Advice For The Newly Diagnosed
If you have been recently diagnosed with Parkinsons disease, you are not alone. Today many people with Parkinsons are looking beyond their doctors alone to keep themselves well. We are here to help empower you by giving you the tools and information you need to lead a healthier, more independent life. Starting today you have the power to make a positive change in your life.
This section of Parkinson.org is unique; all of topics in this section have been written by people who have lived well with Parkinson’s for several years.
Innovative Treatment Modalities For Managing Pain In Parkinson’s
Botulinum toxin
Non-dopaminergic pharmacotherapy may benefit patients with PD-related pain. Botulinum toxin , both A and B derivatives, should be considered in patients who do not respond to dopaminergic treatment optimization.1,8 Botulinum toxin injection provides localized treatment by blocking the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction.4 Local injections of BTX type A or B can be effective for persistent dystonia-related pain and central pain, based on its neuromuscular action in movement disorders plus analgesic mechanism.
A randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled trial concluded that BTX-A in patients with PD is safe and potentially useful in treating limb pain.29 The study was conducted in patients with PD over the age of 30 years with painful limbs not responding to the optimization of anti-Parkinsonian medications. Patients were randomized to receive BTX-A injection or placebo, followed by the other treatment per the crossover design. Depending on the location of pain, patients received up to 200 units in upper limbs or up to 300 units in lower limbs. Patients experienced a significant reduction in their self-reported numerical pain score 4 weeks after the BTX-A injection , but not with placebo . There was no difference between the change with BTX-A compared to placebo . This study demonstrated that targeted BTX-A injections are safe in patients with PD.
Cannabinoids
Foster A Good Relationship
Lastly, maintaining your relationship and communication with the person with Parkinsonâs can be the most challenging and rewarding aspect of caregiving. As Parkinsonâs disease progresses, the roles change and the person with Parkinsonâs may go from being an independent head of the household to a very dependent person requiring a significant level of care. However, research shows that despite high levels of strain, caregivers with good quality relationships have reduced depression and better physical health. Remember, as a caregiver your service to your loved one is beyond measure in terms of love, depth of care, and concern.
Recommended Reading: Would A Weighted Blankets Help Parkinson’s
Facilitating Productive Conversations About Off Episodes With Patients And Care Partners
Patients and care partners might notice that, over time, the response to oral carbidopa/levodopa has become less consistent. Some people may not recognize the patterns in these changes or know how to articulate the experience, and others may also adapt their activities and routines to accommodate their OFF episodes.
As healthcare providers, we can help patients and their care partners identify the patterns in OFF episodes and work with them to proactively address the challenges they face as their disease progresses.
Probing deeper about bothersome symptoms and encouraging people to monitor the times of day they experience more PD symptoms as well as tracking challenges in navigating activities are important areas of discussion for our patients and their care partners.
To learn more about PD OFF episodes and the potential for treatment with KYNMOBI, visit KYNMOBIHCP.com. Please see below for Important Safety Information.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATION FOR KYNMOBI SUBLINGUAL FILM
Contraindications:;KYNMOBI is contraindicated in patients:
- Using concomitant drugs of the 5HT3 antagonist class, including antiemetics and alosetron. There have been reports of profound hypotension and loss of consciousness when subcutaneous apomorphine was administered with ondansetron.
- With hypersensitivity/allergic reaction to apomorphine or to any of the ingredients of KYNMOBI. Angioedema or anaphylaxis may occur.
Warnings and Precautions:
INDICATION
Adjuvant Therapy For More Advanced Parkinson’s Disease
- A choice of dopamine agonists, MAO-BIs or COMT inhibitors should be offered as an adjunct to levodopa for people with Parkinson’s disease who have developed dyskinesia or motor fluctuations despite optimal levodopa therapy.
- COMT inhibitors:
- Reversibly inhibit the peripheral breakdown of levodopa by the COMT enzyme, increasing the amount available for conversion to dopamine in the brain and reducing fluctuations in plasma levels.
- Produce clinical benefits in people with levodopa motor fluctuations and in those with stable responses to levodopa.
- Entacapone should ideally be offered as a combination drug because of poor patient compliance. One study found that early addition of entacapone to combined therapy produced more benefit than if it were introduced at a later stage . Tolcapone should only be used if entacapone fails .
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Bowels
Pathophysiology And Presenting Features
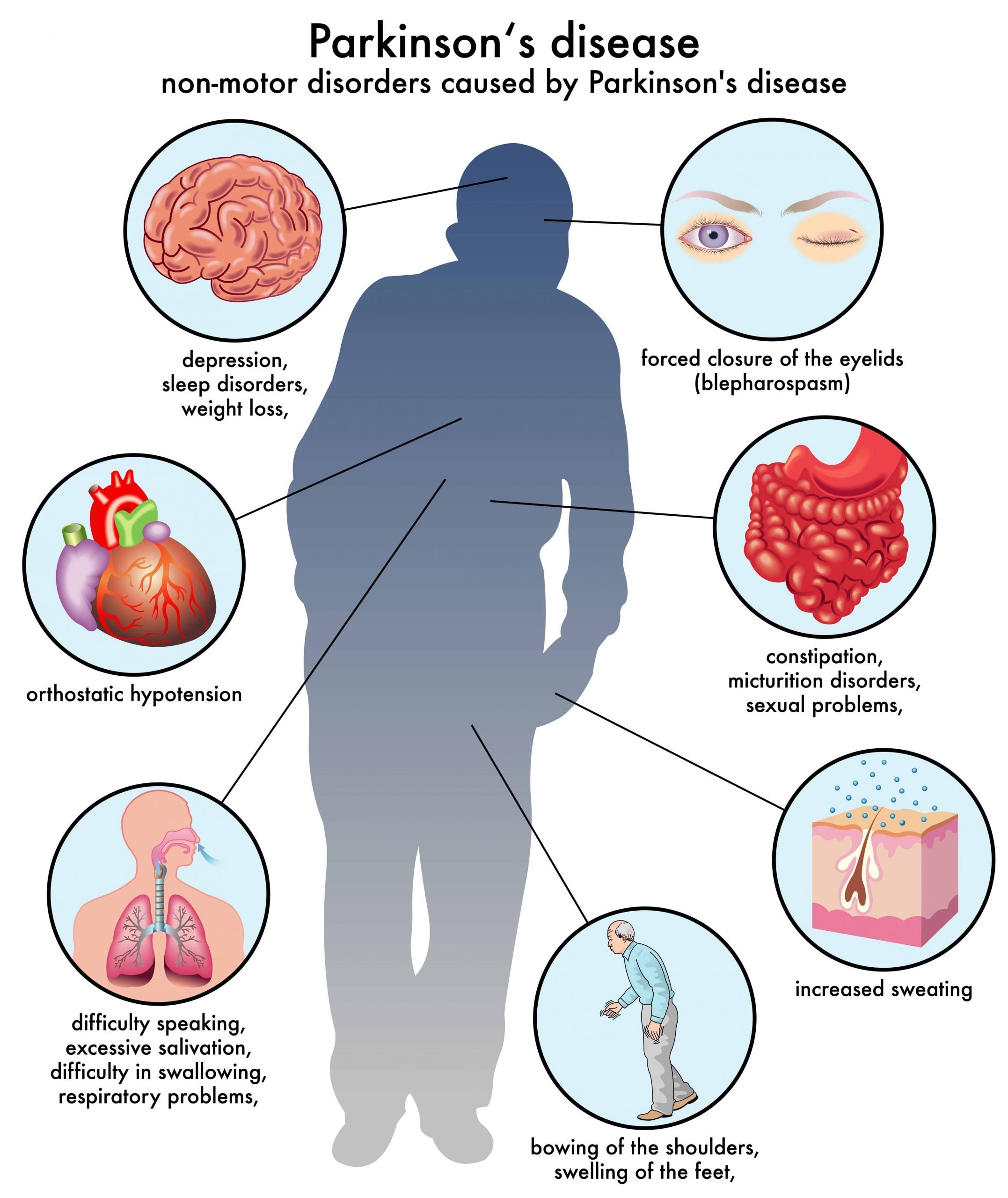
Classic presenting features of PD include motor symptoms, such as bradykinesia, rigidity, rest tremor and postural instability. However, non-motor symptoms, such as depression, cognitive impairment, pain and autonomic disturbances, are also often present and they can severely affect a patients quality of life. There are several information sheets available for patients that cover the management of multiple common types of pain in PD.
The motor symptoms are largely caused by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra compacta, which ultimately reduces dopaminergic input to the striatum and other brain regions. Compensatory mechanisms in the brain are so effective that the clinical symptoms of PD may only develop when around 80% of dopaminergic neurons have degenerated. By contrast, the Braak theory of PD suggests that the disease process starts in the olfactory bulb and lower part of the medulla, and it is not until stage 3 that the substantia nigra becomes involved in the process. There is also direct evidence of Parkinson pathology being spread from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rodents. There are therapeutic implications of gut involvement; it is known that swallowing and the stomach are the two main problems of PD therapy and lead to the use of non-oral therapies.
Pain Management Principles In Parkinson’s Disease
Non-pharmacologic methods with a multidisciplinary pain team should be utilized to provide optimal multimodal treatment in patients with PD.4 Muscle relaxation exercises and walking regularly can improve flexibility and dampen experiences of pain associated with motor symptoms.6 Rehabilitation with a physical therapist can improve gait and balance, targeting pain caused by motor symptoms. Surgical interventions, such as deep brain stimulation or an implanted spinal cord stimulator, may be appropriate for those patients experiencing pain with PD who do not respond to pharmacologic or rehabilitation interventions.1,6,9
Optimization of treatment with levodopa and other antiparkinsonian medications should be the first pharmacological step in managing PD-related pain.6,8 Beyond this recommendation, no evidence encourages the use of specific analgesic agents in any stepwise order, making patient input and assessment of pain type critical to appropriate treatment.
Patients should be prescribed analgesics if optimization of dopaminergic agents is not effective on its own .4
Optimization of Dopaminergic Agents
Safinamide is a selective, reversible MAO-B inhibitor that reduces degradation and reuptake of dopamine to increase levels in the striatum.19 Safinamide also has non-dopaminergic properties that modulate glutamate release via inhibition of voltage-gated sodium channels. This dual mechanism may mitigate pain, especially during off periods.
Recommended Reading: Do Parkinson’s Tremors Get Worse With Stress
Medications For People With Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease result from the progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the brain and other organs such as the gut, which produce a neurotransmitter called dopamine. This causes a deficiency in the availability of dopamine, which is necessary for smooth and controlled movements.;Medication therapy focuses on maximising the availability of dopamine in the brain. Medication regimes are individually tailored to your specific need. Parkinsons medications fit into one of the following broad categories:;
- levodopa dopamine replacement therapy
- dopamine agonists mimic the action of dopamine
- COMT inhibitors used along with levodopa. This medication blocks an enzyme known as COMT to prevent levodopa breaking down in the intestine, allowing more of it to reach the brain
- anticholinergics block the effect of another brain chemical to rebalance its levels with dopamine
- amantadine has anticholinergic properties and improves dopamine transmission
- MAO type B inhibitors prevent the metabolism of dopamine within the brain.
Dopamines Role In The Brain And Body
Dopamine is the reward neurotransmitter that helps us feel motivated to do things like get outside, cook healthy meals, and exercise. It also helps us coordinate movement. When people with Parkinsons dont have enough dopamine, they can get symptoms like depression, apathy, fatigue, tremor, and poor balance. They can even experience freezinga phenomenon in Parkinsons disease where people feel stuck or unable to move.
Its not hard to imagine how the symptom list above would make it difficultif not impossibleto go out for a run, take medications consistently, or want to go to the grocery store to look for ingredients for a new plant-based recipe . These symptoms can even make it hard to take supplements or eat healthy foods since a lack of dopamine can cause difficulties with swallowing. For that reason, we need to make sure dopamine levels are optimized first before we try other natural treatment options in PD.
Dopaminergic drugs and in particular Levodopa , are the closest things to our own bodys dopamine that we can make in a lab. They work. Ive seen people with Parkinsons who couldnt stand up, take a step, or smile become completely transformed within hours of taking their first dose of Levodopa. In my opinion and the opinions of most neurologists, PD specialists, and PD patients, dopaminergic drugs are effective medications. They just have to be taken the right way and with the right nutrients to make them work for you.
Recommended Reading: Is Beer Good For Parkinson’s
Take Pd Medications With Small Snacks Not Meals
Dopaminergic medications need to be taken away from high-fat, high-protein meals because amino acids and peptides compete for absorption across the blood-brain barrier, and high-volume meals can dilute stomach acid and delay the absorption of medication into the bloodstream. If you eat a big steak with your dopamine meds, they wont be absorbed as well as if you ate them with a lower-protein snack;like an apple.
Because of the need to avoid combining protein with dopaminergic medications, people with Parkinsons have to be very careful to make sure they still get enough total protein in the day and that they optimize their nutrition.;Protein;is important because it helps our bodies heal, repair tissues, and balance blood sugar, among many other things. It pays to work with a naturopathic doctor, registered dietitian, or nutritionist who can help you develop a plan that works for you to still optimize your nutrition while you increase your ability to absorb medications. Some of my strategies for PD patients involve an adjusted feeding schedule, protein shakes between meals, small and frequent snacks throughout the day, and;collagen powders;in drinks that my clients dont take with meds.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Side Effects Of Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of PD is clinical and requires bradykinesia, defined as slowness of movement and decrement in amplitude or speed, usually assessed using finger tapping, foot tapping or pronationsupination hand movements. In addition, rest tremor or rigidity is required to confirm a parkinsonian syndrome. Tremor was absent at presentation in 30% in one series of pathologically proven PD. Patients with suspected PD should be referred quickly and untreated to a specialist in movement disorders for evaluation. Key points for discussion at diagnosis include the need to inform vehicle licensing agencies and insurers, signposting to written or web-based information on newly diagnosed PD, and provision of contact details for the local PD nurse specialist .
Current International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease; adapted from Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 2015;30:1591601. At least two supportive criteria and no red flags required for a diagnosis of clinically established Parkinson’s disease. Conditions in italics should be considered if the corresponding exclusion criteria or red flags are present.
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease

At present, we do not know the cause of Parkinsons disease. In most people there is no family history of Parkinsons Researchers worldwide are investigating possible causes, including:;
- environmental triggers, pesticides, toxins, chemicals
- genetic factors
- combinations of environment and genetic factors;
- head trauma.
You May Like: How To Treat Constipation In Parkinson’s Disease
Other Ways To Manage Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
In addition to lifestyle changes, your doctor will likely discuss different medications with you. You may not immediately need prescription drugs to manage your symptoms, or your physician may prescribe you more than one type of medicine. Some of the medications commonly prescribed for Parkinson’s disease include the following.
- Levodopa:;Levodopa is one of the most prevalent treatments for Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacists combine this drug with carbidopa, which helps curb nausea and delivers the medication to the brain, where it gets synthesized as dopamine. It comes in a few different formulations and dosages, which means it may have various brand names such as Parcopa or Sinemet. This drug can help control symptoms like bradykinesia, tremors and stiff muscles.;
Like any medication, levodopa does have side effects. Over time, typically;three to five years, levodopa can cause;dyskinesia, a term used to describe involuntary jerky movement. It can affect the head, arms, legs, face or the entire body. There are medications to manage this side effect, as well as other treatment options.;
Side effects of dopamine agonists may include nausea, dizziness, sleep changes, swelling of the legs and hallucinations, among others.;
This type of medication may increase the side effects associated with levodopa, such as;dyskinesia. Diarrhea, discolored urine and liver damage are also potential side effects of COMT inhibitors.;
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
Read Also: What Are The Plaques Called That Cause Parkinson’s Disease
Managing Depression In Parkinsons Disease
People with Parkinsons, family members and caregivers may not always recognize the signs of depression and anxiety. If you are experiencing depression as a symptom of Parkinsons, it is important to know it can be treated.
Here are some suggestions:
- For information and support on living well with Parkinsons disease, contact our Information and Referral line.
- As much as possible, remain socially engaged and physically active. Resist the urge to isolate yourself.
- You may want to consult a psychologist and there are medications that help relieve depression in people with Parkinsons, including nortriptyline and citalopram .
Inpatient Management Of Parkinson’s Disease
Patients with PD are often admitted to hospital for other reasons, but the unique challenges of the condition mean that outcomes related to PD are often suboptimal. Many hospitals have an alert system to inform members of the PD team of admission to allow proactive in-reach consultations. It is essential that antiparkinsonian medications are given on time and in correct dosage, as sudden reduction or withdrawal of medication can lead to severe morbidity or even mortality due to parkinsonismhyperpyrexia syndrome. Dopamine blocking drugs must not be given. When patients with PD cannot take their usual oral medications, we recommend that an equivalent dosage be given via nasogastric tube. If this is not possible, or enteral medication is contraindicated, cautious use of rotigotine patch can be helpful.
Don’t Miss: What Do Lewy Bodies Do In Parkinson’s Disease
