Are You A Good Candidate For Dbs
The best candidates for DBS surgery are people who:
- Have been diagnosed with Parkinson’s for five years or more
- Have disabling tremors and dyskinesias or severe motor fluctuations
- Experience severe motor fluctuations that cannot be controlled with adjustments to medication schedules
- Often experience significant dyskinesias interspersed with rapids wearing off and off time crises throughout the day
Not everyone is a good candidate for this surgery. It is important to know that some Parkinson’s symptoms respond well to DBS and others do not. The decision to undergo surgery depends on a critical assessment of each person’s specific symptoms.
Symptoms that respond well to intervention include:
- Dystonia (sustained or repetitive muscle twisting, spasm or cramp
Several factors influence the outcome of DBS. One of the best forecasts is your response to levodopa. People whose symptoms still respond well to individual doses of the drug and who have mobility during their “on” periods usually have better results with DBS.
While some people think DBS should not be considered until Parkinson’s medications have become completely ineffective, this is not true. When medications stop working completely, deep brain stimulation won’t work, either. Surgery promises more effectiveness for those who experience complications with medications, such as dyskinesias, but continue to respond well to levodopa.
Those who respond well to DBS tend to be people who:
How Common Is Dbs
Dr. Sheth describes DBS as a very standard treatment. These are procedures that we do week in and week out, he said. It’s not investigational or experimental. Around the world, more than 150,000 patients have had DBS for Parkinson’s or tremor with a success rate of 95%.
Patients need to know that there are these alternatives. They need to know that they’re not necessarily stuck with these symptoms, that there may be a different way to get better control. That discussion is, of course, individual-specific, but the availability of these types of surgical treatments is important for patients to know about.
How Long Do The Benefits Last
Research shows that deep brain stimulation provides both short-lived and long-lasting benefits. The honeymoon phase lingers from a few days to a few months. Some benefits of DBS extend up to 10 years and beyond.1-4
The length of time that DBS benefits last varies from person to person. Research shows that triggering different areas of the brain can result in benefits that span varying lengths of time. Some benefits may decrease over the years, while others remain.1
Also Check: Can Adderall Cause Parkinson’s
How Might Dbs Affect Behavior Or Mood In People With Parkinsons
Behavior and mood has been an area of intense interest in our group since we conducted the NIH COMPARE DBS study many years ago. At an experienced center, if your DBS lead is optimally placed, many experts will share that mood, thinking and disease progression issues will have the greatest impact on outcome. We always monitor for suicidal ideation, apathy and demoralization. You cant congratulate yourself as a clinician too quickly with DBS, as Parkinsons is a chronic disease. Finally, if you have an anxiety disorder, bipolar disorder, or a history of severe depression, it is important you are monitored closely after DBS surgery.
What Happens During The Procedure
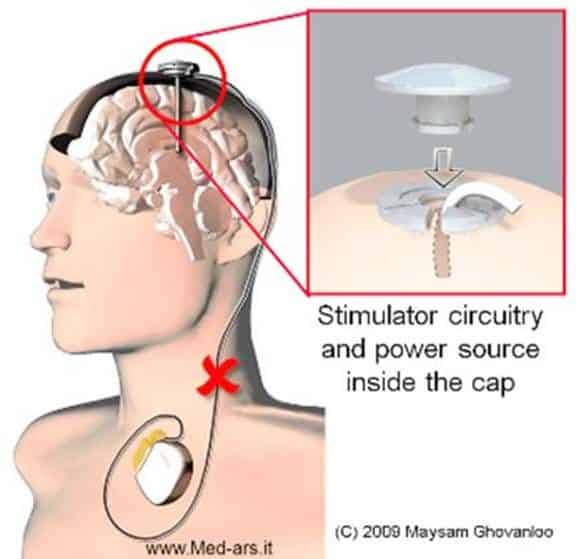
In the operating room, your scalp will be injected with numbing medication. Your head will be placed in a frame to keep it from moving. Small holes will be drilled into your scalp to allow the implantation of electrodes.
Youll be awake during surgery so you can respond to questions and move particular areas of your body when prompted. This, along with imaging tests, helps pinpoint the areas of the brain where symptoms originate. This is where electrodes will be placed.
Electrodes may be implanted on one or both sides of your brain. The neurostimulator will be implanted under the skin near your collarbone or lower in your chest. Leads will go underneath your skin from head to shoulder, connecting the electrodes to the neurostimulator. The tiny holes in your skull will be closed.
After surgery, youll be monitored for complications. Youll spend at least 24 hours in the hospital, but longer if you have complications.
Some risks of surgery are:
- bad reaction to anesthesia
- allergic reaction to materials in the implanted device
- pain or swelling at the surgical site
You May Like: Loving Someone With Parkinsons
Don’t Miss: What Helps With Parkinson’s Disease
Innovative Deep Brain Stimulation Device Reads Brain Signals Allowing For Individualized Treatment For Parkinsons Patients
Pacific Neuroscience Institute at Providence Saint Johns Health Center among first treatment sites
SANTA MONICA Pacific Neuroscience Institute is the first provider in the Providence health system to treat a patient with an innovative surgically implanted Deep Brain Stimulation device.
Used for the management of symptoms of movement disorders such as Parkinsons disease, Percept PC Neurostimulator with BrainSense technology has been developed by Medtronic as a next-generation Deep Brain Stimulation system. The Food and Drug Administration-approved device is the first and only DBS system in the U.S. with ground-breaking BrainSense technology that allows clinicians to capture a patients brain signals, enabling more data-driven, personalized treatment for patients with neurologic disorders, such as Parkinsons disease, essential tremor and epilepsy.
Many patients with PD may be good candidates for deep brain stimulation surgery, said neurologist Melita Petrossian, MD, medical director at Pacific Movement Disorders Center, Pacific Neuroscience Institute. It is a way to reduce off time, increase the amount of time the medication is working on time, reduce tremor and reduce dyskinesias, which are the involuntary movements related to treatment.
M
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation Work
Movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease and other neurological conditions are caused by disorganized electrical signals in the areas of the brain that control movement. When successful, DBS interrupts the irregular signals that cause tremors and other movement symptoms.
After a series of tests that determines the optimal placement, neurosurgeons implant one or more wires, called leads, inside the brain. The leads are connected with an insulated wire extension to a very small neurostimulator implanted under the persons collarbone, similar to a heart pacemaker. Continuous pulses of electric current from the neurostimulator pass through the leads and into the brain.
A few weeks after the neurostimulator has been in place, the doctor programs it to deliver an electrical signal. This programming process may take more than one visit over a period of weeks or months to ensure the current is properly adjusted and providing effective results. In adjusting the device, the doctor seeks an optimal balance between improving symptom control and limiting side effects.
Also Check: How To Rule Out Parkinson’s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
For people with severe motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease that are not adequately controlled by medication, a treatment called deep brain stimulation may offer some relief.
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical placement of a small conductor called an electrode in the brain. The electrode delivers electrical stimulation that blocks the nerve signals that cause tremors.
Specialists at NYU Langones Center for Neuromodulation perform more than 100 deep brain stimulation procedures each year. Our neurologists, neurosurgeons, and psychiatrists provide a thorough evaluation to ensure youre a good candidate for the procedure.
Experience Fewer Symptoms With Deep Brainstimulation
For patients with movement disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor, an effective treatment is available to help significantly reduce their symptoms and make performing daily activities easier.
For appointments
Deep brain stimulation is a therapy used to treat multiple disorders. The most common disorders include Parkinsons disease and essential tremor. It can be used to improve a patients:
- Abnormal muscle activation
It is also being studied in a few psychiatric conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, Tourettes syndrome, depression and addiction.
About DBS surgery
The procedure involves placement of an electrode or lead into a deep structure of the brain typically, one on each side of the brain. These electrodes are secured in place with a plastic cap and connected to extension wires that are tunneled underneath the skin to an implanted generator placed under the skin just below the collar bone, similar to a pacemaker.
The generators last for 3-15 years depending on type implanted and patient use. They are replaced with a simple outpatient surgery. The overall risk of the operation is very low but not zero. In depth discussion with your neurologist and surgeon is needed to determine if you are an appropriate candidate and your risk of the operation.
For above images: ©2021 Medtronic. All rights reserved. Used with the permission of Medtronic.
Recommended Reading: What Is On Off Phenomenon In Parkinson’s Disease
The World’s Smallest Dbs Device
Traditional DBS devices are powered by a pulse generator that is placed under the skin around the chest or stomach area. This is connected to one or two fine wires that are inserted into specific areas of the brain.
The Picostim DBS system, developed by Bioinduction, is the worlds first miniaturised electrical impulse generating pacemaker battery. At about one third of the size of conventional DBS batteries, its small size means it can be implanted directly into the skull, rather than within a pocket under the skin of the chest.
Being able to place the battery in the skull makes it cosmetically invisible and eliminates the need for extension leads running from the chest, and the tunnelling of these wires under the skin of the neck.
It is hoped that by using this new system, the procedure to implant a DBS device will be shortened and simplified without reducing the beneficial effects of DBS treatment.
Dr Alan Whone is a Consultant Neurologist at North Bristol NHS Trust. He is leading the trial and said: ”We are delighted with how this first case went in the operating theatre and with how the patient’s symptoms have been improved over the last year. We are hopeful that if these findings hold up, we will have a significant technical advance by which to improve Parkinson’s care across the world.”
At this time the Bristol team are not asking members of the public to come forward to take part.
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Work
Deep brain stimulation works by modifying abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It was first approved for Parkinsons tremors in 1997 and has become an established treatment to control additional motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
DBS involves three main components:
- Leads: Leads are implanted in the brain in a region responsible for motor activity.
- Implantable pulse generator : A separate procedure is performed to implant a battery-operated device in the chest or in the abdomen. An IPG is similar to a pacemaker for the heart and has been coined by some as a pacemaker for the brain.
- Extension: A thin, insulated wire is passed beneath the skin between the leads and implantable pulse generator to deliver the electrical stimulation from the pulse generator to the leads.
The target area in the brain is first identified by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography . Then, the leads are placed via small holes that a surgeon drills in the skull.
This is considered a minimally invasive surgery that is done in the operating room with local anesthesia. It usually requires an overnight stay.
The IPG is inserted in a separate surgical procedure in the operating room roughly a week later.
After a few weeks, a neurologist begins to program the unit. This process can take several additional weeks to months. When this is completed, people are able to manage the device with a handheld remote control.
Also Check: How To Make A Donation To Parkinson’s Disease
A Way To Manage Symptoms
Previous work from these researchers showed that stimulating the inner ear improved neurological symptoms associated with stroke and traumatic brain injury. This research now shows that ear stimulation has potential in the management of Parkinsons.
Dr Beckie Port, Research Manager at Parkinson’s UK, said:
The results from this small scale study are very exciting. While more research is needed to better understand how delivering this kind of non-invasive stimulation to the nerve in the ear works, it holds a lot of promise to relieve troublesome symptoms that many with Parkinson’s experience.
“Existing Parkinson’s medications are far from perfect. They cannot slow the progression of the condition and often have significant side effects themselves. Pioneering research like this gives us the best hope of finding the breakthrough that will allow us to better manage symptoms and make a life-changing difference to people living with Parkinsons.”
Stereotactic Dbs Vs Interventional Image
Stereotactic DBS surgery requires the patient to be off their medication. During the procedure, a frame stabilizes the head and provides coordinates to help the surgeons guide the lead to the correct location in the brain. The patient gets local anesthesia to keep them comfortable throughout each step along with a mild sedative to help them relax.
During image-guided DBS surgery, such as with interventional MRI or CT scan, the patient is often asleep under general anesthesia while the surgeon uses images of the brain to guide the lead to its target.
Some advanced centers offer both the stereotactic and iMRI-guided options for DBS surgery. In this case, the doctor and patient will discuss which procedure is better based on a number of factors.
For instance, the doctor may recommend an image-guided procedure for children, patients who have extreme symptoms, those who are especially anxious or fearful or those whose leads are going into certain parts of the brain.
Generally, DBS surgery follows this process:
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Cause Neuropathy
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Consult With A Neurologist And A Neuropsychologist
After learning more about DBS, the next step is to make an appointment at a center that specializes in the surgical treatment of Parkinson’s. It is important that anyone considering this surgery be evaluated by a neurologist who is familiar with the procedure, expected benefits and potential risks. If a neurologist thinks you are a good candidate for surgery, and you decide to proceed, meet the neurosurgeon to learn more and prepare for surgery.
Neuropsychological testing is also strongly recommended before proceeding with DBS. This test is often standard to ensure DBS is a good option and help determine how it could affect memory and thinking. DBS will not improve or worsen non-motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s.
You May Like: What Are Parkinson Like Symptoms
How Do I Know If Im A Candidate For Deep Brain Stimulation
Before being considered a candidate for deep brain stimulation , patients with Parkinsons disease must undergo an extensive evaluation process. Ideally, a multidisciplinary team of specialists in the area of movement disorders will assess the patient. This clinical team typically includes a neurologist, neurosurgeon, neuropsychologist and psychiatrist.
If patients are well managed on medications, DBS is not considered. Candidates for DBS are patients who meet one or more of the following criteria:
- Symptoms are not well controlled despite receiving the appropriate dose of levodopa and other medications.
- Symptoms are significantly reducing patients quality of life.
- Abnormal or uncontrolled involuntary movements or motor fluctuations are not improving despite adjustments in medications.
- Four or more doses of levodopa are required a day.
- Tremors that have not been able to be controlled by medications.
Levodopa response test
Patients response to a single dose of levodopa is another test physicians use to identify which patients are likely to benefit from DBS. In this test, patients stop taking levodopa for 8 to 12 hours and then receive a single dose. Patients are likely to benefit from DBS if they have a clear positive response after receiving the single dose of levodopa.
How Does Dbs Work
In DBS surgery, electrodes are inserted into a targeted area of the brain, using MRI and, at times, recordings of brain cell activity during the procedure. A second procedure is performed to implant an impulse generator battery , which is similar to a heart pacemaker and approximately the size of a stopwatch.
The IPG is placed under the collarbone or in the abdomen and delivers an electrical stimulation to targeted areas in the brain that control movement. Those who undergo DBS surgery are given a controller to turn the device on or off and review basic parameters such as battery life.
Read Also: How Early Can Parkinson’s Disease Be Detected
What Are The Risks And Complications Of Deep Brain Stimulation
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and complications. Complications of DBS fall into three categories: surgery complications, hardware complications, and stimulation-related complications.
- Surgical complications include brain hemorrhage, brain infection, wrong location of the DBS leads, and less than the best location of the leads.
- Hardware complications include movement of the leads, lead failure, failure of any part of the DBS system, pain over the pulse generator device, battery failure, infection around the device and the device breaking through the skin as the thickness of skin and fat layer change as one ages.
- Stimulation-related complications occur in all patients during the device programming stage. Common side effects are unintended movements , freezing , worsening of balance and gait, speech disturbance, involuntary muscle contractions, numbness and tingling , and double vision . These side effects are reversible when the device is adjusted.
Recommended Reading: How Does Parkinsons Disease Kill You
You Are About To Exit For Another Abbott Country Or Region Specific Website
Please be aware that the website you have requested is intended for the residents of a particular country or region, as noted on that site. As a result, the site may contain information on pharmaceuticals, medical devices and other products or uses of those products that are not approved in other countries or regions.The website you have requested also may not be optimized for your specific screen size.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Cause Foot Cramps
