Myth: Parkinsons Can Be Cured
Unfortunately, theres no cure for Parkinsons disease at the moment.
Drugs like Levodopa can slow down symptoms by replacing the missing dopamine in the brain, and are particularly effective in the early stages of Parkinsons.
However, working out how to stop brain cells from getting sick in the first place is more difficult.
Parkinsons also affects people in different ways. Rather than a single cure that works for everyone, researchers are looking into a range of new therapies to help different forms of the condition. One of these is gene therapy, which they hope will reprogramme cells to keep them healthy.
Treatment can be confusing, but your doctor will talk through your options and find the best fit for you. Often medication will be combined with physiotherapy or occupational therapy, to help you control the condition better and keep you doing what you love for longer.
Research milestones in the treatment of Parkinsons
Parkinsons UK is a leading charity funding research into new treatment. This year theyve been focusing on overcoming race inequalities in Parkinsons research, as well as using cannabidiol to treat some of the psychological symptoms of the disease. Previous breakthroughs in Parkinsons research include:
Recommended Reading: How Does Parkinsons Disease Develop
How Will My Doctor Test For It
There’s no one test for Parkinson’s. A lot of it’s based on your symptoms and health history, but it could take some time to figure it out. Part of the process is ruling out other conditions that look like Parkinson’s. The docotor may do a DaT scan, which looks for dopamine in the brain. This can aid in a diagnosis.
Because there is no single test, it’s very important to go to a doctor who knows a lot about it, early on. It’s easy to miss.
If you do have it, your doctor might use what’s called the Hoehn and Yahr scale to tell you what stage of the disease you’re in. It ranks how severe your symptoms are from 1 to 5, where 5 is the most serious.
The stage can help you get a better feel for where your symptoms fall and what to expect as the disease gets worse. But keep in mind, some people could take up to 20 years to move from mild to more serious symptoms. For others, the change is much faster.
How Common Is Parkinson’s Disease
The incidence of Parkinsons disease has been increasing in most countries around the world. This is likely due to an increase in life expectancy in the general population, as the condition is seen more often with older age. In the United States, Parkinsons disease affects almost six per 1,000 people age 45 and over.
Read Also: How To Tell If You Have Parkinson’s
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery For Parkinson’s Disease At Ucla
If you’ve been diagnosed with Parkinson’s, your doctor will first prescribe medication. There are many drugs available that improve symptoms, but they have many side effects, including nausea, hallucinations and impulsive behavior. Some patients respond well to medications for years before seeing side effects. In these patients, the drugs may start to wear off quickly, or they may become extremely sensitive to the drugs and experience too much movement
Deep brain stimulation is a surgical option available to patients who are intolerant of medications or who experience serious side effects. This procedure involves implanting electrodes, or wires, deep inside the brain to change irregular brain activity. As a result, it improves motor function in patients with Parkinson’s disease. It is used more often to treat Parkinson’s disease than any other movement disorder.
Plus Common Misconceptions About What Its Like

There are many misconceptions about Parkinsons disease, which has led to widespread misunderstanding about what the disease really is and the effects it has on someone who is living with it.
Many people believe that having Parkinsons means you would look sick, but thats not always the case. Living with Parkinsons disease looks slightly different for everyone. The condition can cause symptoms like tremors or balance issues and mental health struggles such as depression. Learn more about the facts and myths about this disease.
Verywell / Zoe Hansen
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Eyesight
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose non-genetic cases of Parkinsons. Doctors usually diagnose the disease by taking a persons medical history and performing a neurological examination. If symptoms improve after starting to take medication, its another indicator that the person has Parkinsons.
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinsons disease. People with Parkinsons-like symptoms that result from other causes, such as multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies, are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinsons, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to better evaluate the cause. Many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, so it is important to get an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible.
Do You Know The Early Signs Of Parkinsons
The onset of Parkinsons usually happens over the age of 60, however cases have been reported between the ages of 30 and 40 too.
While changing motor skills and tremors are widely recognised as early warning signs, there are a range of lesser known symptoms that my indicate Parkinsons too. These can include:
- Losing your sense of smell
- Speaking in a soft voice than usual
- Changes in your handwriting, i.e taking longer to write things down, or writing thats smaller than usual and bunched together
- Problems getting a good nights sleep
- Unexplained dizzy spells
You may experience these symptoms for a variety of reasons they wont always be caused by Parkinsons disease. Your GP will be able to offer the right support if youre worried about any of the above.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Parkinson’s Off Episode
Myth : Parkinsons Is Only A Motor Condition
Fact: While its true that Parkinsons disease symptoms include shaking and tremor, rigid muscles, slowness of movement, and a frozen or flat expression, its a lot more than that.
Nonmotor symptoms deserve and are getting more attention from doctors and researchers. These symptoms include cognitive impairment or dementia , anxiety and depression, fatigue, sleep problems and more.
For some patients, nonmotor symptoms are more disabling than motor symptoms, which are the focus of treatment. Be sure to talk to your doctor about other issues so you can get all of your symptoms addressed.
Myth : Deep Brain Stimulation Is Experimental Therapy
Fact: Deep brain stimulation, or DBS, is a procedure in which doctors place electrodes in the brain at the point when medications are less effective in masking motor symptoms, such as tremor, stiffness and slowness of movement.
While it may sound frightening and futuristic, its been around and successfully used for decades. DBS works very similarly to a pacemaker, except the wire is in the brain, not in the heart. Its been a standard procedure for the past two decades.
You May Like: Do All Parkinson Patients Shake
Facts About Parkinsons Disease
Shelli Bakken | Mar 21, 2018
What do singer Neil Diamond and actor Michael J. Fox have in common? They are living with Parkinsons disease , a disease that destroys a group of brain cells that produce dopamine.
April is Parkinsons Awareness Month. As a member of the Struthers Parkinsons Care Network, Walker Methodist actively works to provide our teams with education needed to improve care for our residents living with PD.
Many people are not familiar with PD and how it impacts the mind and body and there are a lot of assumptions and myths around the disease. In support of Parkinsons Awareness Month, here are nine facts about Parkinsons disease.
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
At present, we do not know the cause of Parkinsons disease. In most people there is no family history of Parkinsons Researchers worldwide are investigating possible causes, including:
- environmental triggers, pesticides, toxins, chemicals
- genetic factors
- combinations of environment and genetic factors
Don’t Miss: Thc For Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease is movement disorder of the nervous system that worsens over time. As nerve cells in parts of the brain weaken or are damaged or die, people may begin to notice problems with movement, tremor, stiffness in the limbs or the trunk of the body, or impaired balance. As these symptoms become more obvious, people may have difficulty walking, talking, or completing other simple tasks. Not everyone with one or more of these symptoms has PD, as the symptoms appear in other diseases as well.
No cure for PD exists today, but research is ongoing and medications or surgery can often provide substantial improvement with motor symptoms.
Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
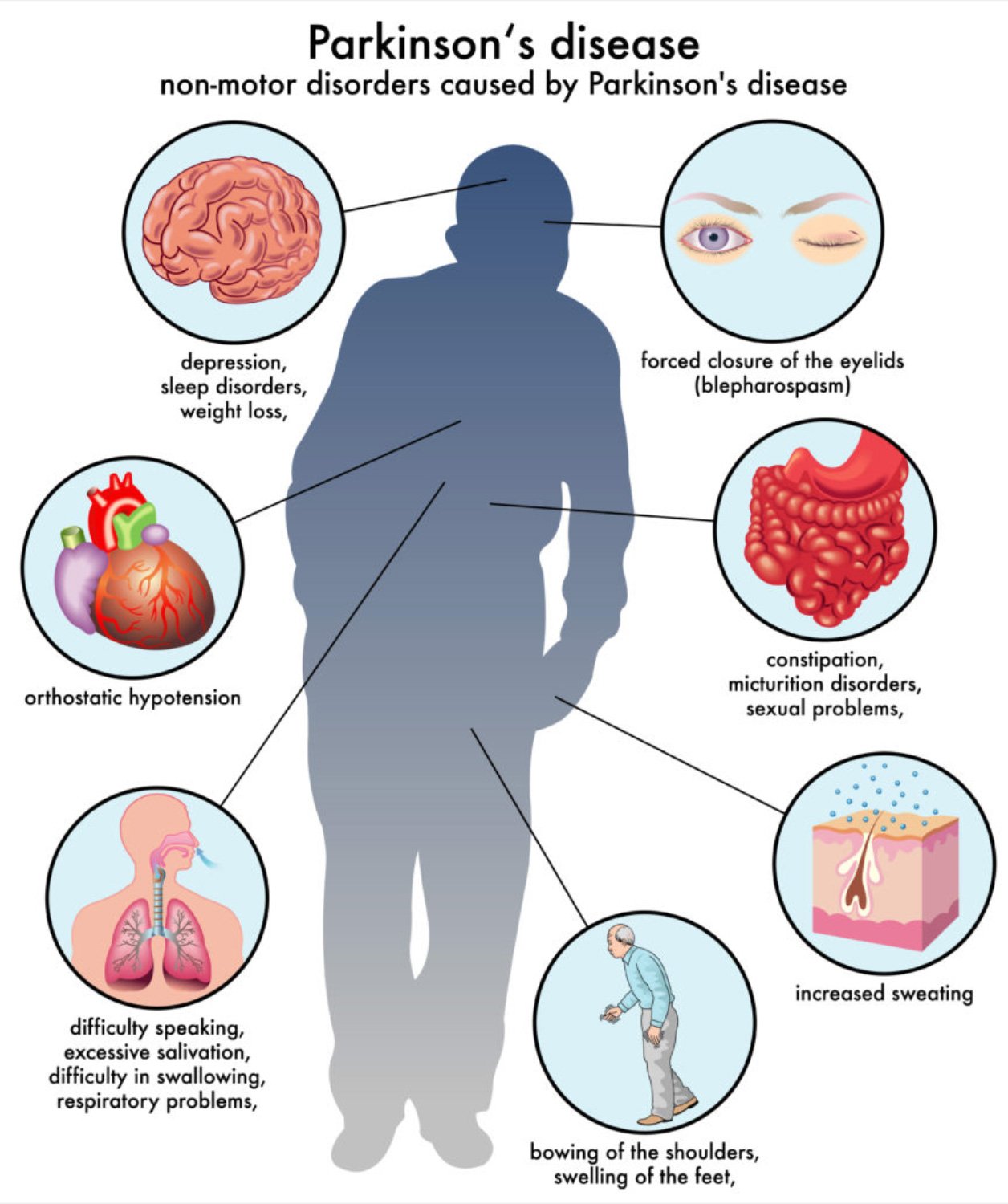
Usually, Parkinson disease begins subtly and progresses gradually.
The first symptom is
-
Tremors in about two thirds of people
-
Problems with movement or a reduced sense of smell in most of the others
Tremors typically have the following characteristics:
-
Are coarse and rhythmic
-
Usually occur in one hand while the hand is at rest
-
Often involve the hand moving as if it is rolling small objects around
-
May be worsened by emotional stress or fatigue
-
May eventually progress to the other hand, the arms, and the legs
-
May also affect the jaws, tongue, forehead, and eyelids and, to a lesser degree, the voice
In some people, a tremor never develops. Sometimes the tremor becomes less obvious as the disease progresses and muscles become stiffer.
Parkinson disease typically also causes the following symptoms:
Walking becomes difficult, especially taking the first step. Once started, people often shuffle, taking short steps, keeping their arms bent at the waist, and swinging their arms little or not at all. While walking, some people have difficulty stopping or turning. When the disease is advanced, some people suddenly stop walking because they feel as if their feet are glued to the ground . Other people unintentionally and gradually quicken their steps, breaking into a stumbling run to avoid falling. This symptom is called festination.
Parkinson disease also causes other symptoms:
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Dementia Support Group
Tips To Keep Your Bladder Healthy
People rarely talk about bladder health, but everyone is affected by it. Located in the lower abdomen, the bladder is a hollow organ, much like a balloon, that stores urine. Urine contains waste and extra fluid left over after the body takes what it needs from what we eat and drink. Each day, adults pass about a quart and a half of urine through the bladder and out of the body.
As people get older, the bladder changes. The elastic bladder tissue may toughen and become less stretchy. A less flexible bladder cannot hold as much urine as before and might make you go to the bathroom more often. The bladder wall and pelvic floor muscles may weaken, making it harder to empty the bladder fully and causing urine to leak.
While you cant control everything that affects your bladder, here are 15 steps you can take to keep it as healthy as possible:
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
| Other names | Diffuse Lewy body disease, dementia due to Lewy body disease |
|---|---|
| of a in a neuron of the scale bar=20 microns | |
| After the age of 50, median 76 | |
| Duration | |
| Variable average survival 4 years from diagnosis | |
| Frequency | About 0.4% of persons older than 65 |
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of characterized by changes in sleep, , , movement, and . Memory loss is not always an early symptom. The disease and is usually diagnosed when cognitive impairment interferes with . Together with , DLB is one of the two . It is a common form of dementia, but the is not known accurately and many diagnoses are missed. The disease was first described by in 1976.
in which people lose the muscle paralysis that normally occurs during and act out their dreamsis a core feature. RBD may appear years or decades before other symptoms. Other core features are , marked fluctuations in or alertness, and . A presumptive diagnosis can be made if several disease features are present, such as symptoms or certain results of , , , and . A definitive diagnosis usually requires an .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Huntington’s Disease And Parkinson’s
Treating Movement Symptoms In Lewy Body Dementia
LBD-related movement symptoms may be treated with medications used for Parkinson’s disease, called carbidopa-levodopa. These drugs can help make it easier to walk, get out of bed, and move around. However, they cannot stop or reverse the disease itself. Side effects of this medication can include hallucinations and other psychiatric or behavioral problems. Because of this risk, physicians may recommend not treating mild movement symptoms with medication. Other Parkinson’s medications are less commonly used in people with LBD due to a higher frequency of side effects.
People with LBD may benefit from physical therapy and exercise. Talk with your doctor about what physical activities are best.
What Does Parkinson’s Do To The Brain
Deep down in your brain, there’s an area called the substantia nigra, which is in the basal ganglia. Some of its cells make dopamine, a chemical that carries messages around your brain. When you need to scratch an itch or kick a ball, dopamine quickly carries a message to the nerve cell that controls that movement.
When that system is working well, your body moves smoothly and evenly. But when you have Parkinson’s, the cells of your substantia nigra start to die. There’s no replacing them, so your dopamine levels drop and you can’t fire off as many messages to control smooth body movements.
Early on, you won’t notice anything different. But as more and more cells die, you reach a tipping point where you start to have symptoms.
That may not be until 80% of the cells are gone, which is why you can have Parkinson’s for quite a while before you realize it.
Also Check: Is Parkinson’s A Motor Neuron Disease
How Is Parkinson’s Treated
It is possible to have a good to great quality of life with PD. Treatment for each person with Parkinsons is based on his or her symptoms, and may include medication and, later, surgical therapy. Other treatments include lifestyle modifications, like getting more rest and exercise.
There are many medications available to treat Parkinsons symptoms, although none yet that reverse the effects of the disease.
Who Does Pd Affect
Getting older is the biggest factor for PD with most people diagnosed in their 60s. In rare cases, some people will develop PD before age 50, known as young-onset PD. Men are 1.5 times more likely to have PD than women.
Directly inheriting the disease is quite rare. Only about 10 to 15 percent of all cases of Parkinsons are thought to be genetic forms of the disease. In the other 85 to 90 percent of cases, the cause is unknown.
Also Check: What Chemicals Cause Parkinson’s Disease
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect Parkinsons disease or need to rule out other conditions, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
New lab tests are possible
Researchers have found possible ways to test for possible indicators or Parkinsons disease. Both of these new tests involve the alpha-synuclein protein but test for it in new, unusual ways. While these tests cant tell you what conditions you have because of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, that information can still help your provider make a diagnosis.
The two tests use the following methods.
- Spinal tap. One of these tests looks for misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins in cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. This test involves a spinal tap , where a healthcare provider inserts a needle into your spinal canal to collect some cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
- Skin biopsy. Another possible test involves a biopsy of surface nerve tissue. A biopsy includes collecting a small sample of your skin, including the nerves in the skin. The samples come from a spot on your back and two spots on your leg. Analyzing the samples can help determine if your alpha-synuclein has a certain kind of malfunction that could increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
How Common Is Parkinsons Disease

The incidence of Parkinsons disease has been increasing in most countries around the world. This is likely due to an increase in life expectancy in the general population, as the condition is seen more often with older age. In the United States, Parkinsons disease affects almost six per 1,000 people age 45 and over.
Dont Miss: Ldn Parkinsons Latest News
Read Also: How Are You Tested For Parkinson’s
Causes Of Parkinson Disease
In Parkinson disease, synuclein forms clumps called Lewy bodies in nerve cells. Lewy bodies consist of misfolded synuclein. Synuclein can accumulate in several regions of the brain, particularly in the substantia nigra and interfere with brain function. Lewy bodies often accumulate in other parts of the brain and nervous system, suggesting that they may be involved in other disorders. In Lewy body dementia Dementia With Lewy Bodies and Parkinson Disease Dementia Dementia with Lewy bodies is progressive loss of mental function characterized by the development of Lewy bodies in nerve cells. Parkinson disease dementia is loss of mental function characterized… read more , Lewy bodies form throughout the outer layer of the brain . Lewy bodies may also be involved in Alzheimer disease Alzheimer Disease Alzheimer disease is a progressive loss of mental function, characterized by degeneration of brain tissue, including loss of nerve cells, the accumulation of an abnormal protein called beta-amyloid… read more , possibly explaining why about one third of people with Parkinson disease have symptoms of Alzheimer disease and why some people with Alzheimer disease develop parkinsonian symptoms.
About 10% of people with Parkinson disease have relatives who have or have had the disease. Also, several gene mutations that can cause Parkinson disease have been identified.
