Psychotic Symptoms And Others
In addition to the symptoms we already mentioned, other symptoms may appear in both diseases. For example, in Alzheimers disease, delirium appears occasionally, while it rarely ever does in Parkinsons. Its vital to remember that delirium is an organic disorder that mainly affects consciousness and attention.
Regarding psychotic symptoms, visual hallucinations can appear in both diseases, more or less in the same proportion. Delusions may also arise. They occur often in Alzheimers and occasionally in Parkinsons.
What Makes Them Different
MS and Parkinsonâs have different causes. They usually start to affect you at different ages, too.
MS often affects people between ages 20 and 50, but children get it, too. Parkinsonâs usually starts at age 60 or older, but some younger adults get it.
MS is an autoimmune disease. That means your bodyâs immune system goes haywire for some reason. It attacks and destroys myelin. As myelin breaks down, your nerves and nerve fibers get frayed.
In Parkinsonâs, certain brain cells start to die off. Your brain makes less and less of a chemical called dopamine that helps control your movement. As your levels dip, you lose more of this control.
Some genes may put you at risk for Parkinsonâs, especially as you age. Thereâs a small chance that people who are exposed to toxic chemicals like pesticides or weed killers can get it, too.
These symptoms are more common if you have MS. They not usually found in Parkinsonâs:
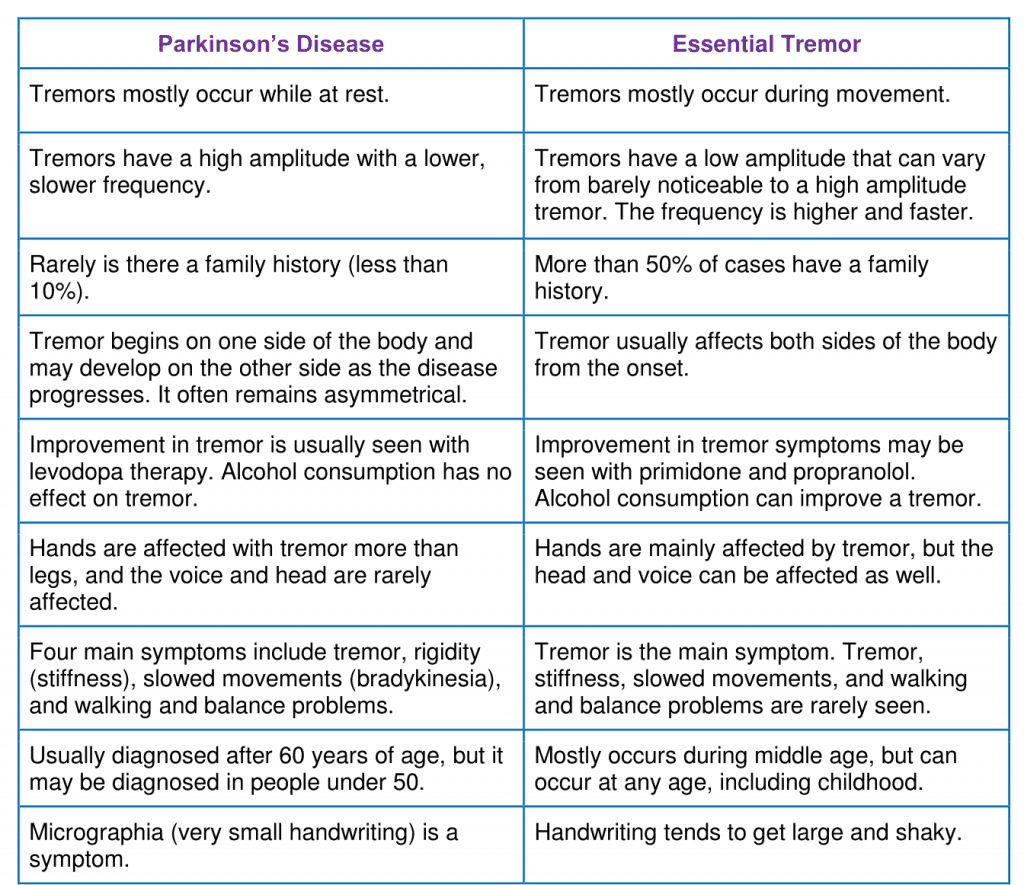
What Are The Symptoms Of Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Like classic Parkinsons disease, atypical Parkinsonian disorders cause muscle stiffness, tremor, and problems with walking/balance and fine motor coordination.
Patients with atypical Parkinsonism often have some degree of difficulty speaking or swallowing, and drooling can be a problem. Psychiatric disturbances such as agitation, anxiety or depression may also be part of the clinical picture.
Dementia with Lewy bodies can cause changes in attention or alertness over hours or days, often with long periods of sleep during the day. Visual hallucinations typically of small animals or children, or moving shadows in the periphery of the visual field are common in DLB. DLB is second only to Alzheimers disease as a cause of dementia in the elderly, and it most commonly affects patients in their 60s.
Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy may have difficulties with eye movements, particularly when looking downward, and with balance when descending stairs, for instance. Backward falls are common and may occur during the early course of the disease. PSP is not usually associated with tremor, unlike Parkinsons disease.
Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Fatal
How Is Parkinsonism Diagnosed
You should be referred to a Parkinsons specialist for the diagnosis of any parkinsonism. They may wish to explore different things before giving you a diagnosis.
Your specialist will look at your medical history, ask you about your symptoms and do a medical examination.
Telling the difference between types of parkinsonism isnt always easy, for the following reasons:
- The first symptoms of the different forms of parkinsonism are so similar.
- In many cases, parkinsonism develops gradually. Symptoms that allow your doctor to make a specific diagnosis may only appear as your condition progresses.
- Everyone with parkinsonism is different and has different symptoms.
Find out more: see our information on symptoms of Parkinsons, and diagnosing Parkinsons.
One of the most useful tests to find out what sort of parkinsonism you may have is to see how you respond to treatment.
If your specialist thinks you have idiopathic Parkinsons, theyll expect you to have a good response to Parkinsons drugs such as levodopa . A good response means that your symptoms will improve. Sometimes, it will only be clear that youve responded to medication when the drug is reduced or stopped, and your symptoms become more obvious again.
If you dont have any response to Parkinsons medication, your specialist will have to look again at your diagnosis.
Although not routinely available, your specialist may wish to carry out some of the tests below.
Current tests available include:
What Is The Difference Between Parkinsonism Vs Parkinsons Disease
What is the difference between Parkinsonism vs Parkinsons disease? In simple terms, Parkinsons is a disease whereas Parkinsonism is a range of symptoms that are usually seen in patients with Parkinsons disease, but sometimes occurring as a result of other neurodegenerative disorders.
Unless you are a medical professional, there might appear to be very little difference between Parkinsons disease and Parkinsonism.
On the surface, they appear to be exactly the same condition: both are characterized by tremors, stiffness, balance issues, and slowness of movement, but this is where the similarities end.
Whereas Parkinsonism encompasses the four main movement problems seen in patients suffering from Parkinsons disease, Parkinsons disease itself is a progressive and highly degenerative disorder that causes many other symptoms as well as those seen in Parkinsonism.
Recommended Reading: Freddie Roach Medical
Prevention Of Parkinsons Disease
Researchers dont know of any proven ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, but avoiding certain risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle may help reduce your risk.
Some studies have shown a diet high in antioxidants along with regular exercise may play a role in preventing Parkinsons. Other findings have suggested that compounds like caffeine, niacin, and nicotine may have a protective effect against Parkinsons disease.
What Causes Huntingtons Disease
Huntingtons disease is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene. The HTT gene is responsible for making the huntingtin protein, which is thought to play an important role in nerve cells of the brain.
In Huntingtons disease, a DNA segment within this gene, called the CAG trinucleotide repeat, is repeated more often than is normal.
Read Also: End-stage Parkinson Disease What To Expect
What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinson’s is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
Depression With Huntingtons Disease
Due to the nature and lower life expectancy of Huntingtons disease, it is common for a diagnosis to lead to depression. Patients with Huntingtons are at a higher risk of suicide.
If you are struggling with your Huntingtons diagnosis or prognosis, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration National Helpline online or call 1-800-662-4357 to seek help.
For more mental health resources, including a helpful list of links and hotline numbers, see our National Helpline Database.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Research And Statistics: Who Has Parkinsons Disease
According to the Parkinsons Foundation, nearly 1 million people in the United States are living with the disease. More than 10 million people worldwide have Parkinsons.
About 4 percent of people with Parkinsons are diagnosed before age 50.
Men are 1.5 times more likely to develop the disease than women.
Prognosis Of Als Vs Parkinsons
ALS is considered as a fatal disease. The damage and death of neurons begins to spread throughout the body. In the later stages, nerve damage will affect areas like breathing and swallowing.
Parkinsons disease in itself is not considered fatal but people do die from complications relating to the condition.
You May Like: What Color Is The Ribbon For Parkinson’s
Does Having Rls Increase The Risk Of Developing Pd
Since RLS affects as much as 4-10% of the US adult population, it is clear that the vast majority of those with RLS do not ever develop PD.
Despite this, it still might be the case that RLS increases the risk of subsequently developing PD. There have been many studies trying to figure this out with conflicting results. Some studies show that there is no increased risk and others show that having RLS confers about a two-fold increased risk of developing PD over the general population.
How Are They Alike

MS and Parkinsonâs both affect your central nervous system, which includes your brain and spinal cord. Thatâs why they both can affect how you move, sleep, feel, and talk.
These diseases both affect your nerves. MS can break down the coating, called myelin, that surrounds and protects your nerves. In Parkinsonâs, nerve cells in a part of your brain slowly die off.
Both can start out with mild symptoms, but they get worse over time.
Common symptoms of both diseases include:
- Shaky fingers, hands, lips, or limbs
- Slurred speech thatâs hard for others to understand
- Numb or weak limbs that make your walk unsteady
- Loss of muscle control that often affects one side of your body at first, then later both
- Spastic limb movements that are hard to control
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Poor balance
Depression is another symptom common to both conditions.
Read Also: Propranolol Increased Total Peripheral Resistance
What Is Lewy Body Dementia
LBD is a chronic, neurodegenerative cognitive disorder, and is the 3rd most common form of dementia.3 Unlike most other forms of dementia, people with LBD have Lewy bodies in the brain. Lewy bodies are abnormally-folded proteins found in the nerve cells of the brain.2 Patients with LBD may experience memory/cognitive problems, visual hallucinations, and Parkinsonism symptoms.4
Treatment Of Als Vs Parkinsons Disease
There is currently no cure for ALS and much of the treatment is aimed at managing the symptoms and trying to slow down the progression of the disease. Ultimately the disease will be fatal and once bodily functions such as swallowing and breathing are affected, the prognosis is very poor.
Typically, around half of those diagnosed with ALS will die within the first three years following their diagnosis. Only 10% of those diagnosed will live beyond 10 years.
Treatment of Parkinsons disease has received a lot more attention with its higher profile in the media. As with ALS, there is currently no cure but there are a wide range of different medications and treatments that are available.
This includes brain stimulation therapy which sends an electrical stimulus to the brain from a device embedded by the collarbone to help alleviate symptoms such as tremors.
Read Also: How Does Parkinson’s Disease Affect Daily Life
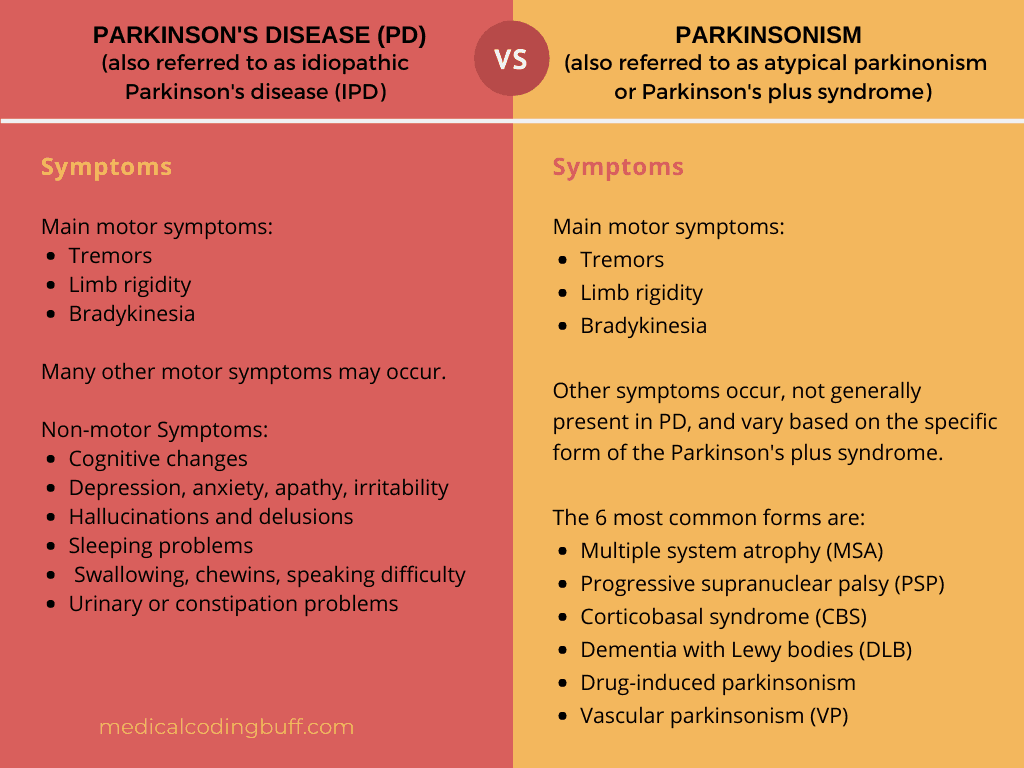
What Is Parkinsonism Is It Different From Parkinsons
Parkinsons disease is the most common cause of parkinsonism, a category of neurological diseases that cause slowed movement.
No quick or easy diagnostic tests exist for Parkinsons disease, so a patient may receive an initial diagnosis of parkinsonism without a more specific condition being confirmed.
Classic Parkinsons disease referred to as idiopathic because it has no known cause is the most common and most treatable parkinsonism.
About 15 percent of people with parkinsonism have atypical variants, which are also known as Parkinsons plus syndromes.
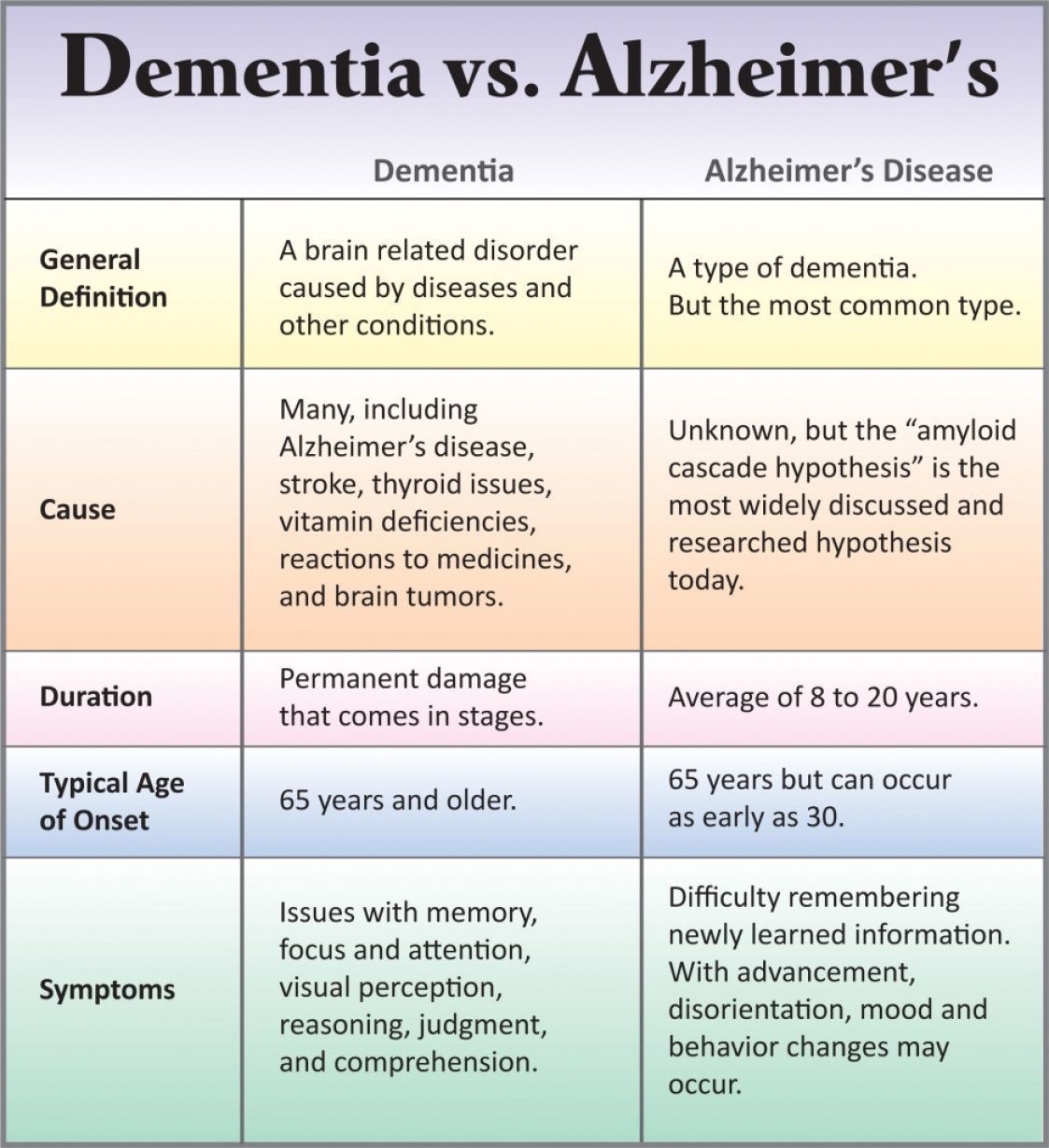
Differences Between Alzheimers And Parkinsons
Were going to group the differences between both illnesses into different blocks and explain what each of them consists of. All of them have been extracted from two reference psychopathology manuals: Belloch, Sandín, and Ramos and the DSM-5 .
The first block of differences between Alzheimers and Parkinsons refers to their type of symptoms. Lets see what they are.
Also Check: What Color Is The Ribbon For Parkinson’s
Summary Ms Vs Parkinsons
Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune, T-cell mediated inflammatory disease affecting the Central Nervous System. Parkinsons disease is a movement disorder characterized by a decline in the dopamine level of the brain. Multiple sclerosis, as stated in its definition, is an autoimmune disease but Parkinsons disease is not an autoimmune disease. This is the major difference between MS and Parkinsons.
What Are The Different Forms Of Parkinsonism
There are three main forms of parkinsonism, as well as other related conditions.
Most people with parkinsonism have idiopathic Parkinsons disease, also known as Parkinsons. Idiopathic means the cause is unknown.
The most common symptoms of idiopathic Parkinsons are tremor, rigidity and slowness of movement.
Vascular parkinsonism affects people with restricted blood supply to the brain. Sometimes people who have had a mild stroke may develop this form of parkinsonism.
Common symptoms include problems with memory, sleep, mood and movement.
Some drugs can cause parkinsonism.
Neuroleptic drugs , which block the action of the chemical dopamine in the brain, are thought to be the biggest cause of drug-induced parkinsonism.
The symptoms of drug-induced parkinsonism tend to stay the same only in rare cases do they progress in the way that Parkinsons symptoms do.
Drug-induced parkinsonism only affects a small number of people, and most will recover within months and often within days or weeks of stopping the drug thats causing it.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Whats The Difference Between Multiple System Atrophy And Parkinsons
Parkinsons and MSA both affect the movement control system and the involuntary autonomic control system and early symptoms can make a differential diagnosis a challenge. MSA, however, tends to progress faster than Parkinsons balance problems and a stooped posture happen earlier and get worse more quickly with MSA and autonomic functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, sweating, bladder function, and sexual problems are more severe in people with MSA.
For more information on multiple symptom atrophy, read this fact sheet.
Wait So What Is Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism refers to the motor symptoms that are typically associated with PD, such as tremors, stiffness, and walking/balance problems. Both PD and LBD are forms of Parkinsonism, meaning that PD patients and LBD patients may experience these motor symptoms.2 Because the Parkinsonism motor symptoms of PD and LBD can be very similar, it can be difficult to differentiate between the two conditions.
You May Like: What Color Represents Parkinson’s Disease
The Purpose Of Clinical Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the parkinsonian syndromes is entirely clinical, as at the present time no imaging, biochemical, or genetic tests definitively diagnose or separate the different diseases. Diagnosis relies on taking a complete medical history that includes timeline of symptoms, recognition of the important clinical signs, and consideration of the differential diagnoses. Individuals diagnostic acumen is substantially influenced by clinical experience, and even among movement disorder specialists, the clinical diagnosis can change over time because of emerging clinical signs.
Can Parkinson Cause Dementia
As we know, Parkinsons disease is a movement disorder, and apart from that, it usually occurs in people over the age of 50 or 60.
However, some young people can also be affected by the disease.
However, if it occurs at a young age before the age of 50 it is called the early onset of Parkinsons disease. Continue readingAre you Afraid Thinking Can Parkinson Cause Dementia?
Recommended Reading: Sam Waterston Tremor
Can You Have Both Parkinsons And Alzheimers
People who already have Parkinsons disease and later develop signs of dementia are diagnosed with Parkinsons dementia.6 However, if you first have Alzheimers disease and develop signs of movement difficulties, you can also have a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease.
Tell us about your experience in the comments below, or with the community.
Clinical Confirmation Of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
The clinical manifestations of PSP-tau pathology are variable, and diagnosis can be difficult at times because of the subtle early signs that may be difficult to discern from other physical or psychological symptoms. The diagnosis of PSP should be considered in all patients presenting with parkinsonism not responding to levodopa therapy postural instability with falls executive dysfunction slowing of vertical saccades/supranuclear vertical gaze palsy or dysarthria/dysphagia .
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Someone Live With Parkinson’s Dementia
Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Neurologists usually describe the progression of Parkinsons symptoms in stages, using the system known as the Hoehn and Yahr scale. These stages are:
- Stage I Symptoms are seen on one side of the body only.
- Stage II Symptoms are seen on both sides of the body. Theres no impairment of balance.
- Stage III Balance impairment has begun. In this mild- to moderate stage of the disease, the person is still physically independent.
- Stage IV This stage is marked by severe disability, but the person is still able to walk or stand unassisted.
- Stage V The person is wheelchair-bound or bedridden unless assisted.
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Of people with dementia, the type of parkinsonism called dementia with Lewy bodies is the second most common cause of dementia, after Alzheimers disease in the elderly. Many are diagnosed at first with Alzheimers disease due to memory or cognitive disorders and then later as dementia with Lewy bodies as the motor symptoms common to Parkinsons progress.
Lewy bodies are abnormal deposits of protein on the nerve cells in the brain. If the production of dopamine, a neurotransmitter, produced by those nerve cells is disrupted due to the buildup of Lewy bodies on those cells, too little dopamine is produced, which can cause the symptoms of Parkinsons.
Read Also: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
A Number Of Medications Can Lead To Dip
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when there is a loss of dopamine neurons in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter used by the brain to control bodily movements, learn and focus, and feel pleasure and enjoyment. Certain types of medications, known as dopamine antagonists, bind to and block dopamine receptors. When dopamine receptors in the brain are blocked, this can cause parkinsonism to occur. There are a number of medications that can cause DIP, including:
Whats The Difference Between Vascular Parkinsonism And Parkinsons
As the name implies, vascular parkinsonism is caused by cerebrovascular disease which affects the blood supply to the brain. Vascular parkinsonism is caused by one or more small strokes, while Parkinsons is caused by a gradual loss of nerve cells. One major difference from Parkinsons is that its not progressive, while Parkinsons becomes worse with time. Another difference is that there are no tremors in vascular parkinsonism.
For more information on vascular parkinsonism, read this journal article.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Cause Memory Issues
