Bowel Incontinence: Another Embarrassing Casualty Of Pd
Fecal Incontinence is where you lose control of your bowels. This blog post explains the primary cause of this in Parkinsons disease. Problems reaching the toilet in time because of mobility, abdominal bloating or cramping compound the problem. Dr. De León has included a check list of things to help minimize occurrences and embarrassment, even to the point of surgery, if necessary.
Ui And Adverse Health Outcomes
The mean follow-up of time of the participants was nearly 8 years . We employed a Cox proportional hazards model adjusted for age, sex, and education to examine the association of baseline UI with incident parkinsonism. Baseline UI was associated with incident parkinsonism . Since we treated UI as a numerical scale, inspection of the hazard ratio suggests that an individual with severe incontinence , had about a 30% increased risk of developing parkinsonism as compared to an individual without incontinence.
Since the pathologic basis for parkinsonism in older adults with and without a clinical diagnosis of PD may vary , we repeated this analysis excluding 65 cases with a clinical diagnosis of PD. Baseline UI remained associated with incident parkinsonism . In a final model, adding terms for seven chronic health conditions and BMI did not attenuate the association of UI with incident parkinsonism .
In further analyses, we examined whether baseline UI was associated with other adverse health outcomes. Baseline UI was also associated with risk of death and incident ADL and mobility disability, but was not associated with incident MCI or AD dementia . These findings were unchanged when we controlled for seven chronic health conditions and BMI .
The Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations of Baseline Urinary Incontinence and Global Cognition in Community-Dwelling Older Adults*
| Model Terms . |
|---|
Papers Of Particular Interest Published Recently Have Been Highlighted As: Of Importance Of Major Importance
Other Formats
Read Also: What To Do For Parkinson’s
Urinary Dysfunction Is Associated With Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Degeneration In Early And Untreated Patients With Parkinsons Disease
Yidong FanAcademic Editor: Received
Abstract
The aim of the present study was to determine the relation between urinary dysfunction and nigrostriatal dopaminergic degeneration in early and untreated Parkinsons disease . The data were obtained from Parkinsons Progression Markers Initiative database. Two hundred and seventy-five patients and 149 healthy controls were included in our analysis. Urinary symptoms were evaluated with the Scale for Outcomes in Parkinsons Disease for Autonomic Symptoms . We performed correlation analyses between 123I-FP-CIT SPECT imaging data and severity of urinary symptoms in patients with PD and healthy controls. Early and untreated patients with PD exhibited worse urinary symptoms when compared with healthy controls. The severity of urinary symptoms significantly correlated with dopamine transporter binding levels in the caudate and the putamen. After controlling for age and sex, the severity of storage symptoms significantly correlated with dopamine transporter binding levels in the less affected side of the putamen . The correlation was observed in both male and female patients . No correlations were found between dopamine transporter binding levels and voiding symptoms in male or female patients, or any urinary symptoms in healthy controls. Worse storage symptoms reflect greater nigrostriatal dopaminergic loss in early and untreated PD.
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Clinical Evaluation
2.3. DAT Imaging
3. Results
Urinary Problems In Parkinsons Disease
This 1-hour webinar is an interview with Dr. Janis Miyasaki, Dr. Jorges Juncos, and retired movement disorder specialist and young onset Parkinsons patient, Dr. Maria De Leon. They discuss the effect of Parkinsons disease on the autonomic nervous system, which regulates many body functions, including bladder control. Urinary problem diagnosis, symptom management and ongoing research on the topic wrap up the hour.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Volunteer Opportunities
Parkinson’s Disease And Voiding Dysfunction
In this 54-minute webinar, urologist Dr. Sidney Radomski explains how voiding function is affected by Parkinsons disease in both men and women. He discusses how an enlarged prostate contributes to voiding problems and management options of voiding dysfunction for those with Parkinsons disease and MSA.
Parkinsons And Urinary Incontinence
Parkinsons causes problems with automatic bodily functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and urinary function. Urinary incontinence is much different than fecal incontinence and usually doesnt start to occur until the later stages of the disease. Urinary incontinence due to Parkinsons is a two-fold problem. The bladder has trouble holding urine in, but, at the same time, its difficult to control the release of urine, leading to some serious discomfort and emergency bathroom visits.
Urinary incontinence problems can come in many forms:
A person with Parkinsons may have to urinate very frequently, complicated by an increasingly difficult time with movement. Once they sit down, they may find it difficult to let go of the urine and void their bladder. While nearly 40% of Parkinsons patients may experience some level of urinary incontinence, only 15% of patients should develop a serious urinary condition.
Don’t Miss: Is Dark Chocolate Good For Parkinson’s Disease
Increasing Your Fibre Intake
Eating the right amount of fibre and drinking enough fluids can help if you have constipation.
To get more fibre in your diet:
- choose a breakfast cereal containing wheat, wheat bran or oats, such as Weetabix, porridge or bran flakes.
- eat more vegetables, especially peas, beans and lentils.
- eat more fruit fresh, stewed, tinned or dried. High fibre fruits include prunes or oranges.
- drink plenty of fluids throughout the day to avoid dehydration. Lots of fluids are suitable, including water, fruit juice,
- milk, tea and squashes. Cut out caffeine to avoid overstimulation of your bladder.
If you find it difficult chewing high-fibre food, you can get some types which dissolve in water. You can also get drinks which are high in fibre.
Try to increase how much fibre you get gradually to avoid bloating or flatulence .
A dietitian can give you further advice. Ask your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse for a referral.
What’s Next For Those Suffering From Urinary Incontinence
I decided I did not want to add another medication to the medicine bag. I was trying to see if there was something I could do besides resigning myself to wearing pads or some other incontinence protection all the time. At 53 years old, I wanted to see if there was a way I could help myself.
Part 2 of this article will address my experiences. I plan to discuss what I lovingly refer to as “PEE PEE PT” – physical therapy to help treat urinary incontinence.
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Cause Blindness
Whats Next For Those Suffering From Urinary Incontinence
I decided I did not want to add another medication to the medicine bag. I was trying to see if there was something I could do besides resigning myself to wearing pads or some other incontinence protection all the time. At 53 years old, I wanted to see if there was a way I could help myself.
Part 2 of this article will address my experiences. I plan to discuss what I lovingly refer to as PEE PEE PT physical therapy to help treat urinary incontinence.
You May Like: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinsons
Bladder Irrigation And Clean Catheterization
Bladder irrigation with various solutions such as aminoglycoside, glycosaminoglycans , povidone-iodine , chlorhexidine solution , and saline with acetylcysteine have been advocated as a management strategy for patients with indwelling catheters or those who require intermittent catheterizations . Although several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of bladder irrigation with various agents , gentamicin remains the best intravesical treatment that has shown efficacy in both the prevention and treatment of recurrent UTIs . Furthermore, the risk of developing antibiotic resistance and systemic adverse effects is low in patients treated with bladder irrigation with gentamicin .
You May Like: Side Effects Of Parkinson Disease Medicine
Don’t Miss: Holistic Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
Difficulty Emptying The Bladder
- Some people with Parkinsons find it difficult to pass urine if the bladder fails to contract when required, or because the sphincter does not let urine out or a combination of the two. This is a result of reduced dopamine levels interfering with the efficiency of the bladder muscles and causing a residual amount of urine to be left in the bladder. This reduces the total amount the bladder can hold and creates a feeling of wanting to empty the bladder very often. Unfortunately, there is an increased risk of urinary infection if the bladder is not emptied completely.
- In some older people, constipation which is often associated with Parkinsons can result in faeces collecting in the rectum. This can result in difficulties in bladder emptying, which may be because of pressure on the urethra, or mediated by the nerves in the region. The bladder is then unable to empty and may continue distending, causing dribbling incontinence.
- Anticholinergic medications can also make emptying problems worse.
Urinary Incontinence: A Non
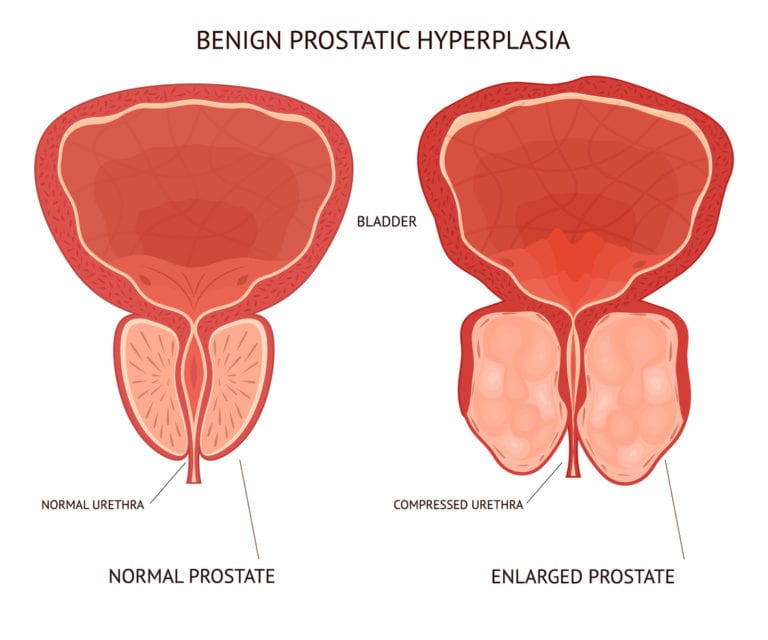
While most people think of Parkinsons disease as a motor disease, it is also a neurodegenerative disease affects the CNS and the ability for the messages from the brain to get to the muscles and nerves. While the motor issues of PD are well known, the non-motor issues are often overlooked – including urinary incontinence.
Read Also: How Does Cbd Help Parkinson’s
Characteristics Of The Included Studies
After duplicating removal, we identified 7,358 articles through the database searching. Screening titles and abstracts led to the elimination of 7,237 irrelevant articles, full-text versions of the remaining 121 potentially eligible articles were assessed. Of those, 79 articles were included in the qualitative synthesis. Overall, 73 studies comprising 14,937 PD patients were identified eligible for the meta-analysis . The procedure was shown flow chart in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Study selection flowchart, performed according to the PRISMA 2020 guidelines.
Sample size ranged from 20 to 3,414. Average age of participants ranged from 57.4 to 76.1 years. The average disease duration of PD ranged from 0.36 to 17.94 years. Forty-seven studies used the scales, 19 used questionnaire, 4 used definitions, and 3 applied mixed methods. We classified 4 studies as high quality, 29 studies as moderate, and 40 studies as low. The results indicated that the overall quality of the included articles was relatively low. There were 65 cross-sectional studies and 8 cohort studies in the included research. The studies were conducted in 29 countries, 27 performed in Europe, 5 in North American, while others were undertaken in the other regions . Table 1 shows the characteristics of included study.
Parkinsons And Fecal Incontinence
Did you know that 65% of Parkinsons patients are affected by constipation, and, many times, the constipation is severe? The beginning stages of fecal incontinence start to occur immediately due to behavioral changes that can even preclude a diagnosis. For example, when someone starts to notice that their hand is shaking a little, they may be nervous about spilling something and reduce their intake of fluids. The trembling hand may be what causes you to call the doctor, but the bowel problems have already begun.
Fecal incontinence also comes in several forms, including:
Parkinsons Disease slows down our gastric motility function, which means that our ability to digest food and move waste through our system has slowed way down. When you mix this with all the medication that a person with Parkinsons has to take and the fact that they arent always getting enough water or movement, constipation is an unfortunate side effect.
This means that a person with Parkinsons can suffer from bowel impaction that needs to be removed or experience a loss of muscle control that can lead to accidents, and near-accidents, that can keep someone with the disease from living their best life. What can be done to treat incontinence in Parkinsons patients?
Read Also: Can Parkinson’s Disease Be Inherited
Treatment Of Bowel Dysfunction In Pd
3.4.1. Dietary Fibers
3.4.2. Cholinergic Drugs
A prior report has shown that pyridostigmine bromide, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, is effective in the amelioration of constipation in PD .
3.4.3. Dopaminergic Drugs
Levodopa and Other Dopaminergic Agonists
3.4.4. Dopaminergic Blockers
3.4.5. Serotonergic Drugs
3.4.6. Other Drugs
Although prior reports have indicated the effectiveness of motilides , neurotrophin-3 and colchicine on constipation in PD, their use remains limited. Type A botulinum toxin injection into the puborectalis muscle and biofeedback ameliorates anismus in PD.
Options For Overactive Bladder In Patients With Parkinsons Disease
Dr. Brucker also led two retrospective studies investigating alternative treatments for OAB in patients with Parkinsons disease. Patients with overactive bladder often have distressing urinary incontinence. When patients have a neurological basis for their bladder dysfunction, the efficacy of available treatments can be difficult to assess.
To shed light on the efficacy and safety of potential treatments, Dr. Bruckers team examined two therapies that have been used in OAB patients without Parkinsons disease one study investigated mirabegron, a novel Beta adrenoceptor agonist approved for OAB in 2012 the other examined onabotulinum toxin A injections . While both treatments have been shown to be safe and effective for OAB, anticholinergic drugswhich increase the risk of cognitive dysfunction and adverse eventsremain the standard of care for patients with Parkinsons disease due to lack of clinical studies.
In the first study, investigators examined records of 50 Parkinsons patients who received daily doses of mirabegron between 2012 and 2017. After 6 weeks of treatment, 50 percent of patients experienced improvement, and 11 percent reported complete resolution of their OAB symptoms. The therapy was well tolerated, and median time to discontinuation was longer than that observed in other OAB patients.
The study findings were published in Neurourology and Urodynamics and Parkinsonism and Related Disorders, respectively.
You May Like: What Is Stage 5 Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment For Over Active Bladder In Parkinsons
Overactive bladder affects up to 27% of men and 43% of women of the global population. Now, add a neurological condition and the problem becomes more challenging. First, there is a list of medications which make the problem worse, so should be avoided. Then, a thorough evaluation and physical exam. Treatment depends on the cause, but evaluating all medications and an adjustment of dopamine medication is often necessary. If you are still having problems, five further treatment options are included.
Eligibility Criteria And Study Selection
Studies were eligible if they met the following criteria: published in peer-reviewed English journals participants were diagnosed according to UK Parkinson’s Disease Society Brain Bank Diagnostic Criteria or MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease reporting the prevalence of LUTS or LUTS subtypes LUTS or LUTS subtypes assessed by validated scales administered by experienced clinicians, self-report questionnaire, or published criteria from classification codes/definition prospective cohort study or cross-sectional study.
The studies were excluded if they: did not provide full text included insufficient or unclear fragmented data for analysis enrolled patients who have been diagnosed with prostate carcinoma, uncontrolled diabetes, as well as any other diseases that cause urinary problems, or taken drugs such as diuretics with small sample size . duplicated publications systematic reviews, meta-analyses, letters, protocols. When results on the same dataset were reported in several publications, only the most complete publication was included in the analysis. Two independent observers evaluated the results and resolved any disagreement by discussion or with recourse to a third arbitrator .
Recommended Reading: What Medications Are Prescribed For Parkinson’s Disease
Bladder Problems In Parkinsons
The primary function of the bladder is twofold to store urine as it is made and then to empty the urine. With Parkinsons, problems can emerge in both areas.
Recent studies suggest that 30-40% of people with Parkinsons have urinary difficulties. Despite the frequency of urinary dysfunction, actual urinary incontinence is relatively uncommon. Troublesome incontinence develops in only about 15% of people with Parkinsons.
The most common urinary symptoms experienced by people with Parkinsons are:
- The need to urinate frequently
- Trouble delaying urination once the need is perceived, creating a sense of urinary urgency
These symptoms usually mean you have an irritable or overactive bladder. Your bladder is signaling the brain that it is full and needs to empty when, in fact, it is not. This can happen at any time, so you might have to get up multiple times during the night to go to the bathroom.
Impairment of bladder emptying is a less frequent but still troublesome feature of urinary dysfunction in Parkinsons. This may be caused by delay or difficulty in relaxation of the urethral sphincter muscles. These muscles must relax for the bladder to empty. This can result in hesitancy in initiating urination, difficulty in generating a stream and incomplete emptying of the bladder. Dystonia involuntary muscle contractions of the urethral sphincter has also been described.
Exercise For Constipation In Parkinsons Disease
Be guided by your doctor, but general suggestions include:
- Talk with your doctor, physiotherapist, exercise physiologist or healthcare professional when planning your exercise program.
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise every day.
- Spend a few minutes warming up and cooling down. This could include marching in place or stretching.
- Start with the easiest exercises first. Slowly introduce the more difficult exercises as your fitness increases.
- Only exercise when other people are at home who can help if necessary.
- Remember: too little exercise and fluid intake with an increase in dietary fibre can worsen constipation for some people.
Also Check: Is Choking A Symptom Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons Disease And Voiding Dysfunction
In this 54-minute webinar, urologist Dr. Sidney Radomski explains how voiding function is affected by Parkinsons disease in both men and women. He discusses how an enlarged prostate contributes to voiding problems and management options of voiding dysfunction for those with Parkinsons disease and MSA.
Prevalence Of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Urinary Incontinence And Retention In Parkinsons Disease: A Systematic Review And Meta
1Department of Neurology, Center for Movement Disorders, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
2China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, Beijing, China
3Department of Neurology, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Also Check: Treatments Available For Parkinsons Disease
Read Also: Medication For Restless Leg Syndrome And Parkinson’s
