Atrial Fibrillation And Wolff
Atrial fibrillation may be particularly dangerous for people with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. The extra pathway can conduct the rapid impulses to the ventricles at a much faster rate than the normal pathway can. The result is an extremely fast ventricular rate that may be life threatening. Not only is the heart very inefficient when it beats so rapidly, but this extremely fast heart rate may also progress to ventricular fibrillation Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation is a potentially fatal, uncoordinated series of very rapid, ineffective contractions of the ventricles caused by many chaotic electrical… read more , which is fatal unless treated immediately.
Managing Episodes Of Supraventricular Tachycardia At Home
Its important that you are able to recognise the potential signs and symptoms of SVT and we will teach you how to do this. If appropriate, we will also teach you and your child vagal manoeuvres which can include blowing in a straw or a balloon. These work on the vagal nerve which regulates the heartbeat.
Most episodes of supraventricular tachycardia only last for a few minutes and do not need urgent treatment. Some episodes may last longer and children may be affected by these. If an episode is prolonged or the person experiences any of the red flag symptoms, they should be taken to the nearest Accident and Emergency department immediately.
The doctors will try some ‘tricks’ to try to slow the heart such as blowing into a syringe, if these are not successful or the SVT is causing other concerns such as low blood pressure, they may use a medication. As a last resort, a shock can be given as a life-saving option.
Red flags
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Wolff
Individuals affected by Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome can experience palpitations, rapid heart rates, difficulty breathing, and lightheadedness as well as near loss of consciousness and complete loss of consciousness. For the most part, these symptoms occur all of a sudden and are not associated with warning signs. Usually, there are no dramatic triggers, however, caffeine, alcohol, and exercise can cause the heart to start racing.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Dos And Donts In Managing Wolff
- DO avoid tobacco, smoking, caffeine, alcohol, pseudo-ephedrine and similar antihistamines, amphetamines, and cocaine.
- DO tell your health care provider about unusually fast heartbeats or near fainting.
- DO keep your doctors appointments.
- DONT stop taking your medicines or change the dosage because you feel better unless your health care provider tells you to.
What Are The Long
Overall, the outlook for children with WPW is excellent. The problem resolves in the majority of infants by 12 months of age although SVT may recur later in childhood.
When the problem persists, radiofrequency ablation has proven to be safe and effective.
Exercise guidelines: Guidelines are best made by a patients doctor so that all relevant factors can be included. Participation in vigorous competitive sports may be restricted until the problem is treated by radiofrequency ablation. If the pathway does not conduct rapidly , usually no activity restrictions are needed .
If an episode of SVT occurs during sports, the child should remove herself/himself from participation until the arrhythmia is converted. Also, activities that involve climbing heights should be avoided since an episode may cause dizziness leading to a fall.
References
Bolling S, Morady F, Caukins H, Kadish A, de Buitleir M, Langberg J, Dick M, Lupinetti F, Bove E. Current treatment for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: results and surgical implications. Ann Thor Surg. 52:461-468,1991.
Deal B, Dick M, Beerman L et al. Cardiac arrest in young patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. PACE 1995 18:815.
Dick M, O’Connor B, Serwer G, LeRoy S, Armstrong B. Use of radiofrequency energy to ablate accessory connections in children. Circulation 84:2318-24, 1991.
Reviewed September, 2012
Read Also: Can Adderall Cause Parkinson’s
How To Manage Or Live With Wpw
There is no way to prevent WPW, but you can prevent complications by learning as much as you can about the disease and working closely with your cardiologist to find the best treatment. Ask your doctor to teach you how to do a Valsalva maneuver.
Here are helpful lifestyle suggestions:
-
Dont smoke.
-
Work with your doctor to keep conditions such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure under control.
-
Eat a heart-healthy diet.
Warning Disclaimer Use For Publication
WARNING: Please DO NOT STOP MEDICATIONS without first consulting a physician since doing so could be hazardous to your health.
DISCLAIMER: All material available on eHealthMe.com is for informational purposes only, and is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment provided by a qualified healthcare provider. All information is observation-only. Our phase IV clinical studies alone cannot establish cause-effect relationship. Different individuals may respond to medication in different ways. Every effort has been made to ensure that all information is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. The use of the eHealthMe site and its content is at your own risk.
If you use this eHealthMe study on publication, please acknowledge it with a citation: study title, URL, accessed date.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
Deterrence And Patient Education
The dysrhythmias causing electrical abnormalities associated with WPW syndrome are a result of a congenital abnormality forming an accessory pathway. There is nothing that can be done to prevent WPW pattern. After WPW syndrome has manifested with the presentation of a tachyarrhythmia, an electrophysiologic study can be performed to map and assess risks of the accessory pathway, and catheter radiofrequency ablation of the pathway can be curative. For patients that this is not an option or preference, antiarrhythmic medications can be a reasonable alternative option.
Treatment Of Wpw Syndrome
-
Maneuvers and drugs to convert heart rhythm
-
Sometimes ablation
Destruction of the extra conduction pathway by catheter ablation Destroying abnormal tissue Abnormal heart rhythms are sequences of heartbeats that are irregular, too fast, too slow, or conducted via an abnormal electrical pathway through the heart. Heart disorders are… read more is successful in more than 95% of people. The risk of death during the procedure is less than 1 in 1,000. Ablation is particularly useful for young people who might otherwise have to take antiarrhythmic drugs for a lifetime.
Read Also: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Are There Any Specific Tachycardias Associated With Accessory Pathways
Cain, ME, Luke, RA, Lindsay, BD. Diagnosis and localization of accessory pathways. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 15. 1992. pp. 801-24.
Reyes, W, Milstein, S, Dunnigan, A. Indications for modification of coexisting dual atrioventricular node pathways in patients undergoing surgical ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 17. 1991. pp. 1561-7.
Klein, GJ, Bashore, TM, Sellers, TD. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med.. vol. 301. 1979. pp. 1080-5.
Dreifus, LS, Haiat, R, Watanabe, Y. Ventricular fibrillation: a possible mechanism of sudden death in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Circulation. vol. 43. 1971. pp. 520-7.
Wellens, HJJ, Durrer, D. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. vol. 34. 1974. pp. 777-82.
Campbell, RWF, Smith, R, Gallagher, JJ. Atrial fibrillation in the preexcitation syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 40. 1977. pp. 514-20.
Sharma, AD, Klein, GJ, Guiraudon, GM. Atrial fibrillation in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: incidence after surgical ablation of the accessory pathway. Circulation. vol. 72. 1985. pp. 161-9.
Dagres, N, Clague, JR, Lottkamp, H. Impact of radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory pathways on the frequency of atrial fibrillation during long-term follow-up: high recurrence rate of atrial fibrillation in patients older than 50 years of age. Eur Heart J. vol. 22. 2001. pp. 423-7.
How Is Wpw Syndrome Treated
If youre diagnosed with WPW syndrome, you have several treatment options, depending on your symptoms. If youre diagnosed with WPW syndrome but dont have any symptoms, your doctor may recommend that you wait and continue follow-up appointments. If youre having symptoms, the treatment may include the following:
Don’t Miss: Early Onset Parkinson\’s Disease
Treatments For Wpw Syndrome
In many cases, episodes of abnormal heart activity associated with WPW syndrome are harmless, don’t last long, and settle down on their own without treatment.
You may therefore not need any treatment if your symptoms are mild or occur very occasionally, although you should still have regular check-ups so your heart can be monitored.
If your cardiologist recommends treatment, there are a number of options available. You can have treatment to either stop episodes when they occur, or prevent them occurring in the future.
Does Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Go Away
Regardless of whether a patient has SVT, however, there is also a risk of more dangerous heart rhythm problems beginning later in life. WPW can sometimes go away on its own over time, although this probably rarely happens after 3-4 years of age.
Is Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome serious? It can be scary to be told that you have a problem with your heart, but WPW syndrome usually isnt serious. Many people will have no symptoms or only experience occasional, mild episodes of their heart racing. With treatment, the condition can normally be completely cured. What happens in WPW syndrome?
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Wpw Syndrome Diagnosed
People experiencing a fluttering or racing heartbeat usually tell their doctors. The same applies to those experiencing chest pain of difficulty breathing. However, if you dont have symptoms, the condition may go unnoticed for years.
If you have a racing heartbeat, your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and conduct tests that measure your heart rate over time to check for tachycardia and diagnose WPW syndrome. These heart tests may include:
What Are The Potential Complications Of Wolff
Wolff-Parkinson-White can lead to significant symptoms from the rapid heart rates and can be alarming when first experienced. In addition, episodes can be disruptive and can last from minutes to hours and in some rare circumstances even days to weeks. The most serious complication of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is sudden death, which is rare and has been estimated to be around 0.25% per year. This very rare occurrence can happen if the short-circuit of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome triggers another arrhythmia called atrial fibrillation that even more rarely can induce ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation can cause sudden death if not treated promptly.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Ribbon Color
How Is Wpw Treated
Treatment depends on the type and frequency of arrhythmias, associated symptoms such as syncope, and presence of structural heart disease. Typically a physician will recommend an ablation procedure to further define the characteristics of the accessory pathway, and ultimately, to eliminate the pathway entirely.
- Observation – If you have no symptoms, you may not require treatment. Your doctor may choose to have regular follow-up without treatment.
- Medications – A variety of drugs are available to treat arrhythmias. Because everyone is different, it may take trials of several medications and doses to find the one that works best for you. It is important to know:
- The names of your medications
- What they are for
- How often and at what times to take them
How Is The Problem Treated
See supraventricular tachycardia. Patients may be treated with heart medicines to prevent episodes of SVT. In general, infants are treated until their first birthday and then the medicines can be stopped. In older children, radiofrequency ablation has become first line treatment as it is safe with high success rates.
You May Like: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Catheter Ablation Of Accessory Pathways
Lesh, MD, Van Hare, G, Scheinman, MM. Comparison of the retrograde and transseptal methods for ablation of left free-wall accessory pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 22. 1993. pp. 542-9.
Jackman, WM, Wang, X, Friday, KJ. Catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways by radiofrequency current. N Engl J Med. vol. 324. 1991. pp. 1605-11.
Kuck, KH, Schluter, M, Geiger, M. Radiofrequency current catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways. Lancet. vol. 337. 1991. pp. 1557-61.
Calkins, H, Langberg, J, Sousa, J. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections in 250 patients: abbreviated therapeutic approach to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Circulation. vol. 85. 1992. pp. 1337-46.
Kay, GN, Pressley, JC, Packer, DL. Value of 12-lead electrocardiogram in discriminating atrioventricular nodal reciprocating tachycardia from circus movement atrioventricular utilizing a retrograde accessory pathway. Am J Cardiol. vol. 59. 1987. pp. 296-300.
Tchou, PJ, Lehmann, MJ, Donga, J. Effect of sudden rate acceleration on the human His-Purkinje system: adaptation of refractoriness in a damped oscillatory pattern. Circulation. vol. 73. 1986. pp. 920-9.
Drago, F, DeSantis, A, Grutter, G, Silverti, MS. Transvenous cryothermal catheter ablation of re-entry circuit located near the atrioventricular junction in pediatric patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 45. 2005. pp. 1096-103.
How Is This Problem Diagnosed
Clinical features: See Supraventricular tachycardia.
Physical findings: Most of the time the physical examination is normal when the child is not having an episode. In about 15% of children, the problem is associated with a heart defect. In this case the child has physical findings associated with that defect.
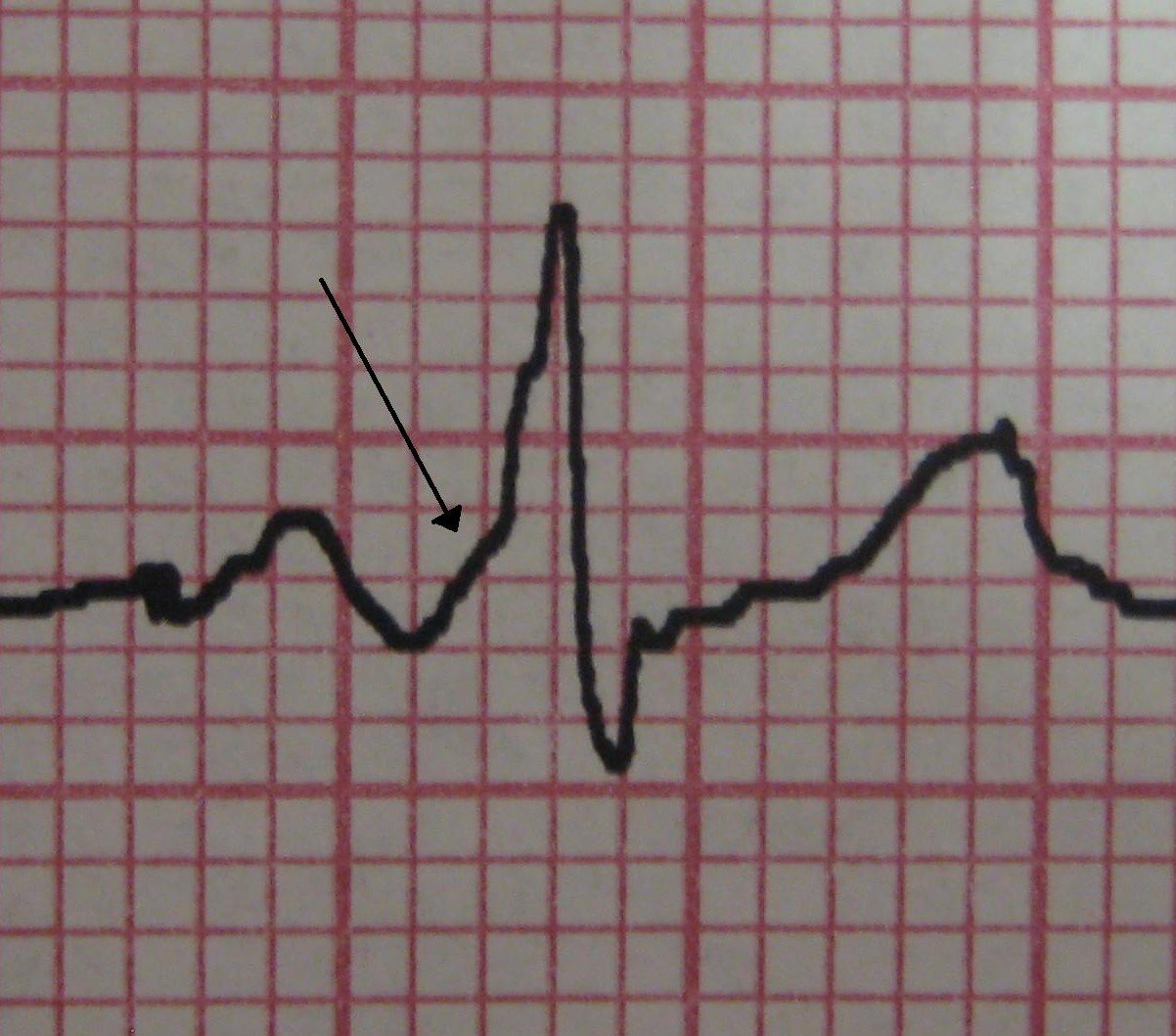
Medical tests: One of the first tests usually done is an electrocardiogram. This is a safe a painless test that involves putting some stickers across the chest. The stickers are connected to a machine that records the hearts electrical activity. In WPW, the resting ECG shows pre-excitation. This finding is quite specific for WPW and helps to confirm the diagnosis. Sometimes, pre-excitation is found on a routine ECG in a person who has no symptoms.
It may be important to record an ECG at the time of symptoms. This is done by device called a transtelephonic ECG recorder. There are different models of these devices available, but they are all able to record an ECG at the time of symptoms. The tracing can then be sent over the phone to a cardiology center where it can be reviewed. Other tests that may be done include a Holter monitor, echocardiogram, and/or exercise test.
Don’t Miss: Early Symptoms Of Parkinson’s In Adults
Further Information And Support
You can get in touch with the Arrhythmia Service on extension 5298, email them on or contact them via MyGOSH once you have registered. More information about MyGOSH is at www.gosh.nhs.uk/your-hospital-visit/mygosh
There are various organisations in the UK that support people with heart problems.
The biggest is the British Heart Federation their helpline is on or you could visit their website at www.bhf.org.uk
SADS UK can also offer help and support call them on or visit their website at www.sadsuk.org.
Pearls And Other Issues
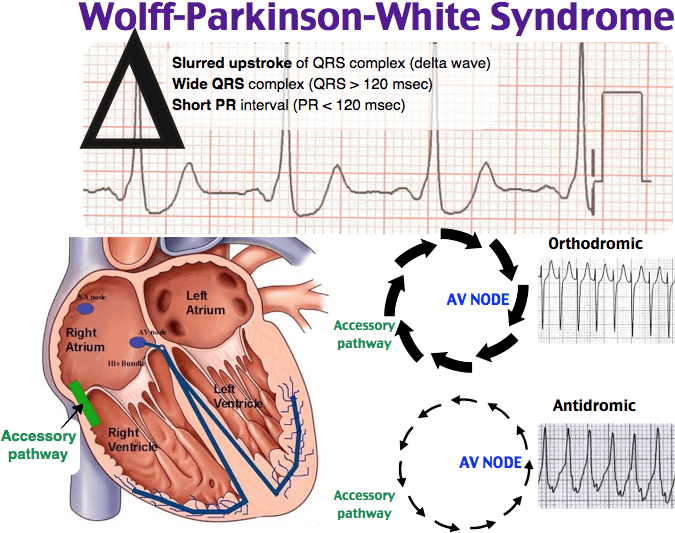
Patients with atrial fibrillation and rapid ventricular response are often treated with amiodarone or procainamide. Procainamide and cardioversion are accepted treatments for conversion of tachycardia associated with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In acute AF associated with WPW syndrome, the use of IV amiodarone may potentially lead to ventricular fibrillation in some reports and thus should be avoided.
AV node blockers should be avoided in atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In particular, avoid adenosine, diltiazem, verapamil, and other calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers. They can exacerbate the syndrome by blocking the heart’s normal electrical pathway and facilitating antegrade conduction via the accessory pathway.
An acutely presenting wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be ventricular tachycardia if doubt remains about the etiology.
Don’t Miss: Tardive Dyskinesia Prognosis
What Causes Wpw Syndrome
When the heart beats, its muscular walls contract to force blood out and around the body. They then relax, allowing the heart to fill with blood again. This is controlled by electrical signals.
In WPW syndrome, there’s an extra electrical connection in the heart, which allows electrical signals to bypass the usual route and form a short circuit. This means the signals travel round and round in a loop, causing episodes where the heart beats very fast.
The extra electrical connection is caused by a strand of heart muscle that grows while the unborn baby is developing in the womb.
It’s not clear exactly why this happens. It just seems to occur randomly in some babies, although rare cases have been found to run in families.
What Can I Do To Manage My Wpw
- Do not smoke. Smoking narrows blood vessels in your heart. Narrow blood vessels make your heart work harder. Smoking can also damage your heart. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help quitting.
- Carry medical alert identification. Wear jewelry or carry a card that says you have WPW. Ask your healthcare provider where to get these items.
- Exercise as directed. Exercise can cause WPW episodes. Ask your healthcare provider how much exercise you need each day and which exercises are safe for you. Ask if you can play sports.
- Limit caffeine. Caffeine can make your heartbeat faster.
You May Like: What Essential Oils Help Parkinson’s
Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
Synonyms of Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
- Accessory Atrioventricular Pathways
- WPW Syndrome
General Discussion
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a rare congenital heart disorder involving irregularities in the electrical system of the heart. In individuals with WPW syndrome, an abnormal alternate electrical pathway , exists between the atrium and the ventricle, resulting in abnormal heartbeat rhythms and faster than normal heartbeats .
The normal heart has four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria and the two lower chambers are the ventricles. Within the right atrium of a normal heart is a natural pacemaker that initiates and controls the heartbeat. The electrical stimulus travels from the pacemaker to the ventricles along a specific pathway consisting of conducting tissue and known as the AV node. The extra electrical pathway in individuals with WPW syndrome bypasses the normal route and causes the ventricles to beat earlier than normal and can allow electrical impulses to be conducted in both directions .
Signs & Symptoms
The symptoms associated with WPW syndrome vary greatly from case to case. Some individuals may not have any abnormal heartbeats or associated symptoms . Although the disorder is present at birth , symptoms may not become apparent until adolescent or early adulthood.
Causes
Affected Populations
Related Disorders
Symptoms of the following disorders can be similar to those of WPW syndrome. Comparisons may be useful for a differential diagnosis.
