Parkinsons Disease Symptoms Everyone Should Know
Parkinsons disease symptoms can include tremor and trouble with movement, along with emotional and cognitive changes.
Parkinsons disease symptoms can vary significantly from person to person. Some people may have range of motor symptoms, like tremor, stiffness, and slow movements. Others may also experience the non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, such as anxiety, cognitive changes, and loss of smell.
It has to do with a chemical messenger known as dopamine, which plays a role in the brains ability to control movement, coordination, and emotional responses. In Parkinsons disease, the brain cells that produce dopamine either stop doing their job or they die out, resulting in both motor and non-motor symptoms. ; Its not always easy to tell if someone you care about has Parkinsons disease. Lets take a closer look at the symptoms of the disease and signs that someone should make an appointment with their doctor.
Read Also: Should Someone With Parkinsons Drive
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Brain
What makes Parkinsons disease distinctive from other movement disorders is that cell loss occurs in a very specific region of the brain called the substantia nigra . The nerve cells, or neurons, in this region actually appear dark under a microscope .
Those dark neurons produce a specific type of neurotransmitter called dopamine. The neurotransmitter dopamine helps to regulate movement. This loss of dopamine is the reason that many treatments for Parkinsons Disease are intended to increase dopamine levels in the brain. Future research will hopefully tell us more about alpha-synuclein. Learn more about APDA research initiatives here.
In addition to decreases in dopamine and the cells that make dopamine, you might also read or hear about alpha-synuclein . We do not yet know what this protein does in the healthy brain, but in Parkinsons disease it clumps up in what are called Lewy bodies. Researchers believe that alphasynuclein build-up contributes to the cause of Parkinsons disease and that it may be possible to develop new treatments based on this idea.
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use the knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world. NINDS conducts and supports three types of research: basicscientific discoveries in the lab, clinicaldeveloping and studying therapeutic approaches to Parkinsons disease, and translationalfocused on tools and resources that speed the development of therapeutics into practice. The goals of NINDS-supported research on Parkinsons disease are to better understand and diagnose PD, develop new treatments, and ultimately, prevent PD. NINDS also supports training for the next generation of PD researchers and clinicians and serves as an important source of information for people with PD and their families.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Awareness Color
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosis is difficult at every stage of the disease, but particularly in the early stages. No single test can provide a diagnosis. A diagnosis will likely involve physical and neurological examinations, conducted over time to assess changes in reflexes, coordination, muscle strength, and mental function. Your doctor might also see how you respond to medicine.
You may need to have brain imaging tests to rule out other conditions that might be causing your symptoms. Such tests could include MRI and CT scans and possibly some other types of scans. Blood tests may also be done to exclude other illnesses.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
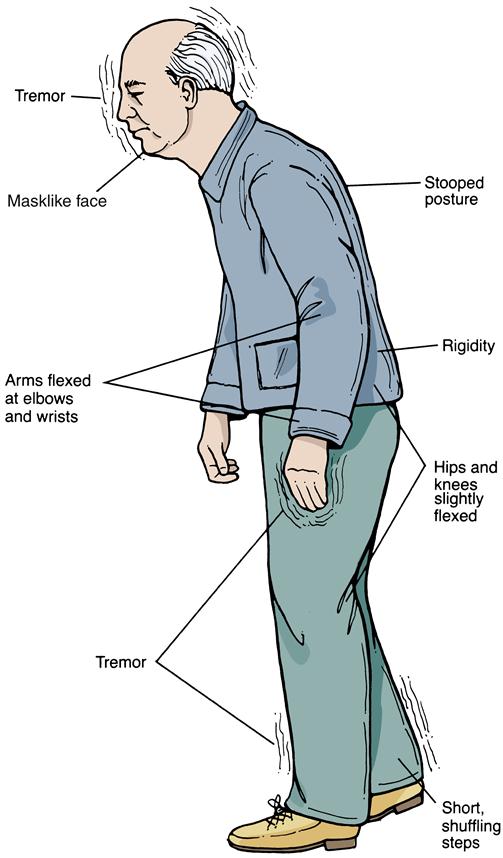
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Recommended Reading: Average Life Expectancy For Parkinson Disease
Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
MedicationIn addition to combating the symptoms of Parkinsons with lifestyle changes such as exercise and/or physical therapy, medication therapy can help control Parkinsons symptoms. Because people with the disease have low levels of dopamine, the main drug therapy is based on increasing dopamine levels in the brain.
The drug levodopa contains a substance that occurs naturally in the body. When taken, the drug is converted to dopamine when it reaches the brain. Levodopa is combined with another substance to ensure it does not convert to dopamine before reaching the brain.
As Parkinsons disease progresses, the benefit from levodopa may become less reliable. In addition, levodopa side effects can include confusion, delusions and hallucinations, as well as involuntary movements called dyskinesia. The dose can be reduced to mitigate these side effects, but sometimes at the expense of losing the benefits of symptom control.
Other types of drugs can be used in combination with levodopa to prolong its beneficial effects. Some of these drugs work by blocking the enzymes known to break down dopamine, whether created naturally in the brain or by levodopa. Other types of medication, including anticholinergics and antivirals, are sometimes used to control physical symptoms such as tremor and involuntary movement. However, patients may find that their limited benefits do not offset the sometimes serious side effects.
External resources for Parkinsons disease:
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson’s: Am I A Candidate
Deep brain stimulation is not a cure, but it can relieve your symptoms from Parkinson’s disease when medications are not an option. Only you and your doctor can decide if this surgical procedure is right for you. You may be a candidate for deep brain stimulation if:
- You have idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Patients with atypical parkinsonism are not candidates.
- You have good motor function and independence during your best “on” state when taking the drug Sinemet.
Don’t Miss: When To Start Levodopa Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease: A Case Study
63-year-old male patient is a Parkinsons disease. Our patient is experiencing classical symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Some of the hallmark clinical manifestations that our patient is experiencing are parkinsonian tremor, which is a tremor when at rest that ceases with voluntary, purposeful movement and reemerges when action terminates. Cogwheel rigidity, which is when muscles move with hesitation and in a ratcheting movement, is another classical manifestation of Parkinsons disease that our patient is
Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
The aetiology of PD is probably multifactorial and there is no available treatment that will halt or stop progression of the disease. Treatment with dopaminergic drugs is symptomatic and aims at correcting the motor disturbances. Levodopa, a prodrug to dopamine, is standard and the most common initial therapy for patients. Early on, response is usually good. With disease progression and less capacity of the system to store dopamine, the majority of patients experience shorter duration of response to individual doses , alternative phases with good and poor response to medication , involuntary movements of the head, trunk or limbs and other motor complications. Other dopaminergic medications are used to manage these fluctuations. They include monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors, catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors, the NMDA receptor antagonist amantadine and dopamine receptor agonists . Surgical therapy, usually with deep brain electrical stimulation, is available for a selected proportion of patients when medical therapy fails to control the motor symptoms.
You May Like: Is Sugar Bad For Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is often divided into two parts: early stage and advanced stage disease.
- Early stage: when symptoms appear and start to affect everyday activities, such as washing, getting dressed and walking.
- Advanced stage: when motor complications occur from the long term use of one of the main treatments for Parkinsons disease, levodopa.
Movement Disorders Similar To Parkinsons
Conditions causing excess movement or decreased movement that are sometimes associated with Parkinsons disease-like symptoms include:
What Movement Disorder Could I Have?
When making a Parkinsons diagnosis, your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms, perform a careful neurological exam, and, if necessary, carry out further tests to rule out other movement disorders.
Your symptoms may be caused by a movement disorder other than Parkinsons disease if:
- You display Parkinsons disease symptoms and features that are characteristic of an additional movement disorder.
- The results of a brain imaging study or laboratory test, such as a blood test, confirm the presence of another movement disorder.
- Your symptoms do not respond to Parkinsons disease medication.
Because movement disorders are not all treated the same way, it is important to get a proper diagnosis as early as possible so you can formulate the right treatment plan with your doctor.
Don’t Miss: When Was Muhammad Ali Diagnosed With Parkinson’s Disease
Stooping Or Hunching Over
Are you not standing up as straight as you used to? If you or your family or friends notice that you seem to be stooping, leaning or slouching when you stand, it could be a sign of Parkinson’s disease .
What is normal?If you have pain from an injury or if you are sick, it might cause you to stand crookedly. Also, a problem with your bones can make you hunch over.
Diagnosis And Management Of Parkinsons Disease
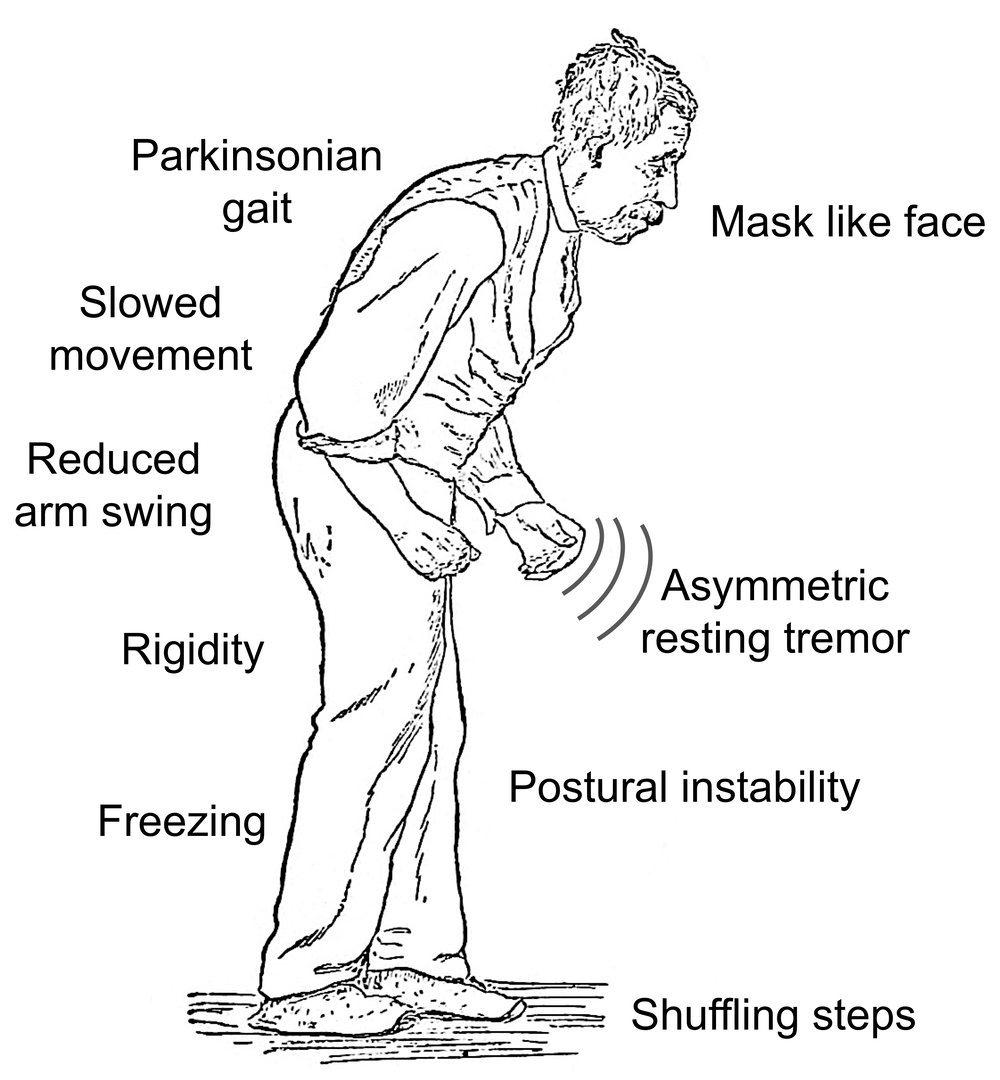
There are no diagnostic tests for Parkinsons. X-rays, scans and blood tests may be used to rule out other conditions. For this reason, getting a diagnosis of Parkinsons may take some time.;;
No two people with Parkinsons disease will have exactly the same symptoms or treatment. Your doctor or neurologist can help you decide which treatments to use.
People can manage their Parkinsons disease symptoms through:;
- seeing a Doctor who specialises in Parkinsons
- medication
- multidisciplinary therapy provided for example, by nurses, allied health professionals and counsellors
- deep brain stimulation surgery .
Recommended Reading: Is Golf Good For Parkinsons
Read Also: When Was Parkinson’s Disease First Discovered
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
| Other names | Diffuse Lewy body disease, dementia due to Lewy body disease |
|---|---|
| of a in a neuron of the ; scale bar=20 microns | |
| After the age of 50, median 76 | |
| Duration | |
| Average survival 8 years from diagnosis | |
| Frequency | About 0.4% of persons older than 65 |
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of characterized by changes in sleep, , , movement, and . Memory loss is not always an early symptom. The disease and is usually diagnosed when cognitive decline interferes with . Together with , DLB is one of the two . It is a common form of dementia, but the is not known accurately and many diagnoses are missed. The disease was first described by in 1976.
in which people lose the that normally occurs during and act out their dreamsis a core feature. RBD may appear years or decades before other symptoms. Other core features are , marked fluctuations in or alertness, and . A presumptive diagnosis can be made if several disease features are present, such as symptoms or certain results of , , , and . A definitive diagnosis usually requires an .
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms; others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Affect Speech
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
The type, number, severity and progression of Parkinsons disease symptoms vary greatly. Every person is affected differently they may not get every symptom.;
Some of the more common symptoms are:
- resting tremor
- rigidity
- blood pressure fluctuation;
- constipation.;
People living with Parkinsons for some time may experience hallucinations , paranoia ; and; delusions . These symptoms are able to be treated so have a talk with your doctor.
Neuropsychiatric Symptoms And Dementia
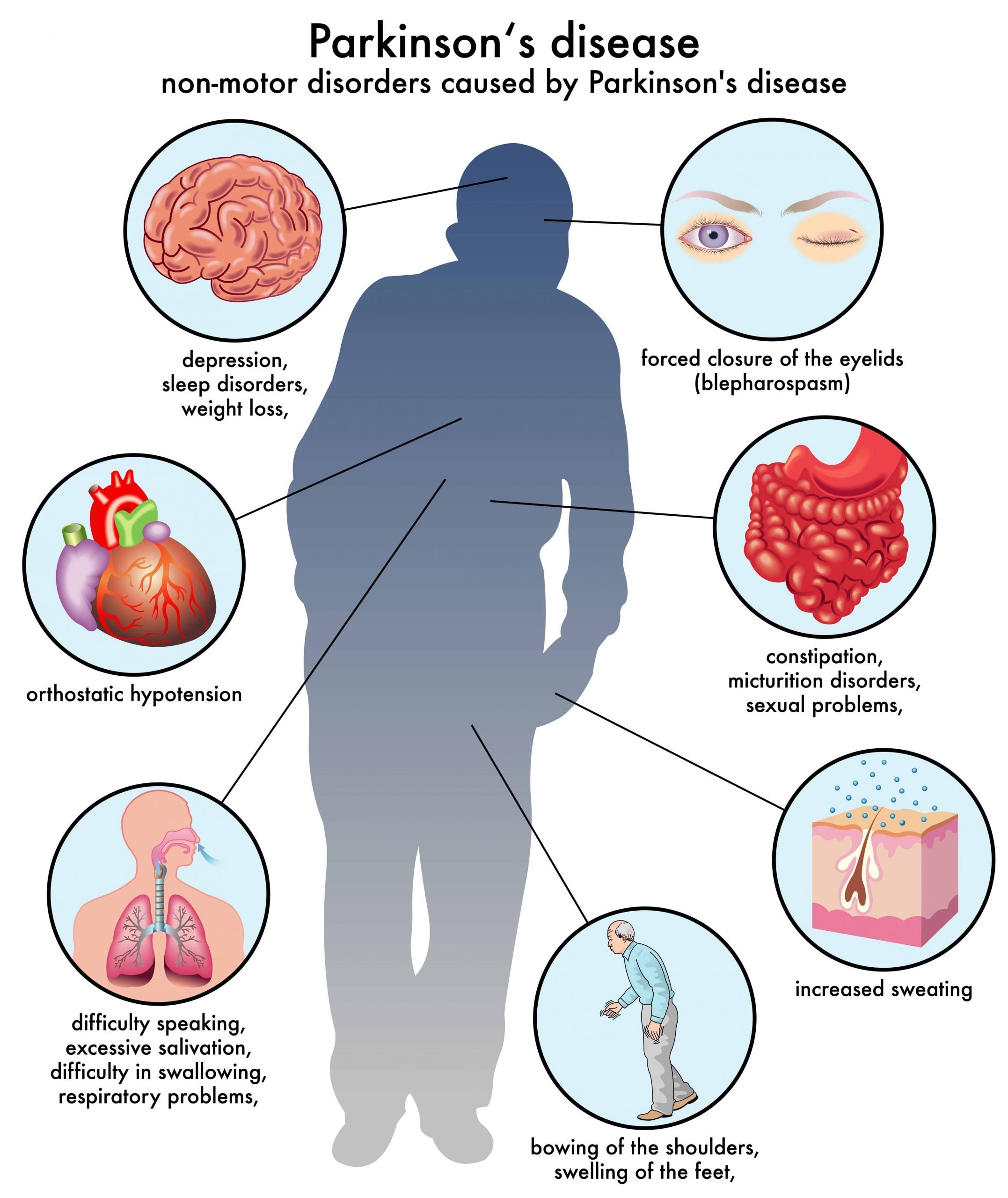
Visual hallucinations and illusions are common in PD and reportedly occur in a third to 40% of patients . Although virtually all anti-parkinsonian medications have been reported to induce hallucinations and psychosis, visual hallucinations have also been reported to occur prior to drug treatment . Neuropathological changes in the amygdala and hippocampus caused by the disease process seem to be implicated in the aetiology . Frequently, images of people, small animals or objects are conceived or the hallucinations may have multiple content. The images may be familiar or not. They last from seconds to minutes, and may recur over the day . Usually, non-demented patients retain insight and the hallucinations are usually not threatening. Less commonly, the hallucinations are olfactory , auditory and tactile . One study showed that visual component was lacking in 10% of cases . Minor visual phenomena such as sense of presence and visual illusions affect 17â72% of patients and delusions about 5% . Higher load of dopaminergic treatment may be related to the hallucinations, but disease severity, cognitive impairment, depression, older age and worse visual acuity may also be important .
Read Also: Why Do Parkinson’s Patients Have Tremors
This Explains Why Patients Can Experience Such Wildly Different Symptoms
Prior to this study, it was generally believed that there was only one type of Parkinsons disease. However, their work revealed that there are actually two major strains of the disease that can leave patients susceptible to a wide range of symptoms.;
Until now, many people have viewed the disease as relatively homogenous and defined it based on the classical movement disorders, said researcher Per Borghammer. But at the same time, weve been puzzled about why there was such a big difference between patient symptoms. With this new knowledge, the different symptoms make more sense and this is also the perspective in which future research should be viewed.;
Parkinsonism can be categorized into four different types. These are:
Primary parkinsonism, Familial neurodegenerative conditions causing parkinsonism.
What is Primary parkinsonism?Primary parkinsonism is due to idiopathic Parkinsons disease. It includes sporadic and familial cases and accounts for about 80% of parkinsonism cases.
What is Secondary parkinsonism?This form of parkinsonism, can be caused by a variety of issues. These include drug induced, infections, toxins, vascular, trauma to brain, hemi-atrophy hemi-parkinsonism, brain tumors, normal pressure hydrocephalus, hypoxia, and metabolic dysfunction.
Two other Parkinson plus conditions are progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasilar degeneration . They differ from Parkinsons disease in that:
Dont Miss: Life Expectancy After Parkinsons Diagnosis
The Parkinson ‘s Disease Foundation
Introduction:The Parkinsons Disease Foundation states that this disease is a chronic and progressive movement disorder. In another words, the disease typically worsens over time. Nearly one million people in the United States live with Parkinsons disease today . The cause of this disease is still being researched and tested, but as of now it is still unknown and has no cure. Since there is no cure, things like medications, treatments
You May Like: Can Surgery Cause Parkinson’s Disease
Clinical Manifestations Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease remains one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases, affecting 1% of the population older than the age of 65. The last 5 years have been marked by rapid developments in the understanding of the pathophysiology of PD as well as the introduction of a number of new drugs for symptomatic treatment of the disease. The diagnosis of PD is still made on purely clinical grounds, based on the original description by Parkinson in 1817. As a result of continuing advances in therapy, it is increasingly important to recognize PD in its earliest stages. It is no less critical to distinguish PD from other causes of parkinsonism because both prognosis and response to treatment are different.
- Previous article in issue
-
Address reprint requests to Amy Colcher, MD, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center, Pennsylvania Hospital, 330 South Ninth Street, Philadelphia, PA 19107
The Evolution Of Critical Symptoms Involved In Diagnostic Procedures Of Pd
- Diagnostic criteria: presence of bradykinesia and at least one of the following symptoms: muscular rigidity, 46 Hz rest tremor and postural instability
- Exclusion criteria: history of repeated strokes or head injury, encephalitis, early severe autonomic involvement or dementia, Babinski sign, negative response to levodopa treatment and MPTP exposure
- Supportive criteria : unilateral onset, rest tremor, progressive course, persistent asymmetry, excellent response to dopaminergic therapy, levodopa-induced dyskinesia, positive levodopa response five years or more and clinical course of ten years or more
Don’t Miss: Are There Any New Drugs For Parkinson’s
