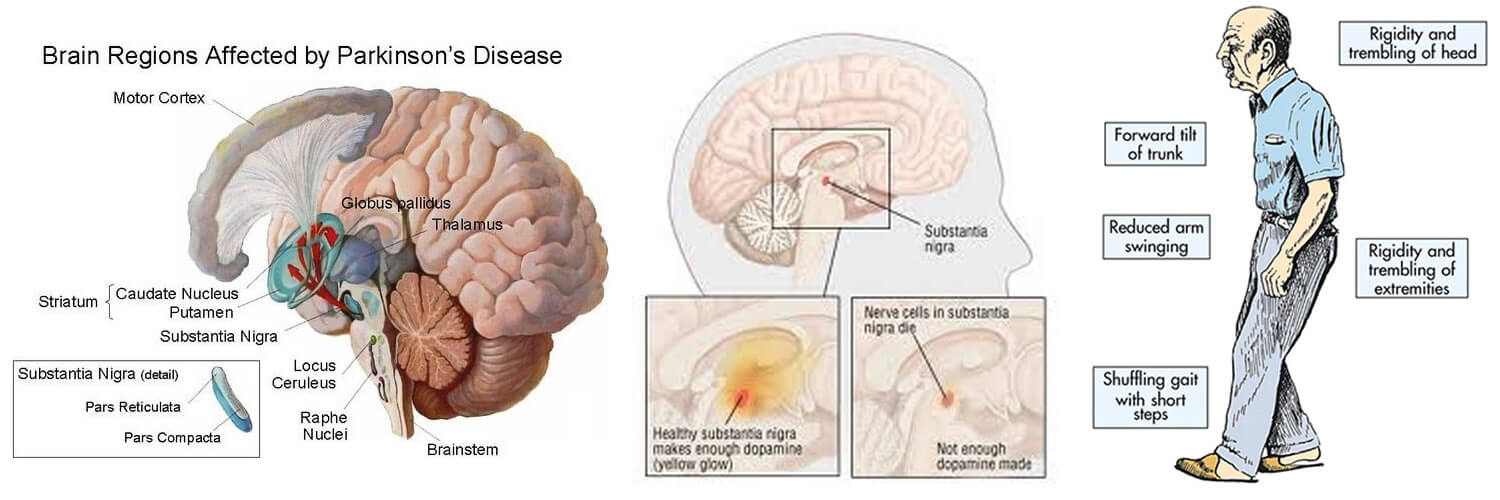
When People Talk About Parkinsons They May Mention The Effects It Has On The Substantia Nigra But Did You Know That There Are Other Areas Of The Brain That Are Affected By The Condition
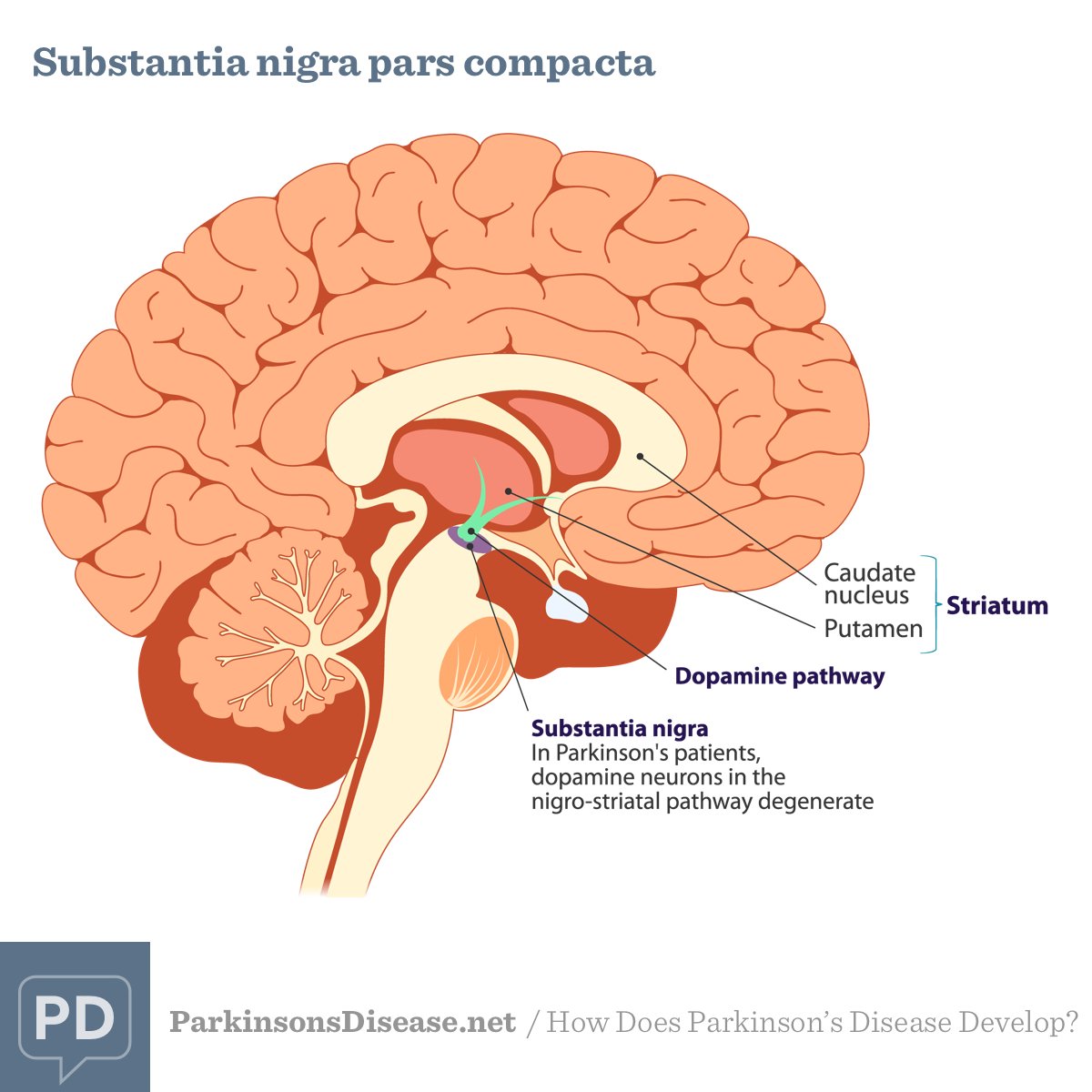
Parkinson’s is a condition that causes the gradual loss of the dopamine-producing brain cells of the substantia nigra — an area of the brain located just above where the spinal cord meets the midbrain. It is these cells that produce and release the neurotransmitter dopamine, which has a key role in turning thought about movement into action.
While this definition of the condition is useful to briefly explain Parkinson’s, the whole story is somewhat more complex. Over the last 30 years, it has become accepted that Parkinson’s also causes a number of non-motor symptoms, such as changes in sleep, smell and even the way we think, which likely involve other areas of the brain.
Now scientists are looking at the broader effects of the condition on the brain in an attempt to better understand why people experience different symptoms. The finding could lead us to new treatments that tackle more than just the motor symptoms of the condition.
Brain Scan Could Identify Which Parkinson’s Patients Benefit Most From Treatment
A new brain scan could help scientists identify which Parkinson’s patients would benefit most from a drug used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder .
The scan can allow researchers to better visualise changes in the part of the brain linked to cognitive decline, a study has suggested.
While previous work has shown atomoxetine – used for people with ADHD – can be advantageous to some Parkinson’s sufferers, until now there has not been an easy way to identify those it might help the most.
The study, funded by the charity Parkinson’s UK and published in the journal Brain, was hailed by one of the researchers as an “exciting step towards individualised therapy for cognitive decline” because it helps identify the people the treatment is most suitable for.
The use of atomoxetine improved the ability to inhibit behaviour – to let the brain “stop and think” before doing the right thing, the charity said.
Improvements with the drug were especially profound in people with the most damage to the locus coeruleus – the region of the brain linked to cognitive decline.
They had lower natural levels of noradrenaline – a brain chemical affected in Parkinson’s which is responsible for processing thoughts and behaviour.
An imbalance of noradrenaline can lead to difficulty concentrating, forgetting things and taking longer to think and process information, or can cause a change in behaviour.
The Heart Of The Matter: Cardiovascular Effects Of Parkinsons Disease
It has long been understood that Parkinson’s disease does not just cause movement symptoms, but also causes a litany of non-motor symptoms with effects throughout the body. One of the organ systems that is affected is the cardiac system, encompassing the heart, as well as the major and minor blood vessels. I received this topic as a suggestion from a blog reader and we will be discussing this important issue today. Please feel free to .
Parkinsons Diseaseassociated Pathological Changes In The Cerebellum
Data Processing Of Nmr Spectra And Multivariate Pattern Recognition
NMR spectra were reduced to integrated regions with a width of 0.01 ppm corresponding to the region of ? 10–0.5. The regions of 4.7–5.2 ppm was removed to eliminate artifacts related to the residual water resonance. The remaining spectral segments were then normalized to the total sum of the spectral intensity to partially compensate for differences in the concentration of many metabolites in the samples. Before multivariate data analysis, the integral values were mean-centered and Pareto-scaled . NMR data sets were imported into SIMCA-P + 12.0 software for multivariate statistical analysis, including principal component analysis discriminant analysis and partial least squares-discriminant analysis . And another data reduced to integrated regions with a width of 0.0015 ppm width corresponding to the region of ? 10–0.5 were used for quantitative analysis.
Whats The Difference Between Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons
In dementia with Lewy bodies, dementia always appears first. There can also be changes in alertness as well as visual hallucinations. However, because of the presence of Lewy bodies throughout the entire brain, characteristics of this disease not only include cognitive characteristics, but also physical, sleep, and behavioral changes. As the disease progresses, the motor symptoms common to Parkinson’s such as tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems will appear.
For more information on dementia with Lewy bodies, visit www.lbda.org.
Whats The Difference Between Corticobasal Degeneration And Parkinsons
The main difference between CBD and Parkinson’s is that it usually starts on one side with the gradual loss of use of one hand or leg , and there may be little flicks of involuntary muscle jerks. Walking and balance difficulties usually occur later in CBD than in Parkinson’s. Also, in CBD, a person may have trouble with purposeful movements, such as buttoning a shirt or cutting food.
For more information on corticobasal degeneration, read this information page.
Parkinsons Diseaseassociated Pathological Changes In The Cerebellum
The presence of dopaminergic innervation and dopamine D1–3 receptors in the cerebellum has been proven . The cerebellum receives a dopaminergic projection from the ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra pars compacta . Pathological changes in the cerebellum following dopaminergic degeneration were reported in patients with Parkinson’s disease and animal models.Rollandet al. showed that degeneration of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons causes dysfunction of both the basal ganglia–thalamic and cerebello-thalamic pathways in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats and MPTP monkeys. Neuronal degeneration in the cerebellum was shown in an MPTP mouse model , characterized by the loss of Nissl-stained Purkinje cells and aggravated by the number of repeated MPTP injections. An MPTP insult also induced the loss of calcium-binding positive Purkinje cells in monkeys . A recent study found that persistent hyperactivation of Purkinje cells correlated with the level of dopaminergic neuronal loss in the substantia nigra in chronic parkinsonian monkeys .
What Is Rem Behavior Disorder And How Is It Connected To Parkinsons
A: REM behavior disorder is different than other sleep problems, like insomnia. People who have it may jerk or kick — it’s as though they are acting out their dreams. In a similar pattern to anosmia, people with idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder have at least a 50 percent chance of eventually developing Parkinson’s disease.
Whats The Difference Between Multiple System Atrophy And Parkinsons
Parkinson’s and MSA both affect the movement control system and the involuntary autonomic control system and early symptoms can make a differential diagnosis a challenge. MSA, however, tends to progress faster than Parkinson’s; balance problems and a stooped posture happen earlier and get worse more quickly with MSA; and autonomic functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, sweating, bladder function, and sexual problems are more severe in people with MSA.
For more information on multiple symptom atrophy, read this fact sheet.
Parkinsons Patients Treatment Needs Identified With New Brain Scan
Image credit: Sudok1/Dreamstime
A novel brain scan could help scientists identify which Parkinson’s patients would benefit most from a drug used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder .
The scan can allow researchers to better visualise changes in the part of the brain linked to cognitive decline, a study has suggested.
While previous work has shown that atomoxetine – a drug used for people with ADHD – can be helpful to some Parkinson’s sufferers, until now there has not been an easy way to identify those it might help the most.
The study, funded by the charity Parkinson’s UK and published in the journal Brain, was hailed by one researcher as an “exciting step towards individualised therapy for cognitive decline” because it helps identify the people the treatment is most suitable for.
“Changes in cognition can interfere with a person’s wellbeing and may stop them from engaging in their regular and enjoyable activities because they feel they become too time-consuming, stressful, and challenging to complete,” explained Dr Katherine Fletcher, the charity’s research communications manager.
The researchers added that an imbalance of noradrenaline can lead to difficulty concentrating, forgetting things and taking longer to think and process information, or can cause a change in behaviour.
Looking at noradrenaline levels and how they are affected means scientists are “taking a step closer to finding better treatments” for the disease, Fletcher explained.
Whats The Difference Between Vascular Parkinsonism And Parkinsons
As the name implies, vascular parkinsonism is caused by cerebrovascular disease which affects the blood supply to the brain. Vascular parkinsonism is caused by one or more small strokes, while Parkinson’s is caused by a gradual loss of nerve cells. One major difference from Parkinson’s is that it’s not progressive, while Parkinson’s becomes worse with time. Another difference is that there are no tremors in vascular parkinsonism.
For more information on vascular parkinsonism, read this journal article.
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy For Parkinsons Disease
The severity of Parkinson’s disease symptoms and signs vary greatly from person to peson, and it is not possible to predict how quickly the disease will progress. Parkinson’s disease itself is not a fatal disease, and the average life expectancy is similar to that of people without the disease. Secondary complications, such as pneumonia, falling-related injuries, and choking can lead to death. Many treatment options can reduce some of the symptoms and prolong the quality of life.
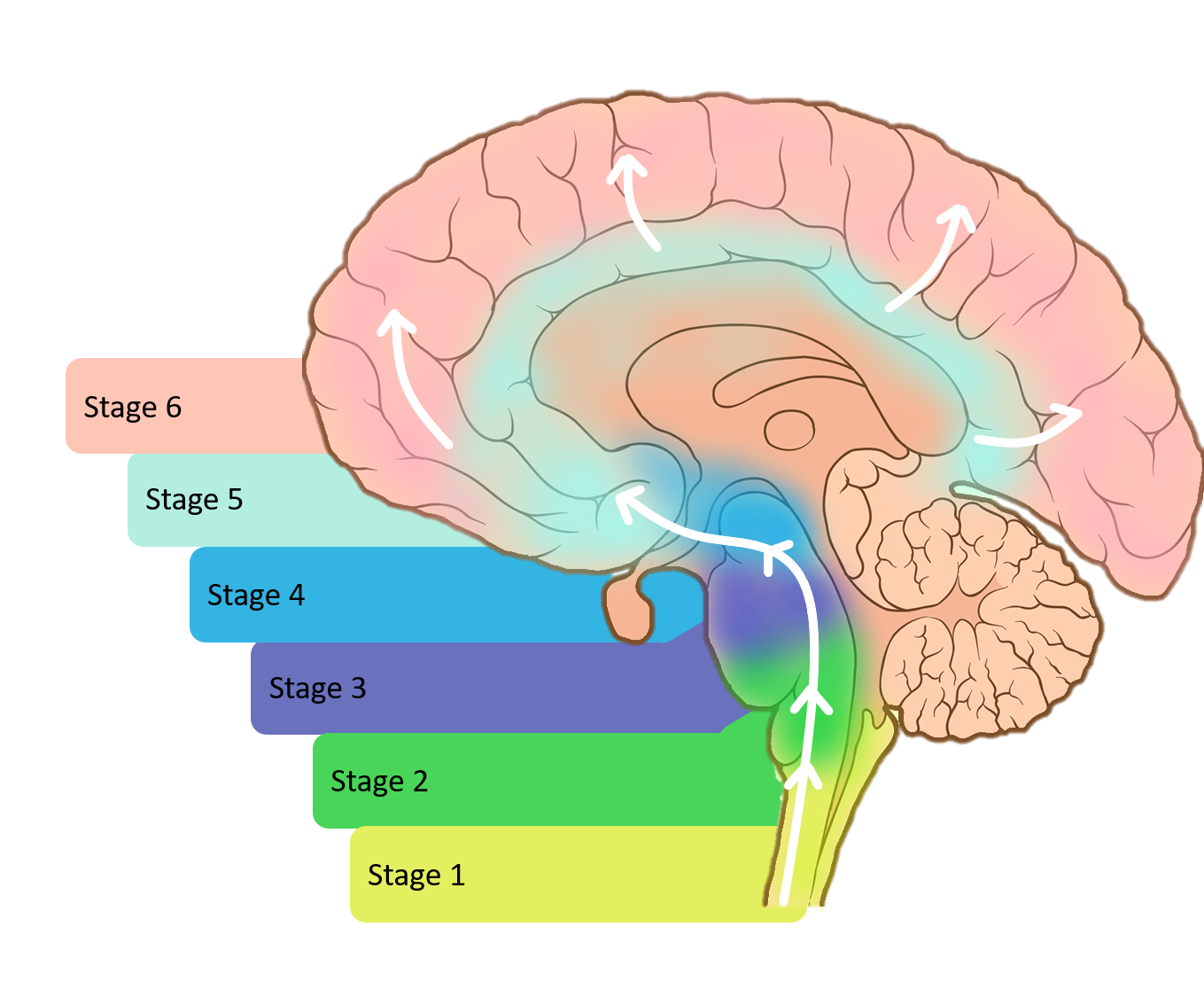
Understand The Progression Of Parkinsons To Help Your Loved One
Parkinson’s disease is progressive, meaning it worsens over time as it moves through these five stages. However, the disease is also highly individual and impacts people differently. The variety of symptoms, severity and speed of progression differs for each individual. In general, the role of a Parkinson’s caregiver is ever-changing, and their demands tend to increase as the disease progresses.
If your loved one is recently diagnosed, knowing what the five-stages of Parkinson’s Disease mean will help you plan for the journey ahead. Most importantly, don’t feel bad for needing additional help. As a loved one and caregiver—you can’t do it all on your own. Professional, expert assistance will ensure your loved one’s progression is monitored and properly managed, and you can focus on spending quality time together.
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinson’s disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didn’t exercise or didn’t start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinson’s, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments — whether medicines or deep brain stimulation — are optimal; and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Improve the quality of your sleep.
Do People Actually Lose Their Sense Of Smell With Parkinsons
A: Yes. It’s a condition called anosmia, and if you have it with no other disease , you have at least a 50 percent chance of developing Parkinson’s disease in the next five to 10 years. What happens is that alpha-synuclein, the protein that clumps in the part of the brain that regulates dopamine and leads to Parkinson’s disease, also aggregates in the olfactory bulb, the part of the brain responsible for your sense of smell. This happens well before the protein accumulations cause motor symptoms.
Parkinson’s Disease Brain Vs Normal Brain: What’s Different
It’s not yet possible to spot the difference between a brain with Parkinson’s and a normal, “healthy” brain on an MRI scan. However, since Lewy bodies were first found in the substantia nigra in 1927, doctors have known they are a feature of Parkinson’s disease. The presence of these Lewy bodies is thought to be what separates people with Parkinson’s disease from the general population. However, Lewy bodies can only be diagnosed with certainty during a brain autopsy after death.
The Cerebellum As A Target For Parkinsons Disease Treatment
While cerebellar dysfunction might contribute to some motor and non-motor signs in Parkinson’s disease, a possible approach for treating parkinsonian symptoms is to attempt to normalize cerebellar function. Surgical treatment, such as deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus improves the motor signs and normalizes cerebellar activation. Levodopa administration can also normalize the activity and connectivity in the cerebello-thalamo-cortical circuit . However, whether it is reduced compensation or alleviation of pathological impairment as a consequence of effective treatment remains unclear. Suppressing cerebellar activity should theoretically answer the question: improvement would mean that the cerebellum is contributing to the manifestations; worsening would mean that the cerebellar activity is compensatory. We suppose that if the main efforts of the cerebellum in Parkinson’s disease are compensatory, suppression of cerebellar activity should be accompanied by further impairments of Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Parkinsons Disease Signs And Symptoms: Before The Diagnosis
Mindy Bixby
Neurologist, Mindy Bixby, DO, discusses the early signs and symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease, commonly referred to as non-motor symptoms.
Dr. Bixby explains how to identify and differentiate these symptoms from other disorders and when it’s time to visit your doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
She also covers therapy and treatment options if diagnosed with Parkinson’s Disease or other movement disorders.
Tags
What Are The Primary Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
There are four primary motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability . Observing two or more of these symptoms is the main way that physicians diagnose Parkinson’s.
It is important to know that not all of these symptoms must be present for a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease to be considered. In fact, younger people may only notice one or two of these motor symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease. Not everyone with Parkinson’s disease has a tremor, nor is a tremor proof of Parkinson’s. If you suspect Parkinson’s, see a neurologist or movement disorders specialist.
Tremors
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
What Can You Do If You Have Early Onset Parkinsons Disease
Work with your healthcare professional to make a plan to stay healthy. This might include the following:
- set up a regular exercise plan to delay further symptoms and signs of early onset Parkinson’s
- have a discussion with family and friends who can provide you with the support when needed
- get-together with a medical social worker to talk about how Parkinson’s may affect your life
- educating yourselves about the disease, its symptoms, and treatments is important
- identifying a medical team to help slowing down the progression of the disease. This could include a primary care physician, neurologist, psychiatrist or a physical therapist.
- discussing the diagnostic approaches and early onset parkinson’s test with your boss or colleagues and creating a plan to keep you working for as long as you desire
What Is Early Onset Parkinson How Common What Are Symptoms
Parkinson’s is a progressive illness that affects the central nervous system. The disease is not easily detected at its early stages. Still, some of the symptoms include impaired balance, lack of limb coordination, and limps and trunk being rigid. Other common signs to look for are depression, sleep disturbance, and loss of smell.
When we feel a little under the weather, we get checked to ascertain what is wrong. A medical check-up first is done to rule out a few things; however, young-onset Parkinson can go undiagnosed for a long time unless you have recurring symptoms. It usually occurs to people under the age of 40.
Stages Of Parkinsons Disease & Its Early And Late Symptoms
Parkinson’s disease is a common neurodegenerative disease. It is characterized by progressive loss of muscle control, stiffness, slowness, and impaired balance. As the disease progresses the patient presents symptoms such as difficulty in walking, talking, and completing simple tasks.
The adult onset of Parkinson’s disease is very common and it is mostly seen in the people aged 60 years or elder. Early onset i.e. age between 21-40 years or juvenile onset i.e. below 21 years of age can also occur. Before knowing the early and late symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, it is necessary to look at the stages of this disease.
Research Roundup: Two Types Of Parkinsons Disease And More
Every week there are numerous scientific studies published. Here’s a look at some of the more interesting ones.
Parkinson’s Disease is Actually Two Diseases
Researchers from Aarhus Universityin Denmark indicating that Parkinson’s disease is actually two types of the disease. This helps explain why there are so many different symptoms and pathways. Parkinson’s is marked by slow deterioration of the brain from accumulation of alpha-synuclein, a protein that damages nerve cells. This causes slow, stiff movements. Some patients apparently have damage to the brain’s dopamine system before damage in the intestines and heart occurs. Other patients have damage to the nervous systems of the intestines and heart before the damage in the brain’s dopamine system. The research was published in the journal Brain.
“With the help of advanced scanning techniques, we’ve shown that Parkinson’s disease can be divided into two variants, which start in different places in the body,” said Per Borghammer, professor of clinical medicine at Aarhus University. “For some patients, the disease starts in the intestines and spreads from there to the brain through neural connections. For others, the disease starts in the brain and spreads to the intestines and other organs such as the heart.”
Epigenetic Changes May Explain Why Humans Live Longer than Other Primates
Biomarker for Neurodegeneration Identified in the Eye
Children and Adults Have Two Distinct Immune Responses to COVID-19
What Are The Primary Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
There are four primary motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability . Observing two or more of these symptoms is the main way that physicians diagnose Parkinson’s.
It is important to know that not all of these symptoms must be present for a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease to be considered. In fact, younger people may only notice one or two of these motor symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease. Not everyone with Parkinson’s disease has a tremor, nor is a tremor proof of Parkinson’s. If you suspect Parkinson’s, see a neurologist or movement disorders specialist.
Tremors
Vocal Symptoms
In Patients Where Parkinsons Disease Starts In The Brain:
The order of symptoms will be opposite patients whose Parkinson’s disease starts in the gut, Borghammer says. “The pathology probably starts inside the brain and doesn’t really create a lot of symptoms initially,” he says. “The first clear symptom to emerge is the motor symptoms, signifying that the dopamine system is damaged.”
The disease then spreads down in the brainstem, where it can cause sleep issues, he says. “Finally, the pathology reaches the peripheral nervous system and causes constipation, urinary problems, and blood pressure problems.”
What Are the Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease?
The Overlaps Between Stress And Parkinsons Disease Part 2
These changes in internal pressure under stress would also explain the feelings of heaviness/being crushed expressed above, since if the internal pressure forces in the body aren’t sufficient to overcome the external force of gravity, it would stand to reason that the body would start to adopt concave shapes, like the classic stooped posture of PD. This is easy to understand with a simple analogy of a balloon. If we pump up the balloon to a high pressure, the balloon would be perfectly round. However, if we then started to deflate it again, decreasing its internal pressure, then the sphere would begin to collapse under gravity: the balloon becomes more rugby ball or american football shaped. This is because the internal pressure pushing outwards is no longer sufficient to completely overcome the external force of gravity. As we keep deflating the balloon , the balloon will continue to flatten out on. Indeed, eventually it will be just be a flat pancake of rubber on the floor, of course.
What Are The Primary Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
There are four primary motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability . Observing two or more of these symptoms is the main way that physicians diagnose Parkinson’s.
Tremors
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
What Diseases And Conditions Resemble Parkinsons Disease
PD is the most common form of parkinsonism, in which disorders of other causes produce features and symptoms that closely resemble Parkinson’s disease. Many disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of PD, including:
Several diseases, including MSA, CBD, and PSP, are sometimes referred to as “Parkinson’s-plus” diseases because they have the symptoms of PD plus additional features.
In very rare cases, parkinsonian symptoms may appear in people before the age of 20. This condition is called juvenile parkinsonism. It often begins with dystonia and bradykinesia, and the symptoms often improve with levodopa medication.
What Are The Symptoms Of Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Like classic Parkinson’s disease, atypical Parkinsonian disorders cause muscle stiffness, tremor, and problems with walking/balance and fine motor coordination.
Patients with atypical Parkinsonism often have some degree of difficulty speaking or swallowing, and drooling can be a problem. Psychiatric disturbances such as agitation, anxiety or depression may also be part of the clinical picture.
Dementia with Lewy bodies can cause changes in attention or alertness over hours or days, often with long periods of sleep during the day. Visual hallucinations — typically of small animals or children, or moving shadows in the periphery of the visual field — are common in DLB. DLB is second only to Alzheimer’s disease as a cause of dementia in the elderly, and it most commonly affects patients in their 60s.
Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy may have difficulties with eye movements, particularly when looking downward, and with balance — when descending stairs, for instance. Backward falls are common and may occur during the early course of the disease. PSP is not usually associated with tremor, unlike Parkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinson’s disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable – reducing symptoms during “on” periods and no longer controlling symptoms during “off” periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they can’t. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinson’s disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare team’s efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinson’s disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinson’s disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare team’s efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinson’s disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein – glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF – to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Clinical Confirmation Of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
The clinical manifestations of PSP-tau pathology are variable, and diagnosis can be difficult at times because of the subtle early signs that may be difficult to discern from other physical or psychological symptoms. The diagnosis of PSP should be considered in all patients presenting with parkinsonism not responding to levodopa therapy; postural instability with falls; executive dysfunction; slowing of vertical saccades/supranuclear vertical gaze palsy; or dysarthria/dysphagia .
What Are The Treatment Options For Parkinsons Psychosis
Because Parkinson’s drugs can cause psychosis, your doctor will likely start by taking you off your medications, one at a time, or adjusting the dose. Changing your medication may make your movement symptoms worse.
Your doctor will keep adjusting your medication. The goal is to get you to a dose that improves your movement without causing hallucinations and delusions.
If changing your medication doesn’t work, the next step is to go on an antipsychotic medication. These drugs prevent psychosis symptoms by altering levels of chemicals in your brain.
Older antipsychotic drugs can make Parkinson’s movement symptoms worse. Newer drugs, called atypical antipsychotics, are less likely to affect your movement. These drugs are off-label, meaning they’re not approved to treat Parkinson’s specifically. They include:
- clozapine
- quetiapine
In 2016, the Food and Drug Administration approved pimavanserin . It’s the first drug designed specifically to treat Parkinson’s disease psychosis. Nuplazid reduces the number of hallucinations and delusions without affecting movement.
Nuplazid and other newer antipsychotic drugs do carry a black box warning. They can increase the risk of death in older people who have psychosis related to dementia. Your doctor will consider this and other risks before prescribing one of these drugs.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications combat Parkinson’s disease by:
Treatment Options For Early Onset Parkinsons Disease
Can Doctors Miss The Early Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
Yes, doctors are human.
There has been a tremendous increase in human knowledge over recent years. It is not possible for a single person to recognize all the symptoms of all the diseases.
Thus, when a patient only has the early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is often missed.
As noted above, the early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease can be vague.
Even if you have some of these symptoms, your diagnosis needs to be confirmed by a physical examination. This examination detects the early signs of Parkinson’s disease.
Sometimes when the doctor examines you, everything might be perfectly normal. This may be due to one of two things:
The last thing to make sure is that you don’t have a disease that can mimic Parkinson’s disease. This can lead to misdiagnosis.
If the doctor is not sure, a test called Trodat/F-Dopa scan may help with diagnosis
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinson’s disease by:
Treatment Options For Early Onset Parkinsons Disease
What Are The Symptom Differences Between Men And Women
Parkinson’s symptoms vary enormously from person to person. PD symptoms include motor symptoms, like tremor and stiffness, and nonmotor symptoms, like depression and fatigue.
Although women report experiencing some symptoms more often than men, research to date has not conclusively shown whether symptoms affect women and men differently. This may be because symptoms vary as much among women as between women and men.
Drugs And Medication Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
A number of different drugs can be used to treat Parkinson’s.
Levodopa
Levodopa is the most common treatment for Parkinson’s. It helps to replenish dopamine.
About 75 percent of cases respond to levodopa, but not all symptoms are improved. Levodopa is generally given with carbidopa.
Carbidopa delays the breakdown of levodopa which in turn increases the availability of levodopa at the blood-brain barrier.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists can imitate the action of dopamine in the brain. They’re less effective than levodopa, but they can be useful as bridge medications when levodopa is less effective.
Drugs in this class include bromocriptine, pramipexole, and ropinirole.
Anticholinergics
Anticholinergics are used to block the parasympathetic nervous system. They can help with rigidity.
Benztropine and trihexyphenidyl are anticholinergics used to treat Parkinson’s.
Amantadine
Amantadine can be used along with carbidopa-levodopa. It’s a glutamate-blocking drug . It offers short-term relief for the involuntary movements that can be a side effect of levodopa.
COMT inhibitors
Catechol O-methyltransferase inhibitors prolong the effect of levodopa. Entacapone and tolcapone are examples of COMT inhibitors.
Tolcapone can cause liver damage. It’s usually saved for people who do not respond to other therapies.
Ectacapone does not cause liver damage.
Stalevo is a drug that combines ectacapone and carbidopa-levodopa in one pill.
MAO-B inhibitors
Early stage
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
