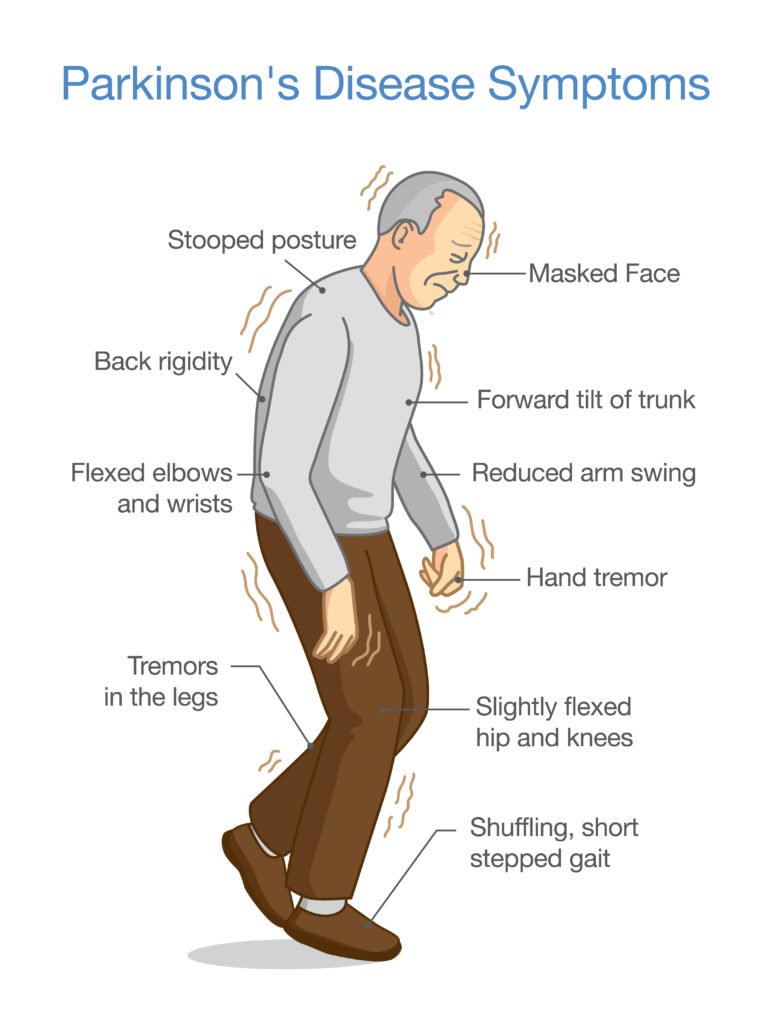
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The main symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are:
- tremor or shaking, often when resting or tired. It usually begins in one arm or hand
- muscle rigidity or stiffness, which can limit movement and may be painful
- slowing of movement, which may lead to periods of freezing and small shuffling steps
- stooped posture and balance problems
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease vary from person to person as well as over time. Some people also experience:
- loss of unconscious movements, such as blinking and smiling
- difficulties with handwriting
- drop in blood pressure leading to dizziness
- difficulty swallowing
- sweating
Many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease could be caused by other conditions. For example, stooped posture could be caused by osteoporosis. But if you are worried by your symptoms, it is a good idea to see your doctor.
Response To Parkinsons Drugs
After examining you, and depending on the severity of your symptoms, your specialist may suggest you take medication for Parkinsons. If your symptoms improve after taking Parkinsons medication for a few weeks or months, your specialist may confirm a Parkinsons diagnosis. However, some people with other forms of parkinsonism will also respond well to these drugs.
Your specialist may suggest you have a scan to help make a diagnosis. However, scans alone cant make a definite diagnosis of Parkinsons, so they are not commonly used.
Here’s What To Do If You Suspect A Problem
Though reaching out to your usual medical care provider is a good first step, you will likely need to pursue a specialized evaluation from a speech language pathologist who is familiar with hypokinetic dysarthria. Parkinson Canada also notes that it may be helpful to meet with an ear, nose, and throat specialist for vocal symptoms, and a neurologist or motor disorder specialist to address any broader concerns.
While there is currently no cure for Parkinson’s that can reverse the course of the illness, several medications and lifestyle interventions can greatly improve patients’ quality of life. A timely diagnosis is key to getting a treatment plan in place, and that begins with knowing the signs.
Recommended Reading: Weighted Bracelet For Essential Tremors
Diagnosis And Management Of Parkinsons Disease
There are no diagnostic tests for Parkinsons. X-rays, scans and blood tests may be used to rule out other conditions. For this reason, getting a diagnosis of Parkinsons may take some time.
No two people with Parkinsons disease will have exactly the same symptoms or treatment. Your doctor or neurologist can help you decide which treatments to use.
People can manage their Parkinsons disease symptoms through:
- seeing a Doctor who specialises in Parkinsons
- medication
- multidisciplinary therapy provided for example, by nurses, allied health professionals and counsellors
- deep brain stimulation surgery .
Do Symptoms Get Worse
PD does not affect everyone the same way. The rate of progression and the particular symptoms differ among individuals.
PD symptoms typically begin on one side of the body. However, the disease eventually affects both sides, although symptoms are often less severe on one side than on the other.
Early symptoms of PD may be subtle and occur gradually. Affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. Activities may take longer to complete than in the past. Muscles stiffen and movement may be slower. The persons face may lack expression and animation . People may notice that they speak too softly or with hesitation, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. This very early period may last a long time before the more classical and obvious motor symptoms appear.
As the disease progresses, symptoms may begin to interfere with daily activities. Affected individuals may not be able to hold utensils steady or they may find that the shaking makes reading a newspaper difficult.
People with PD often develop a so-called parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, taking small quick steps as if hurrying , and reduced swinging in one or both arms. They may have trouble initiating movement , and they may stop suddenly as they walk .
Don’t Miss: Do You Die From Parkinson’s
Why Is Veterans Parkinsons Disease Such A Common Diagnosis
My client who served in the Philippines during the Vietnam War was diagnosed with what is informally called Young-Onset Parkinsons Disease at age 31.
The average age at which most folks are diagnosed with Parkinsons is 58 years old one is diagnosed with Young Onset Parkinsons if they are diagnosed before the age of 50.
The diagnosis of Young Onset Parkinsons is a frighteningly common occurrence in the Veteran community.
Beyond that, traditional onset Parkinsons is increasingly common in the Veterans community. I think there are 2 major reasons .
Here is one of those minor reasons: science is showing us more and more that there are early indicators for the diagnosis of a Veterans Parkinsons Disease: the VA Pacific Islands Health Care System concluded that individuals who have lost their sense of smell are 5 times more likely to be diagnosed with Parkinsons Disease in the future.)
The First Major Reason for the increase in Veterans Parkinsons Disease is that so many Vietnam era Veterans were exposed to dioxin during their military service. .
The VA has conceded in the past that Veterans exposed to Agent Orange have a 70% greater likelihood of being diagnosed with Parkinsons disease.
In fact, Veterans who served boots on the ground in Vietnam are entitled to a presumption that the Veterans Parkinsons Disease was related to their military service.
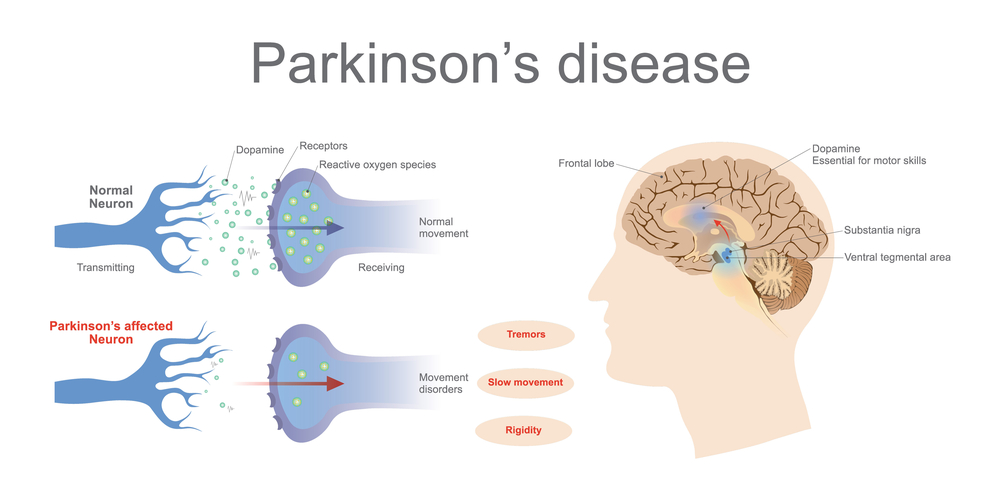
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons occurs when neurons in the part of the brain that control body movement become impaired or die. These neurons are responsible for creating dopamine, an important brain chemical that is vital for normal body function.
With fewer of these neurons in the brain, insufficient dopamine is created. Scientists are still not sure what exactly causes these neurons to become impaired or die.
People with Parkinsons also lose nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system that controls heart rate and blood pressure. This could be why fatigue and a decrease in blood pressure regularly occur with people who have Parkinsons.
While there have been cases of the disease that appear to be hereditary and can be traced to specific genetic mutations, there isnt enough evidence yet to conclusively prove it is passed down from parents to their children.
Most cases of Parkinsons occur randomly, and researchers believe a combination of genetic and environmental factors are responsible.
Don’t Miss: Weighted Blanket For Parkinson’s
Do You Die From Pd Dementia
People with Parkinsons-related dementia often want to know how the disease can impact their lifespan. While people with Parkinsons can expect a similar lifespan to the general population, studies show both Parkinsons disease dementia and Lewy body dementia can shorten lifespan, generally due to medical complications from the disease, rather than the disease itself.
Medications For People With Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease result from the progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the brain and other organs such as the gut, which produce a neurotransmitter called dopamine. This causes a deficiency in the availability of dopamine, which is necessary for smooth and controlled movements. Medication therapy focuses on maximising the availability of dopamine in the brain. Medication regimes are individually tailored to your specific need. Parkinsons medications fit into one of the following broad categories:
- levodopa dopamine replacement therapy
- dopamine agonists mimic the action of dopamine
- COMT inhibitors used along with levodopa. This medication blocks an enzyme known as COMT to prevent levodopa breaking down in the intestine, allowing more of it to reach the brain
- anticholinergics block the effect of another brain chemical to rebalance its levels with dopamine
- amantadine has anticholinergic properties and improves dopamine transmission
- MAO type B inhibitors prevent the metabolism of dopamine within the brain.
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
How Is Parkinsons Diagnosed
Doctors use your medical history and physical examination to diagnose Parkinson’s disease . No blood test, brain scan or other test can be used to make a definitive diagnosis of PD.
Researchers believe that in most people, Parkinson’s is caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Certain environmental exposures, such as pesticides and head injury, are associated with an increased risk of PD. Still, most people have no clear exposure that doctors can point to as a straightforward cause. The same goes for genetics. Certain genetic mutations are linked to an increased risk of PD. But in the vast majority of people, Parkinsons is not directly related to a single genetic mutation. Learning more about the genetics of Parkinsons is one of our best chances to understand more about the disease and discover how to slow or stop its progression.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
Men are diagnosed with Parkinsons at a higher rate than women and whites more than other races. Researchers are studying these disparities to understand more about the disease and health care access and to improve inclusivity across care and research.
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60. Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation has made finding a test for Parkinsons disease one of our top priorities.
Who Gets Early Onset Parkinsons Disease
About 10%-20% of those diagnosed with Parkinsons disease are under age 50, and about half of those are diagnosed before age 40. Approximately 60,000 new cases of Parkinsons are diagnosed each year in the United States, meaning somewhere around 6,000 12,000 are young onset patients.
Is it genetic or hereditary?
The cause of Parkinsons disease is not yet known. However, Parkinsons disease has appeared across several generations of some families, which could indicate that certain forms of the disease are hereditary or genetic. Many researchers think that Parkinsons disease may be caused by genetic factors combined with other external factors. The field of genetics is playing an ever greater role in Parkinsons disease research, and scientists are continually working towards determining the cause or causes of PD.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Read Also: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Advanced And Future Treatments For Parkinsons
While theres no cure for Parkinsons disease, recent research has led to improved treatments.
Scientists and doctors are working together to find a treatment or prevention technique. Research is also seeking to understand who is more likely to develop the disease. In addition, scientists are studying the genetic and environmental factors that increase the chance of a diagnosis.
Here are the latest treatments for this progressive neurological disorder.
In 2002, the FDA approved deep brain stimulation as a treatment for Parkinsons disease. But advances in DBS were limited because only one company was approved to make the device used for the treatment.
In June 2015, the FDA approved the
Passive Manipulation Of Limbs
To test for the presence of rigidity, we need to passively manipulate the limbs of the patient. However, If the disease is in its early stage or the symptoms are well controlled with medications, we may not be able to see rigidity. We will need to use some activation maneuvers, that basically consist in performing repetitive movements with the limb contralateral to the one that is being tested.
Also, there are two types of rigidity:
– Lead-pipe rigidity: where the tone is uniformly and smoothly increased throughout the entire range of movement
– Cogwheel rigidity: where a tremor is superimposed on the hypertonia, making the movement irregular due to intermittent increase and reduction of tone
Upper Extremity Testing
For the upper extremity the most sensitive joint where to check for rigidity is the wrist. To uncover rigidity, passively rotate the wrist and feel for a resistance to the movement. It is very important that the arm of the patient is fully relaxed when rotating the wrist. To do this, place your proximal hand under the patients forearm, while your distal hand grabs and rotates the wrist of the patient. When rigidity is present, the range of motion will be preserved but you will feel a resistance in performing the movement.
Wrist rotation with activation maneuver.
It is also possible to test for rigidity in the elbow by passively flexing and extending the forearm.
Elbow flexion-extension with activation maneuver.
Lower Extremity Testing
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Tests Might I Have
Your doctor may want to start by testing your blood or doing a brain scan to rule out other conditions.
People who have Parkinsonâs disease donât make enough of a brain chemical called dopamine, which helps you move. If those first tests donât show a reason for your symptoms, your doctor may ask you to try a medication called carbidopa-levodopa, which your brain can turn into dopamine. If your symptoms get much better after you start the drug, your doctor probably will tell you that you have Parkinsonâs disease.
If the medication doesnât work for you and thereâs no other explanation for your issues, your doctor might suggest an imaging test called a DaTscan. This uses a small amount of a radioactive drug and a special scanner, called a single photon emission computed tomography scanner, to see how much dopamine is in your brain. This test can’t tell you for sure that you have Parkinson’s disease, but it can give your doctor more information to work with.
It can take a long time for some people to get a diagnosis. You may need to see your neurologist regularly so they can keep an eye on your symptoms and eventually figure out whatâs behind them.
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Read Also: What Is The Prognosis For Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of The Disease
The four primary symptoms of PD are:
- Tremor. Tremor often begins in a hand, although sometimes a foot or the jaw is affected first. The tremor associated with PD has a characteristic rhythmic back-and-forth motion that may involve the thumb and forefinger and appear as a pill rolling. It is most obvious when the hand is at rest or when a person is under stress. This tremor usually disappears during sleep or improves with a purposeful, intended movement.
- Rigidity. Rigidity , or a resistance to movement, affects most people with PD. The muscles remain constantly tense and contracted so that the person aches or feels stiff. The rigidity becomes obvious when another person tries to move the individuals arm, which will move only in ratchet-like or short, jerky movements known as cogwheel rigidity.
- Bradykinesia. This slowing down of spontaneous and automatic movement is particularly frustrating because it may make simple tasks difficult. The person cannot rapidly perform routine movements. Activities once performed quickly and easilysuch as washing or dressingmay take much longer. There is often a decrease in facial expressions.
- Postural instability. Impaired balance and changes in posture can increase the risk of falls.
Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The symptoms and rate of progression of Parkinsons are different among individuals. Effects of normal aging are sometimes confused for Parkinsons. It is difficult to accurately diagnose this disease because there is not a test that can accurately do it.
There are physical and non-physical symptoms that could indicate someone has Parkinsons disease:
Physical symptoms
Early stage symptoms
Parkinson’s disease occurs gradually. At first, the symptoms might not even be noticeable. Early symptoms can include feeling mild tremors or having difficulty getting out of bed or a chair. The person might start to notice that they are speaking softer than usual, or that their handwriting looks different.
Usually, it is friends or family members who are the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. For example, they may notice that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
Also Check: What Do Parkinson’s Patients Usually Die From
