What Does Lewy Body Dementia Look Like
Lewy body dementia affects a persons ability to think and process information and it can negatively impact memory and alter personality. Though it shares aspects of other forms of dementia, there are distinct hallmarks of LBD. Lewy body dementia symptoms include:
- Fluctuating attention/alertness: These shifts can last hours or go on for days. The person may stare into space, appear lethargic or drowsy, and have hard-to-understand speech, appearing a lot like delirium. At other times, the person may have much more clarity of thought.
- Visual hallucinations: Often, these are very detailed hallucinations and visions of people or animals, and they can recur.
- Movement disorders: Parkinsons-like movement issues, such as muscle rigidity, tremors, falls, or a shuffling gait or way of walking, may occur.
Treating Parkinsons Disease Dementia
A treatment plan for PDD typically includes medications that boost the brains level of certain neurotransmitters and help improve memory and processing speed, Dr. Petrossian says. Exercise is also an important part of the treatment planDr. Petrossian recommends skill-based activities like boxing or dance to boost cognitive function as well as fitness. PDD symptoms should be monitored long-term by a neurologist, and in some cases a psychiatrist, says Dr. Okun. In many cases, physical, occupational, speech, and social work therapy can also be useful since PPD affects all aspects of life.
What Does Progression In Stages Mean
There are many different types of dementia and all of them are progressive. This means symptoms may be relatively mild at first but they get worse with time, usually over several years. These include problems with memory, thinking, problem-solving or language, and often changes in emotions, perception or behaviour.
As dementia progresses, a person will need more help and, at some point, will need a lot of support with daily living. However, dementia is different for everyone, so it will vary how soon this happens and the type of support needed.
It can be helpful to think of dementia progressing in three stages:
These are sometimes called mild, moderate and severe, because this describes how much the symptoms affect a person.
These stages can be used to understand how dementia is likely to change over time, and to help people prepare for the future. The stages also act as a guide to when certain treatments, such as medicines for Alzheimers disease, are likely to work best.
Recommended Reading: What Stage Is Freezing In Parkinson’s
Lewy Body Dementia Vs Parkinsons Disease Dementia
Diagnoses of Lewy body dementia include dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. Symptoms in both of these diagnoses can be similar.
Lewy body dementia is a progressive dementia caused by abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. Lewy bodies are also seen in Parkinsons disease.
The overlap in symptoms between Lewy body dementia and Parkinsons disease dementia include movement symptoms, rigid muscles, and problems with thinking and reasoning.
This seems to indicate that they could be linked to the same abnormalities, though more research is needed to confirm that.
The later stages of Parkinsons disease have more severe symptoms that may require help moving around, around-the-clock care, or a wheelchair. Quality of life can decline rapidly.
Risks of infection, incontinence, pneumonia, falls, insomnia, and choking increase.
Hospice care, memory care, home health aides, social workers, and support counselors can be a help in later stages.
Parkinsons disease itself isnt fatal, but complications can be.
Research has shown a median survival rate of about
What Is Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is a movement disorder. It can cause the muscles to tighten and become rigid This makes it hard to walk and do other daily activities. People with Parkinsons disease also have tremors and may develop cognitive problems, including memory loss and dementia.
Parkinson disease is most common in people who are older than 50. The average age at which it occurs is 60. But some younger people may also get Parkinson disease. When it affects someone younger than age 50, its called early-onset Parkinson disease. You may be more likely to get early-onset Parkinson disease if someone in your family has it. The older you are, the greater your risk of developing Parkinson disease. Its also much more common in men than in women.
Parkinson disease is a chronic and progressive disease. It doesnt go away and continues to get worse over time.
Recommended Reading: Is Cbd Good For Parkinsons
Recommended Reading: Brain Stimulation Device For Parkinson’s
What Happens In Dlb
People with DLB may have trouble focusing, remembering things, staying awake during the day, or staying asleep at night. They may become more frustrated or confused because of the lack of sleep. They may also hallucinate and see people, objects, or animals that are not there.
Some people with DLB will need help with walking, while others may have hunched posture or trouble using their hands and feet because of stiff muscles. People with DLB may appear to be better and need less help on some days, only to become worse and more confused again and need more help the next day or in a few days. This is because their energy level and focus will vary.
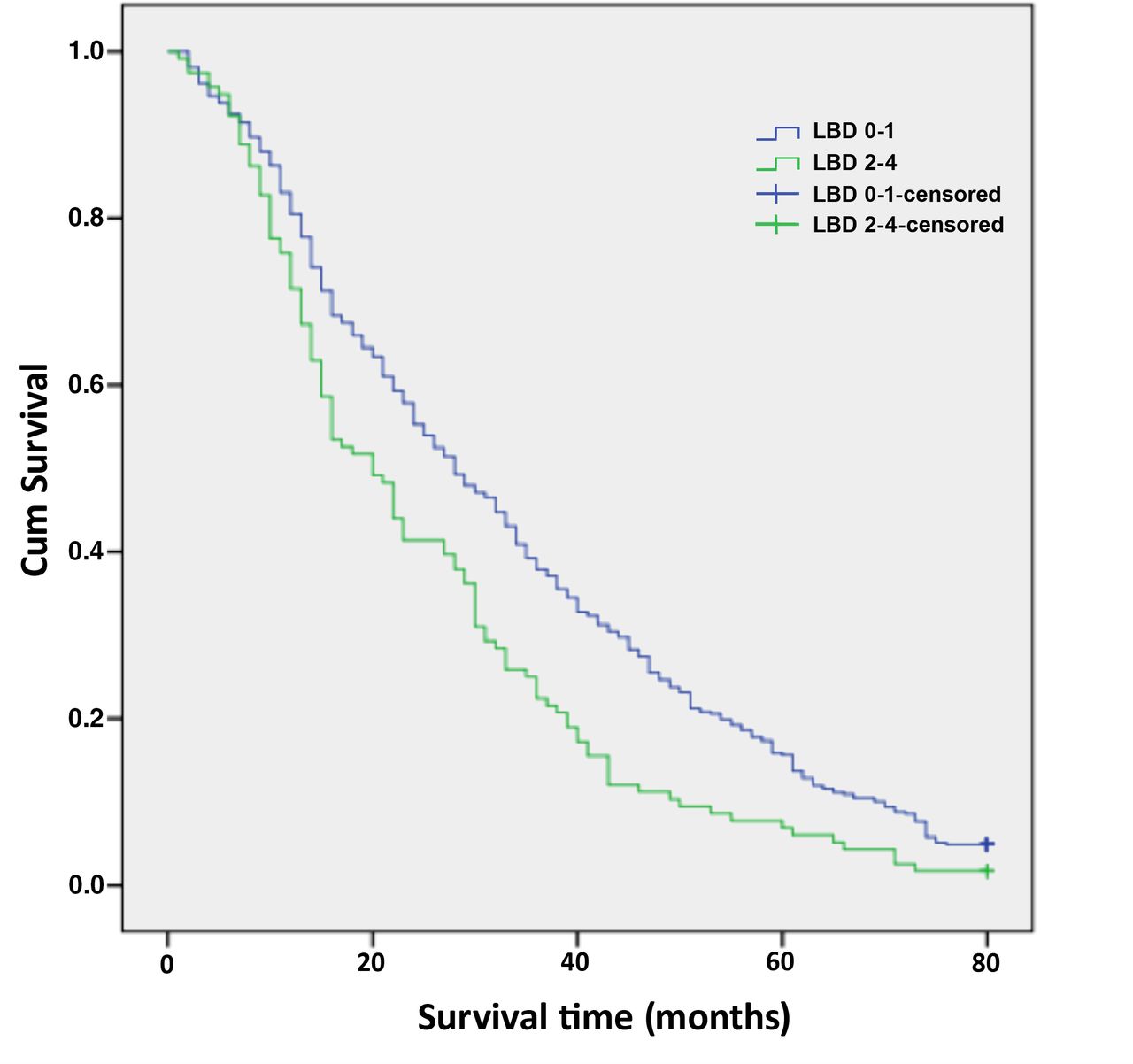
DLB is a disease that changes with time. A person with DLB can live for many years with the disease. Research suggests that a person with DLB may live an average of 57 years with the disease, although this can vary from person to person.
What Are Pd Dementia Safety Concerns
Safety issues should be considered and monitored from the time of diagnosis. As PDD progresses, ensure that your loved one is not left alone.
- Evaluate driving privileges before safety is a concern. Your doctor can make a driving evaluation referral.
- Work out legal and financial issues and safeguard finances. People with dementia are at greater risk of falling victim to scams and fraud.
- Minimize prescription risks. Confirm with the doctor the medication names and doses of the person with PD. If the person is in dementias early stages and capable, fill up their weekly pill box together and monitor use.
- Medical alert systems can be critical in case your loved one falls or wanders outside of the home. Many types of systems are available, from bracelets and pendants to smart watches with fall detection and one-button connections to 911.
- Evaluate gun safety. If your loved one owns a firearm or has one in the home, consider speaking with their doctor about the subject and taking appropriate safety precautions.
Recommended Reading: Apps For Parkinsons Patients
Don’t Miss: What Does Parkinson’s Disease Do To You
How Does Lewy Body Disease Progress
Lewy body disease differs from Alzheimers disease in that the progression of the disease is usually more rapid. However, like Alzheimers disease it is a degenerative condition, eventually leading to complete dependence. Death is usually a result of another illness, such as pneumonia or an infection. The average lifespan after the onset of symptoms is about seven years.
Clinical History And Testing
Diagnostic tests can be used to establish some features of the condition and distinguish them from symptoms of other conditions. Diagnosis may include taking the person’s medical history, a physical exam, assessment of neurological function, brain imaging, neuropsychological testing to assess cognitive function,sleep studies, myocardial scintigraphy, or laboratory testing to rule out conditions that may cause symptoms similar to dementia, such as abnormal thyroid function, syphilis, HIV, and vitamin deficiencies.
If DLB is suspected when parkinsonism and dementia are the only presenting features, PET or SPECT imaging may show reduced dopamine transporter activity. A DLB diagnosis may be warranted if other conditions with reduced dopamine transporter uptake can be ruled out.
Since 2001, 123iodine–metaiodobenzylguanidinemyocardialscintigraphy has been used diagnostically in East Asia , but not in the US. MIBG is taken up by sympathetic nerve endings, such as those that innervate the heart, and is labeled for scintigraphy with radioactive 123iodine. Autonomic dysfunction resulting from damage to nerves in the heart in patients with DLB is associated with lower cardiac uptake of 123I-MIBG.
There is no genetic test to determine if an individual will develop DLB and, according to the Lewy Body Dementia Association, genetic testing is not routinely recommended because there are only rare instances of hereditary DLB.
Read Also: What Chemicals Can Cause Parkinson
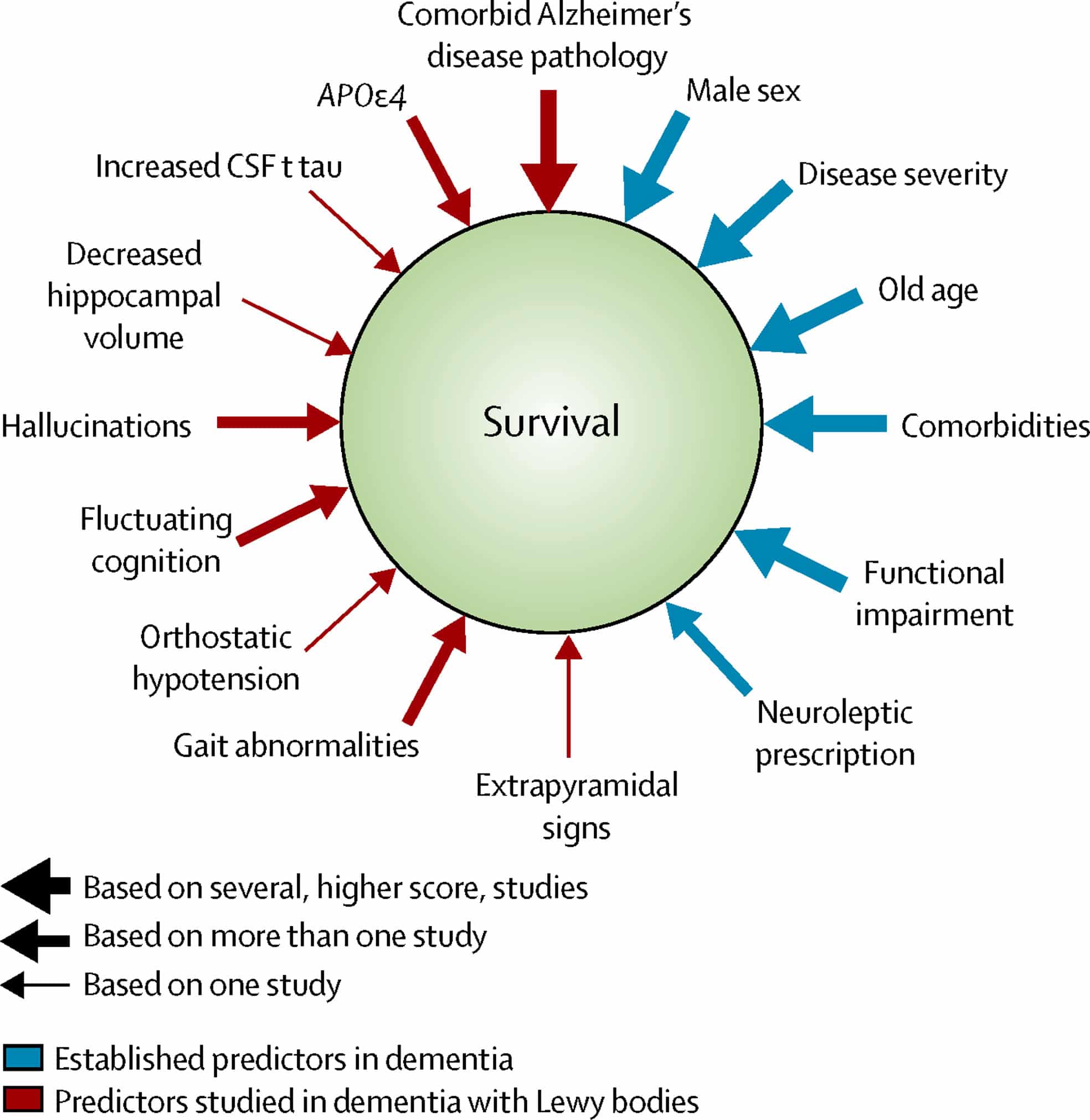
What Are The Causes Of Lewy Body Dementia
The precise cause of LBD is unknown, but scientists are learning more about its biology and genetics. For example, we know that an accumulation of Lewy bodies is associated with a loss of certain neurons in the brain that produce two important chemicals that act as messengers between brain cells . One of these messengers, acetylcholine, is important for memory and learning. The other, dopamine, plays an important role in behavior, cognition, movement, motivation, sleep, and mood.
Scientists are also learning about risk factors for LBD. A risk factor is something that may increase the chance of developing a disease. Some risk factors can be controlled while others cannot. Age is considered the greatest risk factor. No specific lifestyle factor has been proven to increase one’s risk for LBD.
Other known risk factors for LBD include certain diseases and health conditions, particularly Parkinson’s disease and REM sleep behavior disorder, which have been linked to a higher risk of LBD.
Having a family member with LBD also may increase a person’s risk, though LBD is not considered a genetic disease. Variants in three genes APOE, SNCA, and GBA have been associated with an increased risk, but in most cases, the cause is unknown.
What Is Dementia With Lewy Body Disease
Dementia with Lewy body disease is a condition that causes changes in thinking, behavior, and movement. DLB usually starts with thinking and behavior changes that are followed by problems with movement. The movement problems in DLB are similar to those seen in people with more classical Parkinsons disease.
Also Check: How Does Parkinson’s Affect The Body
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a progressive brain disorder that affects mobility and mental ability. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with Parkinsons, you may be wondering about life expectancy.
According to some research, on average, people with Parkinsons can expect to live almost as long as those who dont have the condition.
Stage Two: Very Mild Cognitive Decline
Stage two may bring subtle changes in the individual, such as mild forgetfulness. These instances may include forgetting names or having trouble locating familiar objects. In the second stage of dementia, its difficult or impossible to notice these minor symptoms, and a diagnosis is not yet able to be reached.
You May Like: What Does Parkinson’s Disease Affect
Stage Four: Moderate Cognitive Decline
Many people living with dementia are officially diagnosed during stage four, which is when physicians are able to pinpoint cognitive decline with an exam. At this point, the patient will likely present symptoms such as life-disrupting forgetfulness and out-of-character difficulty performing daily responsibilities. It may become more challenging for those with stage four dementia to manage finances or navigate to new locations.
Michael J Fox Says Having Parkinsons Disease Sucks
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways youve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
Its thought around one in 500 people are affected by Parkinsons disease, according to the NHS. The disease is known to affect the brain, and well-known symptoms include problems like a tremor. According to studies, taking two vitamins could help to lower your risk in later life.
You May Like: Severe Hip Pain Parkinson’s
Managing Sleep Disorders In Lewy Body Dementia
Sleep problems may increase confusion and behavioral problems in people with LBD and add to a caregiver’s burden. A physician can order a sleep study to identify any underlying sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and REM sleep behavior disorder.
REM sleep behavior disorder, a common LBD symptom, involves acting out one’s dreams, leading to lost sleep and even injuries to individuals and their sleep partners. Clonazepam, a drug used to control seizures and relieve panic attacks, is often effective for the disorder at very low dosages. However, it can have side effects such as dizziness, unsteadiness, and problems with thinking. Melatonin, a naturally occurring hormone used to treat insomnia, may also offer some benefit when taken alone or with clonazepam.
Excessive daytime sleepiness is also common in LBD. If it is severe, a sleep specialist may prescribe a stimulant to help the person stay awake during the day.
Some people with LBD have difficulty falling asleep. If trouble sleeping at night persists, a physician may recommend a prescription medication. It is important to note that treating insomnia and other sleep problems in people with LBD has not been extensively studied, and that treatments may worsen daytime sleepiness and should be used with caution. Sleep problems can also be addressed by avoiding lengthy naps, increasing daytime exercise, and avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and chocolate late in the day.
Complications Related To Parkinsons Can Affect Survival
Claudia Chaves, MD, is board-certified in cerebrovascular disease and neurology with a subspecialty certification in vascular neurology.
Parkinsons is a common neurodegenerative disease, and although it is not fatal, research suggests it may influence life expectancy.
A 2012 study in Archives of Neurology examined the six-year survival of nearly 140,000 Medicare beneficiaries with Parkinsons disease in the United States. During the six-year period, 64% of the participants with Parkinsons disease passed away.
The risk of death of those with Parkinsons was then compared to Medicare beneficiaries who did not have Parkinsons or any other common diseases, including:
When controlling for variables like age, race, and gender, the six-year risk of death among people with Parkinsons was found to be nearly four times greater than those Medicare beneficiaries without the disease or other common diseases.
At the same time, the rate of death among those with Parkinsons disease was similar to those with hip fracture, Alzheimers dementia, or a recent heart attackalthough it was higher than those who had been newly diagnosed with either colorectal cancer, stroke, ischemic heart disease, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Also Check: Can Tbi Cause Parkinson’s
Medications At The End Of Life
Many participants described stopping DLB medications near EOL. Occasionally this was associated with a decline:
I would swear in a court of law that the galantamine worked for her And when I couldnt get her to take it is really when I started noticing the decline.
Hospice commonly provided morphine for pain, breathing, or overall comfort. Many participants felt that morphine resulted in a peaceful death, but several participants described morphine as insufficient to address pain or causing paradoxical symptoms. Often hospice needed to supplement morphine with benzodiazepines. Multiple participants described using haloperidol from hospice comfort packs. In one case, this resulted in a severe reaction:
He looked at the strings hanging down from the overhead lights and he thought they were a noose. I mean, it wasnt anything you know, anything I was worried about. I was just relating to how things had been going. And she suggested Haldol. And I didnt research it About two, two and a half hours since he had his Haldol He was suddenly sitting upright Every muscle in his body was clenched. His mouth was clenched. It was opening and closing, opening and closing. His tongue was thrusting out. He almost bit his tongue off at one point and he was groaning and moaning, and he was in terrible pain His temperature skyrocketed From there, his kidneys shut down, and he was gone by Tuesday morning.
Dont Miss: Bicycle Therapy For Parkinsons Disease
How Lewy Body Dementia Progresses
Lewy body dementia and Alzheimer’s disease are both forms of dementia. Lewy body dementia, however, progresses somewhat differently from Alzheimer’s disease. Notably, the symptomsespecially memory losscan fluctuate greatly with LBD. Alzheimer’s tends to worsen more steadily.
One of the hallmarks of Lewy body dementia is the fluctuation of cognitive functioning. Often, a person may function fairly well one day and be totally disengaged with a profound loss of memory the next.
Understanding this variation in cognition can be helpful for caregivers. Without this knowledge, it may seem like the person with Lewy body dementia is “forgetting” on purpose.
This fluctuation can also make it feel like the person is moving back and forth from one stage to another. In reality, the variation in functioning is a normal feature within each stage of the disease.
Don’t Miss: What Disease Is Similar To Parkinson’s
Eat Healthy Meals Throughout The Day
- Consuming a variety of foods from all five food groups provides consistent energy and keeps your immune system healthy. Focus on eating a minimum of five fruits and vegetables each day, eating a variety of high fiber foods, and staying hydrated, all of which help prevent constipation, which is often an issue for people diagnosed with YOPD.
- Watch this to learn how to use nutrition to help you live well with Parkinsons.
You May Like: Parkinsons Double Vision
Evidence That Life Expectancy Calculators For Dementia Actually Work

It turns out that the length of time a person has before needing full-time care, before moving into a care community, and before dying can all be predicted somewhat accurately. This information, though not definitive, can help families get a general understanding of how to plan for the future and what to expect as the disease progresses.
In a study conducted at the department of neurology in Columbia University, groups of people with mild Alzheimers were followed for 10 years and assessed semiannually. Data from these assessments were plugged into a complicated algorithm. The people studied were tested for the following:
Mental status score Cognition and function Motor skills Psychology and behavior Basic demographic information
Other experiments have yielded similar results. A University of Kentucky study analyzed the records of more than 1,200 people with dementia and found that it was possible to accurately predict their life expectancy. Researchers looked at many variables including family history and medical problems like high blood pressure and heart disease, and ultimately realized it came down to three things:
age when the first symptoms appeared gender how impaired someone was when diagnosis was first made
Recommended Reading: How Do They Check For Parkinson’s Disease
