Research Design And Methods
Six independent cross-sectional population surveys were carried out in five geographic areas of Finland in 1972, 1977, 1982, 1987, 1992, and 1997 . In 1972 and 1977, a randomly selected sample making up 6.6% of the population born between 1913 and 1947 was drawn. Since 1982, the sample was stratified by area, sex, and 10-year age-group according to the World Health Organization MONICA protocol . The subjects included in the six surveys were 2564 years of age, and the 1997 survey also included subjects aged 6574 years. Subjects who participated in more than one survey were included only in the first survey cohort. The total sample size of the six surveys was 53,166. The participation rate varied by year from 74 to 88% . After excluding 123 subjects because of prevalent Parkinson’s disease at baseline, 112 subjects because of prevalent type 1 diabetes at baseline or during follow-up, and 1,379 subjects because of incomplete data on any variables required, the present analyses comprise 25,168 men and 26,384 women. The participants gave informed consent . These surveys were conducted according to the ethical rules of the National Public Health Institute, and the investigations were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Autonomic Nervous System And The Heart
In PD, there are two major reasons why the automatic control of the cardiac system is impaired. First, areas of the brain that control this system often contain Lewy bodies and have undergone neurodegeneration. In addition, the autonomic nervous system itself is directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration. This means, when the baroreceptors in the heart and carotid artery sense a drop in blood pressure and try to generate a signal to the heart and blood vessels to increase the blood pressure, the message may not get through. This results in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension , or drops in blood pressure upon standing due to autonomic nervous system dysfunction. There are no medications that can cure nOH by restoring the autonomic nervous system in PD. nOH however, can be treated. Read more about nOH and its treatments here.
Structural problems of the heart such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy are not thought to be part of the pathology of PD, although of course, could co-exist with PD.
Patients Without Levodopa Therapy
To get further insight into whether levodopa therapy might be responsible for the loss of small or large nerve fibers, we examined a subgroup of early-stage patients who had not been exposed to levodopa yet. There was no difference in IENFD, myelinated fibers or SP-positive intraepidermal fibers between these subjects and patients who had been treated with levodopa . P-alpha-synuclein deposits were detected in two patients without levodopa treatment.
Don’t Miss: Can Boxing Cause Parkinson’s Disease
How Can I Prevent Neuropathy
The best treatment is prevention, and strategies for reducing injuries are highly effective and well tested. Since medical procedures ranging from casting fractures to injuries from needles and surgery are another cause, unnecessary procedures should be avoided. The new adjuvanted vaccine against shingles prevents more than 95 percent of cases and is widely recommended for people over 50, including those who have had previous shingles or vaccination with the older, less effective vaccine. Diabetes and some other diseases are common preventable causes of neuropathy. People with neuropathy should ask their doctors to minimize use of medications that are known to cause or worsen neuropathy where alternatives exist. Some families with very severe genetic neuropathies use in vitro fertilization to prevent transmission to future generations.
Parkinsons As A Disease Of Neuronal Connectivity
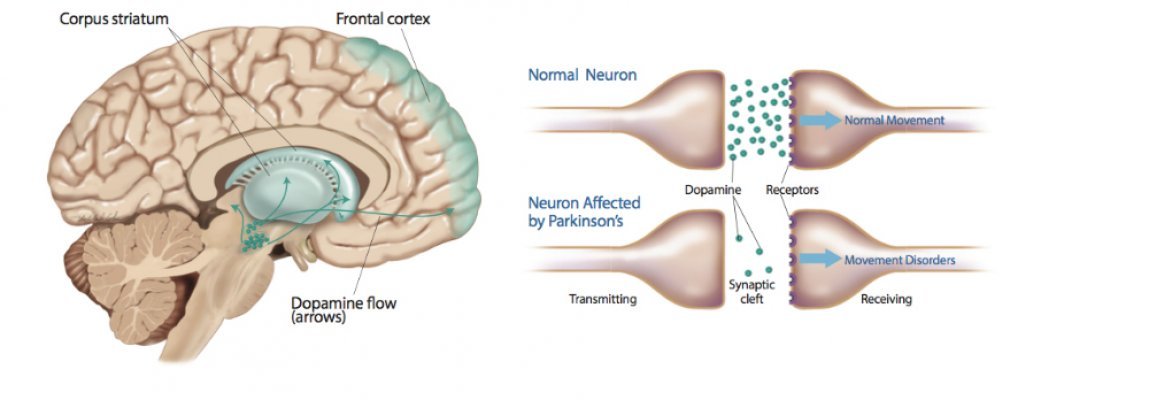
The clinical manifestations of neurodegenerative disorders have been traditionally described from an impaired neuronal circuitry perspective.14 Technological advancements have led to a surge of studies investigating the impact PD has on neural excitability and connectivity utilizing electroencephalogram , neuromodulation techniques, imaging modalities, and graph-analytical methods. Although the field of PD has been somewhat slower to incorporate these concepts compared to other disease models, clinicians now generally acknowledge the complex, multifaceted nature of the disease and the need to pursue multidimensional approaches to study it.
To further establish the clinical applicability of connectome network dysfunction, studies have demonstrated that circuit-specific modulatory therapies, such as repetitive TMS, can alleviate various symptoms of PD, from memory and motor symptoms to depression in PD.31â34 Although from a therapeutic standpoint, there is much to streamline and corroborate with respect to repetitive TMS paradigms and methodologies, there is no denying the potential to providing individualized circuit-specific modulatory therapies.35
Why Do Parkinsons Patients Have Trouble Sleeping
Despite having daytime tremors, Parkinsons patients do not shake in their sleep. However, both Parkinsons disease itself and the medications used to treat it can give rise to a number of sleep problems that lead to insomnia and excessive daytime sleepiness.
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Affect The Brain
Other Causes Of Parkinsonism
“Parkinsonism” is the umbrella term used to describe the symptoms of tremors, muscle rigidity and slowness of movement.
Parkinson’s disease is the most common type of parkinsonism, but there are also some rarer types where a specific cause can be identified.
These include parkinsonism caused by:
- medication where symptoms develop after taking certain medications, such as some types of antipsychotic medication, and usually improve once the medication is stopped
- other progressive brain conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple systems atrophy and corticobasal degeneration
- cerebrovascular disease where a series of small strokes cause several parts of the brain to die
You can read more about parkinsonism on the Parkinson’s UK website.
Page last reviewed: 30 April 2019 Next review due: 30 April 2022
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Also Check: Which Neurotransmitter Is Associated With Parkinson’s Disease
Laboratory Assessment Of Pnp In Pd
In addition, we performed a broad analysis of serum parameters that could be associated with PNP. There were no age independent effects for other etiologies of PNP such as deficits of folate, cobalamin, methylmalonic acid, and homocysteine. Of interest, when age was included as a confounder LED did not correlate significantly with tibial nerve cMAP or with HRUS pathology .
Symptoms Of Peripheral Neuropathy
The symptoms of PN can be non-specific, and a person therefore may not be able to distinguish on their own whether his/her symptoms are due to PN or another condition. PN, however, often results in specific findings on a neurologic exam, such as decreased sensation to pin prick or vibration or the lack of ability to discern which way a toe is being pointed without looking. Other tests such as Electromyogram and Nerve conduction studies may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Small fiber neuropathy which typically causes pain, burning, tingling and/or numbness in the feet, may have normal EMG and NCS and a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. With the appropriate examination and supportive tests however, a neurologist should be able to distinguish the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy from other conditions, including PD, that may cause similar symptoms.
There are many known causes of PN including diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, certain infections, and autoimmune diseases. Many of these causes can be treated, so it is important to know if you do have PN and what the cause is. There are those people; however, who have the signs and symptoms of PN, but no known cause can be identified.
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease Chronic
What Treatments Are Available
Treatments depend entirely on the type of nerve damage, symptoms, and location. Your doctor will explain how nerve damage is causing specific symptoms and how to minimize and manage them. With proper education, some people may be able to reduce their medication dose or manage their neuropathy without medications. Definitive treatment can permit functional recovery over time, as long as the nerve cell itself has not died.
Addressing neuropathys causes. Correcting underlying causes can result in the neuropathy resolving on its own as the nerves recover or regenerate. Nerve health and resistance can be improved by healthy lifestyle habits such as maintaining optimal weight, avoiding toxic exposures, eating a balanced diet, and correcting vitamin deficiencies. Smoking cessation is particularly important because smoking constricts the blood vessels that supply nutrients to the peripheral nerves and can worsen neuropathic symptoms. Exercise can deliver more blood, oxygen, and nutrients to far-off nerve endings, improve muscle strength, and limit muscle atrophy. Self-care skills in people with diabetes and others who have an impaired ability to feel pain can alleviate symptoms and often create conditions that encourage nerve regeneration. Strict control of blood glucose levels has been shown to reduce neuropathic symptoms and help people with diabetic neuropathy avoid further nerve damage.
Specific symptoms can usually be improved
Small Fiber Neuropathy In Parkinson’s Disease: A Clinical Pathological And Corneal Confocal Microscopy Study
Peripheral denervation is established in Parkinson’s disease on skin biopsies.
-
Corneal confocal microscopy can non-invasively visualize corneal nerves.
-
We have shown significant corneal denervation in PD compared to controls using CCM.
-
Corneal denervation relates to skin denervation and parasympathetic dysfunction.
Also Check: How To Diagnose Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Clinical Management Of Ldopainduced Pnp
A strong level of evidence supports a role, at least partial, for vitamins of the group B and related cofactors in the pathogenesis of ldoparelated PNP. Monitoring the plasma levels of vitB6, vitB12, MMA, and Hcy is of utmost importance in patients starting and continuing LCIG therapy, as well as in patients with high oral ldopa intake or at higher risk of PNP . Some researchers suggested a periodic clinical, electrophysiological, and biochemical assessment in patients undergoing LCIG. A basic screening should include regular monitoring of vitB12 and folate since the beginning of the treatment, plus a determination of Hcy and MMA in cases of borderline vitamin levels. Vitamin supplementation should be started in all patients showing biochemical alterations or symptoms of PNP., Other empirical approaches include a prophylactic supplementation with high doses of vitB12 and folate since the beginning of LCIG. Rispoli and colleagues found a very low incidence of subclinical PNP in 30 patients undergoing supramaximal supplementation with vitB12, folic acid, vitB6, and vitB2 since the early onset of LCIG treatment. Although extensive vitB6 supplementation is scarcely recommended because of the interference with decarboxylase inhibitor and the potential neurotoxic effect of pyridoxine megadoses, preliminary evidence suggests that COMT inhibitors might be beneficial to prevent the development of PNP in patients receiving ldopa treatment.
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy

Peripheral neuropathy refers to the many conditions that involve damage to the peripheral nervous system, the vast communication network that sends signals between the central nervous system and all other parts of the body. Peripheral nerves send many types of sensory information to the central nervous system , such as a message that the feet are cold. They also carry signals from the CNS to the rest of the body. Best known are the signals to the muscles that tell them to contract, which is how we move, but there are different types of signals that help control everything from our heart and blood vessels, digestion, urination, sexual function, to our bones and immune system. The peripheral nerves are like the cables that connect the different parts of a computer or connect the Internet. When they malfunction, complex functions can grind to a halt.
Nerve signaling in neuropathy is disrupted in three ways:
- loss of signals normally sent
- inappropriate signaling when there shouldnt be any
- errors that distort the messages being sent
Symptoms can range from mild to disabling and are rarely life-threatening. The symptoms depend on the type of nerve fibers affected and the type and severity of damage. Symptoms may develop over days, weeks, or years. In some cases, the symptoms improve on their own and may not require advanced care. Unlike nerve cells in the central nervous system, peripheral nerve cells continue to grow throughout life.
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s Disease A Genetic Disorder
Median And Ulnar Neuropathy Assessment In Parkinsons Disease Regarding Symptom Severity And Asymmetry
Nilgul Yardimci
1Neurology Department, Minasera Aldan Hospital, Ahmet Taner Kislali Mah. 2741, Street No. 2 Cayyolu, Ankara, Turkey
2Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department, Medical Park Ankara Hospital, Kentkoop Mah., Kentkoop Parkici Yolu, Yenimahalle, Ankara, Turkey
3Biostatistics Department, Medicine Faculty, Hacettepe University, Hacettepe Mah., 06230 Ankara, Turkey
4Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department, Medicine Faculty, Turgut Ozal University, Alparslan Turkes Cad. No. 57, Emek, 06510 Ankara, Turkey
5Neurology Department, Medicine Faculty, Turgut Ozal University, Alparslan Turkes Cad. No. 57, Emek, 06510 Ankara, Turkey
6Neurology Department, Medicine Faculty, Gazi University, Emniyet, Yenimahalle, 06560 Ankara, Turkey
Abstract
1. Introduction
Parkinsons disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, characterised by tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability associated with degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta and the presence of eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions .
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Parkinsons Disease Group
Firstly, the patients were examined for existence of any median or ulnar neuropathy according to the electrophysiologically diagnostic criteria based on control data performed in our laboratory.
2.2. Comparison Group
2.3. Electrophysiological Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
| Variables |
Risk Factor Assessment For Large And Small Fiber Neuropathy
Patients with EMG abnormalities were older: 65.5±3.8 vs. 53±3;years , but abnormalities on SWT scores were not associated with age. In addition, patients with either SWT or EMG abnormalities were not more likely to be older than normal patients. Patients with EMG abnormalities were more likely to be older at the disease onset but there was no significant relationship between EMG abnormalities and disease duration. In addition, there wasnt any significant relationship between the age of disease onset or disease duration and SWT scores .
Regression analysis of tibial and peroneal CMAP amplitudes and conduction velocities or sural SNAP and conduction velocities versus the presence of DM or B12 levels was not significant. In addition, regression analysis also did not disclose any significant relationship between SWT scores and electrodiagnostic parameters, i.e. tibial and peroneal CMAP amplitudes and conduction velocities or between sural SNAP and conduction velocities.
Recommended Reading: What Medications Are Prescribed For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons Symptoms Have Appeared What Happens Next
After the appearance of possible Parkinsons symptoms, a neurologist will perform a comprehensive physical examination and a thorough uptake of ones medical history, including an account of medications past and present to rule out side effects that may mimic the symptoms of Parkinsons. Scans may also be used as a diagnostic tool, such as magnetic resonance imaging of the brain to rule out a structural cause of Parkinsonism.
In addition to a diagnostic and visual exam, a neurological examination testing agility, muscle tone, gait and balance will be conducted. Results are recorded in a table known as the United Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale . This universal scale is a vital tool in documenting the progression of the disease and establishing a timeline of symptoms. Comparisons can be made at subsequent follow-up visits.
Clinically, the diagnosis of Parkinsons is made through the improvement of symptoms after receiving medications that stimulate or imitate the production of the neurotransmitter dopamine, such as levodopa.
Neuropathy Can Be A Cause Of Extreme Tiredness
An underlying problem affecting a main nerve or affecting many nerves can be a cause of tingling and numbness in the hands or arms and legs. An increased feeling of heaviness of the arms or legs or feeling tired from just holding the arms up in the air may be due to problems with the nerves rather than weakness of the muscles. Autoimmune disease or some nutrient deficiencies can be causes of neuropathy, or nerve damage. Other common causes are mentioned later.
Autoimmune disease itself can be very tiring and a cause of muscle cramps and diffuse chronic pain and it could make it very hard to cope with a physically demanding job. Some types of nerve damage can become permanent but may be reversible if caught early enough and the underlying causes are corrected. Vitamin B12 may be poorly absorbed by elderly people or for others with digestive problems; a monthly injection of B12, bypassing the digestive system, is a common treatment.;;Dissolve in the mouth supplements of B12, cobalamin, are also used sucessfully by some people. In Parkinsons Disease neuropathy has been seen and perhaps we should be measuring MMA levels in these patients and treating with cobalamin supplementation to reduce MMA levels and prevent neuropathy.;
Neuropathy may affect approximately 24 million people in the United States.
Since celiac disease may be a cause of neuropathy trying a gluten free diet may be worth trying, .
Summary of tips for protecting against neuropathy:
Jennifer Depew
Also Check: Does Flu Shot Cause Parkinson’s
How Are They Alike
MS and Parkinsonâs both affect your central nervous system, which includes your brain and spinal cord. Thatâs why they both can affect how you move, sleep, feel, and talk.
These diseases both affect your nerves. MS can break down the coating, called myelin, that surrounds and protects your nerves. In Parkinsonâs, nerve cells in a part of your brain slowly die off.
Both can start out with mild symptoms, but they get worse over time.
Common symptoms of both diseases include:
- Shaky fingers, hands, lips, or limbs
- Slurred speech thatâs hard for others to understand
- Numb or weak limbs that make your walk unsteady
- Loss of muscle control that often affects one side of your body at first, then later both
- Spastic limb movements that are hard to control
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Poor balance
Depression is another symptom common to both conditions.
