Working With Your Doctor
Programming the neurostimulator takes place a few weeks after surgery. The settings vary by patient and are set by your neurologist. One question is how much control if any, the patient wants over the settings.
Ive had some neurologists that did not want the patient to have the option of changing the settings. Ive had others who do not hesitate to give the patient some degree of control. I want to be involved in my therapy and to have the capacity to change my settings if needed.
Having the DBS surgery has made a significant difference for me and greatly improved my quality of life. I am thankful that this therapy is available to those with PD and am excited to see what future advancements are made in neurostimulators.
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
For people with severe motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease that are not adequately controlled by medication, a treatment called deep brain stimulation may offer some relief.
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical placement of a small conductor called an electrode in the brain. The electrode delivers electrical stimulation that blocks the nerve signals that cause tremors.
Specialists at NYU Langones Center for Neuromodulation perform more than 100 deep brain stimulation procedures each year. Our neurologists, neurosurgeons, and psychiatrists provide a thorough evaluation to ensure youre a good candidate for the procedure.
How Effective Is Dbs
In randomized clinical trials, DBS has proven to be more effective than continued medical management alone. For patients with Parkinsons disease, DBS has been shown to remarkably increase the amount of on time with good symptom control, and many patients are able to reduce their medications significantly after the surgery.
Post-operation, the DBS electrical current can be turned off if needed and fine-tuned for optimal symptom control using a wireless programmer.
As with any surgery, there are risks and potential complications, but this surgery is well-tolerated for the vast majority of patients.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson Hereditary
Were Leaders In Innovation
At the Aurora Neuroscience Innovation Institute , a multidisciplinary team of world-renowned specialists and experts work together to combine proven surgical approaches with cutting-edge technologies and medical techniques.
Combined with our patient-centered approach, these capabilities create a truly best-in-class patient experience with a focus on better surgical outcomes and improved patient safety. Our team offers comprehensive, innovative and experienced care to address a wide variety of movement disorders and offer you individualized treatment plans.
- Get in touch
How Can Parkinsons New Zealand Help
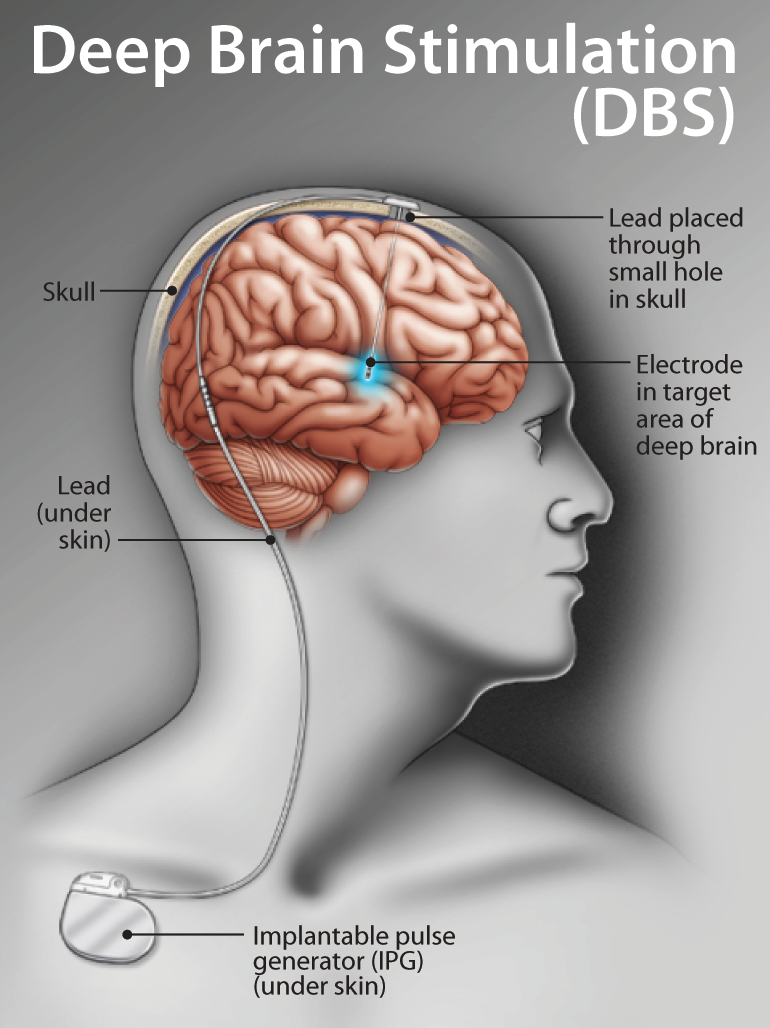
Parkinson’s New Zealand offers information and professional support to people living with Parkinsons. Our team of Parkinsons Community Educators can provide home visits for personalised sessions.
Community Educators work closely with the person with Parkinsons and their carers to develop a medical plan that upholds their health and lifestyle. Community Educators liaise with health professionals that treat Parkinsons in the community, including speech-language therapists, occupational therapists, and physiotherapists.
Parkinsons New Zealand also has support groups for members for sharing their coping strategies, experiences, and is a chance to establish social networks. Programs for people with Parkinsons include exercise, physiotherapy, hydrotherapy, and art or music therapy sessions.
You May Like: Familial Parkinson’s
Weighing The Risks And Benefits
First, did I need DBS? After all, this is brain surgery. And while minimal, there are some serious risks. One is reminded of this when meeting with their neurosurgeon. A brain hemorrhage due to surgery is one risk with permanent brain damage being the result.
I had to weigh this against the benefits of the surgery. For me, the primary benefit is less dyskinesia due to a reduction in the amount of Levodopa I was taking. My dyskinesia was called biphasic dyskinesia since I experienced it right after my Levodopa “kicked in” and when it was wearing off.
It became so debilitating that there were times when I needed a wheelchair to get around. After conferring with my neurologist and neurosurgeon I decided to have the surgery.
What Are The Benefits Of Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS provides good benefit for certain symptoms . Importantly, fluctuations usually improve a lot in response to DBS, since the stimulation goes on in an uninterrupted fashion. Although patients typically still need to take medication after undergoing DBS, they can often reduce their dosages so much that side effects improve substantially. Other symptoms, including balance problems, falls, and often speech impairment, may not respond favorably to DBS surgery.
Unlike older types of surgery for Parkinson’s disease, DBS does not involve intentional destruction of brain tissue. The jamming signal from DBS is adjusted as an outpatient to provide the patients with the optimal symptom relief. Also, as the patient’s condition changes, the pulse generator device can easily be re-programmed. Further surgery is not needed until the battery in the chest is replaced, typically three to five years later.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Power Savings And Adaptive Effect
The mean total electrical energy delivered with aDBS was significantly less than that with cDBS , so that the better improvements in clinical score were achieved with less than half the total electrical energy delivered. Similarly, when averaged over the whole block of stimulation, aDBS was only on 44.2 ± 2.4% of the time. This was well matched by random DBS, which was on 43.3% ± 1.5% of the time .2). Moreover, time on stimulation tended to progressively drop during stimulation in the aDBS mode. This was despite the use of a fixed beta threshold, suggesting that beta bursts became less frequent over the course of aDBS. The mean correlation coefficient between percentage stimulation time over each 10 seconds and total duration of DBS up to that point was 0.23 across subjects . This correlation was also individually significant in 3 of the 8 cases .
Decline in triggered stimulation duration over time. Dependency of proportion of time stimulated on duration of adaptive deep brain stimulation is shown for Subject 5. Solid and interrupted lines are result of linear regression and 95% confidence intervals, respectively. r = 0.567, p< 0.001.
How Deep Brain Stimulation Works
Exactly how DBS works is not completely understood, but many experts believe it regulates abnormal electrical signaling patterns in the brain. To control normal movement and other functions, brain cells communicate with each other using electrical signals. In Parkinson’s disease, these signals become irregular and uncoordinated, which leads to motor symptoms. DBS may interrupt the irregular signaling patterns so cells can communicate more smoothly and symptoms lessen.
Recommended Reading: Sam Waterston Stroke
Mechanism Of Action Of Dbs
Current hypotheses on the action mechanism of DBS include depolarization blockade , synaptic inhibition , synaptic depression , stimulation-induced disruption of pathological network activity , and stimulation of afferent axons projecting to the STN . Depolarization blockade and synaptic inhibition are likely to explain the similarity between the therapeutic benefit of DBS and lesional surgery. Recordings of decreased somatic activation in the stimulated nucleus favor these hypotheses . However, the increased output of projection neurons does not seem to be mediated by these phenomena . Another and currently favored hypothesis is that DBS overrides abnormal spike train patterns by an unphysiological, high-frequency pattern, and thereby masks pathological signals, which cause dysfunction of the remaining elements of the basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical and brainstem motor loop . The exact nature of the abnormal signals and the interaction between stimulation-induced neuronal responses and intrinsic brain activity remains elusive, but abnormalities of the firing rate and pattern of basal-ganglia neurons, changes in oscillatory activity and excessive synchronization at multiple levels of the motor loop have been proposed as pathophysiological correlates of motor symptoms in PD .
Resources For More Information
- Surgical option a potential life-changer for patients with OCD: Read and watch Erins story as she, a lively 21-year-old woman, fought her battle with OCD. This article explores how deep brain stimulation gave Erin her life back. The procedure was the first of its kind performed at Albany Medical Center the only facility offering this treatment between New York and Boston. In Erins own words, “Now, I can be who I really am and tell people my story and hopefully inspire people and help people along the way.
- Karen and Jims Story: A Shared Journey of Life, Love and DBS: Read about Karen and Jim. They were each diagnosed with Parkinsons before they met. Follow them on their journey as they fall in love after meeting each other from an online support group. See how they embraced each other and DBS.
- Kays Story A Parkinsons Disease Patient: Read about Kay, a 68-year-old woman suffering from Parkinsons disease. The article and video explore how DBS helped her regain her life. In Kays own words, Its like I had been turned on again. It was like a miracle.
Also Check: Is Parkinson Disease Hereditary
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
Deep brain stimulation is a therapy most often used to treat symptoms of Parkinsons disease, including tremor, rigidity, stiffness, slowed movement and walking problems. DBS is also used to treat essential tremor, dystonia, Tourette syndrome and obsessive/compulsive disorder .
How does DBS surgery work?
DBS involves implanting a device about the size of a stopwatch under the skin of the chest. The device delivers electrical stimulation to the brain through a thin insulated wire that connects to electrodes placed in the skull. DBS stimulates specific areas of the brain to treat and improve debilitating tremors and Parkinsons symptoms. Essentially, DBS is a brain pacemaker.
What is deep brain stimulation treatment for Parkinsons disease?
Because Parkinsons disease is considered a chronic and progressive disease, symptoms worsen over time. Parkinsons symptoms may include:
- physical tremor of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face
- slowness of movement
What are the benefits of DBS?
Deep brain stimulation has helped people remain in their careers, care for their families, resume favorite activities and once again do simple things in daily life. Clinical studies have shown that deep brain stimulation surgery, when added as treatment for Parkinsons disease, can:
Is Dbs Surgery Right For You
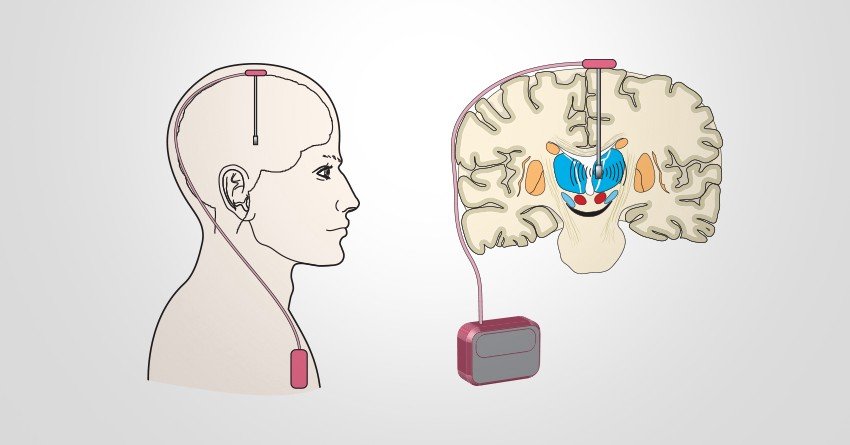
DBS is not an appropriate treatment for everyone with Parkinsons disease. Our neurology specialists carefully evaluate each patient to determine if DBS may be right for them.
If you answer yes to some of the questions below, it could be time to discuss DBS with a Scripps neurologist and find out if you may be a candidate.
- Are there times when medication is not working well and youre experiencing symptoms?
- Do you have trouble with involuntary wiggly types of movements ?
- In a typical day, do you take frequent doses of dopaminergic drugs? Examples include pramipexole , ropinirole , carbidopa/levodopa and carbidopa/levodopa/entacapone .
- Despite having been prescribed different drug combinations, do you experience any of the following side effects: sleepiness, nausea, hallucinations, confusion or thinking problems, lightheadedness upon standing or behavioral/personality changes?
- Do you respond to L-dopa therapy?
- Were you diagnosed with Parkinsons disease more than four years ago?
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
What To Expect After Dbs
Surgery to implant the leads generally entails an overnight stay, while the IPG is usually implanted as same-day surgery. During recovery, your surgeon will talk to you about caring for your wounds, when you can shower, and any activity restrictions. Its usually recommended that any heavy lifting be avoided for a few weeks.
After another two to four weeks, youll return to have your device programmed. This process will continue for several weeks to ensure the stimulation settings are optimal to control your symptoms. During these visits, you will be shown how to turn the device on and off with the handheld device and check the battery level.
Once the programming has been completed, you will have regular follow-up visits to check and adjust the stimulation to maintain the most benefit for your symptoms.
Neurosurgical Care At Brigham And Womens Hospital
The Department of Neurosurgery at Brigham and Womens Hospital , as well as the neurosurgery field in the U.S., were founded by Dr. Harvey Cushing in 1913. Since that time, our team has been devoted to the advancement of neurosurgical care, research, and education. A multidisciplinary staff of more than 100, including 13 clinical faculty, work together to provide patient-focused, world-class medical care for the entire spectrum of neurological diseases. We provide state-of-the-art Parkinson’s disease treatment through revolutionary techniques and advanced technology, such as our Advanced Multimodality Image Guided Operating suite.
Our neurosurgeons provide care at Brigham and Womens Hospital in Boston, as well as our community hospitals Brigham and Women’s/Mass General Health Care Center in Foxborough and Brigham and Women’s Ambulatory Care Center in Chestnut Hill. They perform more than 2,500 surgical treatments each year at these locations for patients from local, national, and international communities.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What You Need To Know
- Surgeons implant one or more small wires in the brain during a surgical procedure.
- The leads receive mild electrical stimulation from a small pulse generator implanted in the chest.
- Proper patient selection, precise placement of the electrodes and adjustment of the pulse generator are essential for successful DBS surgery.
- DBS does not fully resolve the symptoms of PD or other conditions, but it can decrease a patients need for medications and improve quality of life.
Brigham And Womens Hospital Neurosurgical Team
The neurosurgical team at BWH features internationally recognized surgeons who are all faculty at Harvard Medical School. Together they continue to build on our long and distinguished history by offering innovative, compassionate, and patient-centered care, and pioneering groundbreaking advances in the treatment of all neurosurgical conditions. Meet our neurosurgical team.
Read Also: Parkinson Disease Life Expectancy
What Care Is Needed After
On top of the wound care required with any surgery, DBS calls for special follow-up and ongoing care. Depression, falls, nausea, and problems with motor skills and swallowing can occur after DBS. In a follow-up appointment, doctors can address these issues and any other side effects of the device and/or the stimulation.1,2
Some follow-up care will last only a short time, depending on the issue. For instance, DBS can alter a persons mood, personality, and speech. Counseling, drugs, and speech therapy may help with these issues. A doctor can help find the best course of action in each case.1,2
People treated with DBS will need some extra care for the rest of their lives. Each persons device must be maintained and adjusted to meet their unique needs. Dosages of other drugs used to treat PD may also need to change over time.1,2,4
Risks And Side Effects Of Deep Brain Stimulation
Like any surgery, deep brain stimulation can have side effects, and it carries potential risks. Its also important to consider the complications and side effects of medications you take since their dosages can often be reduced following surgery.
While DBS may cause side effects, it may also reduce side effects from medications.
Read Also: Parkinsonian Syndrome Life Expectancy
Pros Of Deep Brain Stimulation
- Symptom Reduction: DBS often reduces symptoms significantly. These include motor symptoms like stiffness, tremor, slowness and dyskinesia. DBS has also been shown to aid in on/off fluctuations, improve mood and quality of life, and increase overall energy level.
- Little to No Damage: In contrast to previous methods, DBS does not damage portions of the brain, nor remove nerve cells.
- Utilizing DBS in addition to levodopa could decrease a persons need for medication, thus, decreasing medication access and cost issues, as well as levodopa side effects.
- Individualized Treatment: Electrodes and stimulation frequency and intensity can be controlled by physicians and the individual with DBS, and can be subjectively altered when needed.
Quality Of Patient Care
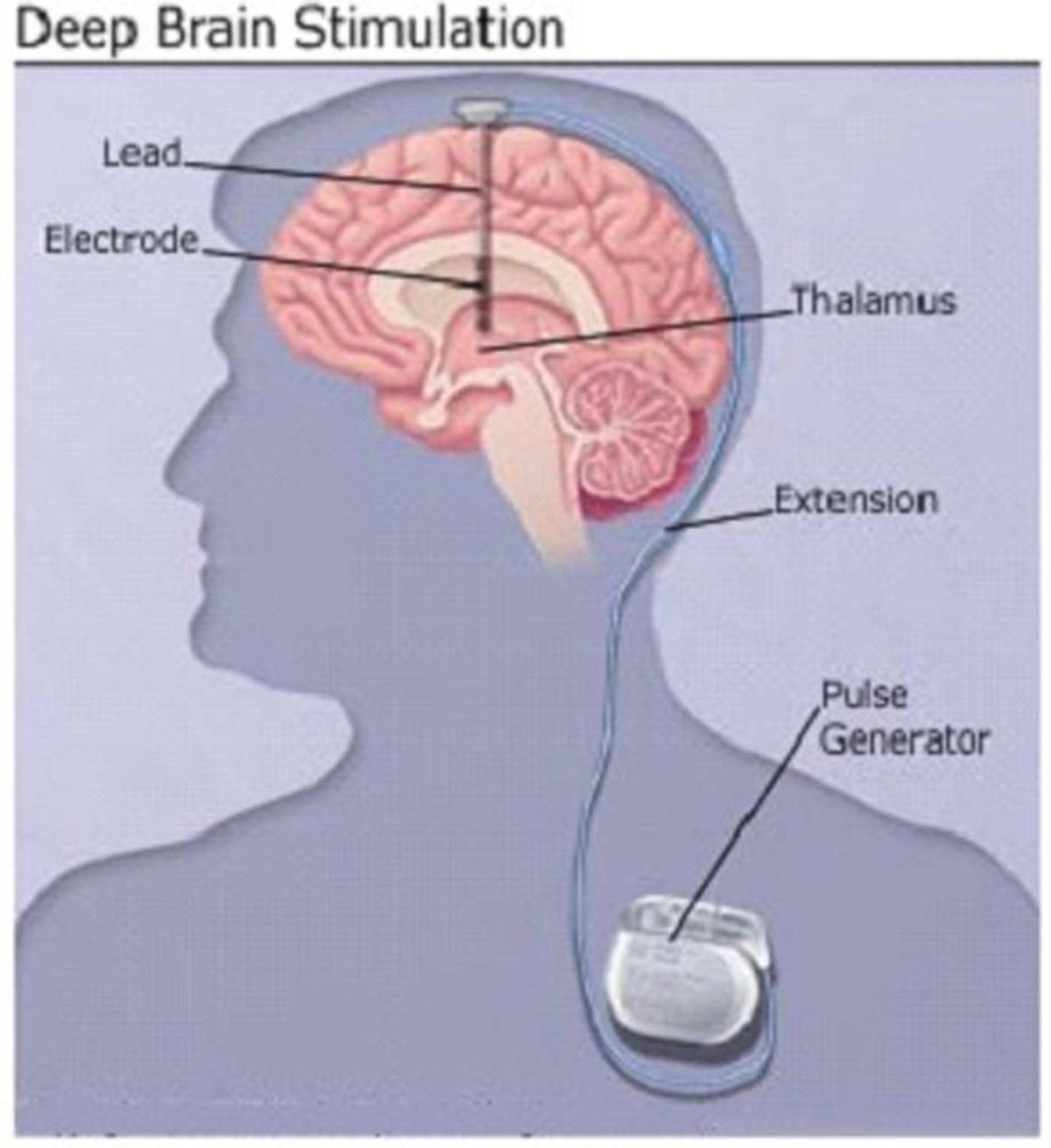
BWH is committed to providing all of our patients with the safest, highest-quality, most-satisfying care possible and follow established protocols that have been shown to improve patient outcomes. Our Inpatient Satisfaction Survey, sent to patients to assess their total care experience, helps us to monitor what we are doing well and areas for improvement. We pride ourselves in the Quality of Patient Care we provide and how we are measured compared with other hospitals.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Someone With Parkinson Live
How Is Deep Brain Stimulation Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation delivers electrical impulses to a targeted area of the brain that is responsible for the movement symptoms caused by Parkinsons disease. The electrical impulses disrupt the abnormal activity that occurs in the brains circuitry, which is causing the symptoms.
There are three areas in the brain that can be targets for deep brain stimulation in patients with Parkinsons disease. They are the subthalamic nucleus, the globus pallidus internus, and the ventral intermediate nucleus of the thalamus. Each of these areas plays a role in the brains circuitry that is responsible for the control of movement.
The specific area in the brain to target in an individual with Parkinsons disease depends on symptoms that need to be treated. For example, deep brain stimulation of subthalamic nucleus is effective for all major movement symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, such as tremor, slowness of movement , stiffness , and problems with walking and balance. Deep brain stimulation of globus pallidus is another effective target for a wide range of Parkinson’s symptoms. The thalamic target is sometimes selected for patients with tremor symptoms. The recommended target for each patient is made collaboratively with the neurologist, neurosurgeon and other caregivers involved in the decision making process.
What Happens During The Procedure
In the operating room, your scalp will be injected with numbing medication. Your head will be placed in a frame to keep it from moving. Small holes will be drilled into your scalp to allow the implantation of electrodes.
Youll be awake during surgery so you can respond to questions and move particular areas of your body when prompted. This, along with imaging tests, helps pinpoint the areas of the brain where symptoms originate. This is where electrodes will be placed.
Electrodes may be implanted on one or both sides of your brain. The neurostimulator will be implanted under the skin near your collarbone or lower in your chest. Leads will go underneath your skin from head to shoulder, connecting the electrodes to the neurostimulator. The tiny holes in your skull will be closed.
After surgery, youll be monitored for complications. Youll spend at least 24 hours in the hospital, but longer if you have complications.
Some risks of surgery are:
- bad reaction to anesthesia
- allergic reaction to materials in the implanted device
- pain or swelling at the surgical site
- infection
Also Check: What Color Represents Parkinson’s Disease

