Need To Know: Dr Ray Dorsey
Dr Ray Dorsey is David M Levy Professor of Neurology and Director at the Center for Health + Technology at the University of Rochester Medical Center, US, which has conducted more than 100 clinical trials including trials that led to the approval of four Parkinsons medications. He recently co-wrote the book,Ending Parkinsons Disease: A Prescription for Action.
No One Definitive Cause Of Parkinsons
There are no biomarkers or objective screening tests that indicate one has Parkinsons. That said, medical experts have shown that a constellation of factors are linked to it.
Parkinsons causes are likely a blend of genetics and environmental or other unknown factors. About 10 to 20 percent of Parkinsons disease cases are linked to a genetic cause, says Ted Dawson, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Institute for Cell Engineering at Johns Hopkins. The types are either autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive .
But that leaves the majority of Parkinsons cases as idiopathic, which means unknown. We think its probably a combination of environmental exposure to toxins or pesticides and your genetic makeup, says Dawson.
Age. The biggest risk factor for developing Parkinsons is advancing age. The average age of onset is 60.
Gender. Men are more likely to develop Parkinsons disease than women.
Genetics. Individuals with a parent or sibling who is affected have approximately two times the chance of developing Parkinsons. Theres been an enormous amount of new information about genetics and new genes identified over the past 10 or 15 years that have opened up a greater understanding of the disease, says Dawson.
Environmental Toxins Linked To Parkinson’s
New Studies Support Link Between Chemicals and Parkinson’s Disease
Researchers say the findings support evidence of a possible link between environmental toxins and Parkinson’s disease and may help explain why some people with genetic risk factors for the disease get it while others do not.
Parkinson’s disease is a common neurological disorder that can occur randomly or as the result of inherited gene mutations.
In the study, which appears in Current Biology, researchers looked at fruit flies lacking both forms of a gene that is associated with the inherited form of Parkinson’s disease. These specially bred fruit flies became extremely sensitive to the herbicide paraquat and the insecticide rotenone and died after exposure.
Don’t Miss: Emotional Trauma And Parkinson’s Disease
Clinicopathological Correlation In Parkinsons Disease
PD is traditionally defined by a series of clinical symptoms. These are predominantly motor disorders that give rise to the rigid-akinetic syndrome. PD is the main aetiology of rigid-akinetic syndromes. Nevertheless, non-motor symptoms are widely distributed in PD patients.
Figure 1
Braaks staging of Parkinsons disease pathology progression. Illustrations showing the intracerebral progression of PD pathology. Schematics of the pathology progression from the ENS. Correlation between PD staging and the appearance of the pathology in different intracerebral structures. Modified from Braak et al. .
Corresponding to structural alterations, there are motor and non-motor symptoms in iPD. The onset of motor features correlates with the loss of dopamine input to the posterior putamen, corresponding to the motor region of the striatum. The main classical features of PD are therefore mainly related to the dysfunction of the motor circuit. As the disease progresses and the loss of dopaminergic neurons increases, the dopaminergic input to other areas of the striatum and the cortex decreases, giving rise to clinical symptoms characteristic of the dysfunction of higher cerebral structures.
Ask Us For A Recommendation
Best neuro-protective foods and supplements.
You may ask us about:
- Supplements scientifically shown to replenish glutathione levels to protect against cell death and toxins
- Glutathione-building supplement for detoxifying metals and pesticides
We hope that you have been inspired for better Parkinson Disease treatments with natural help.
- Knowing that yes, that environmental toxins lead to Parkinson is hopefully less scary, because there are prptective foods and supplements.
- For your best shot at a Parkinson cure, you will want to add the best foods and supplements shown to be neuro-protective.
Metals such as iron are usually high in the brains of Parkinsons patients. Iron can be reduced in the body by:
- not taking iron supplements
- eating less red meat
- donating blood
- drinking green tea and adding curcumin to your food. These contain natural iron-chelating, substances – molecules that bind to and remove iron.
Knowing the causes Parkinson Disease will hopefully help live a fuller and longer life!
—————————————-
1. Int J Mol Sci. Parkinsons Disease: From Pathogenesis to Pharmacogenomics 2017 Mar 18: 551. Published online 2017
2. Front Neurosci. Neurochemical and Behavior Deficits in Rats with Iron and Rotenone Co-treatmen. 2017 Nov 23 11:657. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00657. eCollection 2017.
3. PARKINSONS DISEASE: A SYNDROME NOT ADISEASE Issue: BCMJ, vol. 43 , No. 3, April 2001 , Pages 129-132Clinical Articles By: Donald B. Calne, OC, DM
You May Like: What Are The 5 Stages Of Parkinson’s
A Discussion Of How Environmental Factors Such As Pesticides May Affect Your Risk Of Parkinsons Disease
During my recent interview on Wisconsin Public Radio, many of the callers asked questions related to environmental risks of Parkinsons disease , specifically, exposures related to farming. Those calls prompted me to delve further into this complicated and murky topic.
Before we start discussing specific factors in the environment that may increase risk of PD, lets understand some basic ground rules that will help put this topic in perspective
With that background, let us begin.
Rates Of Parkinsons Disease Are Exploding A Common Chemical May Be To Blame
Researchers believe a factor is a chemical used in drycleaning and household products such as shoe polishes and carpet cleaners in the US
Asked about the future of Parkinsons disease in the US, Dr Ray Dorsey says, Were on the tip of a very, very large iceberg.
Dorsey, a neurologist at the University of Rochester Medical Center and author of Ending Parkinsons Disease, believes a Parkinsons epidemic is on the horizon. Parkinsons is already the fastest-growing neurological disorder in the world in the US, the number of people with Parkinsons has increased 35% the last 10 years, says Dorsey, and We think over the next 25 years it will double again.
Most cases of Parkinsons disease are considered idiopathic they lack a clear cause. Yet researchers increasingly believe that one factor is environmental exposure to trichloroethylene , a chemical compound used in industrial degreasing, dry-cleaning and household products such as some shoe polishes and carpet cleaners.
To date, the clearest evidence around the risk of TCE to human health is derived from workers who are exposed to the chemical in the work-place. A 2008 peer-reviewed study in the Annals of Neurology, for example, found that TCE is a risk factor for parkinsonism. And a 2011 study echoed those results, finding a six-fold increase in the risk of developing Parkinsons in individuals exposed in the workplace to trichloroethylene .
-
Adrienne Matei is a freelance journalist
You May Like: What Kind Of Doctor Diagnosis Parkinson’s Disease
Better Parkinson Prognosis With Protection
One of the known markers for PD is low glutathione in the substantia nigra – which was also the case for these animals that were given rotenone and iron.
Glutathione is the body’s “protective molecule” and is typically depleted in the brains of Parkinsons patients.
Increasing glutathione in the substantia nigra, they found, gave the test animals “dopaminergic neuroprotection” and decreased the damage caused by these toxins.
- This is why glutathione-building supplements are advised by neurologists for a better Parkinson prognosis.
This molecule can also protect against the eventual toxic effect of the Parkinsons medications which cause dyskinesia or “shaking:”
See: Dyskinesia caused by Parkinsons Medications, Carbidopa, Levodopa
Veterans Exposed To Toxic Chemicals At Military Bases Risk Developing Parkinsons
Accumulating evidence suggests that long-term exposure to trichloroethylene may cause deficits in energy, mood, memory, attention, and psychomotor functioning. In addition, some research suggests that exposure to TCE is associated with a significantly increased risk of Parkinson’s diseasea nervous system disorder that deteriorates a persons ability to control their movement over time.
Parkinsons disease can be difficult to initially detect as early symptoms are subtle and occur gradually. Unfortunately, no cure for Parkinsons disease exists today, but treatments are available to help relieve the symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Researchers based their studies on previous findings, which show that exposure to environmental toxins may raise the risk of developing the disease by increasing the rate of oxidative stressan imbalance between free radical activity and antioxidant activity, which can lead to cell and tissue damage. Oxidative stress plays an important role in the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons leading to neurological conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease.
Also Check: Are Intention Tremors Common In Parkinson’s
Has Anything Changed Over Time
Since most of the studies concerning PD and rural living were done decades ago, a recent study sought to revisit this issue since farming life has changed in recent times. Pesticide use is reduced, there has been a large migration from rural to urban areas, and there is less dependence on well water in rural communities.
The new study was conducted in Finland and looked at the incidence of PD in rural versus urban areas. Interestingly, rural living remained a risk factor for PD. It is possible that current diagnoses of PD continue to reflect the environmental exposures of decades ago, and that risk reduction in rural areas due to decreased pesticide use and other changes in farming life may show more benefits in the future. However, the study suggests that we may not yet fully understand how the rural environment affects Parkinsons risk.
The Link Between Parkinsons Disease And Toxic Chemicals
A new book calls the increasing prominence of Parkinsons a man-made pandemic.
-
Send any friend a story
As a subscriber, you have 10 gift articles to give each month. Anyone can read what you share.
Give this article
Michael Richard Clifford, a 66-year-old retired astronaut living in Cary, N.C., learned before his third spaceflight that he had Parkinsons disease. He was only 44 and in excellent health at the time, and had no family history of this disabling neurological disorder.
What he did have was years of exposure to numerous toxic chemicals, several of which have since been shown in animal studies to cause the kind of brain damage and symptoms that afflict people with Parkinsons.
As a youngster, Mr. Clifford said, he worked in a gas station using degreasers to clean car engines. He also worked on a farm where he used pesticides and in fields where DDT was sprayed. Then, as an aviator, he cleaned engines readying them for test flights. But at none of these jobs was he protected from exposure to hazardous chemicals that are readily inhaled or absorbed through the skin.
Now Mr. Clifford, a lifelong nonsmoker, believes that his close contact with these various substances explains why he developed Parkinsons disease at such a young age. Several of the chemicals have strong links to Parkinsons, and a growing body of evidence suggests that exposure to them may very well account for the dramatic rise in the diagnosis of Parkinsons in recent decades.
Also Check: Statins And Parkinson’s Disease
New Proof Of Environmental Link To Parkinson’s Disease
Researchers based their study on previous findings that show exposure to environmental toxins may raise the risk of developing the disease by increasing the rate of oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is related to the body’s ability to eliminate free radicals in the body and can result in cell damage within the body.
In the study, researchers showed that flies lacking forms of the DJ-1 gene were normal under standard conditions. But when they were exposed to high doses of the herbicide paraquat and insecticide rotenone, which have previously been linked to Parkinson’s disease, the flies suffered from extreme oxidative stress and died.
Researchers say these findings suggest that a loss of DJ-1 gene function increases sensitivity to chemicals that cause oxidative stress.
Together, researchers say the results shed new light on the biological connections between the inherited and sporadic forms of Parkinson’s disease and may lead to more effective treatments.
Show Sources
Is There A Common Toxic Mechanism In All These Models That Leads To Neurodegeneration
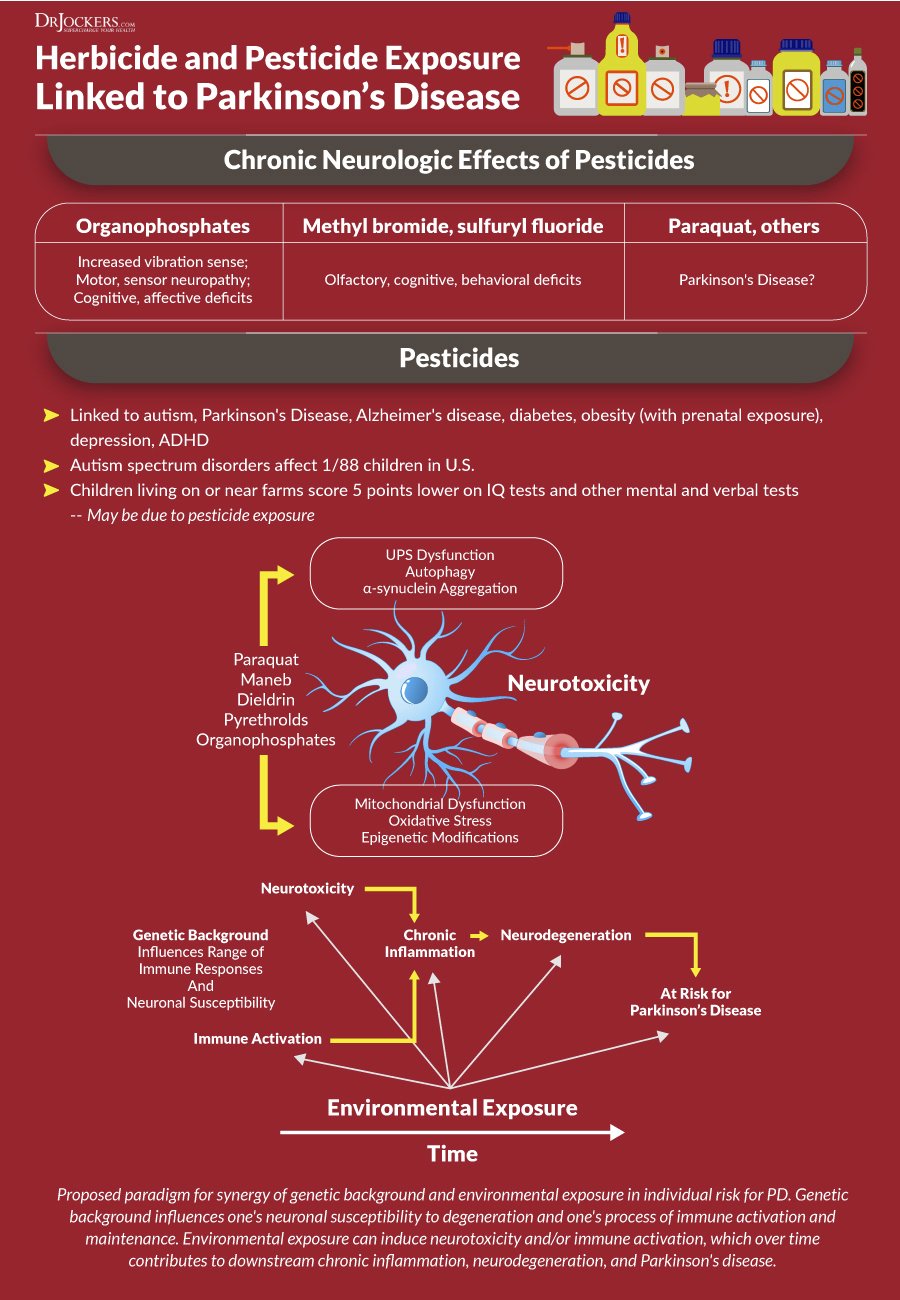
One of the common effects exerted by most of these noxious compounds tested above is the inhibition of mitochondrial NADH CoQ reductase, also known as Complex I, and the production of free radicals, thereby also increasing cellular oxidative stress. The first association between a mitochondrial alteration and PD was made in 1989. Two different groups showed a defect in Complex I activity from SN neurons in PD patients . Later studies have shown that there is an approximately 35% defect in the mitochondrial complex I activity . This deficiency is also present in platelets from PD patients . As mentioned above, a study published in 2011 underlines the importance of Complex I inhibition and oxidative stress in PD pathophysiology in patients. In an epidemiological study, Tanner and colleagues observed in 110 PD cases and 358 controls that PD was strongly associated with the use of a group of pesticides that inhibit mitochondrial complex I, including rotenone, and with the use of a group of pesticides that cause oxidative stress, including paraquat .
Figure 2
Don’t Miss: How Can Stem Cells Cure Parkinson Disease
How Can I Prevent This Condition Or Reduce My Risk Of Developing It
Parkinsonism happens unpredictably in most cases, so it’s usually impossible to prevent it or reduce your risk of developing it. However, there are specific types of secondary parkinsonism that you can reduce the risk of developing. These are:
- Toxin-induced parkinsonism. Its possible to reduce your risk of developing this type of parkinsonism by avoiding toxins or substances that can cause it or by using safety equipment to reduce your exposure to these substances when you cant avoid them.
- Post-traumatic parkinsonism. You can reduce your risk of developing this by using safety equipment to protect yourself from head injuries.
- Vascular parkinsonism. Reducing your risk of developing this involves taking care of your circulatory health, especially the circulation in your brain. Managing this involves maintaining a weight that’s healthy for you, eating a balanced diet and staying physically active.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect a condition that falls under parkinsonism, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
- Blood tests .
- Positron emission tomography scan.
New lab tests forthcoming
There are also new lab tests that, while still experimental or waiting for approval, might be able to help with diagnosing Parkinson’s disease or other conditions like it. These tests look for misfolded or malfunctioning alpha-synuclein proteins in your cerebrospinal fluid or nerves. But more research and testing are necessary before these tests are widely available.
Read Also: What Is Parkinson’s Syndrome
Pesticides And Parkinsons Disease: The Toxic Effects Of Pesticides On The Brain
A study by Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China, finds Parkinsons Disease risk increases with elevated levels of organochlorine and organophosphate pesticides in blood. Among patients with PD, specific organochlorine compounds have greater associations with cognitive impairments, including depression and brain function. Research finds exposure to chemical toxicants, like pesticides, can cause neurotoxic effects or exacerbate preexisting chemical damage to the nervous system. Although the mechanism by which pesticides induce disease development remains unclear, researchers suggest changes in protein enzyme composition and cellular dysfunction from pesticide exposure interrupt normal brain function.
Concentrations of organochlorine pesticides are higher among patients with PD compared to healthy patients. Of the organochlorines, -HCH and propanil concentrations have the greatest association with PD risk through increasing reactive oxygen species levels and decreasing mitochondrial membrane function in SH-SY5Y cells. However, only propanil induced accumulation of -synuclein, a predominant protein in the brain tissue of PD patients. Lastly, using the Hamilton Depression Scale and Montreal Cognitive Assessment scores, researchers discover PD patients have higher depression scores and lower cognitive function.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Specific Pesticides And Their Link To Pd
The evidence that pesticide use is associated with an increased risk in PD, begs the question are there specific pesticides that are most concerning? When data is collected on this topic in large populations, often the participants in the study are unaware of which specific pesticide exposures they have had. This makes it difficult to determine which pesticides to avoid.
Some studies however were able to investigate the risks of specific chemicals. A recent review summarized the current state of knowledge on this topic. The chemical with the most data linking it to an increased PD risk is paraquat, with exposure associated with a 2-3 fold increased PD risk over the general population.
One particularly comprehensive study investigated exposure to 31 pesticides and their association with PD risk. From that data emerged paraquat and rotenone as the two most concerning pesticides.
- Paraquats mechanism of action is the production of reactive oxygen species, intracellular molecules that cause oxidative stress and damage cells.
- Rotenones mechanism of action is disruption of the mitochondria, the component of the cell that creates energy for cell survival.
Interestingly, both mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress are common themes in our general understanding of what causes death of nerve cells in PD.
Read Also: Is Beer Good For Parkinson’s
Exposure To Pesticides In The Military
Agent Orange was an herbicide that US troops sprayed in Vietnam from 1961-1971 to kill trees and crops that provided protection and food to the rival army. It is a mixture of two chemicals: 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Agent Orange was also contaminated with Dioxin, a chemical even more damaging than Agent Orange itself, since it is very long-lasting.
The effects of Agent Orange on both the Vietnamese population and on American soldiers has been studied extensively, but with much variability in the results. Birth defects have been attributed to Agent Orange exposure, as well as multiple types of cancer.
With the understanding that the Veteran community served selflessly on behalf of the American people and therefore deserve the protection and support of the American government, the Agent Orange Act was passed in 1991, allowing the Department of Veteran Affairs to declare certain conditions presumptive to exposure to Agent Orange, even if the scientific data associating Agent Orange with that condition was not airtight.
The list of conditions has grown over the years, and in 2010, PD was added. Read here about how veterans who may have been exposed to Agent Orange and have subsequently developed PD are eligible for VA healthcare and disability compensation. APDA offers a free booklet specifically for veterans to help them find the care and support they need.
