If You Live In South Jersey And Have Questions About The Final Stages Of Parkinsons Disease Or Hospice Care For Your Loved One Please Call Samaritan At 229
![Neural Stem Cell Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease [PD]](https://www.parkinsonsinfoclub.com/wp-content/uploads/neural-stem-cell-therapy-for-parkinsons-disease-pd.jpeg)
Samaritan is a member of the National Partnership for Healthcare and Hospice Innovation, a network of not-for-profit hospice and palliative providers across the country. If you know someone outside of our service area who is living with advanced illness and can benefit from hospice or palliative care, please call 1 -GET-NPHI for a referral to a not-for-profit provider in your area.
Want To Learn More About The Latest Research In Parkinsons Disease Ask Your Questions In Our Research Forum
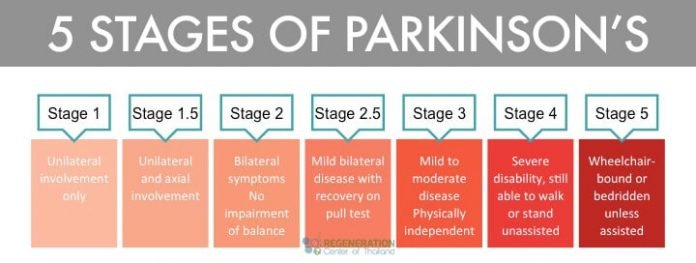
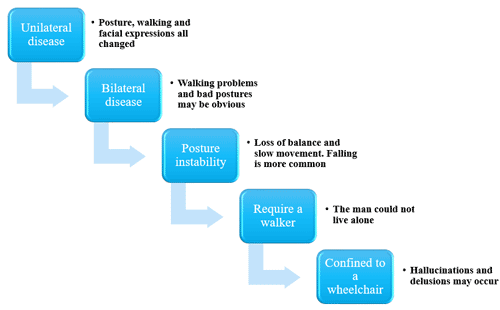
Stage 3As motor symptoms become worse, patients may begin to experience loss of balance leading to falls and movement can become very slow. Although many patients can still live independently they may have difficulty in everyday activities such as eating or dressing.
MORE: How does Parkinson’s disease affect the brain?
Stage 4In this later stage, symptoms are now extremely limiting. Many patients can still stand without assistance but movement is greatly impaired. Most will need help with everyday activities and will not be able to look after themselves.
Stage 5This is the most advanced stage of the disease and most patients will experience difficulty in walking and standing, often requiring a wheelchair. Assistance will be needed in all areas of daily life as motor skills are seriously impaired. In addition, people with advanced Parkinson’s disease may also begin to suffer hallucinations.
MORE: How Parkinson’s disease affects your body.
Parkinson’s News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Can A Patients Ability To Make Decisions In The Last Days Of Life Be Impaired And How Is This Managed
In a North American study of 47 carers of idiopathic PD patients in the last months of life most described the goal of care as comfort, and almost half “of the patients were described as unable to make any decisions in the last month of life.” 10
When presenting, the patient may already be unable to communicate their symptoms and care preferences due to cognitive impairment and confusion. Also, there might be a physical difficulty in communication from severe rigidity. Care should be taken in considering the presence and consequent treatment of an intercurrent illness, and whether dopaminergic medication is exacerbating confusion due to hallucinations and/or psychosis.27
Continued attempts at verbal and non-verbal communication should be made throughout given the often fluctuating symptoms associated with PD and possible improvement in the intercurrent illness. In the absence of a next of kin or other person who is able to inform the clinical team, decisions should be made on a best interest basis as recommended in end of life care guidance.30
How Can I Support Someone With Parkinson’s At The Advanced Or Palliative Stage
In the advanced stages of Parkinson’s, your patient’s care needs may be more complex and require careful planning along with the patient, their family and other health and social care professionals involved.
Palliative care should be holistic, considering the ‘whole person’ to support the personal, social, psychological and spiritual needs of your patient and their family. It should give your patient some control and choice over areas such as treatment options and where they will be cared for, as well as providing advice and support to all the people involved in their care.
Palliative care in Parkinson’s may be supported by a number of professionals, including a Parkinson’s nurse specialist, local hospice or specialist palliative care team, physiotherapist, occupational therapist, speech and language therapist or dietitian. Many people with Parkinson’s also find complementary therapies beneficial.
It is important that you find out whether the person has a care plan in place regarding their preferences for how the issues surrounding advanced Parkinson’s should be managed. This could include legal documentation such as a Lasting Power of Attorney and an advance care plan. Advance care plans include information on what the person’s wishes and preferences are for their care in the future. They may include decisions on any treatments the person doesn’t want to have in the future – this is called an Advance Directive, Advance Decision to Refuse Treatment or Living Will.
What Are The Considerations For Pain Management In The Last Days Of Life In Pd
It is important to consider that pain can be a risk factor for, and associated with, many other symptoms which might be the presenting features in a patient with complex or advanced PD. These include a new or worsened confusion, hallucinations, agitation and symptoms of depression or apathy.
As well as being an underlying cause of another symptom, pain can also be the symptom of other features of PD, such as rigidity, dyskinesia, but also non-motor features, for example, depression and fatigue.
Identifying whether pain is at the root of the presenting complaint and what might be causing the pain is therefore the most important part of the initial history from the patient and the carer. Then using the clinical examination to confirm findings from the history and identify any features not already elicited such as abnormal posturing, or dystonia.
A recent review into the pathophysiology and treatment of pain in PD suggests simple analgesia with paracetamol and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs but advises caution with opiate analgesia as constipation is a recognised problem in PD patients.25 The review mentions, however, the lack of evidence for many widely used analgesics specifically in PD.26
How Can Hospice Help Your Loved One In The Final Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Hospice care is an extra layer of support to help you care for your loved one with end-stage Parkinson’s disease. It is a special kind of care that provides comfort, support, and dignity at the end of life.
The comprehensive program focuses on physical, emotional, and spiritual quality of life through the help of a team of experts. The team includes a board-certified physician, nurse, social worker, certified home health aide , spiritual support counselor, and volunteer.
The nurse will explain the prognosis and what to expect in the upcoming days or weeks. They will also monitor pain and other symptoms. The CHHA helps with personal care needs like bathing and changing bed linens. The social worker helps address social, emotional and practical challenges including complex and inter-related needs. The spiritual support counselor helps explore spiritual concerns.
Most importantly, the hospice team will be there for you during this difficult time, bringing you peace of mind. The team is on call 24 hours a day – even at 2:00 am.
Hospice is about making your final months and weeks as good as possible. This means focusing on what really matters to you.
How Can Parkinson’s Affect Someone At The Advanced Or Palliative Stage
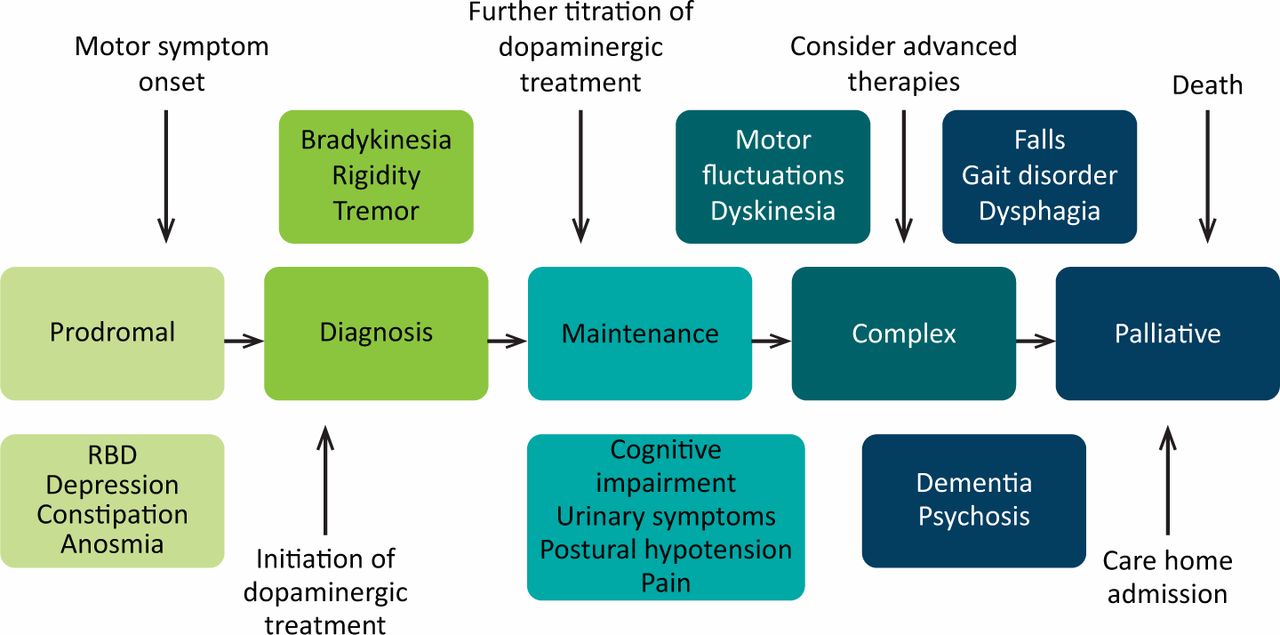
Parkinson’s progresses in stages: diagnosis, maintenance, advanced and palliative. Professionals should have talk to people with Parkinson’s about advance care planning in the earlier stages of the disease. This can allow them to express their wishes and preferences for their care in the later stages of the disease and make plans for the future.
Although the condition progresses differently and at a different speed for each person, the advanced stage can potentially cover a long period of time.
Problems that affect someone with advanced Parkinson’s may include:
- medicines being less effective at managing symptoms than before
- having to take lots of medicines to manage symptoms and side effects
- more ‘off’ periods – when the effects of medication are reduced, and people experience movement fluctuations and involuntary movements
- increased mobility problems and falls
- swallowing difficulties
- less control of their Parkinson’s symptoms, which become less predictable
- pain.
Some of the more advanced symptoms can lead to increased disability and poor health, which can make someone more vulnerable to infection, such as pneumonia. People with Parkinson’s most often die because of an infection or another condition, usually caused by Parkinson’s.
What Are The Important Points Regarding Apomorphine At The End Of Life
Apomorphine is a dopamine agonist, which is given as a subcutaneous infusion either continuously or intermittently and also as single subcutaneous injections. An overview of studies into apomorphine use shows improvement in motor off periods and in dyskinesias.39
Apomorphine has side-effects similar to other dopaminergic medication but also notably nausea and vomiting. Ondansetron is not recommended for nausea in patients using apomorphine due to adverse effects.21
Subcutaneous apomorphine has been used at the end of life in a patient with advanced PD although with the recommendation that this is by a healthcare professional experienced in its use.40
What Are The Important Points Regarding Duodopa At The End Of Life

Duodopa is a continuous infusion of dopaminergic medication administered as a gel into the gut, pumped via a percutaneously inserted gastrostomy tube . There is a requirement for care of the stoma and PEG tube together with functioning of the pump by the patient or carer.41 It reduces the time in motor off periods in advanced PD and quality of life.42 There is evidence of effective treatment up until death from within a case series.43
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy For Parkinson’s Disease
The severity of Parkinson’s disease symptoms and signs vary greatly from person to peson, and it is not possible to predict how quickly the disease will progress. Parkinson’s disease itself is not a fatal disease, and the average life expectancy is similar to that of people without the disease. Secondary complications, such as pneumonia, falling-related injuries, and choking can lead to death. Many treatment options can reduce some of the symptoms and prolong the quality of life.
What Are The Risks Of Not Receiving Any Dopaminergic Medication
There is the possibility of neuroleptic malignant-like syndrome , a life-threatening and distressing condition resulting in rigidity and fever, from withdrawal of therapy.31 This can also occur with sudden cessation of Deep Brain Stimulation .32,33,34 To reduce the risk of this, dopaminergic therapy at the end of life should be continued.27 It should also be noted that in a patient dying of another condition, whose PD is still responsive to dopaminergic medication, the cessation of this also risks aspiration pneumonia.35 Transdermal rotigotine can be used in patients in whom a NG tube may cause excessive distress or is not possible. The dose should be calculated with an accepted converter.36
What Is The Main Cause Of Death In Parkinsons Disease Patients
Parkinson’s is often referred to as a “bespoke” disease because it affects each patient differently. Another factor worth considering is that Parkinson’s disease generally affects people in their 60s, most of whom die of unrelated conditions such as cancer, heart disease or stroke. However, the most common cause of death in those with Parkinson’s disease is pneumonia. This is because the disease can impair your ability to swallow in the later stages, putting you at risk for aspirating food or liquid into the lungs.
Which Medications Can Make Confusion And Hallucinations Worse
As PD progresses, non-motor symptoms including psychosis and hallucinations become more prominent both for the patient and caregivers.9 Dopaminergic medication can exacerbate these symptoms and this can be reduced through a “last in, first out approach.” 27,28 Medications that have an anticholinergic effect also may cause or worsen acute confusion and the anticholinergic burden in the patient’s medication history should be considered.29
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinson’s disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didn’t exercise or didn’t start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinson’s, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments — whether medicines or deep brain stimulation — are optimal; and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Improve the quality of your sleep.
Is Parkinsons Disease Fatal Life Expectancy For Parkinsons Emma-Marie Smith
Worried about your Parkinson’s disease life expectancy? A Parkinson’s disease diagnosis comes with many worries and anxieties. One worry concerns the progression of the disease and whether Parkinson’s disease can be fatal. The issue is rarely straightforward, but there is no reason to think your condition is a death sentence. Many people live for years or decades with their Parkinson’s disease symptoms under control, while the illness progresses more quickly for others. It’s important that you know what to expect when you’re diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, so don’t be afraid to ask questions and air your concerns to your doctor. For now, let’s explore the issue of life expectancy of patients with Parkinson’s disease and address some common concerns.
What To Do With Deep Brain Stimulation At The End Of Life
Deep brain stimulation uses an Implantable Pulse Generator, usually placed in the infraclavicular area, connected to leads within the brain. There is a remote programmer, and also a charging unit in the case of a rechargeable device, which are given to the patient and their carer. It improves dyskinesias and also has a levodopa sparing effect.37
Deactivation of DBS may lead to increased symptom burden as mentioned in the section above and so awareness of features of PHS should be considered if there is failure at the end of life. Supportive treatment should be given if possible,38 and anticipation of symptoms of distress from rigidity and fever.
After death, deactivation of the device with the patient’s handheld programmer is required before removing the pulse generator and battery in the case of a cremation.
What Is The Difference Between Parkinson And Parkinsonism
ParkinsonismParkinson’sparkinsonismparkinsonian
People Also Asked, Is parkinsonism the same as parkinson’s disease?
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative brain disorder that progresses slowly in most people. Parkinsonism is a general term that refers to a group of neurological disorders that cause movement problems similar to those seen in Parkinson’s disease such as tremors, slow movement and stiffness.
Also know, what is parkinsonian syndrome?Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. It is found in Parkinson’s disease , after which it is named, dementia with Lewy bodies , Parkinson’s disease dementia , and many other conditions.
Contents
What To Expect In The Late Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
The late stages of PD are medically classified as stage four and stage five by the Hoehn and Yahr scale:
- Stage Four of Parkinson’s Disease – In stage four, PD has progressed to a severely disabling disease. Patients with stage four PD may be able to walk and stand unassisted, but they are noticeably incapacitated. Many use a walker to help them. At this stage, the patient is unable to live an independent life and needs assistance with some activities of daily living. The necessity for help with daily living defines this stage. If the patient is still able to live alone, it is still defined as Stage Three.
- Stage Five of Parkinson’s Disease – Stage five is the most advanced and is characterized by an inability to arise from a chair or get out of bed without help. They may have a tendency to fall when standing or turning, and they may freeze or stumble when walking. Around-the-clock assistance is required at this stage to reduce the risk of falling and help the patient with all daily activities. At stage five, the patient may also experience hallucinations or delusions.1,2
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinson’s disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable – reducing symptoms during “on” periods and no longer controlling symptoms during “off” periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they can’t. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinson’s disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare team’s efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinson’s disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein – glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF – to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Parkinsons Disease Late Stages: What Will Happen To Me
With advanced Parkinson’s disease, stage 5 life expectancy can be months or years depending on how your condition presents. You are likely to need round-the-clock care at this stage, and you may not be able to move around independently. Patients with late-stage Parkinson’s disease are more susceptible to pneumonia, sepsis, pyelonephritis and decubitus ulcers. Late-stage Parkinson’s also leads to Parkinson’s disease dementia in 50% of cases. For all of these reasons, many late-stage Parkinson’s patients are cared for by loved ones or in a hospice.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinson’s disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
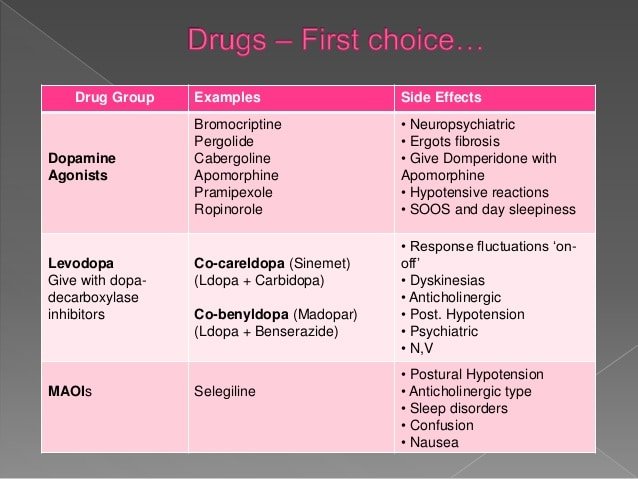
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Caregiving In The Late Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
In late-stage PD, patients have significant mobility challenges. Caregivers likely need to provide more hands-on assistance to help them get around the house. It’s important that caregivers learn safe and effective methods to provide help without injuring themselves. Physical therapists can be a great resource to assess an individual situation and teach effective ways of giving assistance.3
Freezing, a sudden but temporary inability to move, can become more common in late-stage PD. Freezing often happens when initiating movement or navigating around obstacles, and freezing episodes contribute to falls. Caregivers can help their loved one overcome freezing by providing a visual cue to step over, like a laser pointer, or using music or rhythm for the person with PD to walk to.3
Late stage PD can make daily activities, such as getting dressed, much more challenging. Caregivers can make getting dressed easier by ensuring adequate time to account for slow movement, choosing a time when medications are “on” and working well, and assembling all necessary items close to the person. Allowing the person with PD to do as much as they can gives them a sense of participation in the process.3
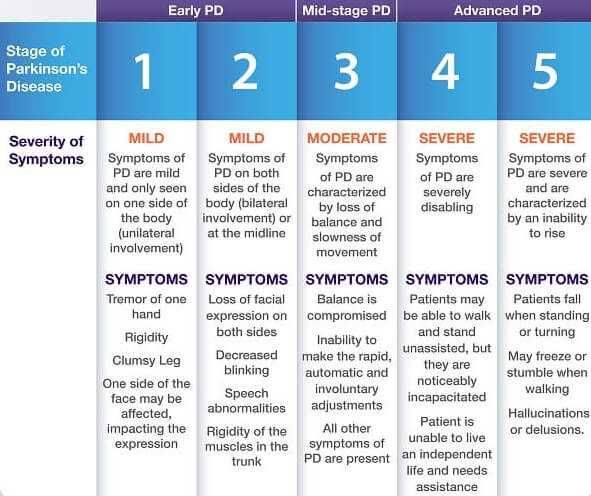
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinson’s disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms; others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
How Long Can A Person Live With Stage 5 Parkinson
When patients reach stage five – the final stage of Parkinson’s disease – they will have severe posture issues in their back, neck, and hips. In end–stage of Parkinson’s disease, patients will also often experience non-motor symptoms. These can include incontinence, insomnia, and dementia.
Additionally, what do Parkinson’s patients usually die from? But the most common cause of death in those with Parkinson’s is pneumonia, because the disease impairs patients‘ ability to swallow, putting them at risk for inhaling or aspirating food or liquids into their lungs, leading to aspiration pneumonia.
Also asked, what happens in stage 5 Parkinson’s?
Stage Five of Parkinson’s Disease –Stage five is the most advanced and is characterized by an inability to arise from a chair or get out of bed without help. They may have a tendency to fall when standing or turning, and they may freeze or stumble when walking.
How quickly can Parkinson’s progress?
While symptoms and disease progression are unique to each person, knowing the typical stages of Parkinson’s can help you cope with changes as they occur. Some people experience the changes over 20 years or more. Others find the disease progresses more quickly.
How Do I Know If My Parkinsons Is Getting Worse
6 Signs Your Parkinson’s Disease Is Progressing Medication not working the way it used to. In the early stages, taking medicine works well to get rid of symptoms. Increased feelings of anxiety or depression. Changes in sleeping patterns. Involuntary movements. Trouble swallowing. Memory or thinking problems. The takeaway.
What Is The Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
There is currently no treatment to cure Parkinson’s disease. Several therapies are available to delay the onset of motor symptoms and to ameliorate motor symptoms. All of these therapies are designed to increase the amount of dopamine in the brain either by replacing dopamine, mimicking dopamine, or prolonging the effect of dopamine by inhibiting its breakdown. Studies have shown that early therapy in the non-motor stage can delay the onset of motor symptoms, thereby extending quality of life.
The most effective therapy for Parkinson’s disease is levodopa , which is converted to dopamine in the brain. However, because long-term treatment with levodopa can lead to unpleasant side effects , its use is often delayed until motor impairment is more severe. Levodopa is frequently prescribed together with carbidopa , which prevents levodopa from being broken down before it reaches the brain. Co-treatment with carbidopa allows for a lower levodopa dose, thereby reducing side effects.
In earlier stages of Parkinson’s disease, substances that mimic the action of dopamine , and substances that reduce the breakdown of dopamine inhibitors) can be very efficacious in relieving motor symptoms. Unpleasant side effects of these preparations are quite common, including swelling caused by fluid accumulation in body tissues, drowsiness, constipation, dizziness, hallucinations, and nausea.
Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms: Life Expectancy
Even though Parkinson’s disease is a serious, progressive condition, it is not considered a fatal illness. People who have Parkinson’s disease usually have the same average life expectancy as people without the disease.
But when the disease is in its advanced stages, Parkinson’s symptoms can lead to life-threatening complications, including:
- Falls that lead to fractured bones
- Pneumonia
- Choking
Thinking about the progression of Parkinson’s disease can be frightening. But proper treatments can help you live a full, productive life for years to come. And researchers hope to one day find ways to halt the progression of Parkinson’s and restore lost functioning.
What Symptoms Can Be Expected In Advanced Pd

- Pain – 86%
- Shortness of breath – 54%
- Problems in swallowing – 40%14
In an analysis of 339 death certificates and medical notes in the UK, pneumonia was found to be a “terminal event in 45%”.13
Caregiver distress with choking and the risk of “choking to death” is also mentioned in a separate study in to experiences regarding all stages of PD.4
In a survey of symptoms and their association with quality of life, in those patients with advanced disease, uncontrolled pain, anxiety and hallucinations were significantly associated with poor quality of life.9
Seizures are also noted in a description of the last phase of Parkinsonian syndromes,15 and in retrospective studies of PD patients’ overall.16,17
These above symptoms often occur on the background of weight loss, pain, and cognitive impairment. It is important therefore to note which medications given at the end of life may exacerbate these symptoms, and which should be considered in anticipation of them.
What Is The Prognosis For Someone With Early
One of the challenges of early-onset Parkinson’s disease is that you will inevitably live longer with the condition, as Parkinson’s alone is not fatal. Early-onset Parkinson’s disease does not always present the same way as late-onset Parkinson’s disease, and there is no definite prognosis. Younger Parkinson’s patients may be more at risk of developing non-motor symptoms, such as depression, sleep disorders, anxiety and urinary issues, which can cause health complications as the disease progresses.
However, early-onset patients also show slower disease progression, and it can take years to move between stages. Each case of Parkinson’s is reviewed on an individual basis, so only your doctor can tell you your prognosis.
Specialized Parkinsons Care At Saint Simeons
Saint Simeon’s is committed to providing a higher quality of life for those in need of Parkinson’s disease. We provide a unique program developed specifically for people with Parkinson’s disease. This program is under the direction of Dr. Mary Nole, who develops customized wellness plans for each participant.
The Parkinson’s disease program at Saint Simeon’s is unlike any other in Oklahoma. Our dedicated nursing staff and wellness team have received specialized Parkinson’s disease education and training to maintain or restore skills that may have deteriorated. Saint Simeon’s Parkinson’s care is endorsed by the Parkinson Foundation of Oklahoma and the American Parkinson Disease Association. For more information, don’t hesitate to contact us today.
What Happens If Parkinsons Is Left Untreated
Many patients eventually have trouble walking, driving, and performing simple daily tasks. Parkinson’s disease is a chronic, progressive condition, and, if left untreated, the symptoms will grow steadily worse. Some viruses, such as a certain strain of influenza A, may also be responsible for bringing on Parkinson’s.
Theory Of Pd Progression: Braaks Hypothesis
The current theory is that the earliest signs of Parkinson’s are found in the enteric nervous system, the medulla and the olfactory bulb, which controls sense of smell. Under this theory, Parkinson’s only progresses to the substantia nigra and cortex over time.
This theory is increasingly borne out by evidence that non-motor symptoms, such as a loss of sense of smell , sleep disorders and constipation may precede the motor features of the disease by several years. For this reason, researchers are increasingly focused on these non-motor symptoms to detect PD as early as possible and to look for ways to stop its progression.
Page reviewed by Dr. Ryan Barmore, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinson’s Foundation Center of Excellence.
*Please note that not all content is available in both languages. If you are interested in receiving Spanish communications, we recommend selecting “both” to stay best informed on the Foundation’s work and the latest in PD news.