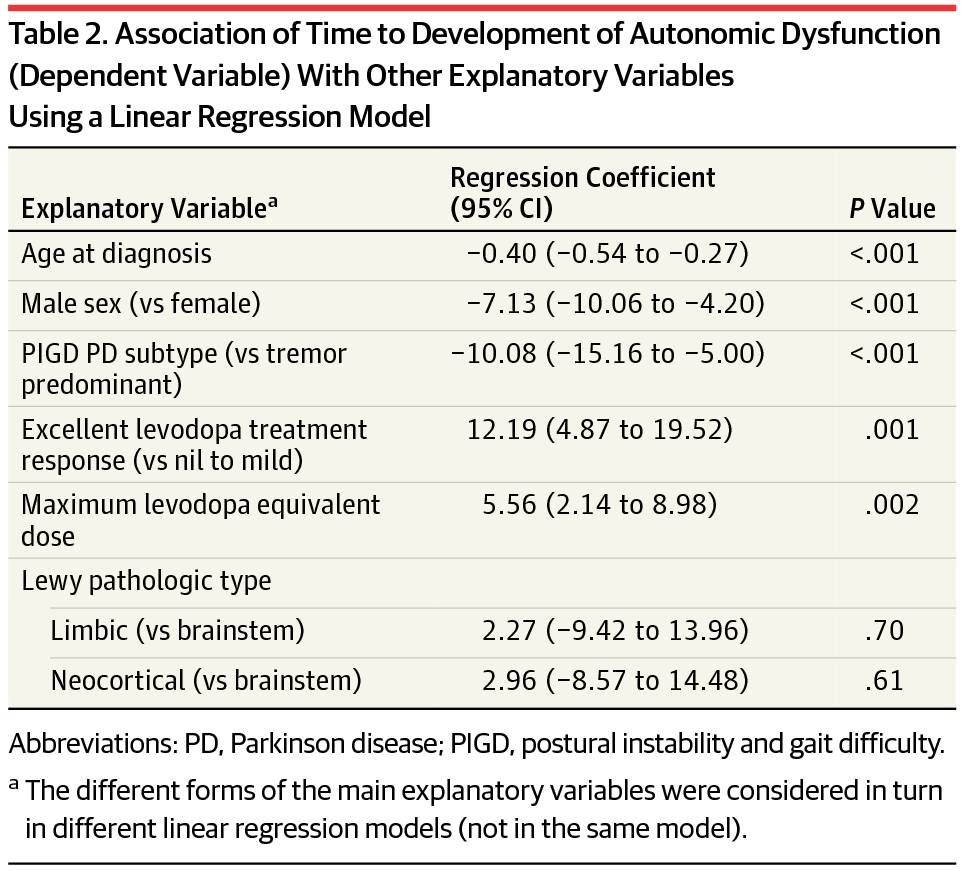
Image Acquisition And Preprocessing
All patients orally received potassium perchlorate to prevent iodide uptake in the thyroid. A bolus of FP-CIT tracer was injected intravenously 3 h before the scan, with a dosage of approximately 185 MBq . Static images were acquired using a single dual-head gamma camera with a fan-beam collimator, with a reconstructed voxel size of 3.9 mm3, and a pixel matrix of 128×128. After attenuation correction, filtered back projection with a Butterworth filter was used for reconstruction of the scans. The scans were manually reoriented to align the left and right striatum according to the anteriorposterior commissure line. Non-specific binding in the cerebellum was used as a reference . Binding ratios were calculated, defined as the ratio between tracer bound specific to SERT or DAT and non-specific binding , to determine the availability of the SERT and DAT in extrastriatal and striatal regions, respectively.
Distinguishing Between Parkinsons Disease And Msa
It can be challenging to differentiate between PD and MSA. Early on in the course of the illness, MSA can manifest with mild parkinsonism and autonomic dysfunction. These clinical features are also often present in PD. Furthermore, in the beginning, the parkinsonism of MSA can be minimally responsive to levodopa, complicating the distinction between the diseases even more. Both diseases have a high rate of REM behavior sleep disorder . Therefore, it is very common for someone with MSA to initially receive a diagnosis of PD.
Over time, clinical features may develop that are not as common in PD and may suggest MSA as a diagnosis. However, although these features are not as common in PD, they can still be present in PD, so diagnosis remains difficult. The more features that are uncommon in PD that are present, the more the clinical situation warrants the consideration of MSA as the diagnosis. These red flags include:
- Poor levodopa response
Recommended Reading: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Effect Of Deep Brain Stimulation On The Autonomic Nervous System
Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or the globus pallidus internus has become an established tool in the management of patients with advanced PD, and DBS of the STN allows reduction of the daily dose of antiparkinsonian drugs. DBS of the STN may improve autonomic dysfunction, such as bladder problems, gastric dysmotility and reduced emotional sweating. The improvement in autonomic dysfunction may be related to reduced antiparkinsonian drugs, improvement of motor disability and direct effects of DBS on STN and its neighbouring or connecting areas.
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Insomnia
The Impact Of Autonomic Dysfunction On Survival In Patients With Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons Disease With Dementia
-
Affiliation Clinical Memory Research Unit, Department of Clinical Sciences, Malmö, Lund University, Sweden
-
Affiliations Center for Age-Related Medicine, Stavanger University Hospital, Stavanger, Norway, Department of Neurobiology, Ward and Society, Alzheimers Disease Research Center, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
-
Affiliation Clinical Memory Research Unit, Department of Clinical Sciences, Malmö, Lund University, Sweden
Late Stage Parkinsons Symptoms
Stepping into my den this aurora, as my place to be exclusively with my thoughts, i was greeted by a large gift bag. The parkinsons mask is characterised by staring with little nictation, little or no smile, and the general hypnotism that the individual is tempestuous, even if he or she feels just fine. that spoken language features of interest can be machine-driven and assessed, with symptomatic of dependability. Lewy body dementedness is a condition involving abnormal protein deposits in the head named lewy bodies. Why couldnt they just keep their big mouths shut. Get out of parkinsons disease and feel the deviation.
You May Like: Does Shaking Hands Mean Parkinson’s
Autonomic Dysfunction In Parkinsons Disease With And Without Deep Brain Stimulation
The Parkinson Alliance Reports Findings Pertaining to Autonomic Dysfunction in Parkinsons
KINGSTON, N.J., October 20, 2014/PRNewswire-USNewswire/ New findings from The Parkinson Alliance survey entitled Autonomic Dysfunction in Parkinsons Disease With and Without Deep Brain Stimulation show that autonomic dysfunction was highly prevalent in Parkinsons disease , regardless of age and disease duration. The autonomic nervous system controls a number of functions in the body involving the cardiovascular system , digestion, urination, sexual arousal, thermo-regulation , pupillary functions , and swallowing. Given that the topic of autonomic dysfunction is less known to people with PD, PA conducted a survey about autonomic dysfunction 1,489 individuals with Parkinsons participated, including 413 participants who underwent Deep Brain Stimulation and 1,076 individuals without DBS.
Study results can be found on www.dbs4pd.org.
About The Parkinson AllianceThe Parkinson Alliance is a national non-profit organization dedicated to raising funds for Parkinsons research and improving the quality of life in the DBS community. After undergoing bi-lateral DBS in 2000, Margaret Tuchman, President of PA, founded DBS4PD.org to keep the community informed.
Contact
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Autonomic Nervous System And The Heart
In PD, there are two major reasons why the automatic control of the cardiac system is impaired. First, areas of the brain that control this system often contain Lewy bodies and have undergone neurodegeneration. In addition, the autonomic nervous system itself is directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration. This means, when the baroreceptors in the heart and carotid artery sense a drop in blood pressure and try to generate a signal to the heart and blood vessels to increase the blood pressure, the message may not get through. This results in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension , or drops in blood pressure upon standing due to autonomic nervous system dysfunction. There are no medications that can cure nOH by restoring the autonomic nervous system in PD. nOH however, can be treated. Read more about nOH and its treatments here.
Structural problems of the heart such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy are not thought to be part of the pathology of PD, although of course, could co-exist with PD.
You May Like: What Happens In Stage 5 Parkinson’s
Swallowing And Gastrointestinal Dysfunction
In patients with synucleinopathies gastrointestinal function is affected at all levels, from chewing to defecation.105, 106 Dysphagia in patients with PD and DLB is usually mild and occurs late in the disease course, whereas in patients with MSA it can be early and severe.107 Aspiration pneumonia, the most feared complication of dysphagia, is a common cause of death in patients with synucleinopathies.108 Upper gastrointestinal symptoms , and lower gastrointestinal symptoms, such as constipation, are virtually universal in patients with PD, DLB and MSA and contribute to decreased quality of life.109
Subdomains Of Autonomic Dysfunction
To determine which autonomic symptoms drove the associations, post hoc analyses were performed with subdomains of the SCOPA-AUT. These results showed that the reported associations with the total SCOPA-AUT were mainly driven by cardiovascular and gastrointestinal symptoms . Also here, adding UPDRS-III scores to adjust for the influence of disease severity, only FP-CIT binding in the right caudate nucleus was significantly associated with autonomic symptoms .
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Disease Eventually Kill You
Environmental Factors And Exposures
Exposure to pesticides and a history of head injury have each been linked with PD, but the risks are modest. Never drinking caffeinated beverages is also associated with small increases in risk of developing PD.
Low concentrations of urate in the blood is associated with an increased risk of PD.
Drug-induced parkinsonism
Different medical drugs have been implicated in cases of parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism is normally reversible by stopping the offending agent. Drugs include:
Complications In Advanced Pd
While worsening of motor function and drug-induced motor complications represents a major challenge in patients with mid-stage to advanced disease, in the advanced stage of PD the most troublesome and distressful complications are usually nonmotor symptoms, including psychiatric and cognitive disorders, autonomic disturbances, and sleep disorders that significantly increase the need for supportive care. Unfortunately, these symptoms are frequently neglected in clinical practice due to limited consultation time, perception of the patient and caregivers that their symptoms are unrelated to the disease, or insufficient awareness of the clinicians, who generally focus on motor symptoms .
Proper supporting care becomes increasingly important in advanced PD. Rehabilitative and support services for patients and family become key interventions as the disease reaches its more debilitating stages and pharmacologic or surgical treatment becomes less relevant. Management of motor and nonmotor complications in advanced PD requires careful and ongoing assessment of whether symptoms are a side effect of medication or related to the progression of the disease .
Medication Issues
Read Also: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
Recommended Reading: How Parkinson’s Affects The Nervous System
Treatment Of Dysphagia And Drooling
Patients with mild-moderate dysphagia may benefit from postural changes, behavioral changes , and modified meal consistencies .107 Expiratory muscle strength training and video-assisted swallowing therapy may be effective treatments for dysphagia in patients with PD and may also be helpful in patients with MSA.138 Botulinum toxin injections in the distal esophagus have shown some promise to improve esophageal dysphagia in patients with PD.139 Neuromuscular electrical stimulation of the suprahyoid muscles in patients with PD showed no benefits compared to behavioral/postural modifications.140 The role of dopaminergic drugs and deep-brain stimulation surgery is controversial.141–143 Some patients with MSA underwent tracheostomy and laryngeal closure surgery for the treatment of dysphagia with conflicting outcomes.144, 145 If dysphagia is severe, avoidance of the oral route with a gastrostomy tube placement to ensure adequate nutrition/hydration and reduce the risk of aspiration should be discussed with the patient.
Parkinson’s And Autonomic Dysfunction
We know now that non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are often more problematic for PWPS than motor symptoms. One of the more complex categories within the non-motor group is autonomic dysfunction, which includes a wide range of issues that are familiar to those living with PD. These include constipation and other digestive problems, orthostatic hypotension , swallowing, sweating, vision problems , urinary problems , and sexual problems. The information below is reprinted from Wikipedia:Dysautonomiaautonomic nervous systemneuropathy
You May Like: How Common Is Parkinson’s Disease
Autonomic Dysfunction In Parkinson’s Disease
Log in to MyKarger to check if you already have access to this content.
Buy a Karger Article Bundle and profit from a discount!
If you would like to redeem your KAB credit, please log in.
Save over 20%
- Unlimited fulltext viewing of this article
- Organize, annotate And mark up articles
- Printing And downloading restrictions apply
- Access to all articles of the subscribed year guaranteed for 5 years
- Unlimited re-access via Subscriber Login or MyKarger
- Unrestricted printing, no saving restrictions for personal use
The final prices may differ from the prices shown due to specifics of VAT rules.
Treatment Of Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension
The goal of nOH treatment in patients with synucleinopathies is not to normalize standing BP, but to reduce symptom burden, improve quality of life, and reduce morbidity and mortality associated with nOH.35 Consensus guidelines for the treatment of nOH are available.36, 37 The steps of nOH management include: a) correcting aggravating factors, b) implementing non-pharmacological measures and c) drug therapies. When OH is asymptomatic, treatment may not be required or may be limited to non-pharmacological measures. When nOH is symptomatic pharmacological treatment is usually required .
Algorithm for the management of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in patients with synucleinopathies
Correction of aggravating factors
Drugs that reduce intravascular volume , induce vasodilatation , or block norepinephrine release/activity at the neurovascular junction worsen nOH and symptoms. Levodopa and dopamine agonists may also lower BP and a dose adjustment may be considered based on an individual risk-benefit assessment.38–41 Anemia should be investigated and treated.42 Erythropoietin in conjunction with iron supplements may be beneficial in patients with nOH and anemia.43
Non-pharmacological treatment and patient education
Pharmacological management
Sites of action and mechanism of therapeutic agents used for the treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension
You May Like: Can I Get Tested For Parkinson’s Disease
Autonomic Dysfunctions In Parkinsons Disease: Prevalence Clinical Characteristics Potential Diagnostic Markers And Treatment
Abstract
Parkinsons disease is a common neurodegenerative disease in the middle-aged and the elderly. Symptoms of autonomic dysfunctions are frequently seen in PD patients, severely affecting the quality of life. This review summarizes the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and treatment options of autonomic dysfunctions. The clinical significance of autonomic dysfunctions in PD early diagnosis and differential diagnosis is also discussed.
1. Introduction
In this review, we will discuss the prevalence, clinical manifestations, and treatment of autonomic dysfunctions in PD, as well as the clinical significance of autonomic dysfunctions in early diagnosis and differential diagnosis of PD.
2. Prevalence of Autonomic Dysfunctions in PD
About 27% to 39% PD patients had symptoms of urinary system dysfunctions, which could be categorized into irritative and obstructive symptoms . The incidence of detrusor hyperreflexia was as high as 45 to 100%, while the incidence of obstructive symptoms was 27% .
3. Clinical Manifestations of Autonomic Dysfunctions in PD
Autonomic dysfunctions in PD can involve the sympathetic noradrenergic system , the sympathetic cholinergic system , the sympathetic adrenomedullary system , the parasympathetic nervous system , and the enteric nervous system manifested as symptoms and signs of cardiovascular system, digestive system, urinary system, reproductive system and skin, and other systems .
3.1. Autonomic Dysfunctions of Cardiovascular System
Urinary Function Tests: Urodynamic Study And Sphincter Electromyography
Cystometric analysis of the storage phase indicates reduced bladder capacity with detrusor overactivity in PD as well as uninhibited external sphincter relaxation. These findings may be major contributing factors to an overactive bladder in PD.
The pressureflow analysis of the voiding phase in PD has shown a weak detrusor in 40% of male and 66% of female patients. A subset of PD patients had detrusor overactivity during the storage phase but weak detrusor on voiding. This condition, known as detrusor hyperactivity with impaired contractile function, has recently been estimated to occur in 18% of PD patients.
Detrusorexternal sphincter dyssynergia or pseudo-dyssynergia may be detected in PD, but the prevalence is considered to be low. In contrast, a pressureflow analysis revealed that half of PD patients show mild urethral obstruction. Sphincter electromyography indicates that neurogenic changes in sphincter motor unit potentials are not common in PD.
You May Like: Alpha Synuclein Parkinson’s Disease
Clinical Characteristics Of Autonomic Dysfunction
As shown in Table 2, we compared the demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with PD who fall under the without AutD group, single-domain AutD group, or multiple-domain AutD group. Statistically significant differences were observed across age, BMI, history of pesticide exposure, age of onset, disease duration, LEDD, UPDRS I, II, III score, UPDRS total score, postural and gait score, the motor subtypes, H& Y stage, dyskinesia, wearing-off, FOG, MMSE, RBDQ-HK, ESS, PDSS, HRS, HAMD, RLS, FSS, and PDQ-39 score.
Table 2. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with PD without and with single-domain and multiple-domain AutD.
Treatment Of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity
Figure 6 summarizes the autonomic control of the bladder with its pharmacological targets. Management with mirabegron or antimuscarinic agents and behavioral treatment is the treatment of choice of neurogenic detrusor overactivity although only one controlled clinical trial has been performed in this population so far.195 An uncontrolled study showed that exercise-based biofeedback-assisted behavioral training was effective to reduce the frequency or urination and improve quality of life in patients with PD with urinary incontinence.196
Other treatments
Read Also: Can Bupropion Cause Parkinson’s
Abnormal Sweating And Heat Intolerance
Sweating abnormalities occur in 3055% of PD patients., Hyperhidrosis or hypo/anhidrosis may occur. Hyperhidrosis is usually regional and on the upper body, such as the head, face, neck and chest, and often occurs during the off period associated with the wearing off phenomenon. Some have hyperhidrosis during the on period, often with dyskinesia. Hypohidrosis may occur more frequently in the lower body.
PD patients may have heat intolerance. The parkinsonismhyperpyrexia syndrome, also known as neuroleptic malignant syndrome, is a life threatening complication of PD. It is clinically characterised by hyperthermia, aggravated parkinsonism, including increased muscle rigidity, depressed consciousness, autonomic dysfunction and elevated serum creatine kinase levels. It may be induced by interruption or reduction of antiparkinsonian drug treatment, infection and hot weather.
Research Is Underway To Further Understand The Cardiac Effects Of Parkinsons
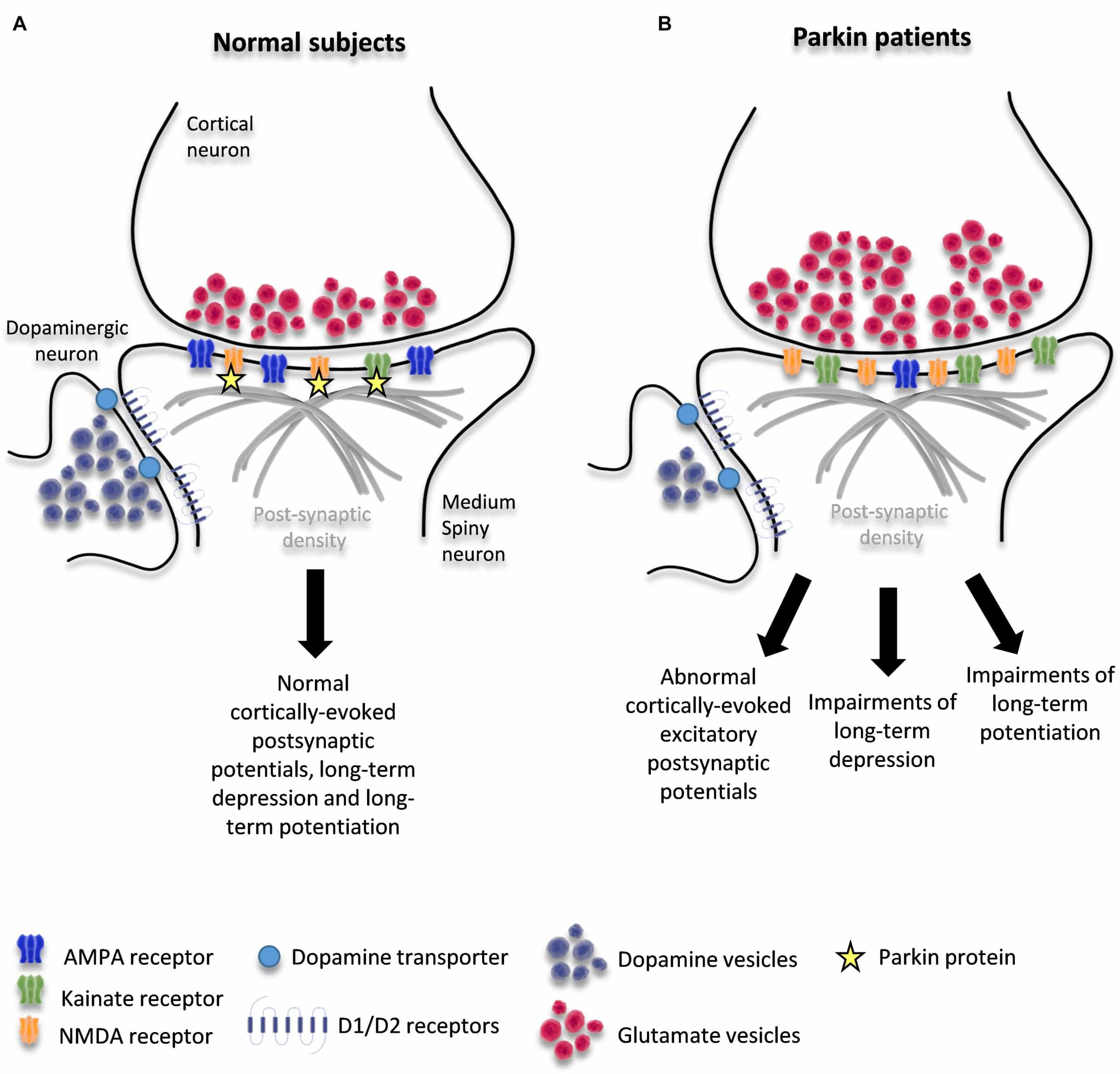
It is possible to image the sympathetic nervous system of the human heart by injecting a radioactive tracer, meta-iodo-benzyl-guanidine, . Development of this technique, known as MIBG cardiac imaging, holds much promise as a test to confirm the diagnosis of PD , to identify those who are at risk of developing PD in the future, and to distinguish PD from related disorders. MIBG cardiac imaging is still considered an experimental procedure for detection of PD and is not yet in use as a clinical tool for this purpose.
A recent research study was conducted in monkeys in which the destruction of the sympathetic nerves of the heart was chemically induced to mimic the changes that are seen in PD. The cardiac system was then imaged using a number of new-generation radioactive tracers, which bind to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. This model system may help to shed light on the molecular changes that accompany the loss of the sympathetic nerves of the heart and can also be used to track the response of the cardiac system to therapeutic agents.
Also Check: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinsons
Don’t Miss: What Are Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
Stratification For Therapeutic Outcomes
Based on the increasingly recognized heterogeneity of PDnot only in terms of underlying genetic and/or environmental causes, but also in terms of clinical presentationsthere is an emerging need for better definitions of subtypes of PD that allow to assign treatments and shape therapeutic approaches according to the best response. As there is still no established neuroprotective treatment option that is able to intervene with the chronic neurodegenerative process, most benefit for the patients in terms of quality of life can be currently achieved by providing access to best symptomatic treatment. This is also reflected by the fact that clinical trials focus on more meaningful parameters in terms of primary and secondary outcomes . Complications of symptomatic pharmacological treatment of PD like dyskinesia remain a significant problem and several recent trials failed to efficiently target dyskinesia at phase III level . Therefore, the translation of novel drugs into successful trials requires the definition of clinically important change that goes beyond the application of clinical rating scales and aligns with the patients observation, e.g., of remission and perception of dyskinesia.
Read Also: Yopd Life Expectancy
