Medicines For Parkinson’s Disease
Medicines prescribed for Parkinson’s include:
- Drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain
- Drugs that affect other brain chemicals in the body
- Drugs that help control nonmotor symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapysuch as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessnessand reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People with Parkinson’s should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, such as being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
Other medicines used to treat Parkinsons symptoms include:
- Dopamine agonists to mimic the role of dopamine in the brain
- MAO-B inhibitors to slow down an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain
- COMT inhibitors to help break down dopamine
- Amantadine, an old antiviral drug, to reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinson’s is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
Body System #7/8: Cardiovascular/circulatory System
The circulatory system permits blood to circulate and transport nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood cells. It also helps fight disease, stabilize temperature and pH, and maintain homeostasis.
Diseases and Disorders of the Circulatory System
- Cardiovascular Disease This disease comprises heart conditions that include diseased vessels, structural problems, and blood clots.
- Arteriosclerosis Fatty deposits in the arteries cause the walls to stiffen and thicken which can restrict blood flow in the body.
- Stroke A stroke is characterized by a blockage of the blood vessels to the brain.
- Hypertension Hypertension is high blood pressure that causes the heart to work harder.
- Aortic Aneurysm This is a condition in which the aorta is damaged and starts to bulge or tear causing severe internal bleeding.
- Peripheral Arterial Disease PAD is the narrowing or blockage of an artery.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency With CVI, sections of the superficial veins of the lower extremities reflux.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Cause Urinary Incontinence
Parkinson’s Disease Is Not One But Two Diseases
- Date:
- Aarhus University
- Summary:
- Researchers around the world have been puzzled by the different symptoms and varied disease pathways of Parkinson’s patients. A major study has now identified that there are actually two types of the disease.
Although the name may suggest otherwise, Parkinson’s disease is not one but two diseases, starting either in the brain or in the intestines. Which explains why patients with Parkinson’s describe widely differing symptoms, and points towards personalised medicine as the way forward for people with Parkinson’s disease.
This is the conclusion of a study which has just been published in the leading neurology journal Brain.
The researchers behind the study are Professor Per Borghammer and Medical Doctor Jacob Horsager from the Department of Clinical Medicine at Aarhus University and Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark.
“With the help of advanced scanning techniques, we’ve shown that Parkinson’s disease can be divided into two variants, which start in different places in the body. For some patients, the disease starts in the intestines and spreads from there to the brain through neural connections. For others, the disease starts in the brain and spreads to the intestines and other organs such as the heart,” explains Per Borghammer.
He also points out that the discovery could be very significant for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease in the future, as this ought to be based on the individual patient’s disease pattern.
Story Source:
Body System #12: Digestive System
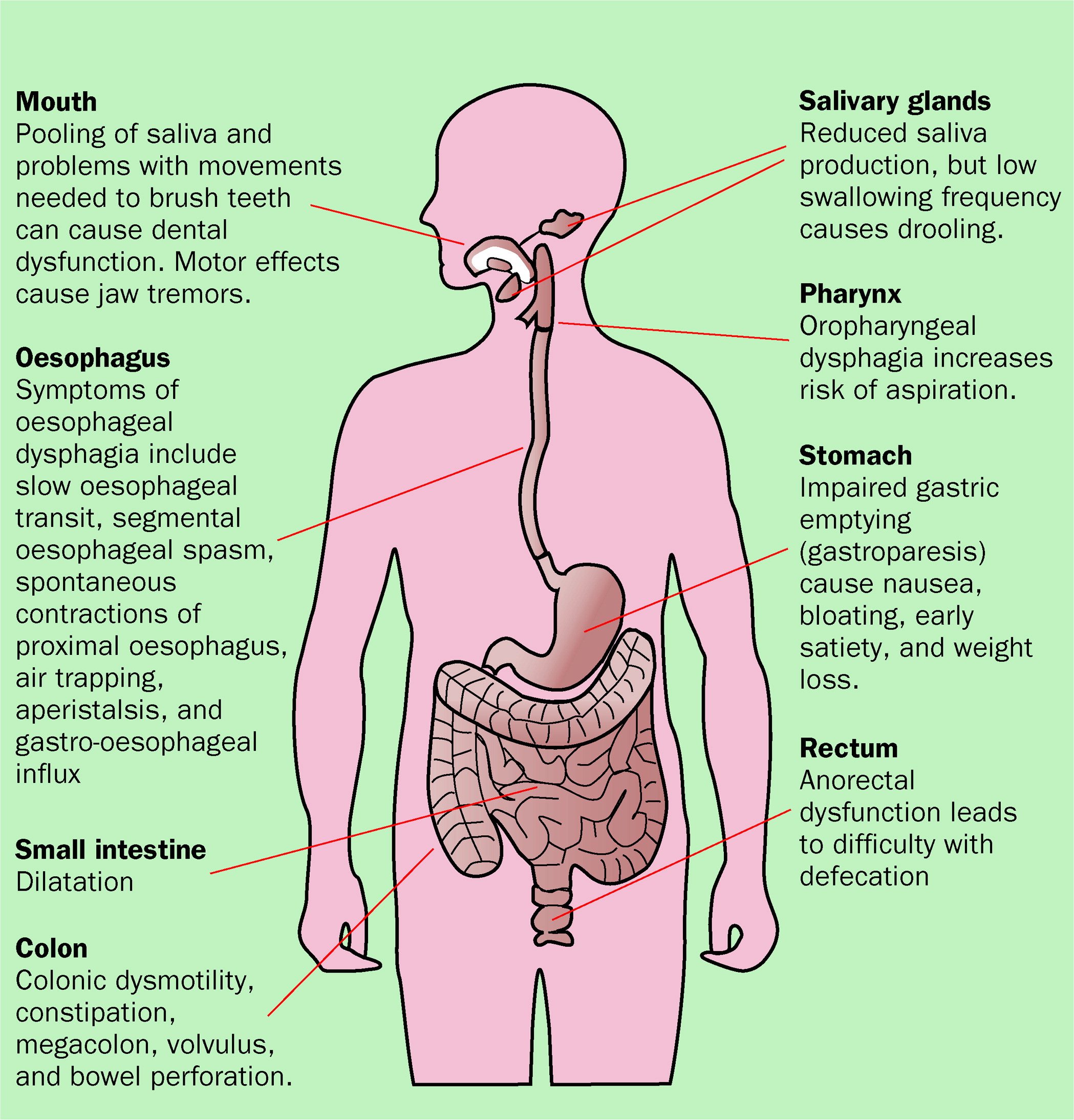
The digestive system breaks down food, extracts nutrients into the bloodstream, and excretes waste. This body system is made up of the digestive tract, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder.
Diseases and Disorders of the Digestive System
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome IBS is an intestinal disorder causing pain in the stomach, gas, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Diverticulitis Diverticulitis is an inflammation of one or more small pouches in the digestive tract.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease GERD is a condition in which stomach acid irritates the esophagus.
- Crohns Disease This is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that affects the lining of the digestive tract.
Does learning about the anatomy and physiology of different body systems interest you? Are you ready for a rewarding career as a medical assistant? The Medical Assistant program at Hunter Business School prepares competent, entry-level medical assistants in the cognitive , psychomotor , and affective learning domains required for professional practice.
Contact us today to find out more about how to become a medical assistant on Long Island.
Don’t Miss: How Is Mitochondria Affected In Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in deep parts of the brain called the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and are responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement. For reasons not yet understood, the dopamine-producing nerve cells of the substantia nigra begin to die off in some individuals. When 80 percent of dopamine is lost, PD symptoms such as tremor, slowness of movement, stiffness, and balance problems occur.
Body movement is controlled by a complex chain of decisions involving inter-connected groups of nerve cells called ganglia. Information comes to a central area of the brain called the striatum, which works with the substantia nigra to send impulses back and forth from the spinal cord to the brain. The basal ganglia and cerebellum are responsible for ensuring that movement is carried out in a smooth, fluid manner .
The action of dopamine is opposed by another neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. In PD the nerve cells that produce dopamine are dying. The PD symptoms of tremor and stiffness occur when the nerve cells fire and there isn’t enough dopamine to transmit messages. High levels of glutamate, another neurotransmitter, also appear in PD as the body tries to compensate for the lack of dopamine.
How Does Parkinson’s Affect The Body
The telltale symptoms all have to do with the way you move. You usually notice problems like:
Rigid muscles. It can happen on just about any part of your body. Doctors sometimes mistake early Parkinson’s for arthritis.
Slow movements. You may find that even simple acts, like buttoning a shirt, take much longer than usual.
Tremors. Your hands, arms, legs, lips, jaw, or tongue are shaky when you’re not using them.
Walking and balance problems. You may notice your arms aren’t swinging as freely when you walk. Or you can’t take long steps, so you have to shuffle instead.
Parkinson’s can also cause a range of other issues, from depression to bladder problems to acting out dreams. It may be a while before abnormal movements start.
Also Check: What Causes Cell Death In Parkinson’s Disease
Innate Immunity In Pd: Microglia Activation
Microglial cells are the principal actors of innate immunity in the CNS responsible for the protection and restoration of neurons . They can be activated by various external or internal insults such as neuronal dysfunction, trauma or certain toxin. Also, a wide range of molecules including viral or bacterial proteins, -syn, cytokines and antibodies are able to induce the activation of microglia . Consequently, microglial cells produce different molecular mediators with chemotactic and immunomodulatory functions. One of them is tumor necrosis factor which in PD plays important roles contributing to the regulation of synaptic plasticity . PD brains are characterized by the presence of HLA-DR+ microglial cells and raised levels of CD68, an activation marker for microglia and macrophages, having a direct relation with -syn aggregations and the duration of disease . Moreover, an increased expression of MHC-II molecules in microglial cells has been observed in chronic neuroinflammation but not in the CNS of healthy subjects . Individuals with single nucleotide polymorphism at MCH-II locus are prone to develop PD, which indirectly proves the importance of adaptive immunity in these patients .
The Effect Of Dopaminergic Medications On Autonomic Measures In Parkinson Disease
Human autopsies reveal dopamine receptors to be in the nucleus tractus solitarius and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus, suggesting that dopaminergic signals regulate visceral autonomic function. Epidemiologic studies observe higher doses of dopaminergic medications and higher disease severity to be related to more autonomic problems, independent of one another. Levodopa can be further metabolized to small amounts of epinephrine and norepinephrine which may lead to sympathomimetic effects. Some studies have found a positive correlation of levodopa and norepinephrine concentrations, while others have not. Constipation in PD may improve with dopaminergic treatment. Although treatment with levodopa has been thought to cause OH, this has not been consistently supported in physiological studies.
Read Also: Are Parkinson’s Tremors Worse In The Morning
Research Is Underway To Further Understand The Cardiac Effects Of Parkinsons
It is possible to image the sympathetic nervous system of the human heart by injecting a radioactive tracer, meta-iodo-benzyl-guanidine, . Development of this technique, known as MIBG cardiac imaging, holds much promise as a test to confirm the diagnosis of PD , to identify those who are at risk of developing PD in the future, and to distinguish PD from related disorders. MIBG cardiac imaging is still considered an experimental procedure for detection of PD and is not yet in use as a clinical tool for this purpose.
A recent research study was conducted in monkeys in which the destruction of the sympathetic nerves of the heart was chemically induced to mimic the changes that are seen in PD. The cardiac system was then imaged using a number of new-generation radioactive tracers, which bind to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. This model system may help to shed light on the molecular changes that accompany the loss of the sympathetic nerves of the heart and can also be used to track the response of the cardiac system to therapeutic agents.
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Autonomic Nervous System And The Heart
Structural problems of the heart such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy are not thought to be part of the pathology of PD, although of course, could co-exist with PD.
The Heart Of The Matter: Cardiovascular Effects Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson Disease Neuropathology In The Autonomic Nervous System
Constipation And Digestive Issues
As Parkinsons disease progresses, your digestive tract will slow down and function less efficiently. This lack of movement may lead to increased bowel irritability and constipation.
In addition, certain medications often prescribed for Parkinsons disease, such as anticholinergics, can cause constipation. Eating a balanced diet with plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains is a good first step remedy.
Fresh produce and whole grains also contain a great deal of fiber, which can help prevent constipation. Fiber supplements and powders are also an option for those with Parkinsons.
Be sure to ask your doctor how to gradually add fiber powder to your diet. This will ensure you dont have too much too quickly and make constipation worse.
Also Check: Does Aspartame Cause Parkinson’s
Systems Of The Body: A Medical Assistants Guide
Are you interested in learning more about how to obtain a diploma in a Medical Assistant program? Part of what you will learn during your Medical Assistant training are different terminology for anatomy and physiology. As a medical assistant student, you will become familiar with body systems and disorders and diseases common to those different body systems. So, how many body systems are there?
Body System #11: Reproductive System
The reproductive system is a combination of bodily organs and tissues used in the process of producing offspring.
Diseases and Disorders of the Reproductive System
- Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer results in a malignant tumor of the cervix.
- Prostate Cancer This type of cancer occurs in a mans prostate, a small sized gland that produces seminal fluid.
- Vaginal Yeast Infection This is an infection caused by a yeast fungus in the vagina.
- Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition where tissue that normally lines the uterus ends up outside the uterus.
- Gonorrhea Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted bacterial infection that may cause infertility if left untreated.
- Erectile Dysfunction This occurs when a man cant keep or get an erection during sexual intercourse.
Also Check: Which President Had Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment For The Motor Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
There are many ways to deal with Parkinsons disease motor symptoms, including medications, occupational therapy and lifestyle adjustments. You may find that tremors make you more susceptible to accidents such as tripping, falling or spilling hot liquids so you must take care and ask for the help and support you need.
Unlike other Parkinson’s motor symptoms, tremors can be hard to treat with medication. However, medicines can be helpful for treating symptoms such as Parkinson’s disease gait impairments, which can have a major impact on your life. The gait of Parkinson’s disease presents slightly differently in each patient. Some experience the Parkinson’s disease shuffling gate, which can make movement markedly slower and make it look like you are “dragging your feet.” You may also experience reduced arm movement while walking.
In Parkinson’s disease, freezing of gait is characterized by hesitation before stepping forward, or a feeling like your feet have frozen to the floor. Frozen gait usually only lasts for a step or two, but you will need to be careful when crossing busy streets and try to minimize your risk of falling wherever possible.
You can talk to your doctor about medications to try, as well your surgical and homeopathic options. However, there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease and no way to stop the symptoms entirely, but scientists are working to change that.
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal; and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
You May Like: What Part Of The Body Does Parkinson’s Affect
Parkinson Disease Neuropathology In The Autonomic Nervous System
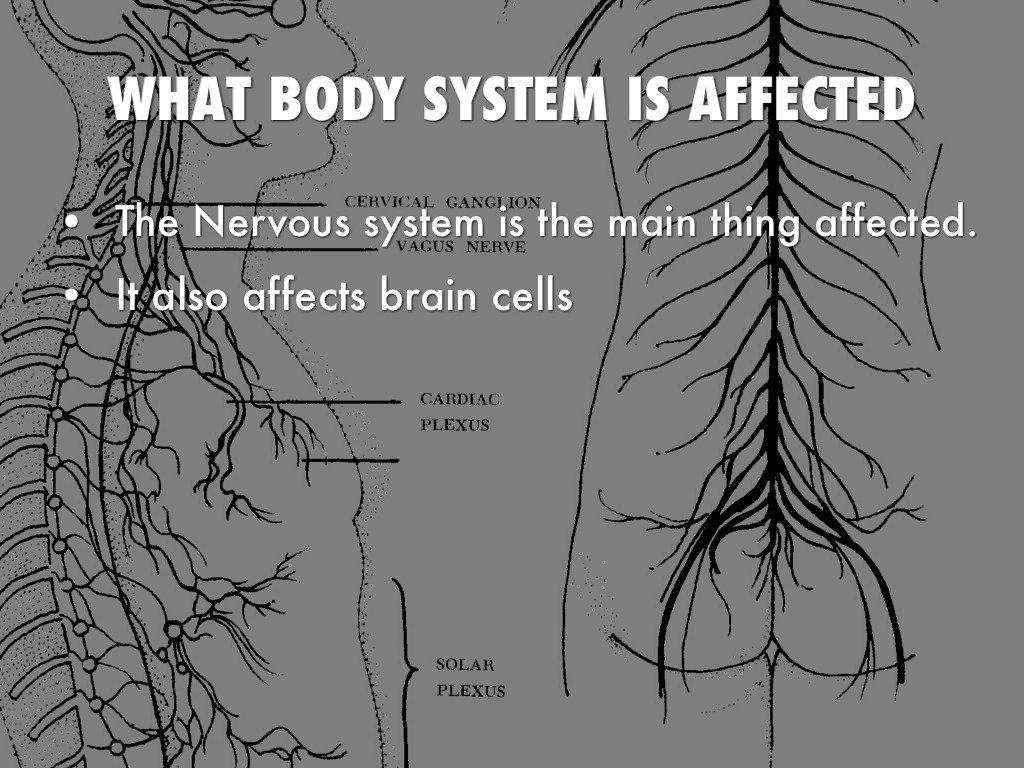
Anatomically, the autonomic nervous system can be divided into central autonomic networks, sympathetic pathways, parasympathetic pathways and the enteric nervous system. Central autonomic networks integrate autonomic function, linking the neocortex, diencephalon and brainstem. At its core is the nucleus tractus solitarius which integrates somatic and autonomic nervous systems and maintains homeostasis with projections to the hypothalamus, limbic structures and descending autonomic tracts. PD pathology has been characterized by intraneuronal inclusions which contain α-synuclein known as Lewy neurites or Lewy bodies . α-synuclein is a presynaptic protein thought to maintain synaptic integrity and be involved with regulation of dopamine synthesis. Although often seen in the absence of neuronal loss, evidence suggests that α-synuclein aggregation is a precursor to neurodegeneration. PD pathology has been observed in a chain of neurons forming autonomic pathways including: the hypothalamus, preganglionic parasympathetic projection neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic sympathetic projection neurons . PD pathology has also been found in several end-organs including the submandibular gland, lower esophagus, duodenum, pancreas, bronchus, larynx, epicardium, adrenal medulla, parathyroid and ovary. illustrates most areas within autonomic pathways where PD pathology has been found.
What Body Systems And Organs Are Affected By Parkinson Disease
5/5Parkinsons diseasebodyorgan systemsaffectedsystem
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in deep parts of the brain called the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and are responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement.
Also, what foods should Parkinsons patients avoid? Eat too many sugary foods and drinks as these can negatively impact your immune system. Opt for naturally sweetened food and reduce your sugar intake to manage Parkinsons symptoms. Eat too much protein. Consuming lots of beef, fish, or cheese may affect the effectiveness of certain Parkinsons medications.
Just so, how does Parkinson disease affect the muscular system?
Unlike some neurological conditions which affect muscle tone, the rigidity in Parkinsons disease affects flexor and extensor muscles equally. Rigidity in Parkinsons disease can prevent you from moving easily, and this lack of easy movement can lead to more stiffness in a downward cycle.
How does Parkinson start?
PD starts with the brain cells, called neurons, which control movement. Neurons produce a substance called dopamine. PD sets in when the neurons die and the levels of dopamine in the brain decrease. Early signs of Parkinsons disease can be easy to miss, especially if they occur sporadically.
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Also Check: What Helps Parkinson’s Patients Sleep
