Increasing Your Fibre Intake
Eating the right amount of fibre and drinking enough fluids can help if you have constipation.
To get more fibre in your diet:
- choose a breakfast cereal containing wheat, wheat bran or oats, such as Weetabix, porridge or bran flakes.
- eat more vegetables, especially peas, beans and lentils.
- eat more fruit fresh, stewed, tinned or dried. High fibre fruits include prunes or oranges.
- drink plenty of fluids throughout the day to avoid dehydration. Lots of fluids are suitable, including water, fruit juice,
- milk, tea and squashes. Cut out caffeine to avoid overstimulation of your bladder.
If you find it difficult chewing high-fibre food, you can get some types which dissolve in water. You can also get drinks which are high in fibre.
Try to increase how much fibre you get gradually to avoid bloating or flatulence .
A dietitian can give you further advice. Ask your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse for a referral.
Breathing Problems And Parkinsons Disease
Usually, trouble breathing is not thought of as a symptom of PD. Those with PD who complain of this will typically have testing of their heart and lung function. This is necessary since, as we continue to emphasize, a person with PD can develop medical problems unrelated to PD and needs every new symptom evaluated like someone without PD. However, often the testing does not reveal a cardiac or pulmonary abnormality. Could difficulty breathing be a symptom of PD itself?
There are a number of ways in which difficulty breathing may be a symptom of PD:
Shortness of breath can be a wearing-OFF phenomenon
Some non-motor symptoms can fluctuate with brain dopamine levels, which means that they change as a function of time from the last levodopa dose. For some people, shortness of breath can be one of the non-motor symptoms that appears when medication levels are low. However, shortness of breath can be due to anxiety which can also be a wearing-OFF phenomenon. Sometimes it is not possible to determine whether the key symptom is anxiety or shortness of breath. Treatment involves changing medication dosing and timing so that OFF time is minimized. You can view this webinar which discusses the concept of wearing OFF and potential treatments.
Abnormal breathing can be a type of dyskinesia
Restrictive lung disease
Aspiration pneumonia
Sleep apnea
Bladder And Bowel Problems
Bladder and bowel problems are common in men and women of all ages, but people with Parkinsons are more likely to have these problems than people who dont have the condition.
If you have Parkinson’s, you may be more likely to have problems with your bladder or bowels than people of a similar age without the condition.
Some of these problems are common in men and women of all ages, whether they have Parkinson’s or not.
Bowel problems are very common in the general public. But any change in bowel habit, particularly if you see blood in your bowel motions, should be reported to your GP.
Whatever the reason for your bladder and bowel problems, you can usually do something to help. It may be that the problem can be cured completely. But if that isnt possible, there are many different ways of managing the symptoms so they dont rule your life.
Don’t Miss: What Color Is Parkinson’s Awareness Ribbon
Effects Of Dopaminergic Therapy: Risk Or Protection
Studies have provided controversial results about the therapeutic effects of dopaminergic stimulation, and the role of drugs commonly used in the treatment of PD is still debated, strictly depending both on disease stage and administration modality.
Most papers strengthen the role of anti-Parkinsonian drugs as a protective factor against the development of respiratory failure. Levodopa increases inspiratory muscle function in anaesthetised dogs , and dopamine improves diaphragm function during acute respiratory failure in patients with COPD . In early stages, the levodopa equivalent daily dose does not correlate with pulmonary functional testing as the disease progresses, anti-Parkinsonian medications may be responsible for the maintenance of the maximal inspiratory mouth pressure and sniff nasal inspiratory pressure . Accordingly, bedtime controlled-release levodopa is associated with less severe obstructive sleep apnoea in PD . Because dopamine is not known to increase muscle strength, it may ameliorate respiratory function by improving muscle coordination by a central activity .
Many authors have investigated the effect of dopaminergic therapy on aforementioned respiratory dysfunction, especially on obstructive and restrictive patterns .
Main findings of major studies we considered about the effects of dopaminergic drugs on respiratory parameters and respiratory dysfunctions
The Dorsal Vagus Nerve And Parkinson’s Disease

The labelling of the branches of the vagus nerve as super- and sub-diaphragmatic takes on added meaning here, since the diaphragm not only provides the dividing line between them, but any dysregulation of the diaphragm will have an affect on the proper function of the vagus nerve and the communication between the branches.
Indeed, according to a premise in the above cited review article, if the diaphragm is limited in its movement, it becomes stiff, dry, tight and frozen. Then, instead of gliding past or stroking the various nerves which pass through it, as it contracts and releases, the diaphragm squeezes or elongates or compresses these nerves over its limited range of motion. This then causes dysfunctions in the nerve systems – and some very vital nerves pass through holes in the diaphragm, including the vagus.
reduced vagal tone may be induced by mechanical stress caused by a dysfunction of the diaphragm, resulting in a compression of the nerve, which induces abnormal vagal function. There is a close relationship between the vagus nerve and the perception of pain. We know that a compression of the vagus nerve can alter its function and, just like a dysfunction of a peripheral nerve, mimicking an entrapment syndrome. We can assume that abnormal tension of the diaphragm in the region of the oesophagal hiatus could cause a compression of the vagus nerve, reducing its anti-pain and anti-inflammatory activity.”
You May Like: Do Dogs Get Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
Increased Feelings Of Anxiety Or Depression
Anxiety and depression have been linked to Parkinsons. In addition to movement problems, the disease can also have an impact on your mental health. Its possible that changes in your emotional well-being can be a sign of changing physical health as well.
If you are more anxious than usual, have lost interest in things, or feel a sense of hopelessness, talk to your doctor.
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Memory Issues
Tips For Coping With Breathing Difficulties
- Work with your doctor to identify and treat any non-PD causes of shortness of breath, such as lung disease, heart disease or lack of physical conditioning and endurance.
- Exercise as much as possible. Shortness of breath may lead a person to move less. Less physical activity reduces the ability to take deep breaths. Staying active improves pulmonary function.
- Take steps to cope with anxiety. Talk with your doctor to figure out what sets off anxiety and find treatments and techniques that work for you.
- Speak to your doctor about getting an evaluation performed by a speech-language pathologist who can help you address issues related to swallowing.
- Give up smoking.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Don’t Miss: Average Life Expectancy For Parkinson Disease
Causes Of Breathing Difficulty In Parkinsons Disease
- Aspiration Pneumonia: It develops when the food particles lodges down the wrong pipe and settle in the lungs to cause infection. The Parkinsons patient usually aspirates in the advanced stages due to marked motor impairment and muscle dystonia, which leads to swallowing difficulties and specific changes in the swallowing pattern. In fact, it is a well established fact that, aspiration pneumonia is the leading cause of death among the patients in Parkinsons disease.
- Although there has been limited research conducted on this topic, but some of these studies have found that the patients of Parkinsons disease usually inhale a lower volume of air with each passing breath, as compared to the healthy people, which might aid to breathlessness.
- It might also be possible that the rigidity of the muscles in the chest and abdomen, which is a symptom of motor impairment associated with Parkinsons disease might lead to breathlessness.
- Wearing off episodes: These episodes are usually experienced among people who have been taking the levodopa for several years as the medication for Parkinsons disease The wearing off episodes manifest when the medications benefit wears off and the shortness of breath occurs before its time for the next dose.
- Chronic lung diseases such as COPD , chronic asthma, emphysema and chronic bronchitis or an acute exacerbation, can cause shortness of breath accompanied by wheezing, cough or chest discomfort.
- Pulmonary embolism.
Symptomatology Correlations Between The Diaphragm And Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The text reviews the diaphragm’s functions, anatomy, and neurological links in correlation with the presence of chronic symptoms associated to IBS, like chronic low back pain, chronic pelvic pain, chronic headache, and temporomandibular joint dysfunction, vagus nerve inflammation, and depression and anxiety. The interplay between an individual’s breath dynamic and intestinal behaviour is still an unaddressed point and the paucity of scientific studies should recommend further research to better understand the importance of breathing in this syndrome.
This article explains the direct links between diaphragm dysfunction and: issues with the pelvic floor, jaw and tongue lower back pain headaches gastroesophageal reflux perceived pain emotional state and body image pain and inflammation the nervous system.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
A New Toilet Or An Alternative
If you have real difficulties getting to the toilet, it may be possible to get a grant to build a new one, perhaps downstairs. An occupational therapist can advise you on this.
Not all homes are suitable for building new toilets, so a commode might be needed. A commode is a moveable toilet that doesnt use running water. It looks like a chair, with a container underneath that can be removed and cleaned after someone has used it. They can be very discreet.
Who Should Get The Pneumonia Vaccine
You should get the pneumonia vaccine if you:
- Are over age 65
- Have a chronic illness, such as Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, heart disease, or lung disease
- Have HIV or AIDS
- Have a weak immune system from another cause, such as from certain kidney diseases and some cancers, or have had your spleen removed
- Are taking drugs, such as prednisone, that weaken the immune system
Also Check: Parkinsons Genetic Link
Apda In Your Community
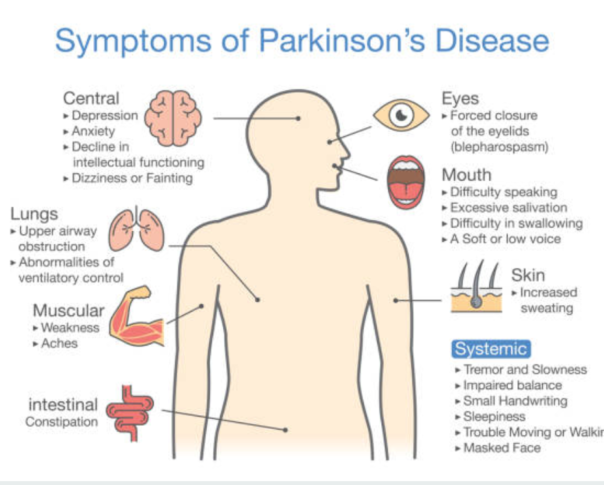
APDAParkinson’s Disease SymptomsCould this be due to Parkinsons Disease? Uncommon non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons Disease
It is common for a person with Parkinsons disease to attribute every new symptom that develops to PD. That is largely because the list of non-motor symptoms commonly associated with PD is so varied, it can seem that almost anything is a symptom of PD! But if you take a closer look, there are some symptoms that are very commonly associated with PD, others that are virtually never associated with PD, and some in between.
Lets divide up non-motor symptoms into the following categories:
How Is Pneumonia Treated
Bacterial pneumonia can be treated with antibiotics — usually by mouth. For more severe pneumonia, you may need to go to the hospital to be treated. Hospital treatment may include oxygen therapy to increase oxygen in the blood, intravenous antibiotics, and fluids. Pain relievers and medicine to reduce fever may also be given. With treatment, bacterial pneumonia usually begins to improve within 24-48 hours.
Viral pneumonia is usually less serious. A stay in the hospital is rarely needed. Antibiotics cannot be used to treat viral pneumonia, but may be given to fight a bacterial infection that is also present. Other drugs, such as those listed above, may be used to lessen symptoms. If you are given antibiotics, make sure you take all of the medicine, even if you feel better. If you stop taking the medicine too early, the infection can come back and may be harder to treat.
For both viral and bacterial pneumonia:
- Drink warm fluids to relieve coughing.
- Rest.
- Don’t rush your recovery. It can take weeks to get your full strength back.
- Don’t smoke.
Also Check: Essential Oils For Parkinson’s
Exercises For Restoring Health Breathing
There are various suggested types of exercise which can help gradually shift the equilibrium point of CO2 intolerance back to healthy states. However, all of these emphasize nose breathing over mouth breathing , and diaphragmatic breathing over chest breathing. This represents an immediate roadblock for people with PD, for whom mouth breathing is likely to have become so ingrained that it feels like the nose is permanently stuffed up, and who have diaphragms which are so frozen that it cannot voluntarily be flexed. However, it is possible to open the nose in the majority cases through some simple exercises. Robert Litman in the above video demonstrates this, and below is another video of Patrick McKeown on the topic. See also my article on how I restored nose breathing with the help of a red light anti-allergy device. It is also possible to restore access to diaphragmatic breathing, as I covered in another article, which explains how I used Block Therapy to achieve this.
Once nasal and diaphragmatic breathing is made possible there are a few different types of breathing exercises one try for restoring CO2 tolerance to more normal levels. It is important to note that these exercises are not necessarily targeted at immediate regulation of the Nervous System, unlike breathing methods designed for in-the-moment relaxation or mobilization, but are aimed at long term retraining of breathing patterns in order to restore healthy oxygenation levels to the brain and muscles.
Off Episodes In Parkinson’s
Off episodes occur when people experience a range of symptoms as their medications wear off or stop working between doses. That can cause motor fluctuations, sensory and psychiatric changes, and other non-motor symptoms, one of which is shortness of breath. It is common among people with PD who have been taking levodopa for many years.
You May Like: Parkinsonian Syndrome Life Expectancy
Addressing Practical Aspects Of Eating And Drinking
Some people with Parkinsons have problems chewing and swallowing. This can make it difficult to eat a diet with plenty of fibre. A speech and language therapist can give advice about this. Ask your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse for a referral. If it takes a long time to eat and your meal goes cold, eat smaller portions and go back for seconds that have been kept warm. You can also get special plates that keep your meals hot the Disabled Living Foundation has more information.
An occupational therapist will also be able to give you some tips and practical advice.
How To Test Your Lungs At Home
If youre worried about your breathing, or you feel that your ribcage is so stiff you cannot take a deep breath, your GP can arrange a test to diagnose any lung problems. This uses a spirometer, which measures the amount of air you can inhale and exhale.
However, there are more fun ways to test this for yourself. Below are four simple checks that will also strengthen your lungs and keep your ribcage flexible. If you find some of these tests difficult, such as becoming light-headed or out of breath, then you know you have some work to do in strengthening your lungs.
Breathing muscles
Using a mirror, watch your body as you breathe. We naturally breathe in using the diaphragm, a large muscle at the base of our ribcage, so you should see your belly expand and your lower ribs move outward. These areas sink back to their normal position when we breathe out. If your ribcage is stiff, you may chest breathe, where you see the upper chest inflate and your shoulders move up and down. This wastes energy and is not an efficient way of breathing. Your GP can refer you to a physiotherapist if you need to learn better breathing techniques.
Lung power
Ribcage flexibility
Exercises you can do at home
This is only a start though, and its best to seek better and more specific advice from your GP to keep your lungs fit and healthy.
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
