Genetics Testing And Research
Although there may be no direct benefit to you at the present time, the results of genetic testing can help further Parkinsons research by allowing scientists to better understand the disease and consequently develop new treatments. For example, a mutation in the gene that codes for the protein alpha-synuclein leads to a specific type of familial Parkinsons disease. Although this mutation only accounts for a small percentage of cases, knowledge of this mutation has had broader effects. The study of this genetic mutation led to the discovery that alpha-synuclein clumps together to form Lewy bodies which have been consistently found in the brains of all individuals with Parkinsons disease not just those with the SNCA mutation. Thus, one gene mutation has led to a critical finding in the field of Parkinsons research.
Genetics testing is a very personal decision but a cautionary note: anytime that genetic testing is considered, particularly in a disease condition where there is no change in treatment based on genetic findings, it would be my recommendation to see a genetics counselor to discuss the impact this information will have on you the patient and your family.
When To See A Doctor About Parkinsons
There isnt one specific test to diagnose Parkinsons disease. Doctors will usually evaluate your symptoms and perform several tests to determine if you have the condition. If you notice the following early warning signs, then you should see a doctor.
The early warning signs of Parkinsons disease include:
Current Genetic Testing Practice
The vast majority of participants ordered genetic testingon ten or fewer patients in the 12 months prior to completing the study.Furthermore, most participants reported that only ten or fewer of theirpatients reported undergoing direct-to-consumer testing . Inaddition, participants reported that few of their patients received genetictesting either in research projects that returned results to patients or in research projects that did not returnresults to patients. For either type of study design , more than 80% of clinicians reported ten patients or fewer who hadgenetic testing. In contrast to genetic testing, DNA banking under researchprotocols was more prevalent. Thirty percent of respondents reported banking DNAfor 11 or more patients in the past year . Consistent withresponses citing limited genetic testing and reporting, caring for patients withknown pathogenic variants was rare among survey respondents. Only 5.5% and 4.9%of responders reported providing care to more than ten known LRRK2 or GBApatients, respectively. In total, participants reported providing care for 490known LRRK2 carriers and 402 known GBA carriers. Providing care for patients withknown Parkin , PINK-1 , SNCA , and VPS35 pathogenic variants was anecdotal .
Read Also: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Genes Connected To Parkinson’s
SNCA
In 1997, researchers at the National Institutes of Health made the first Parkinsons genetic connection, discovering that mutations in the SNCA gene were common in several families who had many members with Parkinsons. While mutations in this gene are rare, they have taught us invaluable information about PD.
The SNCA gene instructs the body to make the protein alpha-synuclein, which for reasons that are not yet known, clumps in the brain cells of people with PD. Study of the SNCA gene led to this understanding that applies to nearly all people with the disease. Since then, alpha-synuclein has been a major target of new drugs for Parkinsons.
LRRK2
Another gene that plays a role in Parkinsons is LRRK2, which accounts for one to two percent of all cases. For people of particular ethnic backgrounds Ashkenazi Jewish and North African Berber descent mutations in the LRRK2 gene account for a much greater number of cases than in the general PD population. Mutations in LRRK2 lead to too much activity of the LRRK2 protein, though recent research indicates people without a mutation can also have overactivity of LRRK2.
Shake It Up are funding several studies into LRRK2 and you can learn more about these here.GBA
PRKN
People Who Already Have Pd: Should I Get Tested And What Do I Do With The Results
Up until recently, even people with PD with a very extensive family history of PD would not necessarily receive genetic testing because there were no clear uses for the results. There has been research directed at figuring out whether PD caused by or associated with certain mutations have particular clinical characteristics . However, there remains so much variability in clinical characteristics even among people with the same PD mutation, that there are still no clear practical implications in knowing whether a PD patient harbors a particular mutation. There is also, so far, no difference in treatment or management of PD whether or not the patient harbors one of the known mutations. That may change however, with the advent of clinical trials that target particular mutations.
There are two genes that have received particular attention recently because medications are being developed that target those with mutations of these genes.
GBAis a gene that increases the risk of developing PD. The gene encodes for the GBA enzyme, a protein used by the body to break down cellular products. Having two abnormal GBA genes causes Gauchers disease, which is characterized by the buildup of these cellular products resulting in fatigue, bone pain, easy bleeding and an enlarged spleen and liver. When a person inherits only one abnormal gene, he or she does not develop Gauchers disease, but does incur a small increased risk of PD. Most people with one mutated GBA gene do not develop PD.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
Can Parkinsons Be Passed From Parent To Child
Its rare for Parkinsons disease to be passed down from parent to child. Most cases of Parkinsons arent hereditary. But people who get early-onset Parkinsons disease are more likely to have inherited it.
Having a family history of Parkinsons disease may increase the risk that youll get it. This means that having a parent or sibling with Parkinsons slightly increases the risk.
In most cases, the cause of Parkinsons disease remains unknown. But researchers have identified multiple risk factors that can increase your chances of getting this disease.
Risk factors for Parkinsons disease include:
- mutations in specific genes associated with Parkinsons
- having a family history of Parkinsons or a first-degree family member with Parkinsons
- being older, especially above the age of 60
- exposure to herbicides and pesticides
- being assigned male at birth
- history of brain injury
Can I Be Tested
Tests are generally arranged through a healthcare professional who can then interpret the results and give advice on how the information can be used.
Genetic testing is now also available from a number of companies who deal directly with people being tested. This can have several implications:
- Your doctor is not automatically informed of results, allowing you to keep findings to yourself if you wish.
- Results will not automatically be passed to your insurance company, although you should check your policy as you may be required to reveal all genetic test information. Failure to do so could invalidate your cover.
- You may not get the opportunity to discuss your test results and their implications with an experienced healthcare professional.
Important! Thoroughly check the credentials of any company offering genetic testing, as not all provide a high standard of service.
You May Like: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Other Factors Influencing Parkinson’s Disease Risk
Other factors besides genetics can influence someone’s chances of developing Parkinson’s disease, including:
- Age: The risk of developing Parkinson’s disease increases as a person ages.
- Sex: Males have a higher chance of developing Parkinson’s disease than females.
- Family history: First-degree relatives of an individual with Parkinson’s disease have a higher chance of developing Parkinson’s disease.
- Exposure to certain chemicals increases the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
Study Examines Genetics Of Parkinsons In Latinos
It also established the Hispanic Parkinsons Advisory Council in December 2019. Led by Mata, the groups goal is to increase Latino participation in PD GENEration. Since the councils inception, PD GENEration has doubled the percentage of Latino participants from approximately 3% to 6%.
Adding more Latinos and Parkinsons patients as a whole could help uncover the true share of those whose cause of disease is familial, environmental, or idiopathic, meaning the specific cause of the disease is unknown.
According to María De León, MD, a Latino woman with Parkinsons who participated in PD GENEration and who is a movement disorder neurologist, PD GENEration gives minorities more information about their disease than ever before. This knowledge will help them in the long run as new medicines are developed, she said.
Patients are then able to participate in further clinical studies and trials and do other treatments that could then lead to further information and developing the science and also perhaps, to a cure of any given subtype of Parkinsons thats caused by genetic difference, said Leon in the joint interview with Mata. Leon, 53, a resident of East Texas, also is part of the Hispanic Parkinsons Advisory Council.
Historically, its been estimated that Parkinsons is caused by genetic factors in about 10% of patients. But for the more than 2,000 people who have been tested through the initiative, that rate is closer to 15%16%.
You May Like: Parkinson Anxiety Scale
Bioinformatics And Clinical Interpretation
Bioinformatics
Clinical interpretation
We provide customers with the most comprehensive clinical report available on the market. Clinical interpretation requires a fundamental understanding of clinical genetics and genetic principles. At Blueprint Genetics, our PhD molecular geneticists, medical geneticists and clinical consultants prepare the clinical statement together by evaluating the identified variants in the context of the phenotypic information provided in the requisition form. Our goal is to provide clinically meaningful statements that are understandable for all medical professionals regardless of whether they have formal training in genetics.
Variant classification is the corner stone of clinical interpretation and resulting patient management decisions. Our classifications follow the ACMG guideline 2015.
The final step in the analysis is orthogonal confirmation. Sequence and copy number variants classified as pathogenic, likely pathogenic and variants of uncertain significance are confirmed using bi-directional Sanger sequencing by orthogonal methods such as qPCR/ddPCR when they do not meet our stringent NGS quality metrics for a true positive call.
Why Should I Participate
-
As part of the study, qualifying participants will receive free at-home genetic testing to determine if you have the G2019SLRRK2 mutation.
-
Get a free explanation of your genetic results from a qualified genetic counsellor if you test positive for the genetic mutation.
-
Have the chance to participate in vital research entirely from home.
-
People who test positive for the genetic mutation and complete this program will automatically have the chance to be assessed for eligibility to take part in a future precision medicine treatment study.
Also Check: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Research Has Been Done And The Need To Improve:
CANTAB Connect for Parkinsons disease is a rapid, reliable, and highly sensitive system for academic research or clinical trials. The CANTAB battery has demonstrated potential advantages when compared to other neuropsychological tests, such as for detecting cognitive impairment in Parkinsons disease7 and also avoiding floor and ceiling effects. It is highly sensitive to disease progression, can discriminate cognitive impairment due to comorbid depression, and detects untoward effects of medications on cognition11-14. It has also been shown to predict conversion to dementia in patients with Parkinsons disease15. The use of CANTAB in research of Parkinsons disease is clinically relevant: cognitive decline measured by the battery correlates with loss of day-to-day functioning in patients with Parkinsons disease16.
Furthermore, CANTAB maximises scope for sample enrichment, and for demonstrating disease modifying capability of interventions.
There are currently over 125 peer-reviewed publications supporting the application of CANTAB in research of Parkinsons disease. To find out more, .
What Are The Benefits Of Genetic Testing
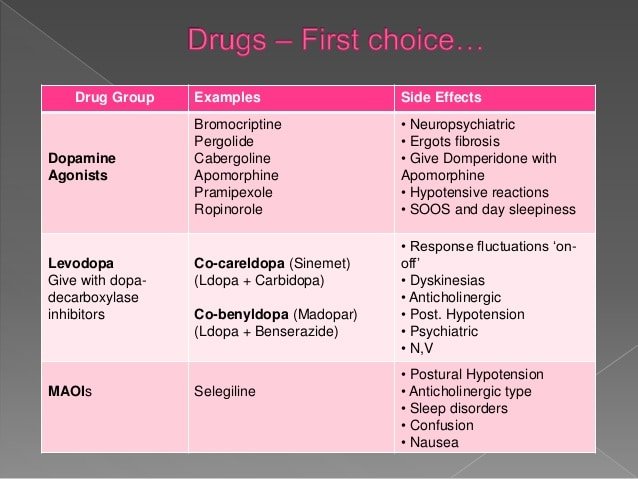
ESCAPE is developing a new therapy for patients with Parkinson’s disease caused by a mutation in theLRRK2 gene. It is hoped that this therapy may be able to stop or slow the progression of the disease. Since most people with Parkinsonâs disease have never been tested for LRRK2 mutations, ESCAPE is providing free genetic testing via mail which is an at-home saliva test. If a patient is found to have a mutation in theLRRK2 gene they will be invited to take part in certain clinical studies for patients with Parkinson’s disease and this specific gene mutation.
Also Check: What Happens When You Stop Taking Carbidopa/levodopa
Who Should Consider A Genetic Test For Parkinsons
There are two groups of people who might consider getting genetic testing and we will discuss each group separately.
Genetic testing for PD is a common request and a number of commercial labs perform panels of genetic testing for PD. You may ask: How can I test myself for Parksinons? Whether youre considering getting a genetic test through your doctor, or performing one at home, its important to note that at-home test dont map the entire gene for mutations. Genetic testing through your doctor will test for GBA, PARK7, SNCA, LRRK2, parkin and PINK1.
Both groups are faced with two questions: Should I get genetic testing? And if so, what should I do with the results? Before we address these two questions, we need to learn more about the complexity of genetic testing in PD.
When Should A Person Seek Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is available for some genes related to Parkinsons disease, but testing may not provide useful information to individuals.
For one thing, a wide range of genes may play a role, and it is not possible to test them all. A person may also have a relevant feature but not go on to develop Parkinsons disease.
For example, only around 0.7% of people with symptoms of Parkinsons disease have changes in the LRRK2 gene, and around 0.3% have changes in the PRKN gene, according to a 2020 review.
Finding out in advance if a young person has the gene may help them prepare for the future if there is strong evidence of a family history of the condition. However, the results are unlikely to be conclusive and may cause unnecessary anxiety.
Anyone who is interested in genetic testing should discuss the pros and cons with a doctor and consider genetic counseling if they decide to go ahead.
The Parkinsons Foundation notes that testing is often hard to access. It can also be costly, and health insurance may not cover it. Genetic counseling can be an additional cost.
Read Also: Does Senator Susan Collins Have Parkinsons
What To Know About Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can help identify changes in our DNA that may be linked to Parkinsons. Learning your genetic status is a personal decision, but the results may help you take action in your health and advance science closer to cures.
Some of the greatest strides in understanding Parkinsons disease and developing new therapies have come from the study of human genetics. Read more below on what to consider before genetic testing and where to access this type of testing.
Navigating Clinical Trials
The Michael J. Fox Foundation’s guide and related materials will help you learn the basics of clinical research and gain an understanding of the valuable contributions made by study volunteers. Learn about genetic research and testing in Chapter 3 of the guide.
Ask the MD
Rachel Dolhun, MD, is a board-certified movement disorder specialist and The Michael J. Fox Foundation’s Senior Vice President of Medical Communications. In this short video, she explains what to expect when you opt for genetic testing and genetic counseling in Parkinson’s.
New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.s Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But thats now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
Also Check: How Did Parkinson’s Get Its Name
What Determines Who Gets Parkinson’s Disease
In most cases inheriting a non-working copy of a single gene will not cause someone to develop Parkinson’s disease. We believe that many other complicating factors such as additional genes and environmental factors determine who will get the condition, when they get it and how it affects them. In the families we have studied, some people who inherit the gene develop the condition and others live their entire lives without showing any symptoms. There is a lot of research on genes and the environment that is attempting to understand how all these factors interact.
Genetic Testing in Parkinson’s Disease
Genetic testing has recently become available for the parkin and PINK1 genes. Parkin is a large gene and testing is difficult. At the current stage of understanding, testing is likely to give a meaningful result only for people who develop the condition before the age of 30 years. PINK1 appears to be a rare cause of inherited Parkinson’s disease. A small percentage of those developing the condition at an early age appear to carry mutations in the PINK1 gene. Genetic testing for the PARK7, SNCA and LRRK2 genes is also available.
Additional Resources
How Hereditary Is Parkinson’s Disease
If your mom or dad gets Parkinson’s disease, you might wonder if you’ll get it, too. The good news is that the chance of inheriting Parkinson’s disease is rare . Just how hereditary Parkinson’s disease is depends on the exact mutation involved.
There are two categories of genetic factors linked to Parkinson’s. The first is “causal,” meaning the gene itself is capable of bringing on the disease.
One example of a causal link to Parkinson’s disease can be found in the SNCA gene. Researchers know of at least 30 mutations on this particular gene that can cause Parkinson’s disease, especially in people younger than 50 years old.
The SNCA gene tells the body how to make a protein called alpha-synuclein. When the gene has a mutation, the body may produce too much alpha-synuclein or versions of the protein with an incorrect shape. Either of these problems can lead to alpha-synuclein to gather in the brain in clusters called Lewy bodies, which disrupt normal brain functioning. Lewy bodies are associated with Parkinson’s, along with a range of other diseases .
Not all genetic mutations cause Parkinson’s disease, though. “Associated” genetic factors for Parkinson’s increase a person’s odds of developing the disease, but aren’t directly responsible for it.
RELATED: Does Having Your Appendix Removed Cause Parkinson’s?
“You’re susceptible, but you need something else present as well ,” Dr. Litvan says. “That could be other genes or it could be an environmental factor.”
You May Like: Parkinson Disease Ribbon
