Deep Brain Stimulation For Movement Disorders
Deep brain stimulation has been approved for the treatment of movement disorders since the 1990s. Numerous studies have proven this surgerys superiority to medical therapy alone. The time to consider DBS surgery is when the quality of life is no longer acceptable on optimal medical therapy as administered by a movement disorder specialist. DBS surgery is very safe and recent advancements in device technology have improved patient outcomes as well.
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation
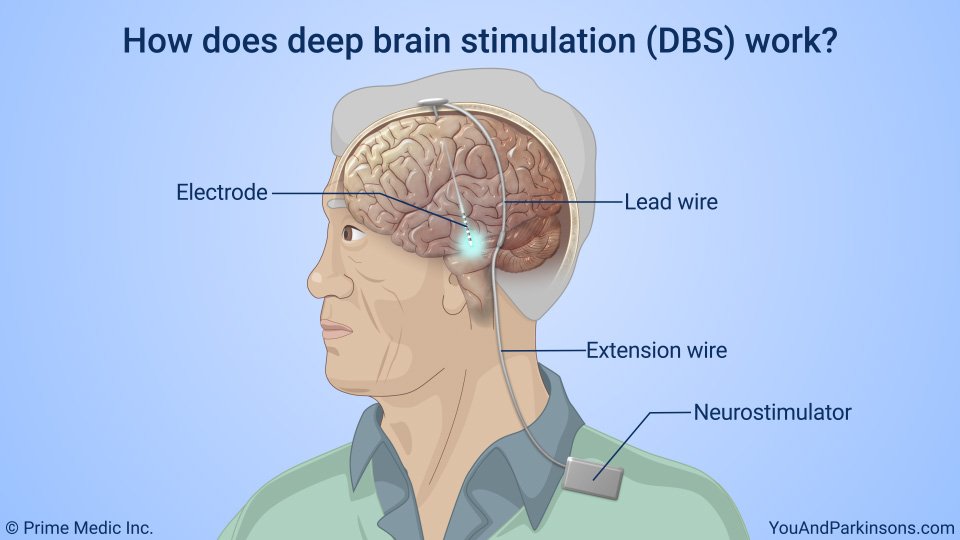
Deep brain stimulation is a surgical procedure that involves implanting electrodes in the brain, which deliver electrical impulses that block or change the abnormal activity that cause symptoms.
The deep brain stimulation system consists of four parts:
- Leads that end in electrodes that are implanted in the brain
- A small pacemaker-like device, called a pulse generator, that creates the electrical pulses
- Extension leads that carry electrical pulses from the device and are attached to the leads implanted in the brain
- Hand-held programmer device that adjusts the devices signals and can turn the device off and on.
In deep brain stimulation, electrodes are placed in the targeted areas of the brain. The electrodes are connected by wires to a type of pacemaker device placed under the skin of the chest below the collarbone.
Once activated, the pulse generator sends continuous electrical pulses to the target areas in the brain, modifying the brain circuits in that area of the brain. The deep brain stimulation system operates much the same way as a pacemaker for the heart. In fact, deep brain stimulation is referred to as the pacemaker for the brain.
How Is Dbs Used For Parkinsons
You may be a good candidate for DBS if you meet the following criteria:
- Your symptoms of Parkinsons substantially reduce your quality of life
- Your symptoms arent well controlled, despite receiving appropriate medications
- You cant tolerate dyskinesia or other side effects from current medications
DBS, in general, uses electrical signals to target certain areas of the brain. For people with Parkinsons, DBS targets parts of the brain known to play a role in the control of movement. These regions include the:
- Thalamus, which relays sensory and motor information
- Subthalamic nucleus, which helps suppress unwanted movement
- Globus pallidus, which helps regulate intentional movement
Research has shown that electrical stimulation from DBS in the subthalamic nuclei may significantly improve motor symptoms associated with PD compared to taking medications alone. Improved motor symptoms may also lead to improvements in overall mobility and comfort, daily functioning, and emotional well-being.
Another study showed that people with PD experienced improved motor function after stimulation in the subthalamic or pallidal areas, but stimulation of these areas affected other symptoms differently. For example, depression worsened after subthalamic stimulation but improved after pallidal stimulation. Your neurologist may decide to stimulate different areas depending on your individual symptoms, needs, and preferences.
Recommended Reading: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Deep Brain Stimulation Works
Exactly how DBS works is not completely understood, but many experts believe it regulates abnormal electrical signaling patterns in the brain. To control normal movement and other functions, brain cells communicate with each other using electrical signals. In Parkinson’s disease, these signals become irregular and uncoordinated, which leads to motor symptoms. DBS may interrupt the irregular signaling patterns so cells can communicate more smoothly and symptoms lessen.
How Does Dbs Compare To Other Methods Of Treatment For Parkinsons Disease
As in Hardys case, every patients treatment begins with medication until it is determined that they can benefit from DBS. Medications are always tried first. Unfortunately, we can only get so far with medications. Oftentimes, many patients try them, and they may work for a little while, said Dr. Sheth.
But at some point, oftentimes the medications stop working as much because the disorder tends to progress over the years. It could get worse, and the medicines may not be able to keep up. Many of the medicines themselves have their own side effects. So, you get to a point where perhaps the medicines are helping to a degree, but they’re causing their own side effects, and exactly when we get to that point is when we introduce the idea of a surgical therapy like DBS.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Disease A Death Sentence
What Is The Best Theory For Why Dbs Works
Before starting, let me note that reading this part is not critical. It is very technical.
As noted before, we dont really understand how DBS works. But there are numerous complicated theories.
Let us look at the simplest & most promising one, in relation to DBS of the most common target. The most common target is the Subthalamic Nucleus .
First, lets see what causes Parkinsons disease.
What happens when you put a wire into the STN and pass a high-frequency current through it?
The other theories are a variation on this theme.
Some DBS effects cannot be explained by this theory.
Many symptoms including tremor and slowness decrease with high-frequency stimulation. But some symptoms like Freezing decrease with low-frequency electrical stimulation.
Why? We dont know.
Therefore, there is a lot more to discover.
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Work
Deep brain stimulation works by modifying abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It was first approved for Parkinsons tremors in 1997 and has become an established treatment to control additional motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
DBS involves three main components:
- Leads: Leads are implanted in the brain in a region responsible for motor activity.
- Implantable pulse generator : A separate procedure is performed to implant a battery-operated device in the chest or in the abdomen. An IPG is similar to a pacemaker for the heart and has been coined by some as a pacemaker for the brain.
- Extension: A thin, insulated wire is passed beneath the skin between the leads and implantable pulse generator to deliver the electrical stimulation from the pulse generator to the leads.
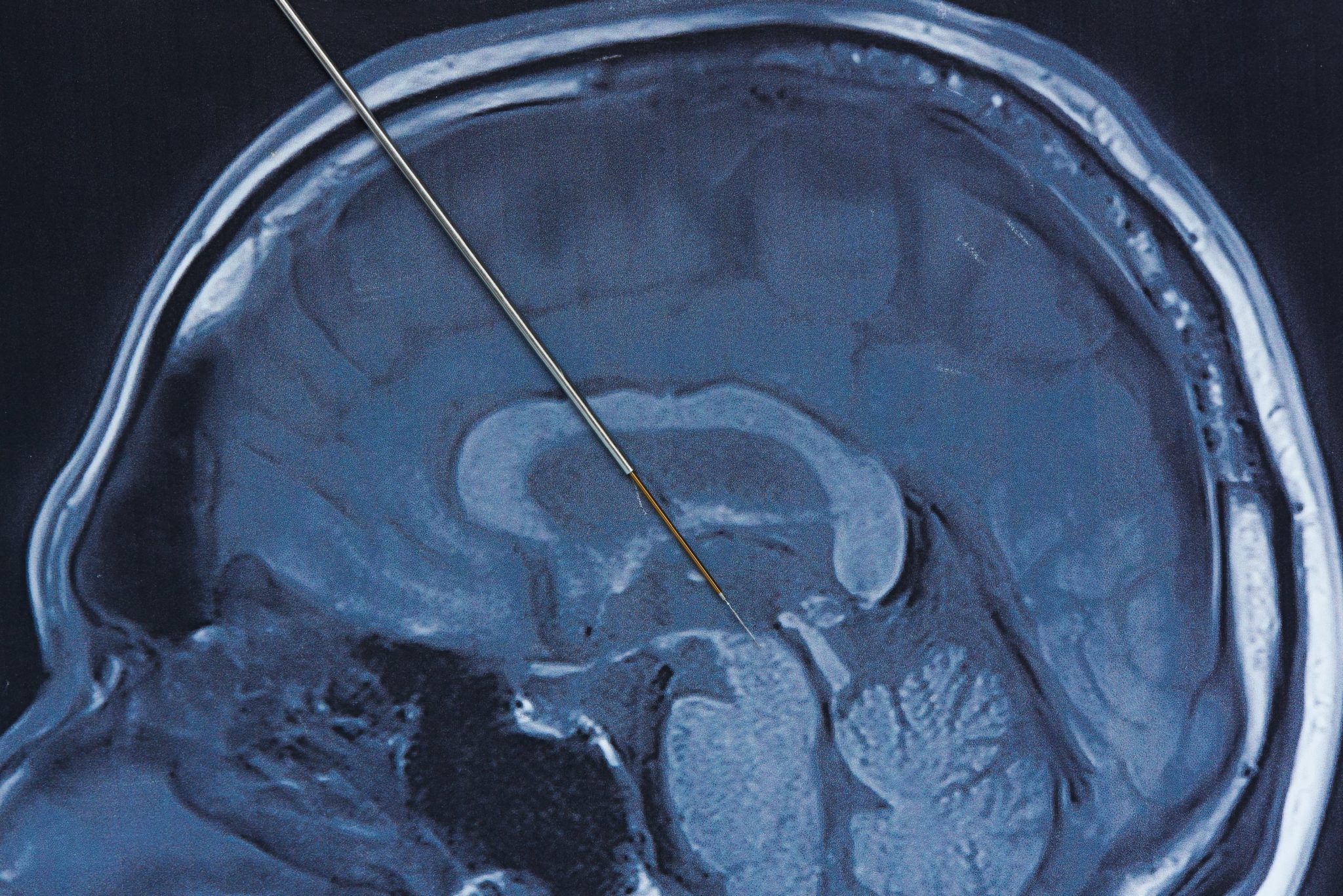
The target area in the brain is first identified by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography . Then, the leads are placed via small holes that a surgeon drills in the skull.
This is considered a minimally invasive surgery that is done in the operating room with local anesthesia. It usually requires an overnight stay.
The IPG is inserted in a separate surgical procedure in the operating room roughly a week later.
After a few weeks, a neurologist begins to program the unit. This process can take several additional weeks to months. When this is completed, people are able to manage the device with a handheld remote control.
Recommended Reading: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Side Effects Of Dbs
As a surgical procedure, DBS may have its own risks and side effects. For instance, one study showed that DBS may also sometimes lead to cognitive issues. There can also be complications from the DBS surgery itself. Side effects and complications of DBS surgery may include:
- Headache
- Temporary swelling and pain at the implantation site
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
What Happens Before Surgery
In the doctor’s office you will sign consent forms and complete paperwork to inform the surgeon about your medical history, including allergies, medicines, anesthesia reactions, and previous surgeries. Presurgical tests may need to be done several days before surgery. Consult your primary care physician about stopping certain medications and ensure you are cleared for surgery.You may also need clearance from your cardiologist if you have a history of heart conditions.
Stop taking all non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines and blood thinners 7 days before surgery. Stop using nicotine and drinking alcohol 1 week before and 2 weeks after surgery to avoid bleeding and healing problems.
You may be asked to wash your skin and hair with Hibiclens or Dial soap before surgery. It kills bacteria and reduces surgical site infections.
No food or drink, including your Parkinson’s medication, is permitted after midnight the night before surgery.
Try to get a good night’s sleep. The DBS surgery involves multiple steps and lasts most of the day, during which you may be awake and off medication.
Morning of surgery
Arrive at the hospital 2 hours before your scheduled surgery time to complete the necessary paperwork and pre-procedure work-ups. An anesthesiologist will talk with you and explain the effects of anesthesia and its risks.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Ribbon Color
Effect Of Medications/neurotransmitter Systems:
Medications used in the treatment of ET and PD may have variable effects on gait and balance. This is due in part to medication side effects and to the effect of medications on various neurotransmitter systems that impact balance and gait control. Those given for tremor in ET can cause confusion, dizziness and sedation. PD medications have a more complex effect upon gait and balance. On the positive side, dopamine replacement therapy can lead to improvements in stooped posture, longer and more even steps, better arm swing, less freezing and a faster gait speed. Unfortunately, PD medications can also lead to dizziness, confusion, impulsivity and dyskinesias, all of which can undermine gait and balance.
In general, it is thought that the effect of dopamine replacement therapy on PD-related symptoms is predictive of the response of those symptoms to DBS. For the most part, this seems to be true, although there appear to be exceptions. For example, it is well established that individuals with PD or ET who have medication resistant tremors are still extremely likely to benefit from DBS. The correlation between responsiveness to medications and response of PD-related gait and balance problems to DBS is a little harder to describe. For example, freezing of gait that occurs predominantly in the OFF medication state, is likely to get better with DBS, but may continue to be a problem after DBS .
Stereotactic Dbs Vs Interventional Image
Stereotactic DBS surgery requires the patient to be off their medication. During the procedure, a frame stabilizes the head and provides coordinates to help the surgeons guide the lead to the correct location in the brain. The patient gets local anesthesia to keep them comfortable throughout each step along with a mild sedative to help them relax.
During image-guided DBS surgery, such as with interventional MRI or CT scan, the patient is often asleep under general anesthesia while the surgeon uses images of the brain to guide the lead to its target.
Some advanced centers offer both the stereotactic and iMRI-guided options for DBS surgery. In this case, the doctor and patient will discuss which procedure is better based on a number of factors.
For instance, the doctor may recommend an image-guided procedure for children, patients who have extreme symptoms, those who are especially anxious or fearful or those whose leads are going into certain parts of the brain.
Generally, DBS surgery follows this process:
You May Like: Life Expectancy After Parkinson’s Diagnosis
Want To Learn More About The Latest Research In Parkinsons Disease Ask Your Questions In Our Research Forum
However, perhaps we seem to be feeling slightly more depressed. Perhaps were having trouble finding our words, and when we do find them, we struggle to get them out. If only one side of our brain was stimulated, perhaps were now noticing how the disease seems to have progressed to the other side. But perhaps that side just wasnt as noticeable prior to the surgery because we were distracted while trying to control the more pronounced side.
There may be more controllable symptoms. There may be less. DBS is not a fix-all. You will still have Parkinsons when you wake up after surgery, but now it may be an even more invisible disease. DBS can control the symptoms. It can give you back so much of what youve missed. It seemingly works miracles but it isnt a cure. Exercise is still vital. Proper medication for the symptoms that DBS doesnt control need to be monitored regularly.
If you are thinking about having deep brain stimulation, talk to others who have been through it. Read about it. Talk to your doctor and ask every question you can think of. Talk to some more people. If you feel its right for you and your doctor supports and recommends the procedure, get the prep work done. If all is a go, then set a date.
Risks Of Deep Brain Stimulation
As with any medical procedure, there are genuine risks of getting the DBS procedure done.
General risks are seizures, infections, blood clots, excessive bleeding, and anesthesia reactions.
There is a risk that DBS may lead to speech and balance-related afflictions from Parkinsons to worsen.
DBS can also worsen depression in some people with Parkinsons.
You May Like: Jack Kornfield Parkinson\’s Disease
Motor Complications In Parkinsons Disease
In addition, there are increased dyskinesias , which refer to abnormal involuntary movements . ON/OFF fluctuations and dyskinesias are known collectively as motor complications.
Whereas levodopa concentration fluctuations can contribute to unpredictable shifts between ON and OFF time, Deep Brain Stimulation remains constant through the day, meaning that there is consistent efficacy throughout the day.
About The Dbs Procedure
Deep brain stimulation therapy uses a small, pacemaker-like device to send electrical signals to an area in the brain that helps fine-tune and control movement. The electrical brain stimulation may, in some cases, block some of the brain messages that cause involuntary and disabling motor symptoms. The device is implanted under the skin in the chest. Small, thin wires connect the device to electrodes placed in your skull, allowing the signals to reach the areas of your brain that are causing your symptoms.
After the DBS system is implanted, your expert DBS programmer adjusts the settings to personalize your DBS therapy. You may need several programming sessions to find your optimal settings. The settings can be adjusted in the future if your symptoms change. Most people do not feel the stimulation, though some may sense a brief tingling when the stimulation is first activated.
A few weeks after the procedure, most patients can resume normal daily activities. Your DBS clinician will let you know when you can try activities that had been difficult for you prior to deep brain stimulation surgery.
DBS surgery recovery and healing
Patients are usually able to return home the day after DBS surgery. Healing can take several weeks, and we will give you medication to manage any pain. Typically, we will not activate your device until your first programming session.
DBS programming sessions
Risks of DBS surgery
You May Like: Parkinson’s Sleep Attacks
Resources For More Information
- Surgical option a potential life-changer for patients with OCD: Read and watch Erins story as she, a lively 21-year-old woman, fought her battle with OCD. This article explores how deep brain stimulation gave Erin her life back. The procedure was the first of its kind performed at Albany Medical Center the only facility offering this treatment between New York and Boston. In Erins own words, “Now, I can be who I really am and tell people my story and hopefully inspire people and help people along the way.
- Karen and Jims Story: A Shared Journey of Life, Love and DBS: Read about Karen and Jim. They were each diagnosed with Parkinsons before they met. Follow them on their journey as they fall in love after meeting each other from an online support group. See how they embraced each other and DBS.
- Kays Story A Parkinsons Disease Patient: Read about Kay, a 68-year-old woman suffering from Parkinsons disease. The article and video explore how DBS helped her regain her life. In Kays own words, Its like I had been turned on again. It was like a miracle.
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
For people with severe motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease that are not adequately controlled by medication, a treatment called deep brain stimulation may offer some relief.
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical placement of a small conductor called an electrode in the brain. The electrode delivers electrical stimulation that blocks the nerve signals that cause tremors.
Specialists at NYU Langones Center for Neuromodulation perform more than 100 deep brain stimulation procedures each year. Our neurologists, neurosurgeons, and psychiatrists provide a thorough evaluation to ensure youre a good candidate for the procedure.
Read Also: Essential Oils For Hand Tremors
How Should I Care For The Surgical Area Once I Am Home
- Your stitches or staples will be removed 10 to 14 days after surgery.
- Each of the four pin sites should be kept covered with band aids until they are dry. You will be able to wash your head with a damp cloth, avoiding the surgical area.
- You may only shampoo your hair the day after your stitches or staples are removed, but only very gently.
- You should not scratch or irritate the wound areas.
Who Can Have Dbs Surgery
If you have worsening Parkinsons symptoms and your medications are not effective enough, then you may be recommended to have the DBS procedure done.
However, DBS will not be recommended in some instances.
These include scenarios where the Parkinsons patient has severe depression, advanced forms of dementia, or have symptoms that are not typically associated with Parkinsons disease.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Mortality Rate
How Is Deep Brain Stimulation Performed
Before the actual procedure begins, for most patients, a head frame is positioned on your head, which keeps your head still during brain imaging and is used to deliver the electrode to the target in the brain. Surgical pins or screws are used to secure the frame to your head. Sedation is typically given during this portion of the procedure.
Your neurosurgeon will implant the deep brain stimulation system in one to three stages.
First, a small hole is made in the skull. The leads, which have electrodes at the ends, are passed through this hole and surgically implanted in the areas of the brain identified as the site responsible for the movements caused by Parkinsons disease.
Most people with Parkinson’s disease will require one lead placed on each side of the brain unless symptoms are mostly one-sided . Each side of the brain controls the opposite side of the body, so each lead is inserted on the opposite side of where symptoms are occurring. Sometimes this procedure is done in stages one lead is placed at one time followed by another surgery for the other side. In other patients, both leads are placed during the same operation. Many times patients are awake during lead insertion. An intraoperative MRI is also sometimes used to image the lead location.
