What Is Huntingtons Disease
Huntington disease usually appears in a persons thirties or forties. Early signs and symptoms can include depression, irritability, poor coordination, small involuntary movements, and trouble learning new information or making decisions. Many people with Huntington disease develop involuntary, repetitive jerking movements known as chorea. As the disease, progresses symptoms become more pronounced. People with this disorder also experience changes in personality and decrease in thinking abilities. Affected individuals usually live about 15 to 20 years after signs and symptoms begin.
There is no care for this disorder, and it is largely determined genetically due to in the HTT gene. The juvenile form of this disorder also exists. Chorea can be controlled with medicines. However, other higher function abnormalities are difficult to control.
Coronal section from an MR brain scan of a patient with HD.
Signs It Might Be Multiple System Atrophy Instead Of Parkinsons Disease
Here are some clues as to whether it is multiple system atrophy or Parkinsons disease. One of the easier distinctions is between PD and MSA-C .If the patient presents with unsteadiness while walking, uncoordinated arms and legs, bladder disturbance and/or dizziness when standing the diagnosis is more likely to be MSA-C. On the other hand, if a person looks Parkinsonian the distinction can be harder, but there are clues:
- In the earlier stages of MSA-P , which is often when people have just been told they have Parkinsons disease, some patients will fall often.Frequent falls also occur in Parkinsons disease, but it typically occurs 10-15 years after diagnosis.
- In patients with MSA the classic Parkinsons drug L-Dopa may work initially but will stop working very quickly.It can continue working in PD patients for many years.
- Dementia is not associated with MSA however, it does occur in patients with lewy body Parkinsons disease.
- Early autonomic nervous system symptoms such as low blood pressure when standing and issues with the bladder are often signs of possible MSA in patients diagnosed with Parkinsons.
- Vocal cord issues are less common but very typical in MSA and much less common in PD.Some examples include difficulty getting words out, odd sighs and even falling asleep during a conversation.
Understanding The Differences Between Parkinsons And Lou Gehrigs Disease
As Parkinsons disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis are both progressive neurodegenerative diseases, many people confuse the terms. Below, senior care experts at Home Care Assistance of Mississauga provide information on the basic differences between Parkinsons and ALS to help you better understand the two diseases.
How Is Huntingtons Disease Diagnosed
Scientists were able to identify the affected gene as a marker for Huntingtons Disease in 1993. A diagnostic test is now available that can identify the presence of the protein huntingtin before symptoms appear. In most cases, genetic counseling is recommended after a positive diagnosis for Huntingtons Disease, as the defective chromosome is indiscriminately passed on to future generations.
Lewy Bodies: More Than Lbd

LBD is characterized by the presence of Lewy bodies in the nerve cells of the brain, meaning that LBD patients have Lewy bodies in the brain.2 However, Lewy bodies are also common with other conditions, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinsons disease. In fact, most people with PD also have Lewy bodies in their brain. However, even if they have Lewy bodies, not all Parkinsons patients will also develop LBD.2
Environmental Factors And Exposures
Exposure to and a history of head injury have each been linked with PD, but the risks are modest. Never having smoked cigarettes, and never drinking caffeinated beverages, are also associated with small increases in risk of developing PD.
Low concentrations of in the blood is associated with an increased risk of PD.
Drug-induced parkinsonism
Different medical drugs have been implicated in cases of parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism is normally reversible by stopping the offending agent. Drugs include:
Symptoms Related To Brain Function Are Different
There is some overlap, but in general, the overall cognitive symptoms that people experience with Parkinsons disease dementia and Alzheimers are different. Alzheimers mainly affects language and memory at the outset, whereas Parkinsons affects problem-solving, speed of thinking, memory, and mood.6
Unlike in Alzheimers disease, people with Parkinsons-related dementia often experience hallucinations, delusions, and paranoid thoughts. Both conditions can lead to , anxiety, and sleep disturbances.4,6
What Are Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Atypical Parkinsonian disorders are progressive diseases that present with some of the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease, but that generally do not respond well to drug treatment with levodopa. They are associated with abnormal protein buildup within brain cells.
The term refers to several conditions, each affecting particular parts of the brain and showing a characteristic course:
- Dementia with Lewy bodies, characterized by an abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein protein in brain cells
- Progressive supranuclear palsy, involving tau protein buildup affecting the frontal lobes, brainstem, cerebellum and substantia nigra
- Multiple system atrophy, another synucleinopathy that affects the autonomic nervous system , substantia nigra and at times the cerebellum
- Corticobasal syndrome, a rare tauopathy that typically affects one side of the body more than the other and makes it difficult for patients to see and navigate through space
How Is Huntingtons Disease Treated
At this point in time, there is no cure for Huntingtons Disease. There is also no known way to slow or prevent the disease from progressing. For now, treatment focuses on the management of symptoms and optimizing the quality of life for those affected. Each person affected by Huntingtons Disease will experience their symptoms uniquely. Meaning no two patients are the same, and no two patients exhibit identical symptoms.
There are a wide variety of medications and therapies that are available to help people with Huntingtons Disease. It is important to practice patience and perseverance when beginning a new medication as it takes time to figure out how these medications interact with your body and with each other. It may take weeks or months to figure out the correct combination and dosage of medications.
Speech therapy is also a very important part of a treatment plan for Huntingtons Disease. One of our highly specialized virtual speech therapists can offer support and guidance on the road to managing symptoms. Connect with one of our speech therapists by scheduling your free introductory calltoday!
How Is Parkinsonism Diagnosed
You should be referred to a Parkinsons specialist for the diagnosis of any parkinsonism. They may wish to explore different things before giving you a diagnosis.
Your specialist will look at your medical history, ask you about your symptoms and do a medical examination.
Telling the difference between types of parkinsonism isnt always easy, for the following reasons:
- The first symptoms of the different forms of parkinsonism are so similar.
- In many cases, parkinsonism develops gradually. Symptoms that allow your doctor to make a specific diagnosis may only appear as your condition progresses.
- Everyone with parkinsonism is different and has different symptoms.
Find out more: see our information on symptoms of Parkinsons, and diagnosing Parkinsons.
One of the most useful tests to find out what sort of parkinsonism you may have is to see how you respond to treatment.
If your specialist thinks you have idiopathic Parkinsons, theyll expect you to have a good response to Parkinsons drugs such as levodopa . A good response means that your symptoms will improve. Sometimes, it will only be clear that youve responded to medication when the drug is reduced or stopped, and your symptoms become more obvious again.
If you dont have any response to Parkinsons medication, your specialist will have to look again at your diagnosis.
Although not routinely available, your specialist may wish to carry out some of the tests below.
Current tests available include:
Knowing That It Is Msa And Not Parkinsons Is Important
Over the years MSA Coalition Board Members have heard the frustration about a slow diagnosis after the initial diagnosis of Parkinsons.While MSA is fatal, knowing the correct diagnosis, is still important.
Multiple system atrophy affects multiple systems in the body.As a result, while there are not MSA specific treatments, treating the various symptoms from sleep disorders, urinary and bowel issues, blood pressure control, etc. can vastly improve quality of life. The earlier an MSA patient is diagnosed, the earlier doctors can establish a plan of action to improve symptoms that can be very disabling. Another factor is that Parkinsons medications typically stop working in MSA patients.
An early diagnosis also allows patients and their families to spend quality time together while they are still able.It also provides time to prepare for end-of-life issues, such as preparing wills and living wills.
What Makes Them Different
MS and Parkinsonâs have different causes. They usually start to affect you at different ages, too.
MS often affects people between ages 20 and 50, but children get it, too. Parkinsonâs usually starts at age 60 or older, but some younger adults get it.
MS is an autoimmune disease. That means your bodyâs immune system goes haywire for some reason. It attacks and destroys myelin. As myelin breaks down, your nerves and nerve fibers get frayed.
In Parkinsonâs, certain cells start to die off. Your makes less and less of a chemical called dopamine that helps control your movement. As your levels dip, you lose more of this control.
Some genes may put you at risk for Parkinsonâs, especially as you age. Thereâs a small chance that people who are exposed to toxic chemicals like pesticides or weed killers can get it, too.
These symptoms are more common if you have MS. They not usually found in Parkinsonâs:
- or , where you feel like the room spins around and you lose your balance
Early Signs And Symptoms Are Different

Parkinsons disease generally begins as a movement disorder. Early signs and symptoms include:2
- Tremor, which often begins in the hand or fingers
- Slowed movement, which may include foot dragging
- Rigidity
- Slowed automatic movements such as blinking, smiling, and swinging your arms when you walk
Alzheimers disease generally begins as noticeable memory loss. Early signs and symptoms include:3,4
- Trouble remembering familiar words
- Challenges performing everyday tasks such as balancing a checkbook
What Are The Different Forms Of Parkinsonism
There are three main forms of parkinsonism, as well as other related conditions.
Most people with parkinsonism have idiopathic Parkinsons disease, also known as . Idiopathic means the cause is unknown.
The most common symptoms of idiopathic Parkinsons are , and of movement.
Vascular parkinsonism affects people with restricted blood supply to the brain. Sometimes people who have had a mild stroke may develop this form of parkinsonism.
Common symptoms include problems with memory, sleep, mood and movement.
Some drugs can cause parkinsonism.
Neuroleptic drugs , which block the action of the chemical dopamine in the brain, are thought to be the biggest cause of drug-induced parkinsonism.
The symptoms of drug-induced parkinsonism tend to stay the same only in rare cases do they progress in the way that Parkinsons symptoms do.
Drug-induced parkinsonism only affects a small number of people, and most will recover within months and often within days or weeks of stopping the drug thats causing it.
What Is The Difference Between Progressive Supranuclear Palsy & Parkinsons Disease
Both PSP and Parkinsons disease show similar symptoms such as stiffness, movement difficulties, and clumsiness, but the severity of the condition is often based on the symptoms.1
Progressive supranuclear palsy is more progressive when compared to Parkinsons disease.2
PSP is a rare brain disorder that causes serious and progressive problems whereas Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disorder that affects movements.3,4
Many studies were conducted based on the facts of the two diseases that presented very similar symptoms, but they are quite different from each other when analyzed in detail.
PSP and Parkinsons have overlapping symptoms, but diagnosis often becomes complicated. However, experts suggest that PSP is more severe with cognitive impairment when compared to Parkinsons disease. Concentration and memory are most severely affected in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy.
Symptom Overlap Between Classic Parkinson’s Disease And Atypical Parkinsonism
As previously established, the four core motor symptoms typical of Parkinsonâs disease can also present in many other disorders, with atypical Parkinsonism referring to this set of overlapping symptoms. Specific examples of these symptom overlaps include autosomal recessive inherited juvenile Parkinsonâs disease with incidences of dystonia, multiple system atrophy with autonomic dysfunction, progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration with irregular eye movements, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis / Parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam with motor neuron abnormalities.
The Association Between Vascular Disease And Pd
The association between ischaemic stroke and vascular risk factors on the one hand and PD on the other has been addressed in several studies. The incidence of ischaemic stroke among PD patients was lower than that of controls in one study , but an association was found in another . Cigarette smoking is recognised as protective for PD and a low incidence of both smoking and myocardial infarction is seen in PD patients . A retrospective case-control study of 178 patients with newly diagnosed PD, and 533 age- and sex-matched controls showed that diabetes, history of smoking, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol and triglycerides were significantly less frequent in PD than controls . Another study looked at the frequency of cerebrovascular lesions in 617 patients with autopsy-proven idiopathic PD and 535 age-matched controls. It found that 44.0% of PD patients had vascular lesions, more than was seen in controls , while acute, often fatal ischaemic or hemorrhagic strokes were less frequent in parkinsonian patients . The study concluded that there is neither a protective effect of PD against stroke nor a greater susceptibility to death from stroke in the populations examined .
Parkinsons & Huntingtons: Whats The Difference
December 9, 2020
- Demystifying Medicine
Many individuals are either indirectly or directly affected by Parkinsons Disease and Huntingtons Disease. However, most people do not know what causes their loved ones to develop these diseases. This video will explain the motor circuit in the brain that is responsible for Parkinsons and Huntingtons Disease and how they differ from each other. Furthermore, patients Sarah and Jade describe their daily lives as well as how they manage the symptoms of their disease.
References
Is Dementia A Symptom Of Both
One of the biggest similarities between PD and LBD is dementia. Some studies have found that approximately 78 percent of PD patients will eventually develop dementia.4 More specifically, almost half of Parkinsons patients will develop a certain type of dementia called Parkinsons Dementia, usually 10-15 years after their initial PD diagnosis.3 People with Parkinsons Dementia commonly experience poor memory and concentration, slowed thinking, confusion, , emotional changes, delusions, and visual hallucinations.
Parkinsons dementia is different than LBD, mainly in which symptoms occur first . Patients with Parkinsons Dementia will first show Parkinsons motor symptoms, followed by dementia many years after diagnosis. Conversely, LBD patients will first show dementia symptoms and may show motor symptoms later.3
Activation Pattern In Control Subjects
The pattern of brain activation induced by unilateral high-frequency passive vibratory stimulation in our control cohort is in keeping with previous PET data on elementary somatosensory function, as reviewed recently by Paulesu and colleagues . Our study confirms that this rather crude sensory stimulus produces strong activation in cortical areas S1 and S2. The pattern of normalized group rCBF increases in our study was markedly lateralized to the contralateral hemisphere, similar to previous reports . Transcallosal connections have, nevertheless, been demonstrated in posterior S1 , adjoining parietal cortex and secondary sensory cortical areas and, likewise, previous PET and functional MRI experiments have provided evidence for bilateral sensory cortical processing in humans. However, it remains an issue of further inquiry with higher temporal resolution imaging modalities, how ipsilateral sensory area recruitment is affected by habituation and/or other task-related issues. For instance, evoked potential recordings in cats indicate that habituation occurs more rapidly in S2 compared with S1 areas .
What Is Parkinson’s Disease

Parkinson’s disease is a chronic neurodegenerative disease. Its symptoms include non-motor symptoms and core motor symptoms . These symptoms in Parkinsonâs disease are due to a loss of nerve cells in the brain, leading to insufficient dopamine levels. Dopamine acts as a messenger for parts of the brain and nervous system which help co-ordinate body movement; a lack of dopamine thus means that certain parts of the brain cannot function as well as it should, subsequently manifesting as the aforementioned symptoms.
Understanding The Differences Between Parkinsonism And Parkinson Plus Syndromes
Parkinsonism means looks like Parkinsons disease. To neurologists this means that the person has a somewhat flexed posture, moves slowly, is stiff and usually walks slowly, with small steps and reduced or no arm swing. We call the syndromes atypical because they usually differ from Parkinsons Disease in a few ways:
Very often when the condition is mild, at the earliest stages, we cant tell whether it is Parkinsons Disease or atypical Parkinsons Disease and we treat it as if it is Parkinsons Disease because we dont have treatments for the atypical Parkinson disorders. Sometimes they respond to the usual Parkinsons Disease medications, but usually they dont. And when they do, the response is not as good as it is with PD.
Parkinson plus syndromes refer to syndromes which look like atypical PD, but also include additional abnormalities that are not seen in PD. These include: abnormalities of eye movements, gait ataxia , dystonia , severe problems with low blood pressure on standing, or changes on the neurological exam that are only detected by the neurologist in the form of abnormal reflexes.
The Proposed Mechanisms Of Vp
Various mechanisms have been discussed as explanation for VP. Ischaemic basal ganglion or white matter lesions disrupting the sensorimotor integration have been suggested . The gait disorder in Binswangers disease was attributed to diffuse vascular lesions disrupting basal ganglia/motor cortex connections and Winikates and Jankovic proposed it as a mechanism for VP.
What Is The Difference Between A Parkinson’s Disease Patient With Dystonia And A Dystonia Patient With Parkinson’s Symptoms
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological movement disorder with a wide array of symptoms that includes slowness of movement, rigidity of muscles, tremor, loss of balance, memory impairment, personality changes, and others. The movement symptoms of Parkinsons disease may be called parkinsonism. Parkinsonism is one aspect of Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms of dystonia and parkinsonism can occur in the same patient because both of these movement disorders seem to arise from involvement of the basal ganglia in the brain. Both parkinsonism and dystonia can each be caused by a great many disorders, and some of these disorders includes features of both parkinsonism and dystonia.
For example, there are the disorders known as dopa-responsive dystonia and x-linked dystonia-parkinsonism . DRD commonly begins in children as a dystonia predominately affecting the feet and being first manifested by an abnormal gait. In these children, features of parkinsonism tend to develop such as slowness of movement and also decreased muscle tone.
When DRD begins in adults, it usually appears first as parkinsonism and can be mistaken for Parkinson’s disease. XDP can also first develop as either dystonia or parkinsonism, and the symptoms of other disorder may occur.
Key Difference Parkinsons Vs Huntingtons Disease
The key difference between Parkinsons and Huntingtons disease is that Parkinson disease is a disorder with rigidity, tremors, slowing of movements, postural instability and gait disturbances usually occurring in old age due to degeneration of the substantia nigra of the midbrain while Huntingtons disease is a familial neurodegenerative disorder usually occurring in a younger population, characterized by emotional problems, loss of thinking ability and abnormal choreiform movements .
Signs It Could Be More Than Parkinsons Disease
Feb 9, 2020 | |
Close to one million people in the US have a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease .Unfortunately, for a small percentage of these people the diagnosis just doesnt seem right. They feel like something more is wrong.Their medicines may not be very effective. They might have severe dizziness and even be prone to fainting.They just sense the disease is progressing faster than expected.
Associated Complications Of Parkinsonism
If the documentation indicates the patient has dementia secondary to parkinsonism, it would be reported as:
- G31.83, Dementia with Lewy bodies
- F02.80, Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere without behavioral disturbance
In the Alphabetic Index under “dementia,” go down to “with” and then to “Parkinsonism.” The two codes G31.83 should be reported. Again, G31.83 should be sequenced first, followed by F02.80.
G31.83 applies to:
- Lewy body dementia
- Lewy body disease
Again, we need to read all the notations at G31, which indicates that F02.80 is to be added as a secondary code in this situation.
What Is The Cause Of Huntingtons Disease
Huntingtons disease happens because of a genetic disorder that causes brain cells death that has the defective gene. The huntingtin gene carries the genetic information that leads to producing a protein of the same name.When the HD gene is present, huntingtin is abnormally made by the cells, causing issues in neurons normal metabolism.
Research has shown there is a CAG repeat in the mutant HTT gene of people with Huntingtons. CAG is one of the many sequences of molecules that build the DNA, which makes the bodys proteins. For huntingtin, there is a particular number of sequences that need to happen in order to produce the protein correctly. So when there is a CAG repeat, more of these sequences lead to abnormally made huntingtin protein. The amount of CAG repeats is proportional to the severity of the disease. If its low, there is a reduced penetrance of the disease.
HD patients get the HTT gene through one of their parents, which gives them the gene plus another mutant allele. This means the person has a 50% chance of developing the disease, and if both parents have it, they have a 75% chance.
What Is The Difference Between Parkinsonism Vs Parkinsons Disease
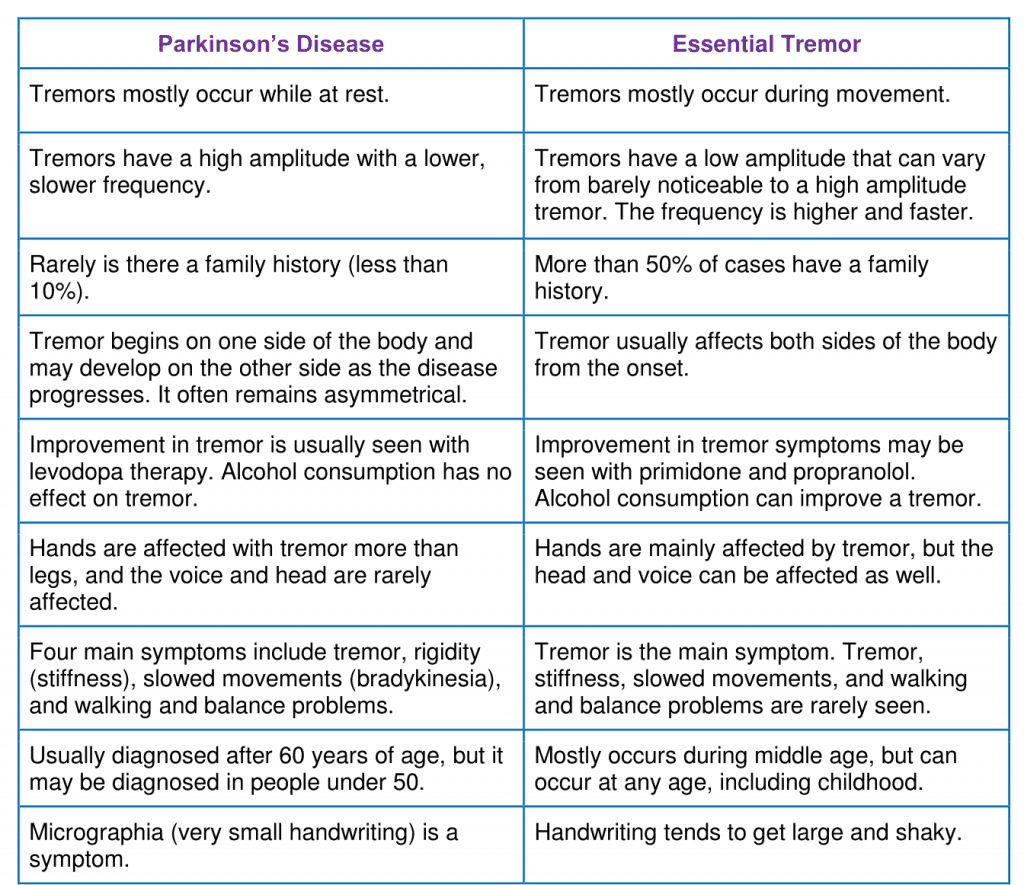
What is the difference between Parkinsonism vs Parkinsons disease? In simple terms, Parkinsons is a disease whereas Parkinsonism is a range of symptoms that are usually seen in patients with Parkinsons disease, but sometimes occurring as a result of other neurodegenerative disorders.
Unless you are a medical professional, there might appear to be very little difference between Parkinsons disease and Parkinsonism.
On the surface, they appear to be exactly the same condition: both are characterized by tremors, stiffness, balance issues, and slowness of movement, but this is where the similarities end.
Whereas Parkinsonism encompasses the four main movement problems seen in patients suffering from Parkinsons disease, Parkinsons disease itself is a progressive and highly degenerative disorder that causes many other symptoms as well as those seen in Parkinsonism.
Research To Find Msa Biomarkers And An Earlier Msa Diagnosis
An important goal of the Coalitions MSA Research Program is to fund and encourage the development of biomarkers to distinguish PD from MSA at a much earlier stage.The stakes are high.An accurate biomarker could lead to quicker development of treatments.In fact, a concern in past clinical trials of MSA treatments that failed is that maybe the patients in the trial are too late stage to show effectiveness.Increasing the number of known early stage MSA patients could improve the likelihood of finding treatments and even a cure.
Whats The Difference Between Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Parkinsons
People with PSP generally progress more rapidly than people with Parkinsons. A person with Parkinsons tends to lean forward while a person with PSP tends to lean backward. Tremors are common in people with Parkinsons and rare in people with PSP. Speech and swallowing abnormalities are more severe and show up sooner in those living with PSP.
For more information on progressive supranuclear palsy, read this fact sheet and insights from the CurePSP organization website.
Parkinsonism Vs Parkinson’s Disease
Often confused as one and the same, Parkinsons disease is actually the most common kind of , accounting for nearly 80% of all cases.2 PD is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the same motor conditions as Parkinsonisms including tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and impaired balance. Other contributing causes of Parkinsonism include multiple system atrophy, progressive supranuclear palsy, and corticobasal degeneration. PD has no directly attributable cause or cure.
