What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative and chronic brain disorder that affects movement. It can affect other brain functions such as learning and memory.;
What Are Symptoms of Parkinsons Disease?
Parkinsons disease usually starts slowly and may only cause mild symptoms early on. As the condition progresses, symptoms may begin to affect a person’s ability to do everyday activities, and as the disease becomes severe, people may need help with self-care.;
The three primary symptoms of Parkinsons disease include:;
- Shaking , which often start in the fingers or hands
- Slow movement
Other symptoms of Parkinsons disease may include:;
- Loss of balance;
- Loss of ability to think clearly
- Losing touch with reality or seeing things that aren’t there
- Sleep problems such as insomnia and daytime sleepiness
- Tiredness
- Sudden drop in blood pressure on standing that causes dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting
How Is Parkinsons Diagnosed
Doctors use your medical history and physical examination to diagnose Parkinson’s disease . No blood test, brain scan or other test can be used to make a definitive diagnosis of PD.
Researchers believe that in most people, Parkinson’s is caused by a;combination of;environmental and genetic;factors. Certain environmental exposures, such as pesticides and head injury, are associated with an increased risk of PD. Still, most people have no clear exposure that doctors can point to as a straightforward cause. The same goes for genetics.;Certain genetic mutations are linked to an increased risk of PD. But in the vast majority of people, Parkinsons is not directly related to a single genetic mutation. Learning more about the genetics of Parkinsons is one of our best chances to understand more about the disease and discover how to slow or stop its progression.
Aging is the greatest risk factor;for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60.;Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
Men are diagnosed with Parkinsons at a higher rate than women and whites more than other races. Researchers are studying these disparities to understand more about the disease and health care access and to improve inclusivity across care and research.;
Aging is the greatest risk factor;for Parkinsons, and the average age at diagnosis is 60.;Still, some people get PD at 40 or younger.
The Michael J. Fox Foundation has made finding a test for Parkinsons disease one of our top priorities.
Living With Parkinsons Disease
Depending on severity, life can look very different for a person coping with Parkinsons Disease. As a loved one, your top priority will be their comfort, peace of mind and safety. Dr. Shprecher offered some advice, regardless of the diseases progression. Besides movement issues Parkinsons Disease can cause a wide variety of symptoms including drooling, constipation, low blood pressure when standing up, voice problems, depression, anxiety, sleep problems, hallucinations and dementia.; Therefore, regular visits with a neurologist;experienced with Parkinsons are important to make sure the diagnosis is on target, and the symptoms are monitored and addressed.; Because changes in your other medications can affect your Parkinsons symptoms, you should remind each member of your healthcare team to send a copy of your clinic note after every appointment.
Dr. Shprecher also added that maintaining a healthy diet and getting regular exercise can help improve quality of life.;Physical and speech therapists;are welcome additions to any caregiving team.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Genetic Link
How Does Parkinsons Progress
Parkinsons is a chronic and slowly progressive disorder. This means that symptoms normally appear slowly and develop gradually over time. The stage at which symptoms appear, speed at which they progress and the severity of those symptoms will vary from person to person. The most important point is that Parkinsons affects everyone differently.
There are a wide range of symptoms, but it is highly unlikely that you will experience every possible symptom. Some of the early symptoms of Parkinsons include handwriting changes, reduced sense of smell, tiredness and constipation. As Parkinsons progresses symptoms will change over time, and new symptoms will emerge. It can take many years for symptoms to progress to a point where they cause problems.
Ultimately symptoms will begin to impact on your day to day life. Many symptoms are related to physical movement, so you may find that walking becomes difficult. You may also experience non-movement symptoms such as mood changes, disrupted sleep or difficulty communicating. As these symptoms worsen it may become difficult to manage all of your daily activities.
Currently, there is no known way to slow the progression of Parkinsons. However, medications and other treatments can help to effectively manage your symptoms. To ensure the effectiveness of medications, they will need to be reviewed regularly by your specialist or doctor.
Drug Therapy And Research
If the disease progresses beyond minor symptoms, drug treatment may be indicated. Drug therapy for Parkinsonâs typically provides relief for 10â15 years or more. The most commonly prescribed medication is L-dopa , and this helps replenish some of the depleted dopamine in the brain. Sinemet, a combination of levodopa and carbidopa, is the drug most doctors use to treat Parkinsonâs disease. Recent clinical studies have suggested, in the younger person, the class of drugs called âdopamine agonistsâ should be used prior to levodopa-carpidopa except in patients with cognitive problems or hallucinations. In those older than 75, dopamine agonists should be used cautiously because of an added risk of hallucinations.
Other drugs are also used, and new drugs are continually being tested. It is common for multiple drugs to be prescribed because many of them work well together to control symptoms and reduce side effects. Contrary to past beliefs, starting Sinemet in newly diagnosed people does not lead to early symptoms of dyskinesia . Current knowledge is that the disease progression causes dyskinesias, not a âresistanceâ to the drug.
Quality of life studies show that early treatment with dopaminergic medications improves daily functioning, prevents falls, and improves a personâs sense of well-being.
Read Also: Parkinson Life Expectancy Early Onset
Hand And Finger Stimulation Exercises
I have done a lot of hand/finger stimulation and experimented to optimize such exercises, in the spirit of Curiosity and Play.;I’ve personally found significant benefit in pursuing this line of research. Indeed, I have managed to recover a lot of my independence and quality of life through hand and finger therapy, and I know just how much of a major part it has played in my own progressive symptom reduction.
I therefore encourage everyone with PD to do as much hand and finger stimulation as possible, through games and play and self-discovery. By doing nothing, the only thing that will happen is that out situation will rapidly become worse, because we will lose the use of our hands quicker and consign ourselves to increased suffering. By applying neuroplasticity techniques , we can delay the worse ravishes of the disease or even, like in my own case, continuously push the symptoms back and recover some independence. I feel this is an important message for those newly diagnosed, in particular.
Here are some suggestions of the type of stimulatory exercises and games which can help, more ideas which I have personally found beneficial will be provided in forthcoming articles.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Read Also: Is Protein Bad For Parkinson’s Disease
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Foster A Good Relationship
Lastly, maintaining your relationship and communication with the person with Parkinsonâs can be the most challenging and rewarding aspect of caregiving. As Parkinsonâs disease progresses, the roles change and the person with Parkinsonâs may go from being an independent head of the household to a very dependent person requiring a significant level of care. However, research shows that despite high levels of strain, caregivers with good quality relationships have reduced depression and better physical health. Remember, as a caregiver your service to your loved one is beyond measure in terms of love, depth of care, and concern.
Don’t Miss: What Brain Structure Is Affected By Parkinson’s
What Is The Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
There is currently no treatment to cure Parkinson’s disease. Several therapies are available to delay the onset of motor symptoms and to ameliorate motor symptoms. All of these therapies are designed to increase the amount of dopamine in the brain either by replacing dopamine, mimicking dopamine, or prolonging the effect of dopamine by inhibiting its breakdown. Studies have shown that early therapy in the non-motor stage can delay the onset of motor symptoms, thereby extending quality of life.
The most effective therapy for Parkinson’s disease is levodopa , which is converted to dopamine in the brain. However, because long-term treatment with levodopa can lead to unpleasant side effects , its use is often delayed until motor impairment is more severe. Levodopa is frequently prescribed together with carbidopa , which prevents levodopa from being broken down before it reaches the brain. Co-treatment with carbidopa allows for a lower levodopa dose, thereby reducing side effects.
In earlier stages of Parkinson’s disease, substances that mimic the action of dopamine , and substances that reduce the breakdown of dopamine inhibitors) can be very efficacious in relieving motor symptoms. Unpleasant side effects of these preparations are quite common, including swelling caused by fluid accumulation in body tissues, drowsiness, constipation, dizziness, hallucinations, and nausea.
Social Engagement And Parkinson’s Disease
See the groundbreaking work of Dr Stephen Porges to understand more about this aspect of our Nervous System and its role in wellness and disease,;based on the fact that mammals have a more evolved part of the Nervous System specifically designed for purposes of Social Engagement and Social Co-operation.
Social Engagement involves mainly the Cranial Nerves and their use in social functions such as making sounds and vocal calls for communication, and in facial expressiveness for transmitting emotional states to each other. Dysregulation of this Social Engagement part of our NS seems now to be a principal underlying cause in many chronic conditions, especially in PD, where loss of voice and loss of facial expression are major symptoms. See
You May Like: Does Alcohol Make Parkinson’s Symptoms Worse
Changes In Sleep With Aging
As people age, they experience a number of changes in their circadian rhythms, and among the most noticeable are the changes in the sleep-wake cycle.; Older people tend to wake up earlier and go to bed earlier than they did when they were younger. ;They wake up more often during the night and have more difficulty going back to sleep than younger people.; They also tend to sleep more during the daytime hours.; Therefore, if one looks at total sleep time over the 24-hour day, the total time spent sleeping changes very little but the distribution of sleep may be quite different.; Younger people experience a consolidated nighttime episode with little or no daytime sleep, whereas older individuals experience sleep episodes throughout the 24-hour day.; Daytime sleepiness is affected by two major factors:; the amount and quality of nighttime sleep, and the strength of the circadian rhythm.; In addition, older people tend to have a reduced amount of N3 or deep slow wave sleep.
Problems With Balance Or Walking
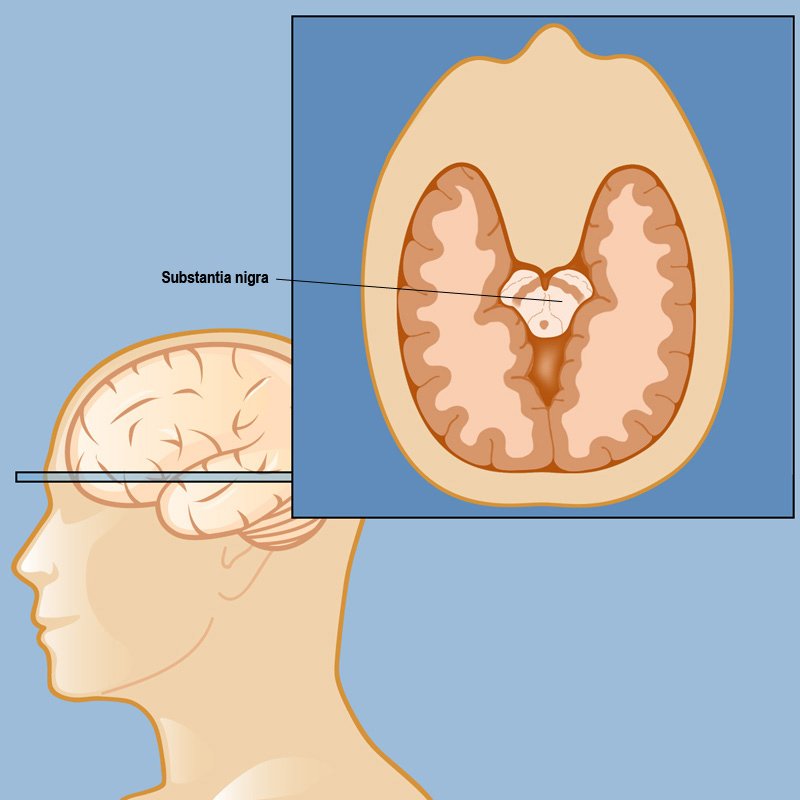
Bradykinesia can also contribute to increasing instability, walking difficulties and changes in gait. An early symptom of this is a decrease in the natural swing of one or both arms when walking. As things progress, the steps you take may become slower and smaller, and you may start shuffling your feet.
Some people with Parkinsons disease may also experience freezing episodes where it can feel like their feet are stuck in place, which can increase the risk of falling.
Recommended Reading: Does Adderall Help Parkinson’s
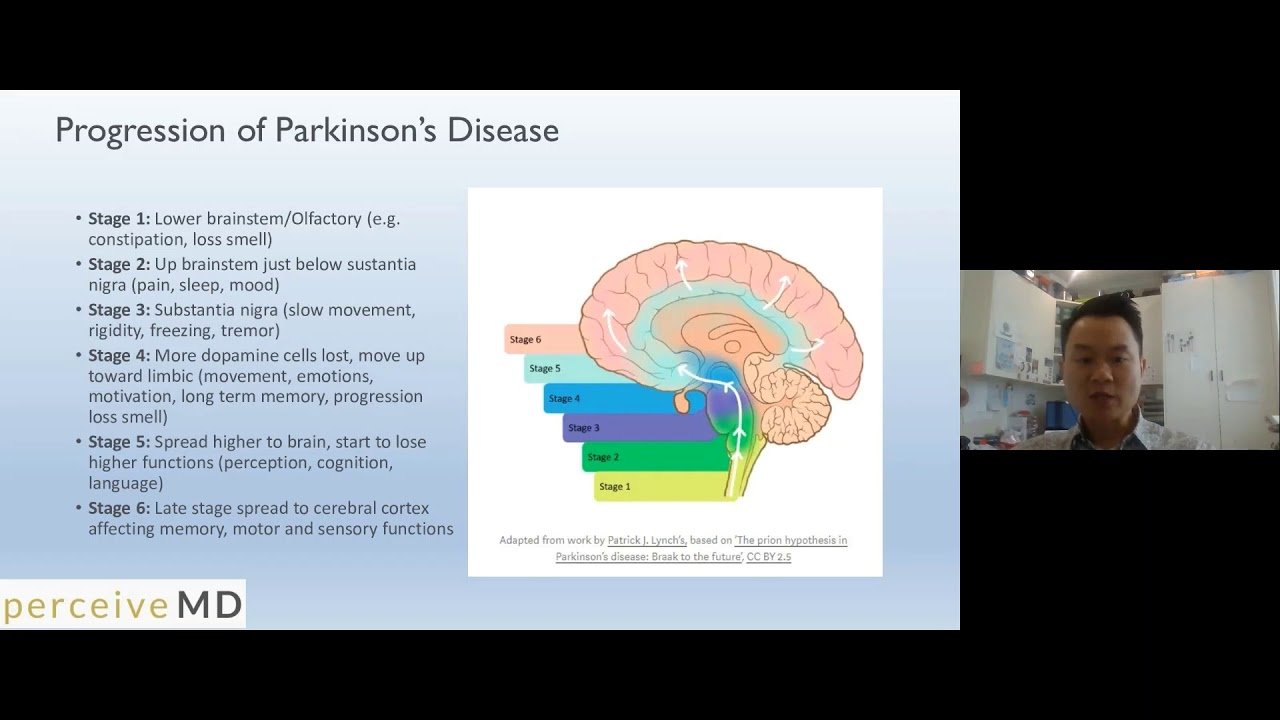
Theory Of Pd Progression: Braaks Hypothesis
The current theory is that the earliest signs of Parkinson’s are found in the enteric nervous system, the medulla and the olfactory bulb, which controls sense of smell. Under this theory, Parkinson’s only progresses to the substantia nigra and cortex over time.
This theory is increasingly borne out by evidence that non-motor symptoms, such as a loss of sense of smell , sleep disorders and constipation may precede the motor features of the disease by several years. For this reason, researchers are increasingly focused on these non-motor symptoms to detect PD as early as possible and to look for ways to stop its progression.
Page reviewed by Dr. Ryan Barmore, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
*Please note that not all content is available in both languages. If you are interested in receiving Spanish communications, we recommend selecting both” to stay best informed on the Foundation’s work and the latest in PD news.
The Cranial Nerves And Parkinson’s Disease
for more about this in the context of PD.
However, I believe there is something unique about the Social Engagement system in humans, even amongst mammals: our hands. We humans also use hands for expressing our emotions in very significant ways too. Indeed, we can communicate very profoundly like this: we have even developed sign languages, so we can and do literally talk with our hands.;
We can also hush each other with hands without making sound ourselves – meaning we can communicate that serious danger is present requiring everyone in the social group to keep quiet to avoid attracting attention, in such a way that we don’t attract attention ourselves.
Orienting is also an important part of the Cranial Nerve function for threat/safety evaluation, including the ability to turn eyes or ears to the source of potential threat. But with our hands we can also, naturally, orient each other to potential threats which we individually may have detected, within social groups – pointing a finger in direction of danger, for example, or signalling to the group to stop in its tracks.;
We can also make very distinct sounds and a wide range of “calls to action” directly with our hands: clapping, clicking fingers, whistling through the fingers, not to mention beating drums,;etc.
I have just communicated all this to you through my hands too, because I typed these words with my fingers!
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
Sleep Disturbances In Parkinson’s Disease
In general, research seems to indicate that people with Parkinson’s disease have more sleep disruptions than similarly aged people without the disease.; The most commonly reported sleep-related problems are the inability to sleep through the night and difficulty returning to sleep after awakening, generally referred to as maintenance insomnia.; Unlike many older adults, patients with Parkinsons disease often find that they have no trouble initiating sleep, but often wake up within a few hours and find sleeping through the rest of the night to be difficult. People with Parkinson’s disease also report daytime sleepiness, nightmares, vivid dreams, nighttime vocalizations, leg movements/jerking while asleep, restless legs syndrome, inability to or difficulty turning over in bed, and awakenings to go to the bathroom.
;Although all the reasons for these sleep changes are unknown, potential explanations include reactions to/side effects of medications and awakening due to symptoms such as pain, stiffness, urinary frequency, tremor, dyskinesia, depression and/or disease effects on the internal clock.;
How Does Parkinsons Start Out
Symptoms start gradually, sometimes starting with a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand. Tremors are common, but the disorder also commonly causes stiffness or slowing of movement. In the early stages of Parkinsons disease, your face may show little or no expression. Your arms may not swing when you walk.
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Cause Urinary Incontinence
Where Does Parkinson’s Disease Start In The Brain Or Gut Or Both
- Date:
- IOS Press
- Summary:
- Does Parkinson’s disease start in the brain or the gut? In a new contribution, scientists hypothesize that PD can be divided into two subtypes: gut-first, originating in the peripheral nervous system of the gut and spreading to the brain; and brain-first, originating in the brain, or entering the brain via the olfactory system, and spreading to the brainstem and peripheral nervous system.
Does Parkinson’s disease start in the brain or the gut? In a new contribution published in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, scientists hypothesize that PD can be divided into two subtypes: gut-first, originating in the peripheral nervous system of the gut and spreading to the brain; and brain-first, originating in the brain, or entering the brain via the olfactory system, and spreading to the brainstem and peripheral nervous system.
“The discussion about the origins of PD is often framed as an ‘either-or’, i.e., either all PD cases start in the gut or all cases start in the brain,” added Dr. Van Den Berge. “However, much of the evidence seems compatible with both these interpretations. Thus, we need to entertain the possibility that both scenarios are actually true.”
“If the brain-first vs body-first hypothesis is correct, we need to intensify the research into understanding risk factors and triggering factors for these two subtypes,” noted Dr. Van Den Berge.
Story Source:
