Pathophysiology And Risk Factors For The Development Of Off Episodes In Parkinsons Disease
C Warren OlanowDepartment of Neurology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA
Levodopa has been used as a treatment for PD for 50 years and remains the most effective therapy available. There are, however, limitations with levodopa, including a lack of control of non-dopaminergic features of PD such as falls and dementia, failure to stop disease progression, and the development of motor complications in the majority of patients.27 Risk factors for the development of these complications have been studied in both open-label and long-term prospective studies which indicate that both OFF time and dyskinesia are associated with young age, high doses of levodopa, and disease severity.8,28 Among these, levodopa dose is the one factor that can be controlled by physicians.
Analyses in this study further indicate that female gender and lower weight correlate with the development of motor complications; this likely reflects the same dose resulting in higher plasma levels in these individuals.28 Recommendations arising from this work suggest that physicians should use the lowest levodopa dose that provides satisfactory symptom control, should consider alternative medications to minimize levodopa dose, and should pay particular attention to the dose given to young women. It may also be necessary to consider patient weight and prescribe the dose on a mg/kg basis.
How Does The Parkinsons Disease Progress
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disease which is essentially progressive. The symptoms tend to worsen with time and the average rate at which the disease progress is around ten years. It is to be taken into account that various factors affect the progression rate and the actual rate varies from patient to patient.
Keeping A Motor Diary
You can help your doctor understand how effective your medications are by keeping diary. Typically a motor diary, or wearing off diary, will include details such as:
- the times of day when you take your Parkinsons medication
- the times of day when you have good symptom control
- which symptoms re-emerge during the day and when
- what symptoms you experience at night
- any other complications you may experience, such as dyskinesia, and their relation to when you take your medication
- it can also be useful to note the timing of meals, drinks and snacks. Make a note of whether eating certain foods affects your symptom control protein, for example, can interfere with the absorption of some medications.
For a sample diary and information on keeping one see .
Getting Medication On Time
Parkinson’s patients who do not get the correct medicine at the right time when they are in hospital, sometimes cannot talk or walk. The health of a majority deteriorated due to unsatisfactory medication management when they are in hospital. Parkinson’s UK believes the NHS could save up to £10m a year and improve the care of Parkinson’s patients if mandatory training is introduced for all hospital staff.
Parkinson UK found:
- “Nearly two thirds of people who have Parkinsons dont always get their medication on time in hospital.”
- “More than three quarters of people with Parkinsons that we asked reported that their health deteriorated as a result of poor medication management in hospital.”
- “Only 21% of respondents told us they got their medication on time without having to remind hospital staff.”
Complementary Treatments For Back Pain
Massage therapy and acupuncture are two complementary treatments that are often used for pain. There have been small studies investigating the use of massage therapy and acupuncture for motor symptoms of PD, but more studies are necessary to s determine if they specifically help with PD pain. You can also view a Q+A about complementary treatments in PD.
How Does The Levodopa Drug Help In Managing The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
In levodopa drug therapy the patient is given the drug which gets synthesized into dopamine in brain. Levodopa is considered to be the most important drug for the management of Parkinsons disease. This drug is generally given in combination with carbidopa in order to prevent nausea, caused by levodopa. It also enhances the effect of levodopa.
Does Parkinsons Disease Impair A Patient Cognitively
Since Parkinsons disease is neurological in nature it does have an effect on a patients cognition. Although the symptoms can be seen at a later stage of progression, the cognitive symptoms can be in form of delusions and hallucinations. The patient may also have issues with remembering events and can be diagnosed with dementia.
Also Read:
Can The Parkinsons Disease Kill A Patient
Parkinsons disease is not really fatal in nature. However, the symptoms associated with Parkinsons disease is actually life threatening that may lead to fatal accidents. Injuries are quite common in Parkinsons disease due to inability to move around effortlessly. This is actually dangerous. Thus, efforts must be taken in order to create a safe environment for patients with Parkinsons disease.
Presynaptic Mechanisms In Wearing
The finding that motor improvement following acute intravenous levodopa challenge lasts longer in de novo and stable patients than in those who are already suffering motor fluctuations was key to the development of the storage hypothesis, which implies that loss of presynaptic dopaminergic terminals reduces the capacity of the striatum to store dopamine and buffer the oscillations in plasma levodopa levels . Certainly, the pharmacokinetics of levodopa-dopamine in the brain is drastically changed after dopaminergic denervation of the striatum. In the rat with a 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the nigrostriatal pathway, peak striatal dopamine levels and the area under the curve for synaptic dopamine availability are significantly lower in animals with larger lesions , which correlates with a shorter duration motor response . In patients, the availability of dopamine in the synapse has been measured by PET using the D-2 receptor antagonist raclopride as the radioligand. Raclopride was administered before and after levodopa intake in patients with and without motor fluctuations, with the result that patients with motor fluctuations demonstrated a greater decrease in raclopride binding than stable patients. Because raclopride competes with dopamine for binding to D2 receptors, reduced raclopride uptake is an index of higher synaptic dopamine levels and, therefore, reduced numbers of dopaminergic terminals .
Clinical Features Of Wearing
As soon as levodopa was introduced into clinical practice for the treatment of PD, it was recognized that the therapeutic response consists of at least two components : the short-duration response , which provides an improvement in motor disability that lasts a few hours after the administration of single doses of levodopa, and the long-duration response , which is a sustained antiparkinsonian effect derived from prolonged administration of levodopa that has been shown to last for up to 2 weeks after cessation of drug treatment . Importantly, both types of response are present from the initiation of therapy, although the SDR is largely unnoticed in the beginning as the LDR masks it .
For many years, the development of wearing-off has been mainly attributed to a shortening of the SDR over time as a result of the progressive reduction in the ability of the nigrostriatal neurons to synthesize and to store dopamine formed from exogenous levodopa . However, a number of studies have shown that the magnitude of the SDR and modifications of the LDR during the course of PD also have a critical role in the development of symptom re-emergence .
Characteristics Of Patients With Wo
According to clinician assessments, patients were divided into the WO group and Non-WO group. Compared with the Non-WO group, the WO group showed younger age at onset , lower weight , longer disease duration , higher H&Y staging , higher daily levodopa dose and daily levodopa equivalent dose , and longer duration of antiparkinsonian medical treatment and levodopa treatment . In terms of the medication types, the WO group used levodopa/benserazide , levodopa/cabidopa , pramipexole , and amantadine more frequently than the Non-WO group. In addition, the WO group was much frequently treated with polytherapy of levodopa and other medications compared to the Non-WO group . No difference was found in the gender ratio or age between the two groups. In order to identify the WO-associated factors, we included all factors that showed significant differences into the multivariate logistic regression model. It showed that disease duration , H&Y staging , and the LED were associated with the occurrence of WO.
Role Of Pulsatile Dopaminergic Stimulation In Motor Fluctuations
The role of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system is primarily to exert a modulatory effect on basal ganglia circuitry, particularly the striatum, but also on other nuclei of the basal ganglia and on thalamic and brain stem regions . Phasic release of dopamine occurs in response to the firing of dopaminergic neurons, and this is mediated by spike-dependent release of dopamine into the synaptic cleft resulting in potent but brief activation of postsynaptic dopamine receptors . Under normal circumstances, neuronal activity adapts quickly to phasic release and firing stops when events lose novelty or relevance . However, the loss of phasic dopamine release is important and it is likely to be responsible for some specific motor and non-motor problems in PD, such as learning deficits, anodynia and, more relevantly in the context of this review, levodopa-induced motor complications.
Fig. 3
A Linearized Discrete Version
If, on the other hand, infectiousness were an onoff phenomenon such that individuals are either infectious, possibly at levels depending on their h-type, or not and if we again assume discrete h-states, we could express the change in the numbers infected as
is the number of infectious subjects of h-type at time t and ; a , n are transmission coefficients that also incorporate the numbers of susceptible. In the linearized situation, these numbers do not change .
Question 7.i
Obviously, Eqs. and look very different. Are they really different, though, in other ways than in their assumption regarding infectiousness over time allows for changing infectiousness while assumes constant infectiousness) and the discrete h-states in ? Is there anything funny about this equation that appears strange to you, especially if you recall the chapter on Kermack & McKendrick’s famous paper?
Paul Bentley, Pankaj Sharma, in, 2012
Amineralizing Perimeter Or Surface
The extent of bone perimeter or surface that exhibits tetracycline fluorescence is an important primary measurement from which many dynamic indices are derived. When a double tetracycline label has been administered, both double and single labels will be seen; this reflects the labeling escape error, caused by initiation of mineralization before the first label or its termination between administration of the two labels , and probably also the switch from an active to resting state in a minority of osteoid seams . Because of the former, the extent of double-labeled surface underestimates the actively mineralizing surface, and the double plus half the single label is therefore used to estimate the mineralizing perimeter. In cases where only single labels can be detected, it has been suggested that the mineralizing perimeter should be expressed as half the singlelabeled perimeter .
In the absence of tetracycline administration prior to biopsy, the osteoid perimeter may provide some indication of bone turnover, with increased osteoid perimeter being characteristic of high turnover states. An increase in the extent of perimeter occupied by resorption cavities does not necessarily imply increased bone turnover, however, as these may not represent active resorption but rather reflect failure of formation to occur in previously resorbed cavities.
Juliet Compston, … David W. Dempster, in, 2018
How To Manage Parkinsons Disease After It Is Diagnosed
Along with the medication so prescribed by the doctor, it is extremely important to bring some form of lifestyle changes in order to manage Parkinsons disease. They include-
Activity: As mentioned earlier Parkinsons disease affects the patients motor abilities, it is thus important to keep the body fit by indulging into exercise regularly. The patient may do any form of exercise which he may like every day to keep the body moving. This does not let the body parts to be stiff and also slows down the progression of the disease.
Additional Help: The caregivers and well-wishers should make attempts to make the environment safe for the patient with Parkinsons disease. Modifying the environment like installing grab bars in washroom and removing obstacles which may hamper movement of the patient is important.
Diet: Having nutritious food is important for patients with Parkinsons disease. It is seen to be beneficial to have right amount of nutrients in order to manage the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The patient should also discuss with the doctor the food to avoid so that they do not interfere with the working of the medicines, especially levodopa.
Characteristics Of The Clinicians
Fifty-one clinicians participated in this study. Among them, 20 clinicians worked in tertiary care hospitals and 31 clinicians worked in secondary care hospitals. Most of the clinicians majored in neurology , and four clinicians majored in traditional Chinese medicine. For the clinicians, the mean years in practice in the field of PD was 9.4 ± 7.8 and the mean number of PD patients that they served per week was 14.7 ± 14.0.
Other Treatments Of Lower Back Pain
NSAIDs which include medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen, as well as acetaminophen, can be very beneficial for pain in PD, as they are for the general population. These medications do not typically have neurologic side effects, so they are well tolerated in people with PD. They can have other side effects though, so as always, discuss all medications that you are taking, including over-the-counter medications, with your doctor. If these medications do not provide sufficient back pain relief, your doctor may prescribe a pain medication. In addition, he/she may refer you for a procedure such as an epidural injection to help with lower back pain. Rarely, surgery may be recommended if a specific structural reason for pain is identified.
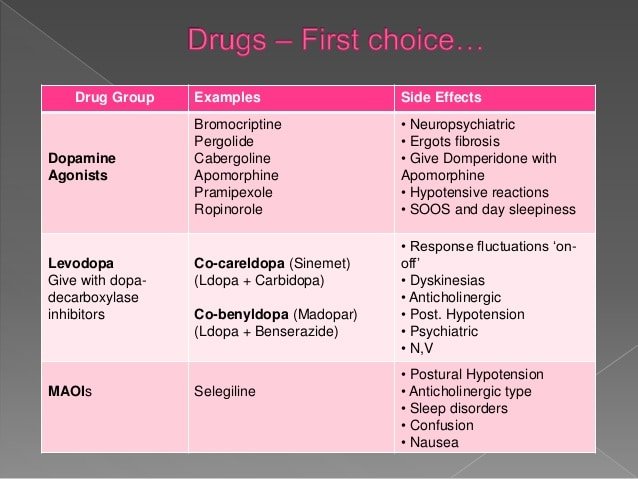
What Are On And Off Periods With Parkinsons Meds
While you might expect that taking a medication on a consistent schedule would guarantee your symptoms would be kept at bay, thats unfortunately not always the case with Parkinsons diseaseand thats the core of the on-off phenomenon, says Ling Pan, M.D., clinical assistant professor of neurology and neurosurgery at NYU Langone Health in New York, NY.
The on period is when the medication is doing its job to prevent tremors and other motor symptoms, explains Dr. Hui. Patients will often feel better fairly soon after taking their doseeven within half an hour, she says. Its almost like a light switch is being switched on, and they can move a lot easier.
That said, Dr. Hui explains, the effect can wear off over several hoursand thats when you hit that off period. When you first start taking the drug, though, its normal to experience a honeymoon period, she says. It may work all day, and you feel great, but overtime as the disease progresses, the medication doesnt less as long, and off-time creeps in slowly and then becomes more noticeable and more regular overtime. Typically, thats when folks with Parkinsons start to cycle between those on and off periods.
Presynaptic Model Of Motor Fluctuations
We develop here a simple mathematical model that shows how motor fluctuations in Parkinsons disease can be explained by alterations in presynaptic mechanisms of dopamine release. Specifically, the model predicts that onoff fluctuations obey probabilistically determined oscillations in vesicular dopamine release. We present support for this model based on recent observations derived from PET studies, as well as from experimental data on both the quantal release of dopamine and dopamine reuptake.
What Time Of Day Are Parkinson’s Symptoms Worse
Morning akinesia is the most common, and often, the first motor complication of PD. It is noticed at awakening after a nightlong treatment-free period, reflecting the dopaminergic nocturnal decline with insufficient nighttime storage or refreshing of the dopaminergic system during nighttime and sleep.
What Causes Motor Fluctuations

Motor fluctuations are caused by a drop in brain levels of dopamine, the chemical that helps your body move smoothly. When you have Parkinson’s, your nerve cells no longer make enough of it.
Taking levodopa acts as a replacement for the dopamine, but as the medicine wears off, the levels of the chemical in your brain drop again. Early in the disease, nerve cells in your brain are able to make enough dopamine so that you don’t have any Parkinson’s symptoms when levodopa wears off.
As your Parkinson’s advances, these nerve cells start to break down. When that happens, your brain can no longer make up for the drop in dopamine levels when your medicine wears off. That’s when you’ll start to notice a return of symptoms like stiffness, tremor, tiredness, or mood changes.
Another reason you might get motor fluctuations is that you have slow movement through your digestive system. That means medicines like levodopa can’t get absorbed from your gut as quickly as they once did.
The Challenge Of On And Off Periods
On and off periods with Parkinsons medications can pose a significantand frustratingchallenge when it comes to managing your symptoms, says Dr. Pan.
On/off periods are a very relevant topic because it actually can cause a lot of disability in Parkinsons, she says. Because when patients are on medications, they can almost feel like normal and do a lot of things, and once medications wear off, they are very disabled and immobilized at times.
To address the issue, your doctor may have you start taking your medication dose more frequentlyfor example, switching from taking a pill every four hours to every three. However, it becomes a logistical challenge of taking medications so often, and there are also risks of excessive dopamine, she says. For example, non-motor symptoms of Parkinsonssuch as psychosisbecome more likely the higher the dose of a dopamine agent you are taking. It becomes a difficult balance of trying to reduce motor symptoms with your medications without taking so much that youre increasing other non-motor symptoms.
Thankfully, scientists have already worked to address this issue by developing new types of medications to help you manage those off-times, says Dr. Hui.
For example, one is a sublingual apomorphine, which is a drug placed under the tongue and can kick you on within 15 minutes. Theres also an inhaler form that works within 15-30 minutes, she says. These different delivery systems can help you maximize on-time quickly.
On / Off In Parkinsons
On/Off Motor Fluctuation in Parkinsons Disease
What does On/Off mean?
The On/Off Phenomenon in Parkinsons Disease is related to uctuating benet of the medications used to treat PD.
Being On describes the time when the Person with Parkinsons feels that their medication is benecial and that their symptoms are well controlled.
Being Off describes the time when the PwP feels that their medication is not working as well as usual, and some of their symptoms may have returned .
The On/Off phenomenon can best be described as a quick, unpredictable reappearance of PD symptoms. Likewise, switching from Off to On can occur just as suddenly. The speed of this shift can be so dramatic that some people have likened this effect to a light switch being turned on and off.
On/Off uctuations are different from the phenomenon known as Freezing, which can also affect people who have had Parkinsons for some time. Freezing is the word used to describe the experience of stopping suddenly while walking or when trying to initiating walking, and people feel as though their feet are frozen or stuck to the ground. While Freezing episodes tend to last only a few seconds, an Off period can continue for minutes, or even hours.
How is the On/Off Treated?
What Can People with Parkinsons Do to Help Themselves?
Acknowledgements:
Other Relevant Information Sheets:
M1.1: Motor Fluctuations in Parkinsons Disease M1.2: Wearing Off in Parkinsons Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Wearing Off
Wearing off is very individual. In some people, motor symptoms such as tremor may be the first sign, whilst for others it might be stiffness and difficulty initiating movement. But wearing off symptoms may not be related to movement at all and may be experienced in the form of increased anxiety, fatigue, a change in mood, difficulty thinking, restlessness and sweating .
If you notice a change in your usual symptom pattern, you should discuss this with your doctor because you may be experiencing wearing off. Your doctor will then be able to adjust your medication regime to provide better symptom control, possibly by reducing the interval between the levodopa doses and increasing the number of daily doses.
Clinician Assessments Of Wo
Clinicians identified WO in 763 patients, with the overall prevalence of WO being 55.1%. Most of the patients with WO were treated with levodopa, whereas 37 patients received dopamine agonists or non-dopaminergic medications. Further analysis showed that the WO frequency varied among different disease durations. WO was identified in 12.9% of patients within 1 year of disease duration. The percentage of patients with WO continuously increased with the disease progression. It reached the highest value of 76.2% in patients with 1015 years of disease duration. Then, it gradually dropped to 67.9% in patients with over 20 years of duration .
In terms of WO evaluation, the most frequently used question was symptom response to medications, with a frequency of 100%. It was followed by the fluctuating features of motor symptoms , timing of symptom response to medications , symptom fluctuation occurring at a fixed time per day, which lasts for days , and fluctuating features of non-motor symptoms . In addition, 56.9% of the clinicians considered that the presence of motor fluctuation was required for WO diagnosis.
Clinical Relevance Of Early Recognition Of Wearing
In clinical practice, treatment is initiated once the compensatory mechanisms operative in early stages of the loss of the nigrostriatal pathway have failed. As a result, there is already a reduced capacity at the presynaptic dopamine terminal level to compensate for changes in dopamine availability associated with fluctuations in plasma and brain levodopa levels after oral administration. Therefore, the output of basal ganglia motor oscillates precariously between various abnormal states. The critical and therapeutically relevant point is that standard short-acting levodopa formulations lead to levels of striatal dopamine and dopamine receptor stimulation different from those prevailing under normal conditions and oscillating between subphysiological and supraphysiological levels. This being a reflection of the peaks and troughs associated with changes in plasma levodopa concentrations that characterize the use of standard levodopa preparations. Thus, standard levodopa administration does not restore the normal physiology of the basal ganglia , but induces, through pulsatile stimulation, molecular abnormalities such as phosphorylation of NMDA subunits and upregulation of AMPA receptors in medium spiny striatal neurons that underlie wearing-off .
Loading Vesicles With Dopamine: The Effect Of Levodopa Treatment
The human nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway consists of about 1 million pigmented neurons . Each nigral dopaminergic cell has between half a million and one million release sites along its highly branched axon in the striatum . The number of synaptic vesicles per release site is 200500 and the average number of dopamine molecules per vesicle is probably somewhere between 2000 and 5000 . Hence, it can be estimated that the normal nigrostriatal system contains some 1018 molecules of dopamine. In Parkinsons disease, this number is reduced by at least 50%.
The Bottom Line On On/off Periods With Parkinsons Meds
Managing the cycling between on and off periods with Parkinsons medications can be incredibly frustrating, but luckily, there are a number of effective ways to help reduce the peaks and valleys of motor symptoms.
Scientists are still exploring new and improved ways to help combat off periods with Parkinsons drugs, according to the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinsons Research. You may even consider participating in one of these clinical trials, which you can learn more about with the Michael J. Fox Foundations clinical trial matching tool.
Even more exciting is the fact that researchers are also working diligently to try to improve Parkinsons treatments in generalreally looking into the crux of the disease to try to slow its progression overall, which would in turn help with this on-off period struggle, says Dr. Hui.
There are a number of clinical trials going on, so I think we should also stay tuned for development of to slow progression of disease, she says.
Treatment Options For Off Episodes
If you show signs of the Parkinsons disease ON-OFF phenomenon, your doctor may wish to adjust or change your medication. You might be advised to shorten intervals between doses or take your medication on a different schedule. Your doctor may also suggest taking a dopaminergic agent to keep you ON for longer periods.
Scientists are also working on new treatments to reduce OFF episodes in PD patients. a new levodopa drug in the form of an inhalation powder will launch in the first quarter of 2019. This new treatment has been approved by the FDA to treat OFF periods by administering levodopa directly to the bloodstream. It will become available on prescription through a network of specialty pharmacies in the U.S.
APA ReferenceSmith, E. . Parkinsons Disease OFF Episodes: Physical & Emotional Effects, HealthyPlace. Retrieved on 2021, August 25 from https://www.healthyplace.com/parkinsons-disease/effects/parkinsons-disease-off-episodes-physical-emotional-effects
