Breathing Problems In Parkinsons Disease: A Common Problem Rarely Diagnosed

Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s disease. It is characterized by bradykinesia tremor, rigidity, and postural instability. Potential non-motor manifestations of PD include depression, anxiety, constipation, overactive bladder symptoms, dementia, and sleep disturbances.
Although James Parkinson, in 1817, described breathing abnormalities in his “Essay on the shaking palsy”, there has been limited research on this important non-motor symptom.
People living with Parkinson’s may present with a wide variety of respiratory symptoms, ranging from shortness of breath at rest to acute stridor. Shortness of breath can be very distressing for patients and clinicians alike. Multiple investigations may be undertaken, looking for infection, blood clots and heart problems. Although these potential causes of breathing abnormalities need to be excluded, clinicians must remember that PD itself and its medications can cause SOB; and that normal investigations should not automatically lead to a diagnosis of anxiety, depression or lead to inappropriate treatment plans.
Several different patterns of breathing abnormality may be found in PD:
KM Torsney, D Forsyth
Symptoms That May Be Related To Pd But That Few People Know About
People with PD and care partners may suspect that a particular symptom is related to PD, but they can’t find information about it, so they are not sure. Two symptoms that pop up in this category are runny nose and breathing problems, which we’ll focus on today. Of course, if these are new symptoms for you, they could be indicative of a new problem, including infection with COVID-19, so make sure to get yourself checked out by your doctor. However, if all else is ruled out, PD could be to blame. Excessive sweating and specific skin disorders are in this category as well and have been addressed previously.
Parkinsons Disease: The Warning Sign Found In A Persons Breath mediabestHealth News
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive nervous system disorder that cannot be cured, although the sooner it is picked up the better. Steps can be taken to slow down its progression, helping a person with Parkinson’s to maintain quality of life for as long as possible. The symptoms of Parkinson’s are mainly related to movement because it leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain. However, occasionally the symptoms can appear in unusual areas of the body including in the way you .
Parkinsons Is A Condition Which Produces Three Major Symptoms:
- Tremor
- Rigidity
- Akinesia
In addition, because of postural instability, poor balance can be a feature. These symptoms are also associated with disturbance of gait , particularly as Parkinson’s progresses.
The symptoms may occur alone or in combination. They usually start on one side of the body and after a period of several years will then involve the other side of the body.
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms

Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinson’s disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didn’t exercise or didn’t start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinson’s, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments — whether medicines or deep brain stimulation — are optimal; and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Improve the quality of your sleep.
Coronavirus And Parkinsons Disease: What You Need To Know
- Sep 22, 2020
Having Parkinson’s disease comes with many uncertainties and anxiety. On top of this now is the concern about coronavirus pandemic. PD symptoms can worsen when you also have another illness. And some of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease may increase the risk for complications from this respiratory virus, such as difficulty breathing or swallowing. Other factors that may increase risk of complications are older age and having other serious medical conditions such as heart disease, respiratory illnesses, diabetes, and kidney failure. The added stress from worry over catching the new virus and the need to remain at home can also increase PD symptoms.
Meanwhile, much of the country is beginning to open, which makes it more important than ever to remain safe – and know what to do if you feel sick.
Understanding the Main Symptoms of Coronavirus
The list of coronavirus symptoms has grown to include cough, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, fever, chills or shaking, muscle pain, headache, sore throat, and recent loss of smell or taste. For more information on these and other signs of coronavirus, visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control .
When to Contact the Doctor
Before a trip to the emergency department for possible coronavirus symptoms, check with your doctor.
You should also check with your doctor’s office to see if you can use a telehealth visit for regular appointments. These virtual visits are now covered by Medicare due to the pandemic.
Tags
Other Symptoms To Spot For Potential Early Warning Signs
A telltale sign you have Parkinson’s is slight shaking or tremor in your thumb, finger, hand or chin, the health site says.
It adds: “A tremor while at rest is a common early sign of Parkinson’s disease.”
It is worth noting that a person with Parkinson’s disease can also experience a wide range of other physical and psychological symptoms.
According to the NHS, these include depression and anxiety, balance problems , loss of sense of smell , problems sleeping and memory problems.”
What Happens When The Lungs Arent Working At Their Best
When the muscles and joints that work our breathing mechanisms become weak or stiff, the lungs become less efficient. This means a person may be short of breath and more easily tired when carrying out everyday tasks. Some people find it hard to cough strongly enough to clear phlegm, which can develop into a chest infection.
It might sound scary, but exercising the lungs is critically important for people with Parkinson’s. Pneumonia is the main reason people with the condition are admitted to hospital in an emergency, and respiratory complications, such as a chest infection or pneumonia, can be life-threatening.
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinson’s disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable – reducing symptoms during “on” periods and no longer controlling symptoms during “off” periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they can’t. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinson’s disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare team’s efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinson’s disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein – glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF – to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Clinical Evaluation To Assess Breathing Abnormalities
A physician should evaluate shortness of breath and any other breathing abnormalities. Potential causes of breathing difficulty include heart and lung conditions, which should be ruled out. People with PD often see general practitioners for medical care in addition to neurologists. It is important for such providers to be aware that PD and associated medications can cause shortness of breath.3
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinson’s disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Effects Of Dopaminergic Therapy: Risk Or Protection
Studies have provided controversial results about the therapeutic effects of dopaminergic stimulation, and the role of drugs commonly used in the treatment of PD is still debated, strictly depending both on disease stage and administration modality.
Most papers strengthen the role of anti-Parkinsonian drugs as a protective factor against the development of respiratory failure. Levodopa increases inspiratory muscle function in anaesthetised dogs , and dopamine improves diaphragm function during acute respiratory failure in patients with COPD . In early stages, the levodopa equivalent daily dose does not correlate with pulmonary functional testing; as the disease progresses, anti-Parkinsonian medications may be responsible for the maintenance of the maximal inspiratory mouth pressure and sniff nasal inspiratory pressure . Accordingly, bedtime controlled-release levodopa is associated with less severe obstructive sleep apnoea in PD . Because dopamine is not known to increase muscle strength, it may ameliorate respiratory function by improving muscle coordination by a central activity .
Many authors have investigated the effect of dopaminergic therapy on aforementioned respiratory dysfunction, especially on obstructive and restrictive patterns .
Main findings of major studies we considered about the effects of dopaminergic drugs on respiratory parameters and respiratory dysfunctions
Dyspnea Is A Specific Symptom In Parkinsons Disease
Article type: Research Article
Affiliations: Department of Neurology, Expert Center for Parkinson’s Disease, INSERM UMRS_1171, Lille University Medical Center, LICEND COEN center, Lille, France | CHU Lille, Lung Function Department, Univ Lille, INSERM 1019, CNRS UMR 8204, Institut Pasteur de Lille, Center for Infection and Immunity of Lille, Lille, France | Univ. Lille, CHU Lille, EA 2694 – Santé Publique: Épidémiologie et Qualité des Soins, Department of Biostatistics, Lille, France | CHU Lille, Department of Allergy and Respiratory Medicine, Competence Center for rare lung diseases, Univ. Lille, CNRS, INSERM, Institut Pasteur de Lille, U1019 – UMR 8204 – CIIL – Center for Infection and Immunity of Lille, Lille, France | CHU Lille, Department of Medical Pharmacology, Lille University INSERM 1171, Lille, France
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Caroline Moreau, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, Expert Center for Parkinson’s Disease, INSERM UMRS_1171, Lille University Medical Center, LICEND COEN Center, Lille, France. Tel.: +33 320445962; E-mail: .
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease, dyspnea, non-motor symptom, anxiety, ventilatory dysfunction
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-191713
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 785-791, 2019
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinson’s disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms; others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Shaking Hands Or Tremor And Shortness Of Breath
- Medical Author: Sabrina Felson, MD
Reviewed on 6/15/2020
Hand tremor with shortness of breath may reflect hyperventilation, anxiety, or panic attack. Hyperthyroidism can result in atrial fibrillation with shortness of breath and a fine tremor. Advanced Parkinson’s can result in shortness of breath and tremor. Call your doctor.
While the list below can be considered as a guide to educate yourself about these conditions, this is not a substitute for a diagnosis from a health care provider. There are many other medical conditions that also can be associated with your symptoms and signs. Here are a number of those from MedicineNet:
Correlation Between Pneumological Drugs And Pd

In this scenario, the effects of drugs commonly used by the pneumologist should also be considered. For instance, some studies recently reviewed by Hopfneret al. postulated the possible correlation between ?-adrenoreceptors and PD . Anticholinergic drugs are frequently used for obstructive pulmonary disorders and systemic anticholinergics may play a part in PD . Acetylcholine has a key role in modulating dopaminergic activity in the basal ganglia, and its inhibition may increase central dopaminergic tone . Anticholinergic bronchodilators might have central effects, as reported by some authors . An effect on motor disturbances in PD may be reasonable, even if to our knowledge this has not been investigated in the current literature. However, it should be considered that anticholinergics may be associated with cognitive impairment and delirium , and these adverse effects may be even more common in the advanced stage of PD, when dementia is a very common feature.
Deep Brain Stimulation And Respiratory Failure
DBS is an effective strategy for the treatment of advanced PD, thus improving motor fluctuations and bradykinesia.
Nonetheless, the classical target of the subthalamic nucleus -DBS reserves stimulation-induced side effects in the long-term period, comprising gait and speech impairment, as well as a progressively worsening of tremor. In this scenario, only few papers have specifically investigated respiratory failure. In particular, STN-DBS may increase the risk of a fixed epiglottis and modify velopharyngeal control ; these effects seem to strictly depend on frequency parameters, with low-frequency stimulation leading to a clinical improvement, whereas higher frequencies are associated with a detrimental effect on velopharyngeal control .
In support of this view, Hammeret al. have recently found that in STN-DBS patients, respiratory changes do not correlate with limb function, but speech-related respiratory and laryngeal control may benefit when the stimulation is delivered at low frequencies and shorter pulse width . In addition to stimulation frequency, other factors may account for these correlations, including variability in localisation of the active DBS electrodes, individual variability in somatotopic organisation of STN, stimulation fields and potential current spread beyond the STN target . Data on the relationship between respiratory changes and novel DBS targets, such as the pedunculopontine nucleus , have not been extensively reported so far.
Symptoms That Are Commonly Associated With Pd
These symptoms include sleep disorders, abnormalities in blood pressure, urinary problems, constipation, depression, and anxiety. Even though these symptoms are so commonly seen in PD, they are also commonly associated with other issues that have nothing to do with PD, so it is vital to keep an open mind about their cause. If any symptom is new or worsening, it could be an indication of a new medical problem. For example, urinary problems are extremely common in PD, but may be a sign of an enlarged prostate, which can be treated in an entirely different way.
The Issue Of Pneumonia In Parkinson’s Disease
Aspiration pneumonia represents a dramatic complication that may explain the acute/subacute onset of fever and respiratory insufficiency in a PD patient. Physiologically, swallowing requires adequate coordination between pharyngeal and respiratory musculature, but this mechanism is frequently impaired in PD . Dysphagia is typical in the advanced stages of disease, on average 10–11?years after motor symptoms onset , when bradykinesia, rigidity and dyskinesias are predominant; however, a cough dysfunction in more than 50% of asymptomatic PD patients has been demonstrated and this may also contribute to silent aspiration and increased risk of pneumonia . Moreover, in these patients the cough mechanism becomes weak because of cough reflex impairment and chest wall rigidity, further increasing the risk of aspiration . A blunted urge to cough , a respiratory sensation that precedes the cough reflex, is also present and correlates with the severity of dysphagia and consequently, with an increased risk of aspiration .
Tips For Coping With Breathing Difficulties

- Work with your doctor to identify and treat any non-PD causes of shortness of breath, such as lung disease, heart disease or lack of physical conditioning and endurance.
- Exercise as much as possible. Shortness of breath may lead a person to move less. Less physical activity reduces the ability to take deep breaths. Staying active improves pulmonary function.
- Take steps to cope with anxiety. Talk with your doctor to figure out what sets off anxiety and find treatments and techniques that work for you.
- Speak to your doctor about getting an evaluation performed by a speech-language pathologist who can help you address issues related to swallowing.
- Give up smoking.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinson’s Foundation Center of Excellence.
Practical Recommendations For The Clinician
Neurological and pneumological dysfunction are strictly connected in PD patients. Pneumologists should be aware that breathing problems in this class of patients may be a direct consequence of disease progression and/or of the dopaminergic stimulation, as already mentioned for dyspnoea due to levodopa-induced diaphragmatic dyskinesias. Moreover, pneumologists should consider the spirometric abnormalities that could be found even in the early stages of the disease, and the potential therapeutic role on the airways function exercised by dopaminergic stimulation more than that seen with conventional inhaled drugs. Neurologists, in the same way, should always consider the role of pneumological evaluation in the clinical history of a PD patient and focus on respiratory function as a potential therapeutic target to improve quality of life in a patient complaining of breathing disturbances. Finally, the physician should remember also the potential benefit of pulmonary rehabilitation on functional respiratory tests and exercise tolerance even in the early stages , and it is reasonable to consider a respiratory training program in parallel with dopaminergic therapy in patients who report respiratory symptoms.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Decreased facial expressions: You may not smile or blink as often as the disease worsens; your face lacks expression.
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
Medical Recognition Of Breathing Disorders
The existence of these breathing disorders have been known about, but largely ignored, in medical circles, for decades. Indeed, L.C. Lum, a cardiologist at Papworth & Addenbrookes Hospitals, Cambridge, UK, wrote an article on this entitled “Hyperventilation: the Tip of the Iceberg” in 1975. Here are some relevant excerpts:
“…this syndrome… shows up in medical clinics under many other guises. This is merely the tip of the iceberg; the body of the iceberg, the ninety nine per cent who do not present , presents a collection of bizarre and often apparently unrelated symptoms, which may affect any part of the body, and any organ or any system. The many organs involved are often reflected in the number of specialists to whom the patient gets referred, and my colleagues have variously dubbed this the ‘multiple doctor’ or the ‘fat folder syndrome’. Indeed the thickness of the case file is often an important diagnostic clue.”
Lum lists many symptoms, many of which are also common in PD: palpitations, disturbance of consciousness/vision, shortness of breath. “asthma” chest pain, dysphagia, muscle pains, tremors, tension, anxiety, fatigability, weakness, exhaustion, sleep disturbance nightmare, constipation, diarrhea, twitching eyelids, headache, giddiness, difficulty in breathing, weak limbs, painful limbs, vague pain, weakness, irritability, insomnia.
How Do I Prevent Falls From Common Hazards

- Floors: Remove all loose wires, cords, and throw rugs. Minimize clutter. Make sure rugs are anchored and smooth. Keep furniture in its usual place.
- Bathroom: Install grab bars and non-skid tape in the tub or shower. Use non-skid bath mats on the floor or install wall-to-wall carpeting.
- Lighting: Make sure halls, stairways, and entrances are well-lit. Install a night light in your bathroom or hallway and staircase. Turn lights on if you get up in the middle of the night. Make sure lamps or light switches are within reach of the bed if you have to get up during the night.
- Kitchen: Install non-skid rubber mats near the sink and stove. Clean spills immediately.
- Stairs: Make sure treads, rails, and rugs are secure. Install a rail on both sides of the stairs. If stairs are a threat, it might be helpful to arrange most of your activities on the lower level to reduce the number of times you must climb the stairs.
- Entrances and doorways: Install metal handles on the walls adjacent to the doorknobs of all doors to make it more secure as you travel through the doorway.
Breathing Problems And Parkinsons Disease
Usually, trouble breathing is not thought of as a symptom of PD. Those with PD who complain of this will typically have testing of their heart and lung function. This is necessary since, as we continue to emphasize, a person with PD can develop medical problems unrelated to PD and needs every new symptom evaluated like someone without PD. However, often the testing does not reveal a cardiac or pulmonary abnormality. Could difficulty breathing be a symptom of PD itself?
There are a number of ways in which difficulty breathing may be a symptom of PD:
Shortness of breath can be a wearing-OFF phenomenon
Some non-motor symptoms can fluctuate with brain dopamine levels, which means that they change as a function of time from the last levodopa dose. For some people, shortness of breath can be one of the non-motor symptoms that appears when medication levels are low. However, shortness of breath can be due to anxiety which can also be a wearing-OFF phenomenon. Sometimes it is not possible to determine whether the key symptom is anxiety or shortness of breath. Treatment involves changing medication dosing and timing so that OFF time is minimized. You can view this webinar which discusses the concept of wearing OFF and potential treatments.
Abnormal breathing can be a type of dyskinesia
Restrictive lung disease
Aspiration pneumonia
Sleep apnea
Exercises For Restoring Health Breathing
There are various suggested types of exercise which can help gradually shift the equilibrium point of CO2 intolerance back to healthy states. However, all of these emphasize nose breathing over mouth breathing , and diaphragmatic breathing over chest breathing. This represents an immediate roadblock for people with PD, for whom mouth breathing is likely to have become so ingrained that it feels like the nose is permanently stuffed up, and who have diaphragms which are so frozen that it cannot voluntarily be flexed. However, it is possible to open the nose in the majority cases through some simple exercises. Robert Litman in the above video demonstrates this, and below is another video of Patrick McKeown on the topic. See also my article on how I restored nose breathing with the help of a red light anti-allergy device. It is also possible to restore access to diaphragmatic breathing, as I covered in another article, which explains how I used Block Therapy to achieve this.
Once nasal and diaphragmatic breathing is made possible there are a few different types of breathing exercises one try for restoring CO2 tolerance to more normal levels. It is important to note that these exercises are not necessarily targeted at immediate regulation of the Nervous System, unlike breathing methods designed for in-the-moment relaxation or mobilization, but are aimed at long term retraining of breathing patterns in order to restore healthy oxygenation levels to the brain and muscles.
Respiratory Dysfunction In Parkinsonisms
As described above, the presence of respiratory dysfunction in PD may be explained, at least in part, by dysregulation in basal ganglia and in other brainstem structures that control the central respiratory drive or peripheral airway muscles. In this scenario, it is reasonable to assume the presence of some kind of dysfunction in other forms of Parkinsonism, either secondary or primary degenerative, in which these structures may be involved .
Besides this, to the best of our knowledge, systematic studies on degenerative parkinsonians are still lacking, with only few data currently available about MSA and DLB, two degenerative disorders belonging to ?-synucleinopathies along with PD.
Inspiratory stridor is probably related to vocal cord paralysis or vocal cord and laryngeal dystonia, leading to glottis closure , and the presence of nocturnal stridor is classically considered an important predictor of sudden death in these patients . No data about the role of dopaminergic therapy or DBS are available in MSA, and some authors proposed an approach with CPAP or botulinum toxin injection into vocal cords . Obstructive sleep apnoea has been related to pharyngeal narrowing due to brainstem neurons degeneration , and similarly to other forms of obstructive apnoea CPAP is the preferential treatment.
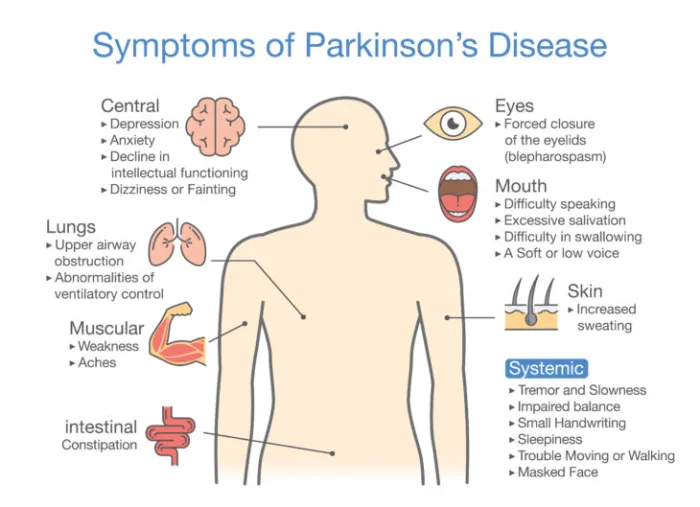
Parkinson’s Diseasesigns And Symptoms
Parkinson’s generally progresses slowly, sometimes taking years for symptoms to appear. The disease usually strikes adults over age 50, although it has been diagnosed as early as age 20. About 15 percent of Parkinson’s patients have a family history of the disease.
Because it develops gradually, most people have many years of productive living after being diagnosed.
Some of the first symptoms commonly experienced with Parkinson’s include the following:
- Rigidity Arms and legs become stiff and hard to move
- Tremors Rapid shaking of the hands, arms or legs
- Slowed movements Difficulty starting or completing movements, called bradykinesia
- Impaired balance Lack of balance or difficulty adjusting to sudden changes in position
These symptoms may make it difficult for you to walk, pick up and hold things, eat, write, or react quickly to prevent injury if you fall.
Other symptoms include difficulty speaking or swallowing, drooling, stooped posture, inability to make facial expressions, oily skin, cramped handwriting, shortness of breath, constipation, increased sweating, erectile dysfunction, difficulty sleeping, problems urinating and anxiety.
UCSF Health medical specialists have reviewed this information. It is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace the advice of your doctor or other health care provider. We encourage you to discuss any questions or concerns you may have with your provider.
Breathing & Respiratory Difficulties
Some people with Parkinson’s disease may experience shortness of breath. There is no clear cause underlying respiratory dysfunction in PD, its frequency or the effect that medications have on respiration. Several reasons for shortness of breath in PD include:
- “Wearing off” is a common experience among people with PD who have been taking levodopa for several years. These occur when the medication benefit wears off and PD symptoms return before the next dose.
- Respiratory dyskinesia refers to an occurrence of irregular and rapid breathing when levodopa medications reach their peak effect. These may accompanied by involuntary body movements, typically experienced as dyskinesia.
- Anxiety is a common symptom of PD that may also exacerbate shortness of breath, whether by itself or as a consequence of wearing off of the medication.
- Aspirationpneumonia is a pneumonia that develops after food or liquid “goes down the wrong pipe.” Advanced PD can increase the risk of swallowing difficulties, choking and aspiration pneumonia.
- Non-PD health issues include conditions such as asthma, allergies, lung disease, heart disease and other conditions that may cause shortness of breath.
