Your Deep Brain Stimulation Questions Answered
In this 1-hour webinar Dr. Helen Brontë-Stewart discusses the goal of DBS, what to expect and how to prepare for DBS surgery, dual therapy and how to blend DBS and medication, pros and cons of fixed vs. rechargeable batteries, symptom relief from DBS, unexpected and surprising symptoms DBS helps, programming, developments and innovation in DBS, and more.
Dont Miss: How Long Can Someone Live With Parkinsons
What Is The Recovery Time
Your healthcare provider is the best person to tell you what to expect regarding your recovery time and when you will notice changes in your symptoms and how you feel. They can tell you the likely recovery time you’ll need, which can vary depending on other factors like your overall health, other conditions you have and your personal circumstances.
Most people will need to stay in the hospital for one day after surgery to implant the DBS leads in their brain. Surgery to implant the pulse generator is usually a procedure where you go home the same day.
Overall, recovery time generally takes several weeks. Your healthcare provider will likely have you do the following:
- Avoid any kind of activity for about two weeks after each procedure: This includes things as minor as household chores or sexual activity. You should not lift anything heavier than 5 pounds .
- Avoid moderate- or high-intensity activity for at least four to six weeks: This includes exercise and physical labor. Most people can return to work or their usual routine after this.
- Use caution when moving or stretching: You should avoid making certain movements, like raising your hands over your head, for several days after surgery to implant the pulse generator. Your healthcare provider will tell you how long youll need to restrict your movements.
How should I care for the surgical area once I’m home?
Deep Brain Stimulation At Michigan Medicine
For carefully selected patients with Parkinsons disease, Essential Tremor, and Dystonia, deep brain stimulation offers a therapeutic surgical option that can reduce or eliminate movement-related problems and greatly improve quality of life. At the University of Michigan Health System, our STIM program brings together a team of medical experts who are leaders in their respective fields and on the cutting-edge of the latest research.
Dont Miss: Chairs For Parkinsons Patients
You May Like: Are Hallucinations A Symptom Of Parkinson’s Disease
Awake Vs Asleep Surgery
Standard DBS surgery is performed while you are awake and requires that you stop taking the medicines that control your Parkinson’s symptoms. During surgery, you are asked to perform tasks to help guide the electrode to the precise location in the brain.
Being awake during brain surgery, or being off medicine, is unsettling for some people. Asleep DBS is an alternative option at some centers.
Asleep DBS surgery is performed while you are unconscious and under anesthesia. Surgery takes place in an MRI or CT scanner to target and verify accurate placement of your DBS electrodes. Ask your surgeon if asleep DBS is an option for you.
| Must hold medications the morning of surgery | Don’t have to hold medications |
Risks And Side Effects Of Deep Brain Stimulation
Like any surgery, deep brain stimulation can have side effects, and it carries potential risks. Its also important to consider the complications and side effects of medications you take since their dosages can often be reduced following surgery.
While DBS may cause side effects, it may also reduce side effects from medications.
Recommended Reading: How Prevalent Is Parkinson’s Disease
Will I Have To Limit My Activity Following Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
- You should not engage in light activities for 2 weeks after surgery. This includes housework and sexual activity.
- You should not engage in heavy activities for 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. This includes jogging, swimming, or any physical education classes. Anything strenuous should be avoided to allow your surgical wound to heal properly. If you have any questions about activities, call your doctor before performing them.
- You should not lift more than 5 lbs. for at least 2 weeks.
- You should not raise your arms above your shoulders or over bend or stretch your neck.
- Depending on the type of work you do, you may return to work within 4 to 6 weeks.
Living With A Stimulator
Once the DBS has been programmed, you are sent home with instructions for adjusting your own stimulation. The handheld controller allows you turn the stimulator on and off, select programs, and adjust the strength of the stimulation. Most patients keep their DBS system turned on 24 hours day and night. Some patients with essential tremor can use it during the day and turn off the system before bedtime. Your doctor may alter the settings on follow-up visits if necessary.
If your DBS has a rechargeable battery, you will need to use a charging unit. On average charging time is 1 to 2 hours per week. You will have a choice of either a primary cell battery or a rechargeable unit and you should discuss this with you surgeon prior to surgery.
Just like a cardiac pacemaker, other devices such as cellular phones, pagers, microwaves, security doors, and anti theft sensors will not affect your stimulator. Be sure to carry your Implanted Device Identification card when flying, since the device is detected at airport security gates.
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Parkinson’s And Alzheimer’s
What Happens During Deep Brain Stimulation
This procedure actually involves two to three surgeries that usually happen at different times. The first one or two procedures are to insert the stimulation leads into each side of your brain at the same or separate times. The second procedure is to implant the stimulator battery known as a pulse generator under the skin of your upper chest.
Before these surgeries happen, your healthcare provider will usually insert an intravenous line to give you IV fluids. An IV also allows them to give you medications during the procedure as needed.
Lead placement
This procedure usually starts with your healthcare provider shaving the hair on your scalp. This makes it easier to place your head into a special frame that will hold your head still. The frame is set with four pins in your skull. This is done while youre under sedation, and you likely wont remember this part.
Once the frame is set, theyll bring in an intra-operative CT scanner to take images of your brain and identify the trajectory used for the electrode placement. Once the CT scan is complete, the entry point is identified, sedation is turned back on and your head is cleaned with surgical prep. Local anesthetic is then injected to numb that area of your scalp and skull. Your neurosurgeon will then make a small cut .
Pulse generator placement
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation
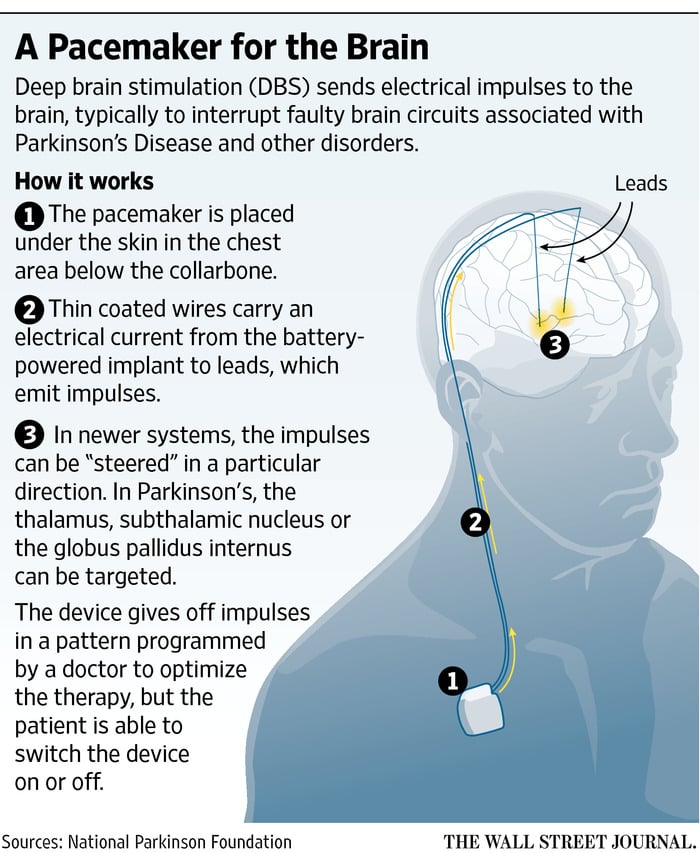
Deep brain stimulation is a medical procedure that involves a mild electrical current delivered to a specific part of your brain. The electricity in that current stimulates the brain cells in that area, which can help several conditions. The current reaches your brain through one or more wires attached to a small device implanted underneath your skin near your collarbone.
Read Also: Is Hand Shaking A Sign Of Parkinson’s
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Work
Deep brain stimulation works by modifying abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It was first approved for Parkinsons tremors in 1997 and has become an established treatment to control additional motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
DBS involves three main components:
- Leads: Leads are implanted in the brain in a region responsible for motor activity.
- Implantable pulse generator : A separate procedure is performed to implant a battery-operated device in the chest or in the abdomen. An IPG is similar to a pacemaker for the heart and has been coined by some as a pacemaker for the brain.
- Extension: A thin, insulated wire is passed beneath the skin between the leads and implantable pulse generator to deliver the electrical stimulation from the pulse generator to the leads.
The target area in the brain is first identified by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography . Then, the leads are placed via small holes that a surgeon drills in the skull.
This is considered a minimally invasive surgery that is done in the operating room with local anesthesia. It usually requires an overnight stay.
The IPG is inserted in a separate surgical procedure in the operating room roughly a week later.
After a few weeks, a neurologist begins to program the unit. This process can take several additional weeks to months. When this is completed, people are able to manage the device with a handheld remote control.
The Symptoms That Dbs Treats
Deep brain stimulation is used primarily to treat the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, but this can vary somewhat between the different placement sites. Symptoms treated include:
- Abnormal movements : Dyskinesias are often a side effect of medications for Parkinsons disease and include involuntary movements such as twisting, head bobbing, squirming, and more.
DBS is not usually helpful with walking problems or balance, though improvements in the symptoms above can indirectly affect walking. It also does not provide significant benefits for non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons such as cognitive changes, mood changes , or problems with sleeping.
The benefits of DBS can be estimated by looking at how a person responds to levodopa. Symptoms that respond to levodopa will often respond to DBS . But symptoms that are not changed with levodopa are unlikely to be improved by DBS.
DBS often allows for a reduction in the dosage of levodopa, which in turn can result in fewer involuntary movements and a reduction in off time. The result is often improved quality of life.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Parkinson’s
The Many Ways To Define Early Dbs & How Early Is Too Early
A recent study suggested that DBS in less advanced cases may be feasible and efficacious . Trials published in the literature to date have not included patients with short disease durations or patients without motor fluctuations. The neuroprotective effects of surgery have not been substantiated, and thus cannot be ethically used to argue for earlier intervention in individual patients. There is a solid argument evolving for cost savings with early DBS. However, arguments based on motor, non-motor and quality of life features have less of an evidence base at this time. Better methodologically constructed and adequately powered clinical trials with carefully conceived end points will need to be performed in order to settle the questions surrounding early DBS intervention.
Early DBS covers several scenarios. Consider the example of a 60-year-old patient diagnosed with PD 24 years prior, experiencing life-altering disability from tremor, despite maximal combinations of levodopa, dopamine agonists and anticholinergics. Most clinicians and multidisciplinary surgical teams would agree that this could be a reasonable case for early intervention.
In our opinion, the most controversial scenarios for early intervention are:
We believe that patients who fall into these above categories should, in most cases, have DBS performed only in the context of an Institutional Review Board-approved clinical research trial.
What Happens During Surgery
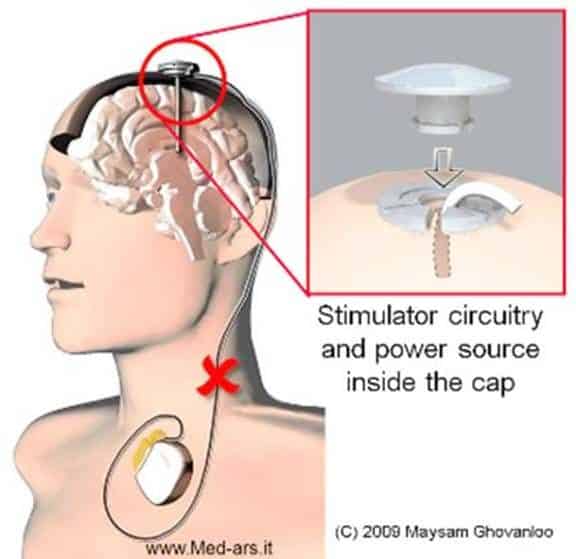
For stage 1, implanting the electrodes in the brain, the entire process lasts 4 to 6 hours. The surgery generally lasts 3 to 4 hours.
Step 1: attach stereotactic frameThe procedure is performed stereotactically, which requires attaching a frame to your head. While you are seated, the frame is temporarily positioned on your head with Velcro straps. The four pin sites are injected with local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. You will feel some pressure as the pins are tightened .
Step 2: MRI or CT scanYou will then have an imaging scan, using either CT or MRI. A box-shaped localizing device is placed over the top of the frame. Markers in the box show up on the scan and help pinpoint the exact three-dimensional coordinates of the target area within the brain. The surgeon uses the MRI / CT scans and special computer software to plan the trajectory of the electrode.
Step 3: skin and skull incisionYou will be taken to the operating room. You will lie on the table and the stereotactic head frame will be secured. This prevents any small movements of your head while inserting the electrodes. You will remain awake during surgery. Light sedation is given to make you more comfortable during the initial skin incision, but then stopped so that you can talk to the doctors and perform tasks.
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s Caused By Too Much Dopamine
What Happens During The Dbs Procedure
Most DBS procedures are performed with the patient awake under local anesthesia, with their head immobilized in a rigid frame, so that the surgical team can monitor patient response to the electrode placement as it occurs. A few centers are now offering image-guided placement, in which the surgery is performed under general anesthesia without the frame. The pulse generator is usually implanted during a second surgery, scheduled about a week after the first.
What Happens Before Deep Brain Stimulation
Before this procedure, your healthcare provider will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of having a DBS device implanted. Theyll also explain the possible risks that come with this surgery. Theyll also verify that you can have this surgery, which can involve other imaging scans or lab tests to look for any reasons you may not be able to have the procedure.
If you still decide you want to have the DBS implanted, your provider will then have you get detailed magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography scans of your brain. These scans will help your provider decide which location is the best place to place the wires for the DBS.
Before the procedure, your provider will also talk to you about the following:
Recommended Reading: Why Do Boxers Get Parkinson’s
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
For people with severe motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease that are not adequately controlled by medication, a treatment called deep brain stimulation may offer some relief.
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical placement of a small conductor called an electrode in the brain. The electrode delivers electrical stimulation that blocks the nerve signals that cause tremors.
Specialists at NYU Langones Center for Neuromodulation perform more than 100 deep brain stimulation procedures each year. Our neurologists, neurosurgeons, and psychiatrists provide a thorough evaluation to ensure youre a good candidate for the procedure.
First Patient In The World Receives Cutting
The trials first patient, Tony Howells, received the device in November 2020. He got diagnosed with Parkinsons about nine years ago when he noticed a slight tremor in his right hand. Tony said that even something simple, such as tying shoelaces, became a huge ordeal. What should take a few seconds ended up taking him three or four minutes due to the pain and tremors.
Mr. Howells said:
You cant understand how frustrating is until it happens to you. Just doing your shoelaces up is a major operation it affects your every day life no end.
He said that before the operation, he went for a walk with his wife and only got 200 yards from the car. He reluctantly had to turn around and cut the trip short because he couldnt walk any farther.
However, twelve months after the surgery, he went out for Boxing Day again and walked 2.5 miles. He said he couldve even walked farther! Tony also enjoys being able to play golf again and move more quickly, in general.
The surgery only took three hours, about half the time of a traditional DBS implantation. Tony also said he felt a bit tired after the surgery but had no pain. Additionally, he noted that an uncomfortable side effect from his Parkinsons disease medication, dystonia, had disappeared. Dystonia refers to involuntary muscle contractions that cause repetitive or awkward movements.
To say I am happy about having DBS is an understatement, its a great way to give somebody their life back, Tony said.
Also Check: How Do Neurologists Diagnose Parkinson’s Disease
Simultaneous Implantation Into Two Brain Sides Versus A Staged Approach
When considering a simultaneous versus staged approach to DBS, some explanation of the different approaches is required. Two DBS leads may be placed in the same intraoperative sitting , or alternatively they may be separated by days, weeks or months. Similarly, the batteries may be placed on the same day, or alternatively placed days, weeks or even a month following lead insertion. Although there is no data to support the utility for timelines of these various approaches, some DBS interdisciplinary teams feel that extended intraoperative time may be an important factor in increasing complications, particularly in the elderly patient , the frail patient or in the patient with multiple comorbidities. Some teams have also begun to exercise caution in operating on patients over 70 years of age, although this point is highly debatable among the experts.
Research To Improve Deep Brain Stimulation
Researchers are working to improve upon existing DBS devices and methods to help treat more symptoms and more people. Some researchers are putting electrodes in a different area of the brain the pedunculopontine nucleus to treat walking and balance problems that don’t typically improve with present-day DBS. Others are developing a “smart” DBS device that can record a person’s unique brain signals and deliver electrical stimulation only when needed, such as when symptoms return, rather than continuously, as the current systems do. This could help reduce side effects such as numbness and weakness and lengthen the battery life of the neurostimulator, which would result in a longer time between battery replacement procedures.
Scientists also are planning to test deep brain stimulation in the first years after a Parkinson’s diagnosis to see if the therapy may slow or stop disease progression. Testing in Parkinson’s models showed the therapy may help protect brain cells, and a small human trial showed motor symptoms improved after early-stage DBS.
Don’t Miss: What Is Wolf Parkinsons White Syndrome
