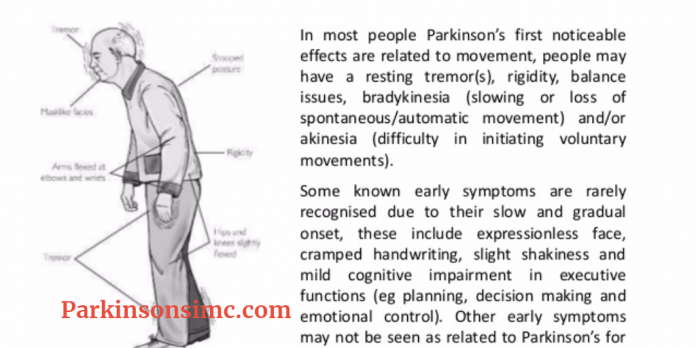
Passive Manipulation Of Limbs
To test for the presence of rigidity, we need to passively manipulate the limbs of the patient. However, If the disease is in its early stage or the symptoms are well controlled with medications, we may not be able to see rigidity. We will need to use some activation maneuvers, that basically consist in performing repetitive movements with the limb contralateral to the one that is being tested.
Also, there are two types of rigidity:
-;;;;;; Lead-pipe rigidity: where the tone is uniformly and smoothly increased throughout the entire range of movement
-;;;;;; Cogwheel rigidity: where a tremor is superimposed on the hypertonia, making the movement irregular due to intermittent increase and reduction of tone
Upper Extremity Testing
For the upper extremity the most sensitive joint where to check for rigidity is the wrist. To uncover rigidity, passively rotate the wrist and feel for a resistance to the movement. It is very important that the arm of the patient is fully relaxed when rotating the wrist. To do this, place your proximal hand under the patients forearm, while your distal hand grabs and rotates the wrist of the patient. When rigidity is present, the range of motion will be preserved but you will feel a resistance in performing the movement.
Wrist rotation with activation maneuver.
It is also possible to test for rigidity in the elbow by passively flexing and extending the forearm.
Elbow flexion-extension with activation maneuver.
Lower Extremity Testing
Technologies Assessing Limb Bradykinesia In Parkinsons Disease
Article type: Review Article
Authors: Hasan, Hasana | Athauda, Dilan S.a; b | Foltynie, Thomasa; b | Noyce, Alastair J.a; c; d; *
Affiliations: UCL Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London, UK | Sobell Department of Motor Neuroscience and Movement Disorders, The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, London, UK | Blizard Institute, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary University London, London, UK | Reta Lila Weston Institute of Neurological studies, UCL Institute of Neurology, London, UK
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Alastair J. Noyce, Reta Lila Weston Institute of Neurological studies, UCL Institute of Neurology, 1 Wakefield Street, London WC1N 1PJ, UK. Tel.: +447595676891; E-mail: .
Keywords: Hypokinesia, Parkinson disease, technology, outcome assessment, ambulatory monitoring, review
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-160878
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 65-77, 2017
Abstract
Background: The MDS-UPDRS is the most widely used scale for rating impairment in PD. Subscores measuring bradykinesia have low reliability that can be subject to rater variability. Novel technological tools can be used to overcome such issues.
Objective: To systematically explore and describe the available technologies for measuring limb bradykinesia in PD that were published between 2006 and 2016.
Functional Imaging Studies Of The Effect Of Surgery And Deep Brain Stimulation On Bradykinesia
Many imaging studies have been driven by the model of basal ganglia function outlined in the early 1990s. Overactivity of the inhibitory output projections from the basal ganglia to the thalamus in Parkinson’s disease was supposed to remove facilitatory thalamocortical drive, particularly to midline cortical motor areas . PET and fMRI activation studies had shown that these areas were less activated during movement in patients, and therefore pallidotomy was expected to improve activation by restoring normal levels of basal ganglia output .
Most studies on movement-related changes in metabolic activity have reported similar findings both after pallidotomy and during subthalamic nucleus stimulation . In tasks in which a free-choice joystick movement is used, increased activation of preSMA and anterior cingulate cortex is usually accompanied by increased activation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Although most reports of activation-induced metabolism suggest that there is no change in the primary motor cortex, there are some suggestions that stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus may reduce activity in the resting state . Whether this is related to a general reduction in rigidity or other involuntary muscle activity or to reduced input to the cortex via pathways direct from the subthalamic nucleus is not known.
Also Check: What Is Rigidity In Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Bradykinesia In Parkinson Disease
BradykinesiaParkinson’s diseasebradykinesia
Bradykinesia symptoms
- dragging one or both feet when walking.
- having little or no facial expressions.
- freezing muscle reactions may slow to the point that the muscles become immobile, or freeze, for a period of time.
Furthermore, what causes Bradykinesia? Bradykinesia describes slow movement or a difficultly moving the body on demand. Bradykinesia is most often caused by Parkinson’s disease, and may be related to muscle weakness, rigid muscles, or tremors. It is related to akinesia, which is when a person has difficulty performing voluntary movements.
One may also ask, why do Parkinson’s patients have Bradykinesia?
Bradykinesia is one of the early signs of a movement disorder such as Parkinson’s or parkinsonism. It is caused by reduced levels of dopamine in the brain and is often first noticed by family and friends. Reduced quality of movement is a sign of Parkinson’s rather than a symptom brought on by the condition.
What is Cogwheeling in Parkinson’s?
Cogwheeling in Parkinson’s disease is that jerky feeling in your arm or leg that you can sense when rotating that limb or joint. It is an early symptom of Parkinson’s.
What Is Bradykinesia In Patients With Parkinson Disease
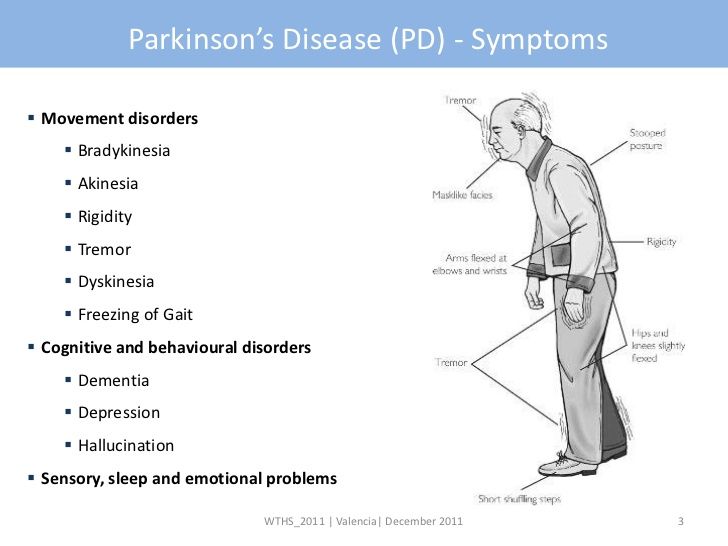
Bradykinesia refers to slowness of movement. Symptoms of bradykinesia are varied and can be described by patients in different ways. These may include a subjective sense of weakness, without true weakness on physical examination; loss of dexterity, sometimes described by patients as the “message not getting to the limb”; fatigability; or achiness when performing repeated actions.
Read Also: What Other Diseases Mimic Parkinson’s Disease
Bradykinesia In Parkinson S Disease Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons Disease
What is bradykinesia in parkinson disease. In Parkinsons this slowness happens in different ways. Symptoms generally develop slowly over years. The other two are tremors and slowed movement called bradykinesia.
In fact along with rigidity and resting tremor bradykinesia is one of the cardinal motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease. There was a striking lack of relation between the measures that reflect bradykinesia and hypokinesia. Bradykinesia or slowness of movement is one of the three main signs of Parkinsons along with tremor and rigidity stiffness.
Hypokinesia however emerged prominently only in the more affected patients. Bradykinesia is noticeable as the gradual loss and slowing down of spontaneous movement which may appear as a decrease in facial expressions and a chronic abnormal stillness. Reduced quality of movement is a sign of Parkinsons rather than a.
The progression of symptoms is often a bit different from one person to another due to the diversity of the disease. The use of levodopa or dopamine agonists did. It is reported by approximately 98 percent of patients.
A reduced ability to move is seldom constant especially in the early stages of Parkinsons disease. Reduction of automatic movements such as blinking or swinging your arms when you walk. The name of the condition is literally translated to mean slow movement.
Therefore cogwheel rigidity can help. Symptoms of bradykinesia are varied and can be described by patients in different ways.
Treating Bradykinesia In Parkinsons Disease
Currently, no cure exists for PD, and there are no known treatments to stop or slow the progression of the disease. Treatments are available that help manage the symptoms and may include medications, surgery , and complementary or alternative medicine.
Most patients with PD are started on medication to help manage their symptoms. Initial therapy is usually levodopa , dopamine agonists, and/or monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors. The combination of levodopa and carbidopa is the most effective treatment available for the management of motor symptoms of PD. However, it can cause a side effect known as dyskinesia, which are abnormal involuntary movements. Dopamine agonists are less effective on the motor symptoms of PD but have a lower rate of causing dyskinesia, although they have other side effects. MAO-B inhibitors are less effective than levodopa or dopamine agonists, however they have fewer side effects. Choice of therapy should be customized to the individual patient with an understanding of the risks and benefits of each class of medication.5
In addition to medication, physical therapy can help with muscle cramps, and regular exercise and stretching are beneficial to strengthen muscles and maintain flexibility. Assistive devices such as walkers or canes can be helpful.
You May Like: How Much Does Parkinson’s Medication Cost
Symptoms Generally Develop Slowly Over Years
Bradykinesia is slowness or difficulty in body movement and is one of the early signs of Parkinsons disease. Bradykinesia is slowness or difficulty in body movement and is one of the early signs of Parkinsons disease. The name of the condition is literally translated to mean slow movement. Bradykinesia refers to slowness of movement. Bradykinesia can result from various conditions including a. As a result the VA separately rates bradykinesia whether or not a veteran has filed or lacks a diagnosis for a Parkinsons VA disability claim.
How Long Does End Stage Parkinsons Last
Symptoms usually get worse over time, and new ones probably will pop up along the way. Parkinson’s doesn’t always affect how long you live. But it can change your quality of life in a major way. After about 10 years, most people will have at least one major issue, like dementia or a physical disability.
Don’t Miss: Do Parkinson’s Tremors Get Worse With Stress
Rest And Action Tremor
We noted above that action tremor can contribute to weakness in Parkinson’s disease. In addition, rest and action tremor can also be a factor in prolonging reaction times. Hallett and colleagues and Wierzbicka and colleagues showed that patients with Parkinson’s disease tend to time the onset of agonist muscle activity at the elbow or wrist with the time of activation of the same muscle in any ongoing tremor . This could, on average, slow the initiation of any movement.
Action tremor can also be a factor in pacing the speed of voluntary alternating movements. Logigian and colleagues showed that voluntary movements are entrained by action tremor if patients attempt to move at frequencies close to that of their natural action tremor . The extent of the entrainment depends on the amplitude of the patients’ ongoing tremor.
Key Facts Of Bradykinesia
-
Bradykinesia of Parkinson’s disease involves two intrinsic nuclei of substantia nigra pars compacta and subthalamic nucleus in basal ganglia.
-
Gait initiation of bradykinesia is regulated by off-latency motor program of primary posture and on-latency motor program of gait in the homogeneous movement.
-
Off latency of primary posture motor program is prolonged with stages of disease.
-
The cognitive circumstance prolonged both off and on latency in bradykinesia.
-
Slow gait speed correlated with the unsynchronized off/on-latency interval.
-
Bradykinesia is the difficulty in terminating the motor program of primary posture.
-
Bradykinesia of heterogeneous movements is the difficulty in switching the sequential movements of ongoing motor programs within on/on-latency interval.
-
Bradykinesia in Parkinson’s disease is directed by dual functions of basal ganglia regulating the time and space of synergic movement.
Roberto Erro, Maria Stamelou, in, 2017
Recommended Reading: How To Donate To Parkinson’s Research
Financial Disclosures/conflicts Of Interest
Full financial disclosures of all the authors for the past year: DA and HH no financial disclosures. TF has received research grants from Michael J Fox Foundation, European Union FP7, John Black Charitable Foundation and Brain Research Trust. He has received honoraria for speaking at meetings sponsored by Brittania, Medtronic and UCB, and has served on Advisory boards for Oxford Biomedica & Bial. TF and DA are investigators on the Exenatide-PD study which utilizes the BRAIN test alongside a battery of other assessments. AJN Salary: Parkinsons UK, Barts Health NHS Trust. Grants: Parkinsons UK, Élan/Prothena Pharmaceuticals, GE Healthcare. Shares: LifeLab Ltd. Advisory board: myHealthPal. Honoraria: Global Kinetics Corporation, Henry Stewart Talks, Britannia Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Non-financial: AJN designed the existing version of the BRAIN test which features in this manuscript and is the Principal Investigator on the PREDICT-PD study .
What Are The 8 Causes Of Bradykinesia

Parkinsons disease is the most common cause of Bradykinesia.
Bradykinesia meaning simply, slowness of movement, may also be due to other causes.
Some patients who walk slowly may not have true-bradykinesia at all! They may be walking slowly because they are afraid of falling down. Thiscautious gait is due to a problem in the balance system of the body.
Thus, it is very important for the doctor to confirm that you have true-bradykinesia.
Even if you do have truly slow movements, you may not have Parkinsons disease.
There are 4 main features of Parkinsons disease. Most patients with Parkinsons disease will have two or more of these symptoms:
| 4 Cardinal signs of Parkinsons disease |
|---|
|
|
|
|
Even amongst these conditions, only the first 3 conditions can truly be called Bradykinesia. This topic is discussed in greater detail here:
Recommended Reading: Can Anxiety Cause Parkinson’s Symptoms
Physiological And Behavioral Phenomena
PD bradykinesia has been linked to the degeneration of dopamine neurons in the SNc and VTA. It becomes evident only when approximately 50% of dopamine neurons die . Dopamine depletion in the brains of humans and animals leads to a number of changes possibly relevant to bradykinesia in neuronal, electromyographic and movement parameters. Some of these changes include:
Want More Practical Articles Like This
You can find much more inourEvery Victory Counts®manual.Its packed with up-to-date information about everything Parkinsons, plus an expanded worksheets and resources section to help you put what youve learned into action.Request your free copy of theEvery Victory Countsmanual by clicking the button below.
Also Check: How Does Parkinson’s Disease Affect The Spinal Cord
What Does Shuffling Gait Look Like
According to Dr Horak, shuffling gait occurs in people with Parkinsons because small steps are taken without the normal heel and toe making contact with the ground meaning that the feet slide forward instead of being lifted up off the floor.
Normal gait speed depends upon a rapid push down of the toes into the floor. Without this push, shuffling gait depends upon the use of the hip muscles to move the legs and body forward with a shuffle, she explains.
Those who already experience freezing of gait also tend to be subject to shuffling gait. Freezing, says Horak, is basically an extreme form of shuffling gait but without any forward motion. Shuffling gait is not limited to the feet people with Parkinsons can also notice shorter strides and reduced arm movement when walking. Not only does this mean walking takes far more effort, but the likelihood of tripping over low objects on the floor increases too.
Though, Dr Horak says, a change in gait is not always obvious in the early stages of Parkinsons, as a symptom, it is one of the hallmarks of Parkinsons and can be one of the most debilitating.
Dr Fay Horak recently co-authored a study on the effects of exercise on gait and brain connectivity.
How Bradykinesia May Appear
Patients with PD experience symptoms in varying severities, and with the progression of the disease, the severity of the symptoms changes over time. Bradykinesia may show up in a variety of ways, including:
- Difficulty with repetitive movements, like tapping a finger
- Trouble with everyday functions, like dressing themselves, cutting their food, or brushing their teeth
- Reduced facial expressions 1,2
Recommended Reading: Are Bananas Good For Parkinson’s
Why Do Parkinson’s Patients Have Bradykinesia
Bradykinesia is one of the early signs of a movement disorder such as Parkinsons or parkinsonism. It is caused by reduced levels of dopamine in the brain and is often first noticed by family and friends. Reduced quality of movement is a sign of Parkinsons rather than a symptom brought on by the condition.
You may ask, What is Cogwheeling in Parkinson’s?
Cogwheeling in Parkinsons disease is that jerky feeling in your arm or leg that you can sense when rotating that limb or joint. It is an early symptom of Parkinsons.
Preparation To Move: Activation Of Specific Brain Areas
EEG, MEG, PET, functional MRI and magnetic stimulation techniques have all been used in an attempt to understand which parts of the motor system are functioning abnormally in akinetic patients with Parkinson’s disease. However, because brain activity during movement reflects both outgoing motor commands and the sensory input that results from moving, studies of motor activity have concentrated on the period just before the onset of movement when changes in sensory input are minimal. In most instances, the movements are self-paced; reaction tasks involve pre-movement sensory input that can complicate the interpretation of the data obtained. A general finding from these studies is that there is underactivity of midline cortical motor areas, perhaps coupled with extra activation of lateral premotor areas. The former may be related to difficulties in preparing instructions to move; the latter may be an active process of compensation and may be related to the improvement in performance that can be observed when external cues are given to guide movement .
Read Also: How Long One Can Live With Parkinson’s Disease
Stiff Muscles Causing Slowness:
This is relatively uncommon. Some conditions can cause painful swelling and fibrosis of muscles. Others conditions can cause them to be in a state of perpetual contraction.
Surely, if the muscles are inflamed, painful and stiff, movements will become slow.
Examples: Neuromyotonia, Fibrosis secondary to Emery-Dreifuss, dermatomyositis
Note that there is some subtlety here. Stiff muscles can also be a symptom of Parkinsons. If the slowness is due to stiff muscles, it is not bradykinesia.
On the other hand, if both the slowness and stiffness are due to a brain problem, then it;is bradykinesia. Differentiating one from the other requires care, and medical expertise.