Motor Features Of Parkinsonism
Parkinsonian motor signs often develop concurrently with or subsequent to these problems and are also diagnostically very useful. These motor signs are often symmetric, and bradykinesia and gait impairment are more common than rest tremor. However, the variance of the motor presentation is high. Some patients may present with a classic asymmetric pill-rolling tremor of PD while others may have no motor concerns yet will display clear extrapyramidal dysfunction on examination. In contrast to patients with PD, who have a sustained beneficial response to PD medications such as carbidopa/levodopa, patients with DLB often have a limited response to such medications. These patients nonetheless show reduced dopamine transporter activity on single-photon emission computed tomography or positron emission tomography imaging, when performed. Generalized myoclonus can also occur in some patients with DLB.
Discuss Lewy Body Dementia Diagnosis With Family
Not all family members may understand or accept LBD at the same time. This can create conflict. Some adult children may deny that their parent has a problem, while others may be supportive. It can take a while to learn new roles and responsibilities.
Family members who visit occasionally may not see the symptoms that primary caregivers see daily and may underestimate or minimize your responsibilities or stress. Professional counselors can help provide guidance on how families can work together to manage LBD.
Although LBD and Alzheimer’s disease are different disorders, they share similar family concerns. For more information, read Helping Family and Friends Understand Alzheimer’s Disease and Helping Children Understand Alzheimer’s Disease.
Who Does Lewy Body Dementia Affect
Lewy body dementia typically affects people over the age of 50. The older you are, the more at risk you are for developing the condition. Men and people assigned male at birth are more likely to have Lewy body dementia than women and people assigned female at birth.
A family history of LBD and Parkinsons disease also increases your risk of developing it.
Read Also: How Can You Prevent Parkinson’s
The Last Version Of Dlb Criteria Suggests The Use Of The General Term Lbd
The next subtype of LBD is the DLB phenotype. In contrast to PDD, this phenotype is a bit better bordered, its definition is more intelligible and the pathological finding is unique. This is characterized by diffuse alpha-synucleinopathy, accompanied in most cases by Alzheimers changes, especially senile plaques.
The birth of the DLB as a nosological entity was complicated and took many years of scientific debates, consensus meetings, publications, which ran continuously for almost the last decade of the 20th century. Finally, the existence of pathological co-habitation of Alzheimers pathological changes together with the diffuse appearance of LBs led the expert panel to the opinion, that the former attempts to name this disease were always the attempts to describe the findings typical for DLB.
The first clinical diagnostic criteria were published by McKeith et al. in 1996 the revised version came in 2005 and the last revision is from 2017,,. In the last revision, the nosological entity DLB has been classified rather as one of the phenotypes in the broader spectrum of LBD.
Lewy Body Dementia Symptoms
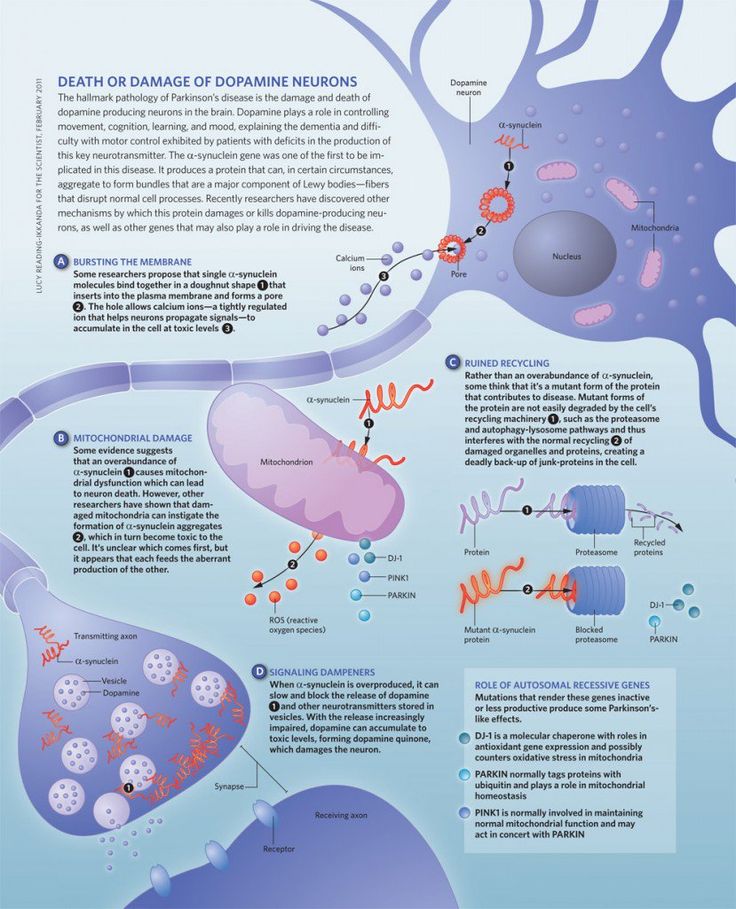
Symptoms of LBD can fluctuate but usually become progressively worse over time. Early in the disease, fluctuations between normal and abnormal behavior, mood, and cognitive ability can occur. The central feature of this disease is progressive dementia shown by deficits in attention and minor dysfunctions in the early stages that can progress to severe dementia.
In severe dementia, the persons inability to carry out normal daily functions, loss of recognition of family members, and other severe cognitive, behavior and mood problems can render the individual virtually helpless. Other features include fluctuating cognition, visual hallucinations, and spontaneous features of Parkinsonism such as body stiffness, tremors, shuffling gait, emotionless facial features and/or decreased coordination.
As mentioned previously, the diagnosis is made on the basis of symptoms and their time of occurrence in patients. However, most doctors that make the diagnosis also typically use other tests primarily to rule out other causes for the symptoms.
There are no sensitive or specific blood or urine tests that diagnose LBD. However, routine laboratory tests such as a basic metabolic panel, CBC, thyroid studies, vitamin B12 levels and tests for syphilis, Lyme disease, or HIV also may be ordered. MRI, CT scans, and other studies of the brain are used to help distinguish LBD from other problems that have similar symptoms.
Also Check: How Does A Neurologist Diagnose Parkinson’s
How Can We Support The Sleep/wake Cycle Of Dlb
For people with DLB who are confused about the day-night cycle, some daily strategies can be helpful. At night, starting a lights out routine that happens at the same hour every day, where all curtains are closed and lights are turned off, can help the person understand that it is sleep time. During the day, opening the curtains, allowing patients to spend as much time in the daylight as possible, avoiding naps, and organizing stimulating activities, can be helpful. Having lots of calendars and clocks in every room might also help a person with DLB be less confused about the time of day.
Diagnosis: Parkinsons Dementia Or Dementia With Lewy Bodies
During assessment, a specialist may look at when the dementia symptoms first appeared before reaching a diagnosis of Parkinsons dementia or dementia with Lewy bodies.
If there have been motor symptoms for at least one year before dementia symptoms occur, specialists will often give a diagnosis of Parkinsons dementia.
If dementia symptoms occur before or at the same time as motor symptoms, specialists will usually give a diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies.
However, it should be noted that in some cases of dementia with Lewy bodies, no motor symptoms develop at all.
Theres no single test diagnosis is made through several different assessments, usually starting with an appointment with your GP or Parkinsons nurse.
Some people find it helps to go to the appointment with someone who knows them well, who can give the GP or Parkinsons nurse information about changes theyve noticed.
Your GP can discuss your symptoms with you and carry out a physical examination, including blood and urine tests, to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms .
Your GP may also review your medication, in case your symptoms are side effects.
If your GP thinks you have dementia, they can refer you to a specialist, such as a neurologist, psychiatrist or geriatrician.
You might be referred to a memory clinic or memory service. In some areas of the country, you can refer yourself to these services.
But if you feel you need to see the specialist again, you can ask to be referred back.
Don’t Miss: How Often Does Parkinson’s Disease Occur In The Population
Lifespan In Parkinsons Nearly Identical To General Population
A new study finds that, overall, lifespan for those living with Parkinsons disease is nearly identical to those in the general population. The study looked at a group of diseases called synucleinopathies, including Parkinsons. The results appear in the May 15 online edition of JAMA Neurology.
Lewy bodies clumps of alpha-synuclein protein that accumulate in certain brain cells are the hallmark of PD. The clumps also occur in less common diseases such as multiple system atrophy , dementia with Lewy bodies , and PD dementia in which symptoms can be similar to those of typical Parkinsons.
Researchers led by Rodolfo Savica, M.D., Ph.D., at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, MN, compared lifespan and cause of death among people with synucleinopathies compared to the general population. They examined the medical records of all 461 people diagnosed with synucleinopathies in Olmsted County, MN, between 1991 and 2010. The scientists also analyzed records from individuals closely matched for age and sex who did not have these diagnoses.
Results
What Does It Mean?
Overall, the study reminds us that people with Parkinsons can live many years with the disease. With that in mind, people living with these diseases, their care partners and their families can take steps to plan for their health care and make important financial decisions.
Reference
Dont Miss: Stabilizing Spoon For Parkinsons
Dlb In Psychiatry Of Old Age Services
The research team reviewed the case notes of 9449 individual patients, of whom 4504 had a dementia diagnosis , other diagnoses being mainly functional psychiatric disorders or cognitive problems falling short of dementia . Patients with DLB comprised 4.6% of all dementia cases. Prevalence in individual services ranged from 2.4 to 5.9%, and was significantly higher among NE services than in EA services . No significant variation in prevalence was observed within each region .
Fig. 1
DLB prevalence by region and service. DLB dementia with Lewy bodies, EA East Anglia, NE North-East England, AI services
The diagnosis of the expert panel concurred with the diagnosis documented in the clinical notes in 97% of PDD cases consented for detailed notes review and in 100% of recruited PD cases .
Don’t Miss: How To Slow The Progression Of Parkinson Disease
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
What Is The Life Expectancy For People With Lewy Body Dementia
The average life expectancy of Lewy body dementia is five to eight years after the initial diagnosis. But some people with LBD live up to 20 years after their diagnosis.
This short average life expectancy could be due to a lack of knowledge regarding LBD among healthcare providers and the population and difficulty in distinguishing it from other similar conditions. This often leads to a delay in diagnosis, which delays the onset of specific therapy.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Parkinson’s
Tests For Dementia With Lewy Bodies
There’s no single test for dementia with Lewy bodies.
The following may be needed to make a diagnosis:
- an assessment of symptoms for example, whether there are typical symptoms of dementia with Lewy bodies
- an assessment of mental abilities this will usually involve a number of tasks and questions
- blood tests to rule out conditions with similar symptoms
- brain scans, such as an MRI scan, CT scan or a SPECT scan these can detect signs of dementia or other problems with the brain
Wait So What Is Parkinsonism
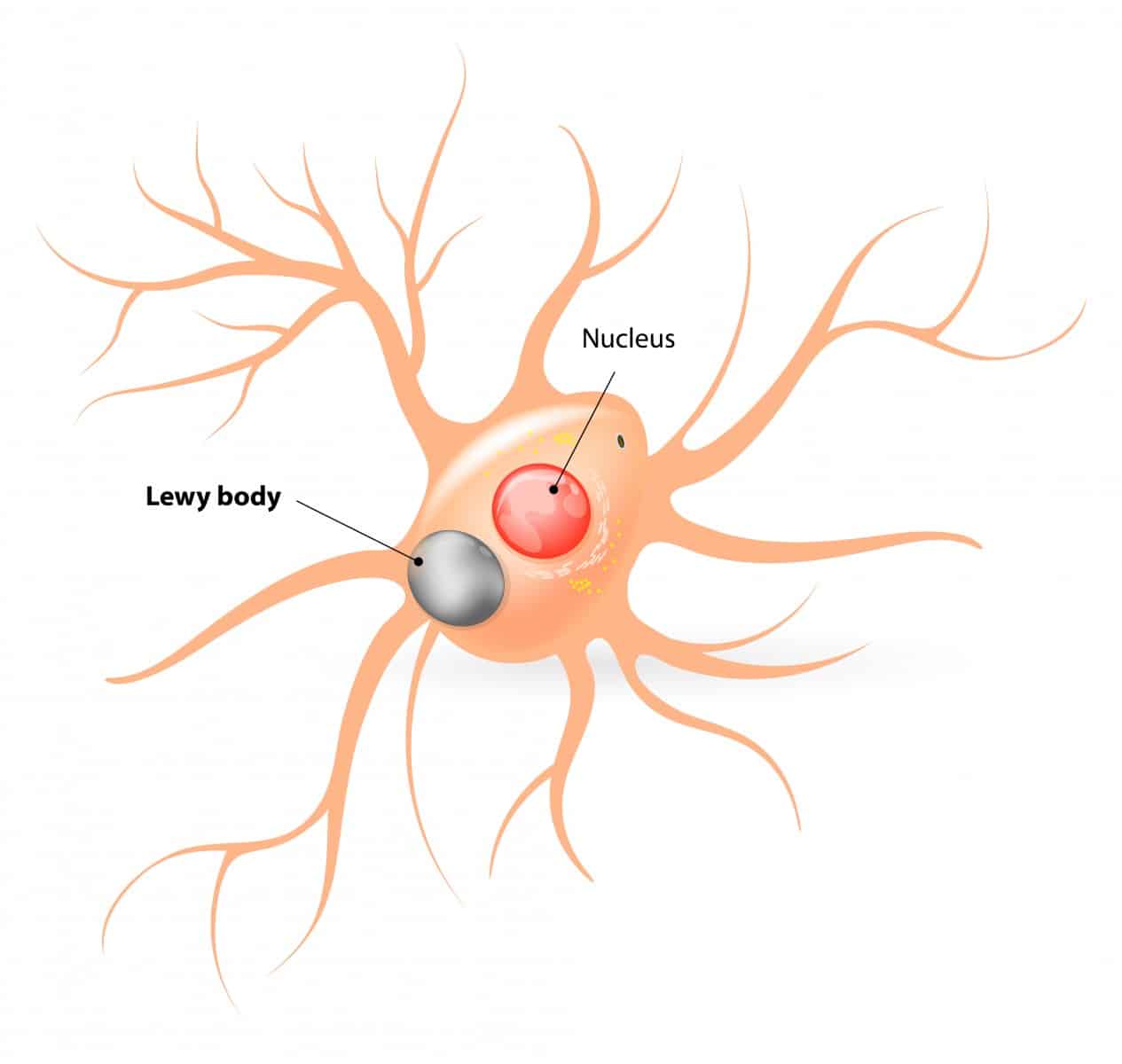
Parkinsonism refers to the motor symptoms that are typically associated with PD, such as tremors, stiffness, and walking/balance problems. Both PD and LBD are forms of Parkinsonism, meaning that PD patients and LBD patients may experience these motor symptoms.2 Because the Parkinsonism motor symptoms of PD and LBD can be very similar, it can be difficult to differentiate between the two conditions.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Silverware
Don’t Miss: What Can Help With Parkinson’s Disease
Memory And Thinking Problems
You may experience forgetfulness, slowed thinking and difficulty concentrating. You might find it harder to follow conversations, and remember some words and names. This can make communication difficult.
You may also find it increasingly difficult to make decisions, plan activities and solve problems. This can make everyday activities harder.
Also Check: Weighted Silverware
Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinson Disease Dementia
, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, University of Mississippi Medical Center
Dementia with Lewy bodiesParkinson disease dementia
Dementia is chronic, global, usually irreversible deterioration of cognition.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is the 3rd most common dementia. Age of onset is typically > 60.
Lewy bodies are spherical, eosinophilic, neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions composed of aggregates of alpha-synuclein, a synaptic protein. They occur in the cortex of some patients who have dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurotransmitter levels and neuronal pathways between the striatum and the neocortex are abnormal.
Lewy bodies also occur in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson disease Parkinson Disease Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive, degenerative disorder characterized by resting tremor, stiffness , slow and decreased movement , and eventually gait and/or… read more , and dementia may develop late in the disease. About 40% of patients with Parkinson disease develop Parkinson disease dementia, usually after age 70 and about 10 to 15 years after Parkinson disease has been diagnosed.
Both dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease dementia have a progressive course with a poor prognosis.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Stiffness In Morning
What Is Lewy Body Dementia Causes Symptoms And Treatments
On this page:
Lewy body dementia is a disease associated with abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. These deposits, called Lewy bodies, affect chemicals in the brain whose changes, in turn, can lead to problems with thinking, movement, behavior, and mood. Lewy body dementia is one of the most common causes of dementia.
LBD affects more than 1 million individuals in the United States. People typically show symptoms at age 50 or older, although sometimes younger people have LBD. LBD appears to affect slightly more men than women.
Diagnosing LBD can be challenging. Early LBD symptoms are often confused with similar symptoms found in other brain diseases or in psychiatric disorders. Lewy body dementia can occur alone or along with other brain disorders.
It is a progressive disease, meaning symptoms start slowly and worsen over time. The disease lasts an average of five to eight years from the time of diagnosis to death, but can range from two to 20 years for some people. How quickly symptoms develop and change varies greatly from person to person, depending on overall health, age, and severity of symptoms.
In the early stages of LBD, symptoms can be mild, and people can function fairly normally. As the disease advances, people with LBD require more help due to a decline in thinking and movement abilities. In the later stages of the disease, they often depend entirely on others for assistance and care.
Stages Of Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy body dementia usually takes five to eight years to progress from diagnosis to death. Some cases may progress faster, while others may progress much more slowly. Regardless of the speed of progression, the timeline of Lewy body dementia is usually distinguished by early, middle, and late stages.
Unlike other forms of dementia, Lewy body dementia does not always progress predictably through each stage. This makes it impossible to know for sure how many years each stage will last or how slowly or quickly the disease will progress.
Don’t Miss: What Disease Is Like Parkinson’s
What Are Pd Dementia Safety Concerns
Safety issues should be considered and monitored from the time of diagnosis. As PDD progresses, ensure that your loved one is not left alone.
- Evaluate driving privileges before safety is a concern. Your doctor can make a driving evaluation referral.
- Work out legal and financial issues and safeguard finances. People with dementia are at greater risk of falling victim to scams and fraud.
- Minimize prescription risks. Confirm with the doctor the medication names and doses of the person with PD. If the person is in dementias early stages and capable, fill up their weekly pill box together and monitor use.
- Medical alert systems can be critical in case your loved one falls or wanders outside of the home. Many types of systems are available, from bracelets and pendants to smart watches with fall detection and one-button connections to 911.
- Evaluate gun safety. If your loved one owns a firearm or has one in the home, consider speaking with their doctor about the subject and taking appropriate safety precautions.
Recommended Reading: Apps For Parkinsons Patients
Who Gets Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Around 5% of people with a diagnosis of dementia are recorded as having DLB, but there is good evidence that the condition is under-diagnosed. Scientists think DLB may account for up to 20% of all dementia.
Dementia with Lewy bodies affects men and women roughly equally. As with most other types of dementia, DLB becomes increasingly common over the age of 65. It can also affect people younger than this.
There is not much evidence that anything we might be exposed to during our lives increases the risk of DLB. Having a traumatic head injury may increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease later in life, but its not known whether this also applies to DLB.
Almost all people who develop DLB have a sporadic form, which means that the main cause is unknown. Some genes may increase the risk of developing DLB.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinsons Be Reversed With Exercise
How Is Lbd Different From Parkinsons Or Alzheimers
These diseases are similar in a lot of ways. But there are some key differences in the symptoms that affect people with LBD and when those symptoms happen.
LBD may not cause short-term memory loss like Alzheimerâs. People with both conditions have trouble with thinking, alertness, and paying attention. But in LBD, those problems come and go. The disease can also cause hallucinations, often in the first few years someone has LBD. People with Alzheimerâs usually donât have hallucinations until the later stages.
People with LBD also often act out their dreams and make violent movements when theyâre asleep. Itâs called REM sleep behavior disorder. Sometimes, itâs the first sign that someone has LBD.
LBD and Parkinsonâs disease both cause movement problems, like stiff muscles and tremors. But most people with Parkinsonâs donât have problems with their thinking and memory until the very later stages of their disease. Sometimes, they donât have it at all. In the type of LBD known as Parkinsonâs disease with dementia, these problems begin much sooner.
People with LBD also need different drugs for their condition than the ones that treat Parkinsonâs or Alzheimerâs.
How Exactly Is Lewy Body Dementia Related To Alzheimers Disease And Parkinsons Disease
Lewy body dementia is a broad, general term for dementia in which lewy bodies are present in the brain. Dementia with lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia are two related clinical disorders that make up the general broader category of Lewy body dementia. Sometimes LBD is first diagnosed as Parkinsons disease or Alzheimers disease based on its symptoms.
- Parkinsons disease dementia : You might be diagnosed with Parkinsons disease if you start out with a movement disorder typical to Parkinsons but then have your diagnosis changed to PDD when dementia symptoms develop.
- Alzheimers disease : You might start out with memory or cognitive disorder that leads to a diagnosis of AD. Over time, other distinctive symptoms begin to appear and your diagnosis is then changed to dementia with lewy bodies. Distinctive symptoms of LBD include the changes in attention, alertness and cognitive ability changes in walking and movement visual hallucinations REM sleep behavior disorder and severe sensitivity to some antipsychotics used to treat hallucinations.
Dont Miss: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Read Also: What Tests Are Done For Parkinson’s
