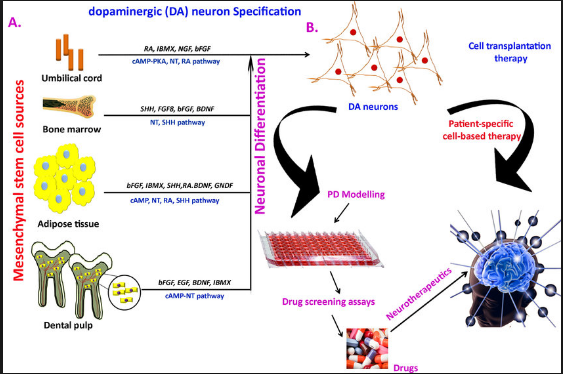
Results Of Cell Surgical Network For First 201 Patients Receiving Stem Cells For Parkinsons Disease
The improvement does appear to reduce after about 1 year, so repeated treatments appear to be warranted. Remember when looking at these results that most of these patients have been on standard Parkinsons Disease medications for several years. Some patients note increased effectiveness of their Parkinsons Disease medications after stem cell therapy.
How Long Does A Stem Cell Therapy Take
The initial analyses and counseling can be done without you having to travel to Offenbach . This period can be 2 weeks up to months depending on the availability of patients slots. If you live further away, we will conduct the initial discussions by telephone or video conference. For the actual treatment, you will travel to Offenbach.
Pathophysiology Of The Disease
Basal ganglia motor circuitry: Parkinson’s disease is predominantly a disorder of the basal ganglia, which are a group of nuclei situated at the base of the forebrain . The striatum, composed of the caudate and putamen, is the largest nuclear complex of the basal ganglia. The striatum receives excitatory input from several areas of the cerebral cortex, as well as inhibitory and excitatory input from the dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra pars compacta . These cortical and nigral inputs are received by the spiny projection neurons, which are of 2 types: those that project directly to the internal segment of the globus pallidus , the major output site of the basal ganglia; and those that project to the external segment of the globus pallidus , establishing an indirect pathway to the GPi via the subthalamic nucleus . The actions of the direct and indirect pathways regulate the neuronal output from the GPi, which provides tonic inhibitory input to the thalamic nuclei that project to the primary and supplementary motor areas .
Figure 2: Anatomy of basal ganglia. View Figure 2
Two pathways exist within the basal ganglia circuit, the direct and indirect pathways , as follows:
Figure 3: Basal ganglia circuitry in Parkinson’s disease. View Figure 3
â¢In the direct pathway, outflow from the striatum directly inhibits the GPi and SNr; striatal neurons containing D1 receptors constitute the direct pathway and project to the GPi/SNr
Common symptoms:
b.Terminates with movement
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Affect Eyesight
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease often go unnoticed. Often one-sided symptoms are first to give indications, as listed below. When noted, a proper diagnose by neurologist needs to be made, as all symptoms can have other causes too:
- Writing changes towards the end of words and sentences
- Balance and posture problems
- Tremor usually starting with the hand at rest or in the thumb and forefingers rolling against each other
- Slowed movements
Scientists Turned Parkinson’s Disease Patient’s Skin Cells Into Brain Cells Now He Can Tie His Shoes Again

Scientists have helped a man with Parkinson’s disease swim, ski and tie his own shoes again by reprogramming his skin cells and implanting them inside his brain.
The team at McLean Hospital, Massachusetts, and Massachusetts General Hospital took the skin cells of a 69-year-old patient with the degenerative disorder and turned them into what are known as pluripotent stem cells, which can develop into almost any type of cell in the adult body. The stem cells were tweaked to become dopaminergic neurons. These die off in people with Parkinson’s disease. The findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
To check the cells wouldn’t be rejected by the man’s body, the researchers first grafted them on to the brains of lab mice and looked for signs of immune system response.
Next, they developed an implanting technique involving a syringe to insert the cells into his brain. They used the approach in two first-of-their-kind surgeries in 2017 and 2018, according to a press release from McLean Hospital. In two surgeries focused on either side of the brain separated by six months, surgeons placed a total of eight million dopaminergic neurons inside the patient’s brain. The doctors had to seek special permission from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to carry out the procedures.
This article has been updated with comment from Dr. Jeffrey Schweitzer.
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Disease Cause Seizures
Parkinsons Disease: How Could Stem Cells Help
What do we know?
Tremors, muscle rigidity and other symptoms of Parkinsons disease are caused by the death of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. Dopamine producing neurons throughout the brain are affected, but the substantia nigra is the primary brain region where neurons are lost.
People affected by PD often develop abnormal protein clumps in their brain called Lewy bodies. These clumps are made of a protein called alpha-synuclein.
Levodopa is the primary drug used to treat PD. Levodopa is converted into dopamine when in the body, which compensates for lost dopamine-producing neurons.
What are researchers investigating?
Approximately 5% of people with PD have inheritable gene mutations linked to PD. Researchers are investigating what causes PD in the other 95% of patients in clinical studies, animal models and cell models.
Transplantation of young brain cells from human foetuses into people with PD has shown promising results in previous clinical trials. The current TRANSEURO study is re-examining this treatment method with the aim of minimising side effects and measuring efficacy.
Scientists can now make dopamine-producing neurons from both human embryonic stem cells and human induced pluripotent stem cells . Neurons made from human ESCs and iPSCs mature into human dopamine-producing neurons, survive and function after transplantation into mouse, rat and monkey models of PD.
What are the challenges?
Replacing lost cells
What Are The Early Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
Early symptoms and possible warning signs of Parkinsons disease are: Writing becomes difficult and font is getting involuntarily smaller One sided tremor or shaking Involuntarily index finger and thumb rolling Dizziness or fainting Change of facial expression known as mask face Soft or lower voice then usual Sleep problems usually accompanied with sudden movements Walking and otherwise subconscious movements only seem possible when actively imitating them Hunching over or stooping
You May Like: Does Adderall Help Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
The underlying cause for the death of nerve cells in the brain are unknown. Several factors are known to play a role:
- Genes: Specific gene mutations were shown to increase the risk for PD
- Environment: Exposure to certain toxins may increase PD risk.
- Age: Usually the age of 60 is the age where PD is most prone to happen
- Sex: Men are more likely to develop PDOccurring changes in PD
changes may be related to Lewy bodies;and the alpha-synuclein ;that is contained within these Lewy bodies
Legal And Ethical Questions
Stem cell research and treatment is a matter of considerable debate and many people are opposed on ethical grounds, although others believe that the benefits of such research far outweigh ethical concerns. There is strict regulation in all European Union Member States and many other countries to ensure that research is carried out legally and ethically.
Opposition to research using cells from an embryo tends to arise due to:
- the belief that embryonic stem cell research involves the destruction of the earliest developing cells and some regard this as destroying a human life
- concern about the creation of embryos with the intention of destroying them once certain cells have been extracted
- objections to any kind of genetic research, which is perceived as undermining human dignity and interfering with nature.;
Fortunately new techniques are being developed which will enable researchers to extract embryonic stem cells without destroying an embryo. But this will no doubt remain an area of controversy and personal opinion for some time.
The improvements achieved in the field of;Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells; is likely to make;them the stem cell type of choice in the future, although iPS clinical trials are probably further away than trials using embyronic stem cell therapies.
Content last reviewed: May 2018
You May Like: Can Drugs Cause Parkinson’s Disease
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease may include many symptoms depending on the severity of the affected person. Early signs of this condition often go unnoticed. However, as the disease progresses, you can expect the following symptoms:
- Difficulty writing
- Loss of involuntary movements
- Slowed overall movements
- Tremors or shaking
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in the brain. This loss of nerve cells within the brain results in a reduced amount of dopamine being created which acts as a messenger between the parts of your brain that control voluntary and involuntary movement. Therefore without that vital connection, your brain starts losing the ability to effectively control movement. Currently, it is unknown what causes the deterioration of nerve cells associated with Parkinson’s Disease . Currently, it is believed that both environmental factors, as well as genetic factors, may play a role in the loss of nerve cells.
Parkinson’s Disease is a lifelong condition that can greatly impair the ability of one’s daily functions. Traditional treatments only address the symptoms of the condition, but researchers are excited about the possibilities of certain gene therapies andÂ;stem cell therapy, which may have the ability to reverse damage and halt the progression of the disease.
Also Check: What Is Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson’s Disease
The First Clinical Trials
Already the early reports of behavioral recovery following implantation of dopamine-rich fetal VM tissue in 6-OHDA-treated rats had obvious clinical implications, raising the possibility that the dopamine cell replacement approach could be possible to develop to a transplantation therapy for PD patients. However, from a clinical perspective, there were two main problems: First, the practical one. Would it be possible to collect sufficient amounts of human fetal brain tissue from routine induced abortions, avoiding contamination, identify the VM containing the dopamine neurons and then implant the tissue into the PD patients brain without adverse effects? Second, and most important, the ethical problem. Would it be ethically and morally acceptable to collect and use tissue from aborted human fetuses for intracerebral transplantation in PD patients in order to ameliorate their motor symptoms? At that time, no guidelines for the use of such tissue were available.
Patient Services At Anova Institute For Regenerative Medicine
- Located in the center of Germany, quick access by car or train from anywhere in Europe
- Simple access worldwide, less than 20 minutes from Frankfurt Airport
- Individualized therapy with state-of-the-art stem cell products
- Individually planned diagnostic work-up which include world-class MRI and CT scans
- German high quality standard on safety and quality assurance
- Personal service with friendly, dedicated Patient Care Managers
- Scientific collaborations with academic institutions to assure you the latest regenerative medical programs
Strahlenbergerstr. 110
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Huntington’s Disease And Parkinson’s
Is There Any Guarantee That A Stem Cell
There is no therapy, be it an experimental or established treatment, for which your treating physician can promise or even guarantee a therapeutic success. In the case of innovative and experimental therapies such as stem cell therapy, doctors must perform a benefit-to-risk-analysis for each individual case and ensure that the therapy is beneficial to the patient and these benefits outweigh the risks. Only when this is the case, your doctor will suggest treatment with stem cells.
Repairing The Brain: Cell Replacement Using Stem Cell
Issue title: The Times They Are a-Changin: Parkinsons Disease 20 Years from Now
Guest editors: Patrik Brundin, J. William Langston and Bastiaan R. Bloem
Article type: Review Article
Authors: Henchcliffe, Clairea; * | Parmar, Malinb; *
Affiliations: Department of Neurology, Weill Cornell Medical College, and Department of Neurosurgery, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York NY, USA | Wallenberg Neuroscience Center and Lund Stem Cell Center, Lund University, BMC, Lund, Sweden
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Claire Henchcliffe, Department of Neurology, Weill Cornell Medical College, 428 East 72nd Street, Suite 400, New York, NY 10021, USA. Tel.: +1 212 746 2584; E-mail: . and Malin Parmar, Wallenberg Neuroscience Center and Lund Stem Cell Center, Lund University, BMC A11, 221 84 Lund, Sweden. Tel.: +46 46 2220620; E-mail: .
Keywords: Dopamine neurons, Parkinsons disease, stem cell therapy
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-181488
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 8, no. s1, pp. S131-S137, 2018
Abstract
Recommended Reading: Can Surgery Cause Parkinson’s Disease
So What Are Stem Cells
Stem cells are cells that have not yet specialized in the body, meaning they have not grown to a particular type of cell with a specific function . A stem cell can become many different cell types in the human body. The process of stem cells become new types of cells is called differentiation. This process is the most important aspect of stem cell therapies, as the cells become the type of cells required for your body to heal. Stem cells are also self-replicating. This allows them to multiply into identical copies of the stem cells that have already gone through differentiation in the body. For example, if stem cells were used to treat a neurological injury, cells administered during treatment could become nerve cells, and then replicate to create exponentially more nerve cells on their own. This drastically increases the effectiveness of stem cell treatments over time.
Clinical Trials For Stem Cell
Table 3. Summary of clinical studies in cell transplantation for PD.
Figure 1. Systematic analysis of various factors associated with clinical outcomes using positron emission tomography readings of Parkinsons disease patients with fetal ventral mesencephalic cell transplantation. Statistical comparison was performed on various parameters against fold change of PET readings pre- and post-transplantation. Age on onset: old vs. young PD patients. Disease stage in mild and severe conditions. Disease duration: long vs. short . Student t-test, *p< 0.05, ***p< 0.001.
Figure 2. Systematic analysis of various factors associated with clinical outcome in fVM cell transplantation in PD patients using UPDRS motor scores. Statistical comparison was performed on varying parameters against the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale motor scores of pre- and post-transplantation. Age on onset: old vs. young PD patients. Disease stage in severe vs. mild condition. Disease duration: long vs. short . Two-way ANOVA, Sidaks multiple comparisons test, **p< 0.005, ***p< 0.001.
Don’t Miss: Can Diabetes Cause Parkinson’s Disease
Stem Cell Therapy: Challenges And Promises
In their review, Dr. Henchcliffe and Prof. Parmar examined the evolution of stem cell therapy and its uses for replacing damaged neurons in Parkinsons.
If successful, using stem cells as a source of transplantable dopamine-producing nerve cells could revolutionize care of the patient in the future, they say.
A single surgery, the authors go on to state, could potentially provide a transplant that would last throughout a patients lifespan, reducing or altogether avoiding the need for dopamine-based medications.
More than 3 decades ago, pioneering studies that transplanted stem cells to treat Parkinsons used fetal cells obtained from the midbrain of aborted embryos.
However, there were numerous ethical issues with the procedure, as well as a host of side effects. These included transplant rejection and involuntary movements called dyskinesias.
Recent advances in stem cell technology mean that the materials from which stem cells are derived are different and varied. For instance, researchers can use a persons own skin to collect pluripotent cells and reprogram them directly into neuronal cells.
Cells can also be reprogrammed directly in the brain by injecting the conversion genes instead of the human skin cells. Researchers can also derive stem cells from the persons own blood.
As Dr. Henchcliffe says, Right now, we are just talking about the first logical step in using cell therapies in .
Development Of The Cell Suspension Technique And Steps Toward The Clinic
In three papers published in Experimental Brain Research we showed that human fetal VM tissue from 69 week old aborted fetuses survived well after transplantation to the striatum, provided that the animals were immunosuppressed by daily injections of cyclosporine. The grafted neurons were efficient in re-innervating the previously denervated striatum, reverse amphetamine-induced rotation, restore dopamine release, and form normal synaptic contacts with the host striatal projection neurons. In these experiments we were also able to identify the appropriate landmarks to be used for dissection of the dopamine-rich ventral midbrain tissue. In parallel, and in collaboration with labs in Stockholm, Marseille and Oxford, we performed a series of studies of rat-to-rat VM cell suspension transplants using microdialysis and in vivo voltammetry to monitor the extent of recovery of dopamine release, and we used electron microscopy and tract-tracing techniques to study the integration of the grafted dopamine neurons into host striatal circuitry, and the synapses made by the outgrowing axons onto denervated striatal projection neurons in the host.
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Caused By Too Much Dopamine
Are Stem Cells A Cure For Parkinsons Disease
Currently not. However, stem cells already hold a great potential for treating most neurodegenerative diseases, especially Parkinsons Disease, to slow down or prevent the progression of the disease. This makes it worthwhile for patients and medical professionals alike to consider stem cell-based therapies for specific cases. Each case must be evaluated individually to ensure that the benefits outweigh the risks. In general, it can be said that for cell-based therapeutics which act on a transmitter and paracrine level, the individual success is currently not possible to be predicted. We therefore recommend that you contact us to get an expert opinion on your case and the possibilities we can offer.
Stem Cell Research And Parkinsons
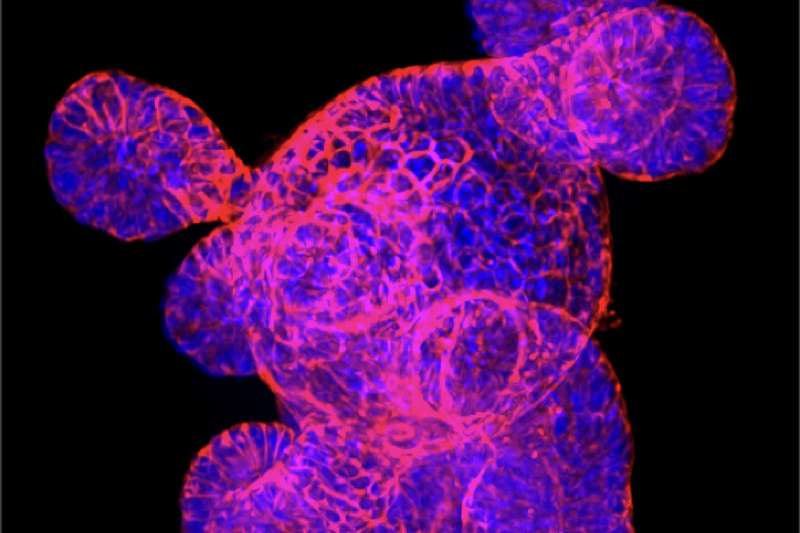
The aim of stem cell research in Parkinsons is to understand how nerve cells develop, why some die and how healthy cells can be used to replace damaged brain cells. With this knowledge it may be possible to replace the damaged cells in the brain by introducing healthy dopamine-producing cells generated from stem cells grown in the laboratory. Healthy dopamine-producing cells derived from stem cells could also be useful to researchers in testing new treatments.
Researchers are particularly interested in embryonic stem cells as they have the potential to develop into all types of cells in the body, including the brain. More research is needed in order to understand the way these cells work to ensure that replication can be controlled and a safe treatment developed.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Most Common Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
