with accurate cost-benefit analyses.
