Recombinant Gingipain R1 Protease And Alexa 488
Purified fibrinogen with Alexa 488 was prepared to a final concentration of 2 mg.mL1. Clots were prepared by adding human thrombin as per the above protocol. Clots were also viewed with the confocal microscope and fluorescent fibrinogen was excited at 488 nm, with emission measured at 508 to 570 nm. As the gingipains antibody used above has the same excitation and emission as the purified fibrinogen, we could not trace the added gingipains with this antibody. We also incubated purified fluorescent fibrinogen with LPS from P. gingivalis with and without RgpA . Where we combined the LPS and the RgpA, both were added simultaneously followed by an incubation period of 30 min.
The Analysis Of Clots Formed From Fibrinogen Incubated With Recombinant Gingipain R1
Confocal microscopy was used to visualize the clot structure of purified fibrin marked with Alexa 488, with and without exposure to recombinant gingipain R1 , and with and without exposure to P gingivalis LPS . Note that fibrinogen was pre-incubated with the inflammagens,
followed by clot formation with thrombin. is a representative purified fluorescent fibrin clot, showing a fibrin network with distinctive fibers. shows a representative fibrin clot after fluorescent fibrinogen was incubated with P. gingivalis LPS. Fibrin networks display a denser and more matted network. Purified fibrinogen was also exposed to two concentration of RgpA and 500 ng L1 . RgpA greatly inhibited fibrin formation synthesis in a concentration-dependent manner. A combination of both the LPS and RgpA was also added simultaneously to purified fibrinogen, and the resulting clot is shown in . Interestingly, this clot appeared similar to the clot where only LPS was added . Although the interactions between the various protease domains, and RgpA in particular, with LPS and their combined affects on fibrin is unknown, LPS is known to bind to domains of
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases And Parkinsons Disease
Issue title: Special Issue: The Gut-Brain Axis in Parkinsons Disease Revisited
Guest editors: Teus van Laar
Article type: Review Article
Authors: Brudek, Tomasza; b; *
Affiliations: Research Laboratory for Stereology and Neuroscience, Copenhagen University Hospital, Bispebjerg-Frederiksberg Hospital, Copenhagen, Denmark | Copenhagen Center for Translational Research, Copenhagen University Hospital, Bispebjerg and Frederiksberg Hospital, Copenhagen, Denmark
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Tomasz Brudek, Research Laboratory for Stereology and Neuroscience, Copenhagen University Hospital, Bispebjerg-Frederiksberg Hospital, Nielsine Nielsens Vej 6B, building 11B, 2nd floor, DK-2400 Copenhagen NV, Denmark. Tel.: +45 38635600; E-mail: .
Keywords: Parkinsons disease, inflammatory bowel disease, Crohns disease, ulcerative colitis, enteric nervous system, brain-gut axis, gastrointestinal track inflammation, inflammation
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-191729
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 9, no. s2, pp. S331-S344, 2019
Abstract
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
Neuroinflammation In Pd Neurotoxin Models
Epidemiological evidence suggests there is a significant environmental component to sporadic PD. As a result, efforts to identify environmental PD toxins have yielded several chemicals that cause Parkinsonism in rodents and primates. Considerable evidence suggests that these compounds work by inducing oxidative damage in target cells. Research has also found that these PD toxins exert a robust inflammatory response and that anti-inflammatory therapies are protective in animal models. This supports the theory that DA neurons are lost in PD due to an especially high susceptibility to oxidative damage which may be the result of, at least in part, inflammatory response. We will now discuss three of these toxins in the context of neuroinflammation.
Collection Of Whole Blood And Preparation Of Platelet Poor Plasma Samples From Healthy Controls And Pd Patients
Whole blood from healthy controls and PD patients were collected using sterile sampling techniques in citrated, EDTA and SST tubes that were kept at room temperature for 30 min. This is within the prescribed manufacturer protocol for blood collection. PPP was prepared from citrate tubes that were centrifuged at 3000 ×g for 10 min at room temperature . The PPP was subsequently aliquoted into labeled 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes, and stored at 80°C until cytokine analysis. EDTA whole blood and SST were analyzed by the local PathCare laboratory for HbA1c, TC, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol , high-density lipoprotein cholesterol , TG and non-high-density lipoprotein ; TC/HDL ratio was calculated as a marker of cardiovascular risk.
Read Also: End Stages Parkinsons
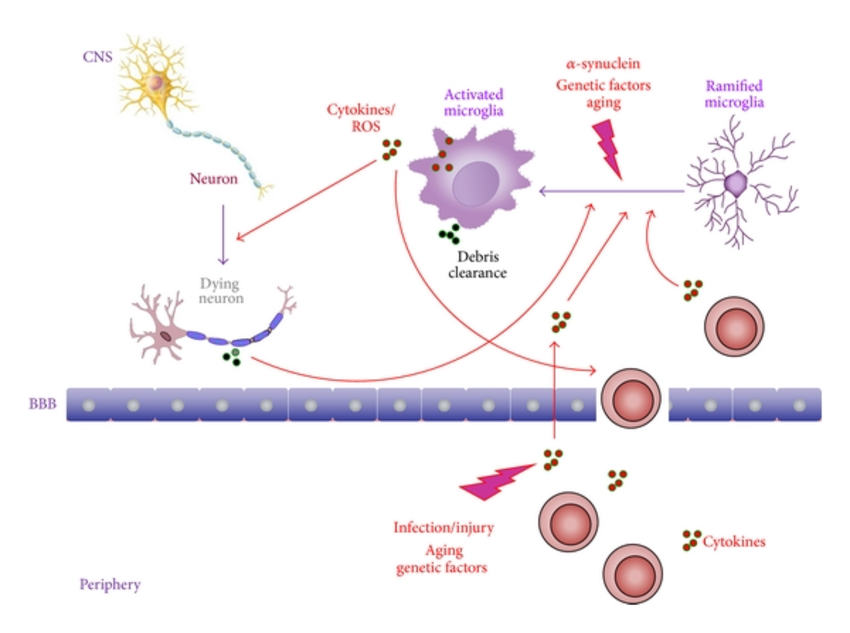
Innate Immunity In Pd: Microglia Activation
Microglial cells are the principal actors of innate immunity in the CNS responsible for the protection and restoration of neurons . They can be activated by various external or internal insults such as neuronal dysfunction, trauma or certain toxin. Also, a wide range of molecules including viral or bacterial proteins, -syn, cytokines and antibodies are able to induce the activation of microglia . Consequently, microglial cells produce different molecular mediators with chemotactic and immunomodulatory functions. One of them is tumor necrosis factor which in PD plays important roles contributing to the regulation of synaptic plasticity . PD brains are characterized by the presence of HLA-DR+ microglial cells and raised levels of CD68, an activation marker for microglia and macrophages, having a direct relation with -syn aggregations and the duration of disease . Moreover, an increased expression of MHC-II molecules in microglial cells has been observed in chronic neuroinflammation but not in the CNS of healthy subjects . Individuals with single nucleotide polymorphism at MCH-II locus are prone to develop PD, which indirectly proves the importance of adaptive immunity in these patients .
Neuroinflammation In Parkinsons Disease
The fact that microglia respond and change their morphology, expression of receptors, and secretory products in all forms of CNS damage and disease means that if we are to understand their functional role in the outcome of the disease, we need to define their phenotype carefully at different stages of the disease process. Cells of the macrophage lineage are known to exist in different forms sometimes referred to as classically activated after exposure to -interferon, or alternatively activated after exposure to interleukin-4 or -13 . It is now apparent that following tissue injury, they exist in many different phenotypes that cannot be readily divided up into a small number of discrete subsets . Furthermore, the phenotype is not fixed, and the secretory and cell surface receptor profile of macrophages can be rapidly changed within a few hours both in vitro and in vivo . Defining the phenotype requires diverse tools and cannot be predicted from a small number of markers detected by immunocytochemistry.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Ethical Clearance And Consent
The study received ethical clearance from the Health Research Ethics Committee of Stellenbosch University, South Africa and the Health Department of Western Cape research number . Written informed consent was obtained from all participants followed by whole blood sampling. All participants received a unique number that was used to guarantee discretion throughout this study. All investigators were certified in Good Clinical Practice and ethical codes of conduct.
What Is Niehs Doing
Increasing evidence suggests environmental factors contribute to chronic inflammation. A review2 of scientific literature conducted by NIEHS-funded researchers affiliated with the National Toxicology Program found the environment plays a role in inflammation in both positive and negative ways, such as:
- Environmental chemicals The federal Toxicology in the 21st Century, or Tox21, program shows how chemicals we commonly encounter may alter molecular pathways that underlie inflammation.
- Nutrition Diets high in refined grains, alcohol, and processed foods can alter gut microbiota and lead to intestinal and immune changes.
- Microbiome Studies of various microbiome imbalances and disease states show connections to inflammation.
- Social and cultural changes Disrupted sleep patterns, psychosocial stress, artificial light, and other factors influence the immune system.
- Developmental origins Childhood obesity, psychological stress, exposure to microbes in infancy, and prenatal conditions are linked to inflammation.
- Physical activity When skeletal muscles contract, they release proteins that can reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Also Check: Is Parkinsons Fatal
Is Parkinsons An Autoimmune Disease
Parkinsons disease is a neurological condition resulting from an imbalance of dopamine and acetylcholine, two chemical messengers in the brain that help control movement.; Too little dopamine leads to problems with gross and fine motor coordination.; It is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, in conjunction with increasing age. ;More recently an immunological cause has been under investigation.; Below we examine the possibility of a connection between Parkinsons and autoimmune disease.
What are the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease?
Aside from those above, Parkinsons patients may present with a fairly wide range of other signs and symptoms, which are alternately present or absent depending on the individual.; They may experience psychological issues such as depression or anxiety, which is likely the result of biochemical changes within the brain, coupled with the considerable burden of living with Parkinsons.; And some patients will exhibit varying degrees of autonomic dysfunction, where the automatic/involuntary functions of the body, such as urination or sweating, are disrupted.; Still others have trouble maintaining their balance during normal activities.
Have there been studies linking Parkinsons to an autoimmune trigger?
Does the research indicate that, similar to hypothyroidism, Parkinsons has an autoimmune and non-autoimmune root cause?
Questions for your doctor:
Epidemiological Evidence For A Link Between Ibd And Pd
With consistent genetic and functional evidence established between PD and IBD, epidemiological studies have emerged investigating IBD as a risk factor for PD. In 2016, Lin et al. were first to investigate associations between PD and IBD in a Taiwanese nationwide retrospective cohort study. The study concluded that IBD was associated with a 35% increased risk of PD which was most pronounced in CD patients . Another retrospective study by Fujioka et al. investigated the occurrence of CD with PD by searching the medical records of 876 PD patients and subsequently looked for incidences of prior or current CD. The study found that the co-occurrence of CD with PD was consistent with the number of cases expected in the general population . However, limitations to this study was the relatively small number of subjects. Furthermore, the study was based on medical records and the research team did not perform any confirmatory tests to detect the presence of CD in the patients.
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson Disease Fatal
Glucocorticoids Inflammation And Parkinsons Disease
Inflammation is normally a tightly regulated process that acts to prevent pathogen invasion as well as cellular injury, whilst at the same time enabling tissue repair. Several endogenous mechanisms act to regulate the immune cell functions, which are involved in triggering an inflammatory process. Among them, the steroid hormone, glucocorticoid, is a known major regulator of immune system and inflammation. Glucocorticoids are one of the most potent and effective anti-inflammatory agents in clinical use ever since the isolation of cortisone and its clinical application in the early 1950s by the Nobel Prize winners Hench, Kendall and Reichstein .
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Genetic Link
Inflammation And Pd Models
There are several models of PD, both toxin based and gene based, used to study disease progression and/or therapeutic development. In many of these models, inflammatory mechanisms are reported to play roles in the pathogenesis and manifestation of the disease in various animal models. In the remainder of this chapter, we will focus on characterizing the inflammatory response seen in the various models.
Parkinsons Driven By Inflammation Genetics And The Environment
David Standaert, M.D., Ph.D., said that early interventions involving anti-inflammatory drugs could help to slow progression of the disease.
In 1817, James Parkinson published An Essay on the Shaking Palsy, describing the disease that now bears his surname. The British surgeons proposed treatment bloodletting proved ineffective, and the intervening two centuries led to no breakthroughs for patients.
The reality is that today, we still dont have a treatment that slows or alters the progression of Parkinsons disease, said David Standaert, M.D., Ph.D., during a Jan. 8 talk at NIEHS. He is chair of the neurology department at the University of Alabama at Birmingham . We can help patients function better, but were not changing the underlying nature of the disease.
Parkinsons disease is complex, involving genetic and environmental factors, and their interaction. Guohong Cui, M.D., Ph.D., head of the NIEHS In Vivo Neurobiology Group, invited Standaert to discuss the role immunity plays in the disorder. Both researchers seek to discover ways to slow advancement of the condition and make it less severe.
Dr. Standaert is an established researcher in the Parkinsons field, which is one of the major areas my lab works in, said Cui. His team examines how pesticides interact with genetic factors associated with the disease and ways to slow dopamine loss, which is a hallmark of the disorder.
Read Also: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
Lrrk2 Activity In Health And Disease: Elevated Ros Levels In Inflamed Lrrk2 Mutant Brain
Two key factors can contribute to the development of Parkinsons disease: inflammation and genetics. The former is a response to injury or infection, while the latter is one of the unique physical features that defines each of us.
Neither factor alone may be sufficient to cause this disease and its steady breakdown of the nervous system, which means if you can correct one of the two factors, you might halt the entire process.
Dr. Michael Schlossmacher, a member of the University of Ottawa Research Institute, is focusing on the link between inflammation and the mutation of a specific gene, called LRRK2, found in people with Parkinsons disease.
This work changed profoundly with the discovery that the LRRK2 mutation also showed higher levels of particular chemicals known as Reactive Oxygen Species when there was an inflammatory stimulus, the bodys response to an inflammation.
These molecules apparently respond to inflammation throughout the body, including in the brain and the central nervous system, says Schlossmacher.
The results of this work were recently published in the high-profile journal Science Translational Medicine, where a Canadian team concluded the LRRK2 gene could represent a crucial controlling mechanism for inflammation within the body.
Restoring the genes function could help identify the underlying problem in Parkinsons disease.
Search
The Histamine And Dopamine Relationship
Scientists have been studying the relationships between allergic reaction, histamine release, dopamine restriction and Parkinsons Disease. In addition to inflammatory response, histamine also plays a role in brain function and can affect the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine. Studies have shown that a rise in histamine levels corresponds with a decrease in dopamine response. And medications that restrict histamine production increase dopamine response. Additionally, allergic reaction leads to an increase in histamine production and a simultaneous drop in dopamine levels, which are two major issues in Parkinsons Diseasehigh histamine and low dopamine.
With this information, many people have turned to changes in their diets to help fight inflammation and control the symptoms of Parkinsons. For those with allergies, the implication is that being diligent to avoid allergens that have even a mild effect can be very helpful in preventing or mitigating Parkinsons symptoms.
While dietary restriction cant cure Parkinsons,;researchers have seen a reduction in Parkinsons symptoms when the diet is restricted;to limit foods that cause an inflammatory response.
As always, be sure to consult your doctor before making any dietary changes. But be armed with questions that might help you both figure out what course might best help your individual situation.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Innate Immune Regulation By Grs In Microglia During Dopamine Neurodegeneration
Nigral dopamine neurodegeneration triggered by MPTP is significantly reduced by pharmacological treatments with GC agonists e.g., corticosterone that artificially increase GCs above endogenous levels, conversely adrenalectomy augments dopamine neuronal loss indicating that high levels of GCs present during MPTP intoxication protect dopamine neurons. Immuno-labeling of GR revealed its localization mainly in the nucleus of microglia and its quantification was carried out in substantia nigra and striatum in saline and MPTP injected mice. The results showed that number of microglia with nuclear GR augmented from 35% in resting state to 7080% 3 days after MPTP injections, which then declined to almost normal levels after 3 weeks. Measurement of endogenous corticosterone levels showed a three-fold rise 1 day after MPTP . Importantly, these results indicate that GR activation during endogenous rise in corticosterone levels is progressive concurring loss of dopamine neurons . However increasing GC levels by corticosterone treatment results in significant neuroprotection likely because GR activation in microglia is rapid enough to counteract the inflammatory response mounted by activated glia.
Gastrointestinal Tract Inflammation Of Patients With Pd
GI symptoms are among the most bothersome of PD symptoms. In a cohort study from the early 90s it has been shown that those symptoms occurred more frequently in PD patients than in controls including abnormal salivation, dysphagia, nausea, constipation, and defecatory dysfunction. Except for defecatory dysfunction, symptoms did not correlate with treatment but instead correlated with disease severity .
Lewy pathology affects the GI tract in PD . PD mice show a strong immune response in the gut , and colonic biopsies of PD patients show evidence of a structural dysfunction of the intestinal barrier, reinforcing the idea of a role of the GI tract in the initiation and/or the progression of the disease . Enteric inflammation occurs in PD which further strengthen the role of peripheral inflammation in the pathophysiology of PD . Further, in non-human primates, colitis-associated inflammation is concomitant to alterations in -syn and p--syn expression in colonic myenteric ganglia . Autopsy studies performed on human subjects with Lewy Body disorders have consistently shown that -syn aggregates are found in the ENS in nearly every case examined . Still there is a lack of evidence from prodromal PD GI samples which could help to establish a better link between PD initiation and GI inflammation.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
