What Is The Difference Between Drug Induced Parkinsons Disease And Typically Occurring Parkinsons Disease
It has been seen that drug-induced Parkinsonism usually occur on both sides of your body while usual Parkinson’s starts from one side of the body. Apart from this, the medication-induced signs generally are seen to go away after the medicine is finished. However, it may take few months to stop, but is does stop eventually. On the contrary, the typically occurring Parkinson’s disease cannot be reversed. Another thing to be kept in mind is that medication-induced Parkinson’s disease is not progressive, unlike the typical Parkinson’s disease.
Delayed Administration And Contraindicated Drugs Place Hospitalized Parkinsons Disease Patients At Risk
Problem: One-third of all patients with Parkinson’s disease visit an emergency department or hospital each year, making it a surprisingly common occurrence.1 The disease affects about 1 million people and is currently the fourteenth leading cause of death in the US. Hospitalization can be risky for patients with Parkinson’s disease when viewed from the perspective of pharmacological management.
Patients with Parkinson’s disease require strict adherence to an individualized, timed medication regimen of antiparkinsonian agents. Dosing intervals are specific to each individual patient because of the complexity of the disease. It is not unusual for patients being treated with carbidopa/levodopa to require a dose every 1 to 2 hours. When medications are not administered on time, according to the patient’s unique schedule, patients may experience an immediate increase in symptoms.2,3 Delaying medications by more than 1 hour, for example, can cause patients with Parkinson’s disease to experience worsening tremors, increased rigidity, loss of balance, confusion, agitation, and difficulty communicating.2 Studies show that three out of four hospitalized patients with Parkinson’s disease do not receive their medications on time, or have had doses entirely omitted.4 According to the National Parkinson Foundation, 70% of neurologists report that their patients do not get the medications they need when hospitalized.2
Two case examples
Other medication safety concerns
References
Serotonin Reuptake Blocking Antidepressants Fluoxetine Sertraline And Paroxetine
Several other medications have been reported to cause drug-induced parkinsonism and to worsen parkinsonism in people with Parkinson disease, including the serotonin reuptake blocking antidepressants fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine. Two calcium channel blockers available in Europe and South America , which are piperazine derivatives, are thought to cause drug-induced parkinsonism by blocking dopamine receptors. Reports of parkinsonism induced by other drugs, such as lithium and amiodarone, are so rare that only after parkinsonism has developed should the possible drug effect be taken into account. Because lithium is not known to block dopamine receptors, another mechanism is likely. Some animal data implicate an effect of lithium on intercellular signalling via G-protein coupled receptors . One antidepressant, amoxapine, has dopamine receptor-blocking properties and, therefore, may induce parkinsonism. Parkinsonism as a transient side effect of alcohol withdrawal has been reported without later development of Parkinson disease, but it is unknown how common this is .
Any Medication That Blocks Dopamine In The Body Can Cause Parkinsons Symptoms
You may have heard of Parkinson’s disease , a movement disorder. Someone with it may have characteristic signs, such as a pill-rolling tremor in the fingers or a hunched forward posture. You may recognize someone with this disease from the faltering, tiny steps they take when they walk or by their rigidly emotionless face.
The cause of Parkinson’s disease is mostly unknown. Some people develop Parkinson’s-like symptoms after treatment with certain medications. This is called drug-induced parkinsonism or secondary parkinsonism. Certain medications can also worsen symptoms in someone who already has Parkinson’s disease.
Any medication that blocks dopamine in the body can cause Parkinson’s symptoms. Dopamine is a brain chemical that helps control movement. Common dopamine-blocking drugs are antipsychotics. They are used to treat certain mental illnesses or severe nausea. Less commonly, certain types of calcium channel blockers cause drug-induced parkinsonism. These drugs may be used to treat chest pain and high blood pressure, or irregular heart rate.
Top Medicines That Worsen Parkinsons Disease Or Cause Secondary Parkinsonism
Medications to avoid
Some medications can worsen movement symptoms of PD, including slowness, stiffness, tremor and dyskinesia. These drugs, listed below, are used to treat psychiatric problems such as hallucinations, confusion or gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea. The stress of your illness, hospital stay or new medicines can increase your risk of hallucinations while hospitalized. Common anti-hallucination medicines to be avoided are listed by generic or chemical name followed by the trade name.
Anti-hallucination medicines to avoid
Note: the anti-hallucination medicines Quetiapine or Clozapine can be used. The following should be avoided:
- aripiprazole , chlorpromazine , flufenazine , haloperidol , molindone , perphenazine , perphenazine and amitriptyline , risperidone , thioridazine , thiothixene
Anti-nausea medicines to avoid
- metoclopramide , phenothiazine , promethazine
Medicines to avoid if you are on Rasagiline or Selegiline
- Pain medicines – Meperidine , Tramadol ,Antispasmodic medicine Flexeril , Dextromthorphan and St Johns Wort.
- This is not a complete list of medicines to avoid. If you have questions about other medications, ask your pharmacist or doctor.
Drugs Associated With Parkinsonism And Other Abnormal Involuntary Movements
There are numerous drugs and drug classes that are associated with the development of parkinsonism and other abnormal involuntary movements. Drug-induced parkinsonism is often not recognised, especially in the non-psychiatric patient , The side effect often develops within 1 month of the start of treatment, with 60% of patients developing it by this time point and 90% within 3 months .The potency of antipsychotics is defined by their ability to block the D2 receptors. Therefore, high-potency neuroleptics tend to have a greater propensity to cause extra-pyramidal side effects. However, some high-potency neuroleptics that also have anticholinergic properties are associated with fewer motor side effects. Atypical antipsychotics tend to have broader pharmacodynamic effects, and it is thought that their activity at 5HT2a receptors mediate efficacy with less need for blocking of the D2 receptors in the mesolimbic pathways and therefore in the substantia nigra.
The evidence surrounding iatrogenic dystonias is less well developed. Conventional neuroleptics are clearly implicated as are calcium channel blockers. Additionally, there are several case reports noting an association with olanzapine, carbamzaepine, lithium, imipramine, gabapentin and ziprasidone. Other dystonias are less clearly associated with iatrogenic causes.
Anesthetic Drugs May Interact With Medications Used For Parkinsons Disease
Lorri A. Lee, MD; Tricia A. Meyer, PharmD, MS, FASHP
An estimated one million people in the United States have been diagnosed with Parkinson’s Disease making it one of the most common neurological disorders in patients. This number is estimated to double in the next 30 years as PD is associated with increasing age. PD patients have a deficiency of dopamine in their brain and many of their medications are used to increase this neurotransmitter. They are frequently very sensitive to missing even one dose of their Parkinson medications and may exhibit increased rigidity, loss of balance, agitation, and confusion if their dosing schedule is delayed. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome or parkinsonism-hyperpyrexia syndrome can develop if their medications are held too long or as a result of serious infection.1 Many drugs used in the perioperative period, such as metoclopramide, butyrophenones , and phenothiazines have anti-dopaminergic activity that can worsen the symptoms of PD.
PD patients may be prescribed selective MAOI-B medications such as selegiline and rasagiline that inhibit metabolism of dopamine. Though caution is still advised, several studies have demonstrated that the risk of serotonin syndrome with these selective MAOI-B drugs is extremely low, even in combination with serotonergic antidepressants.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare for this article.
Patients With Parkinsons Disease Are At Risk For Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
November 21, 2016
What Are The Other Forms Of Medicines That Can Cause Parkinsons Disease
Some of the other common medicines which can cause Parkinson’s disease may include some forms of anti-depressants, anti-nausea drugs, drugs used for the treatment of vertigo, drugs used for epilepsy and anti-arrhythmics. It should be remembered that not all drugs in these classes may cause signs of Parkinsonism. The doctor generally makes the patient aware of the side-effects before prescribing a certain form of drugs. Nevertheless, it is important from the patient’s part to ask about the side-effects of the prescribed medicines.
How Can You Improve Aggressiveness And Hallucinations In Parkinsons
Hallucinations may spark anger or aggression in a person with Parkinson’s disease. Some ways to help include:
- Reassure them, tell them they are safe.
- Speak slowly and calmly.
- Ask questions about the person’s feelings.
- Listen to the person, don’t interrupt.
- Avoid sudden movements.
- Give the person space and a way out, so they don’t feel cornered or threatened.
- Make an “emergency plan” ahead of time for what you and others in the house will do if the person experiencing hallucinations becomes a danger to themselves, you, or anyone else.
- When it is safe, help the person speak with their healthcare provider about making a plan to address the hallucinations.
Not All Drugs In These Classes Will Cause Symptoms Of Parkinsonism
What’s the difference?
Drug-induced parkinsonism usually develops on both sides of the body, while typical Parkinson’s disease does not. Also, drug-induced parkinsonism usually does not progress like typical Parkinson’s.
Unlike Parkinson’s, drug-induced symptoms usually go away after the drug is stopped. It may take several months, though, for the symptoms to completely stop. If the symptoms remain, then it is possible that the drug may have “unmasked” underlying Parkinson’s disease.
Who is at risk?
- Female: Women are twice as much at risk as men.
- Elderly: Older people are more likely to be on multiple medications or to have underlying Parkinson’s disease.
- Those with a family history of Parkinson’s disease.
- People with AIDS.
A Critical Reappraisal Of The Worst Drugs In Parkinsons Disease
What are the worst drugs for Parkinson’s disease patients? Couldn’t a simple list be assembled and disseminated to the Parkinson community? Recently Ed Steinmetz, an experienced neurologist in Ft. Meyers, FL pointed out to me, a list approach published in the Public Citizen Newsletter . The approach was to list every drug associated with a single confirmed or unconfirmed symptom of Parkinson’s disease or parkinsonism. Parkinson’s disease is defined as a neurodegenerative syndrome , whereas parkinsonism encompasses a wider net of drug induced and other potential causes. In parkinsonism symptoms are similar to Parkinson’s disease, but patients do not have Parkinson’s disease. Patients and family members confronted with a simple “drug list” approach may falsely conclude that most medicines are bad for Parkinson’s disease, and that any medicine may cause parkinsonism. This concept is in general, incorrect. Although the approach is well-meaning, it is in need of a major revision, as Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism are too complex to summarize by simple lists. In this month’s column I will try to summarize the key information that patients and family members need to know about the “worst pills,” for Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism.
A Florida Parkinson’s Treatment Blog by Michael S. Okun, M.D.
UF Center for Movement Disorders & Neurorestoration, Gainesville FL
How Are Parkinsons Disease And Substance Use Disorders Linked
As the Michael J. Fox Foundation notes, the exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is unknown, but there is a consensus that genetics and the environment each play a key role. In terms of genetics, some research supports that Parkinson’s disease can develop due to one genetic mutation of the gene LRRK2. When this is the case, more than one individual in a family with this genetic mutation will develop Parkinson’s disease. Regarding environmental causes, research suggests that the use of certain drugs can set off chemical events in the brain that lead to the onset of Parkinson’s disease or at least the development of symptoms typically associated with this disorder.
This article focuses on some of the illicit drugs that, according to research, may be responsible for the development of Parkinson’s disease-like symptoms. The drugs that will be considered herein are heroin, cocaine, methamphetamine, and amphetamine. While each of these drugs has a different chemical structure, when their component chemical parts are broken down, they affect similar areas of the brain, such as the substantia nigra region.
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinson’s disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didn’t exercise or didn’t start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinson’s, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments — whether medicines or deep brain stimulation — are optimal; and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Improve the quality of your sleep.
Disadvantages Of Regional Anesthesia Over General Anesthesia
Regional anesthesia will not eliminate Parkinson’s symptoms, such as tremor or rigidity, except in the areas directly affected by the anesthetic.
Tremor can interfere with some monitoring device and makes it more difficult to interpret.
If the surgery is delicate, the surgeon may want the patient to be absolutely still.
The surgical procedure may not be possible under regional anesthesia.
Two Areas In Which Parkinsons Disease May Bring About Death
I. Falls
PD patients are at an increased risk of falling and bad falls can lead to death. This usually occurs as a complication of a fall that requires hospitalization, particularly if it involves surgery. While most people do not fracture their hips when they fall, some do, and hip surgery, while routine, is still major surgery. It carries the risk of infection, delirium related to pain medications and anesthesia, heart failure, pneumonia, blood clots in the legs that then go to the lungs, and general weakness from immobility. Hip fractures are probably the main cause for death for those who fall, but people can fracture other bones and require surgery. They may fracture their ribs, which leads to reduced coughing, because of the pain, and an increased risk of lung infections . It is surprisingly uncommon for Parkinson’s Disease patients to die from brain injuries related to falls, but it still may occur.
II. Pneumonia
What Causes Pain In Cases Of Parkinsons Syndrome Sufferers
Methamphetamine And Amphetamine Abuse And Parkinsons Disease
The National Institute on Drug Abuse reports that methamphetamine and amphetamine abuse can increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
A main insight from this research is that abuse of these types of drugs damages dopamine neurons in the brain. As Parkinson’s disease is a dopamine-related disorder, it makes sense that individuals who abuse drugs, and thereby damage their dopamine neurons, may develop symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Since, as discussed earlier, dopamine plays a key role in muscle coordination and functionality, dopamine damage results in motor impairment, a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease.
One research study found a near 300 percent increase in the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease in people who have abused methamphetamine or amphetamine. This risk is alarming when one considers that despite public knowledge of the devastating effects of methamphetamine abuse, in 2014, an estimated 438,000 Americans in the 26+ age group were currently using this illicit drug. Note that the 2014 National Survey on Drug Use and health, from which this statistic is taken, did not expressly collect data on amphetamine use, so the estimated number of amphetamine abusers for that survey year is not available. When amphetamine abuse does occur, it is often in the form of prescription medications such as Adderall and Ritalin.
The good news is that recovery from substance abuse is always possible.
What Causes Constipation In People With Parkinson’s Disease
In some people with Parkinson’s disease, constipation may occur due to the improper functioning of the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating smooth muscle activity. If this system is not working properly, the intestinal tract may operate slowly, causing constipation.
Also, medications used to treat Parkinson’s disease can cause constipation.
For Your Good Health: Can Lyme Disease Lead To Parkinsons
DEAR DOCTOR. ROACH: Can Lyme Disease Put A Person Into Parkinson’s Disease? I tested positive for Lyme – I had the rash, a fever, and a terrible headache. After a month on doxycycline, my left arm started shaking and my neurologist diagnosed me with Parkinson’s. The doctor said it had nothing to do with Lyme disease. What is your opinion? – SM
ANSWER: I can absolutely understand why you suspect that the neurologist might be wrong. Chance seems too much to believe. However, I think your neurologist is probably right. The different types of neurological complications of Lyme disease are many.
The most common are any combination of meningitis symptoms ; Disorders of the cranial nerves ; and damage to peripheral nerves causing pain and weakness or numbness, often similar to sciatica .
A detailed neurological exam by a neurologist would look for signs of Parkinson’s disease – not just the tremors you described, but muscle stiffness and gait changes. These would be very unusual in Lyme disease. I found cases that resembled some aspects of Parkinson’s disease, but they improved with treatment.
It’s possible that the stress of Lyme disease hastened the onset of Parkinson’s disease you were meant to be. I say your neurologist is “probably right” because what I’ve found – the lack of data to show a correlation – doesn’t mean there isn’t a correlation, and it is possible that time can prove the Lyme -Borreliosis related to Parkinson’s. However, I think it is unlikely.
Types Of Hallucinations In People With Parkinsons Disease
Hallucinations involve the five senses: sight, smell, touch, hearing, and taste.
People with hallucinations have sensory experiences that feel real to them, but are not actually happening and are not apparent to anyone else.
Types of hallucinations include:
- Auditory: Hearing things
- Gustatory: Tasting things
For people who experience Parkinson’s-related hallucinations, the hallucinations are usually visual. They are typically non-threatening, but less commonly they can be of a threatening nature.
Often people with Parkinson’s disease psychosis see small people or animals, or loved ones who have already died. They are not interacting with them, just being observed.
Auditory hallucinations are more common in people with schizophrenia, but can happen with Parkinson’s disease. With Parkinson’s disease, auditory hallucinations are usually accompanied by visual hallucinations.
More specific types of hallucinations experienced by people with Parkinson’s disease include:
Who Are At Risk Of Developing Drug Included Parkinsonism
Some patients may be at a higher risk of developing medication-induced Parkinson
ism than others. Some of the risks include-
Women: Women are seen to be two times as much at risk of having drug inducing Parkinson’s disease than men.
AIDS Patients: People with AIDS are at a higher risk.
Family History: Patients having a family history Parkinson’s disease are at a higher risk of having drug induced Parkinsonism.
Elderly: Since elder people are usually on multiple medicines, they are at risk of having drug induced Parkinsonism.
Antipsychotics To Induce Dyskinesia And Similar Symptoms
Usage of antipsychotics drugs in Parkinson’s disease patients is complicated because of their tendency to block D2 i.e. dopaminergic receptors, which are responsible to induce dyskinesia and related extra pyramidal symptoms. Antipsychotic drugs highlight significant difference associated with the affinity towards D2 receptors.
Conditions That Mimic Shuffling Gait Seen In Parkinsons:

Please read the article on shuffling gait. It describes 5 causes of shuffling of gait.
The most crucial mimic to remember is Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus .
The person with NPH feels like he is stuck to the ground. This is a “magnetic gait”. It is easy to mistake this for Parkinson’s disease.
For example, see this video posted by the Hydrocephalus Association of America on youtube:
NPH can be treated by implanting a small shunt pipe. This shunt drains excess water around the brain into the abdomen.
Myth 4: Aside From Medication There Isnt Much You Can Do
Fact: This “it is what it is; there’s nothing I can do to help myself” myth is counterproductive. There is a lot you can do — chiefly, keeping as active as you can. A recent study found that patients with Parkinson’s who took part in weekly, hourlong exercise sessions were able to do more in their daily lives than those who did not.
Cholinesterase Inhibitors Widely Used To Treat Dementia
Cholinesterase inhibitors, widely used to treat dementia, may cause worsened parkinsonism, primarily increased tremor . Large double-blind trials of rivastigmine, a cholinesterase-inhibiting drug, in both dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease dementia have demonstrated that rivastigmine is well tolerated without significant worsening of motor function overall, although tremor may increase . The other cholinesterase inhibitors have been less well studied but appear to have similar benefits and side effects.
How To Talk To Someone With Hallucinations Or Delusions
- It is usually not helpful to argue with someone who is experiencing a hallucination or delusion. Avoid trying to reason. Keep calm and be reassuring.
- You can say you do not see what your loved one is seeing, but some people find it more calming to acknowledge what the person is seeing to reduce stress. For example, if the person sees a cat in the room, it may be best to say, “I will take the cat out” rather than argue that there is no cat.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinson’s Foundation Center of Excellence.
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinson’s disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable – reducing symptoms during “on” periods and no longer controlling symptoms during “off” periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they can’t. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinson’s disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare team’s efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinson’s disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein – glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF – to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Naturaltreatment For Parkinsons #6 Magnesium & Iodine:
Magnesium is vital for the health of the entire nervoussystem, especially the protective layer that surrounds the nerves . Magnesiumis also essential for the production of dopamine and helps protect dopaminergicneurons in the substantia nigra from degeneration. In addition to this, new evidence is showing that low levels of magnesium in the brain causes a build-up ofheavy metals – a major factor in the development of Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s,epilepsy and MS. In a recent trial, 30 epileptics were given 450 mg ofmagnesium daily and this successfully controlled their seizures. Ifmagnesium can help epilepsy patients, it can certainly help Parkinson’s sufferers. Worldrenowned magnesium expert and author, Dr Carolyn Dean, has both Parkinson’s andAlzheimer’s disease in her “top 55 health conditions caused by amagnesium deficiency” list and says that magnesium is 100% essential for the preventionand treatment of both of these diseases… Dr Carolyn Dean Interview
In regards to iodine, well-known researcher and author,Dr James Howenstein, says…
“Iodineis found in large quantities in the brain and the ciliary body of the eye. A lackof iodine may be involved in the production of Parkinson’s disease andglaucoma.”
“Inthe brain, iodine concentrates in the substantia nigra, an area of the brainthat has been associated with Parkinson’s disease.”
David Brownstein M.D. 9
Best Sources of Magnesium and Iodine…
-What You’ll Need
1 cup of Magnesium Chloride Flakes
1 cup of Distilled Water
Myth 6: Deep Brain Stimulation Is Experimental Therapy
Fact: Deep brain stimulation, or DBS, is a procedure in which doctors place electrodes in the brain at the point when medications are less effective in masking motor symptoms, such as tremor, stiffness and slowness of movement.
While it may sound frightening and futuristic, it’s been around and successfully used for decades. DBS works very similarly to a pacemaker, except the wire is in the brain, not in the heart. It’s been a standard procedure for the past two decades.
Natural Remedy For Parkinsons #4 Chlorella And Borax:

If you have a neurological disease such as Parkinson’s orAlzheimer’s, the importance of removing heavy metals from the body – especiallyfrom the brain and nervous system – cannot be overstated. Heavy metalsaccumulate in the brain and nervous system at a rapid rate and cause damage tothe neurological pathways and “brain inflammation”. Fluoride is one ofthe worst, however, mercury, lead, aluminium and cadmium are also extremely dangerous.Chlorella and borax not only remove these heavy metals completely, theycontinue to prevent further toxic build-ups.
Chlorella is a miracle blue-green algae and one of themost powerful detoxifiers and chelators yet discovered. Whenit’s combined with cilantro, its benefits are enhancedsignificantly. A Russian study found that chlorella, combined with cilantro,was able to remove all heavy metals from the body, including fluoride and mercury,with no adverse or harmful side effects. You can purchase chlorellain powdered form online or from most health food stores. Just make sure you buythe Broken Cell Wall Chlorella as this is the strongest and most bio-available.For dosage recommendations, simply follow the directions on the container.
Naturalremedy For Parkinsons #10 Foods You Must Avoid
The foods and liquids you should be eating and drinkingmore of to help you along include:
The foods you should be avoiding or not eating at allinclude:
What Is Special About Parkinsons Syndrome Sufferers
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
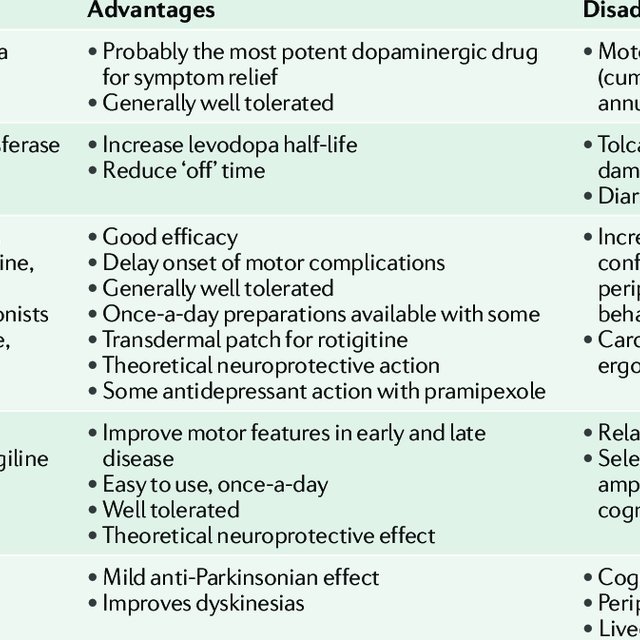
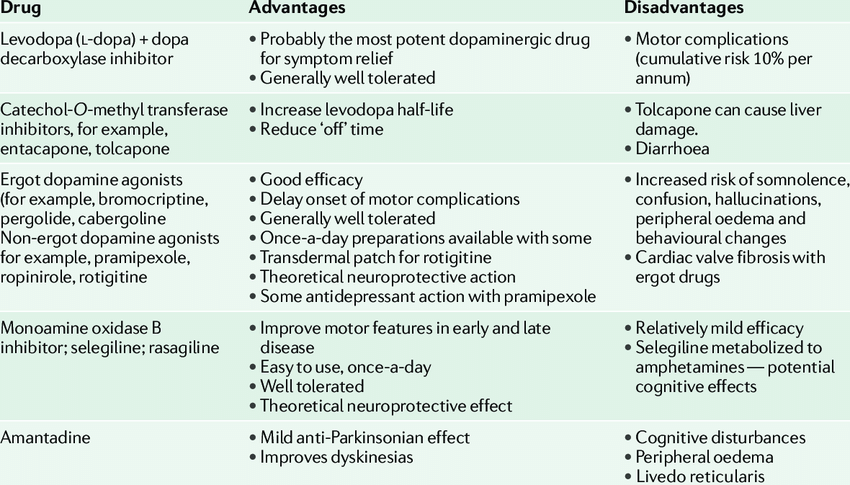
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinson’s disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Conditions That Can Cause Tremors Besides Parkinsons:
The tremor of Parkinson’s disease occurs even at rest. Hence it is called a rest tremor. Very few other conditions produce rest tremor.
But, many other diseases produce a tremor which is seen only when moving, for example when writing. This is called an Action tremor or posturokinetic tremor. Even these diseases are sometimes misdiagnosed as Parkinson’s disease.
| Causes of Rest Tremor |
|---|
|
2. Excessive stress, coffee or smoking 3. Medications such as bronchodilators, valproate and lamotrigine 4. Chromosomal problems such as Fragile-X syndrome 5. Parkinson’s disease itself! And many others… |
Which Test Can Be Done When The Diagnosis Is In Doubt
I request a small set of tests on almost all patients I diagnose with Parkinson’s. These detect some mimics of Parkinson’s disease.
Some doctors don’t request all these tests. And for a good reason.
The diagnosis of Parkinson’s mimics is primarily based on a careful history and examination. Even in my practice, these tests change the diagnosis only in a minority of patients.
I like the additional confirmation provided by these tests. They also have other benefits. For example, they help me determine the proper dosages of medications like Amantadine.
| Simple tests to detect Parkinson’s Mimics |
|---|
| 1. MRI-Brain – with size measurements of brain parts called the midbrain and pons. I usually also request a unique picture called SWI, which shows iron inside the brain.
2. Blood tests: |
But when the diagnosis s really in doubt, there is another brain scan that can be done.
A Trodat scan. Or even better – an F-DOPA scan. Both these scans measure dopamine activity inside the brain.
You can read more about Trodat & F-DOPA scans by clicking here.
These scans are not perfect. Let me tell you why very quickly:
In Parkinson’s disease, dopamine activity inside the brain is deficient. This deficiency produces an abnormal scan. If the Trodat/F-DOPA scan is normal, it is unlikely that you have Parkinson’s disease.

