Take Care Of Yourself
Probably one of the most important, and sometimes difficult, things caregivers can do is to take care of themselves. This includes maintaining mental and physical health by making and keeping your own medical and dental appointments. As a caregiver, it is important to keep your job whenever possible as it provides not only financial help and possibly insurance coverage, but also a sense of self-esteem. Join a support group;for caregivers;if possible. Support groups help you meet people who are going through what you are going though, vent frustrations, give and receive mutual support, and exchange resource information and coping strategies. Whenever possible get your sleep, take breaks, make and keep social activities, and try to keep your sense of humor.
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinson’s may experience some of these more common “hallmark” symptoms:
- Bradykinesia – slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest – involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity – stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability – sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
Ways To Boost Dopamine
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter thats great to have in abundance. When you do, your brain is flooded with pleasurable feelings and a sense of satisfaction and reward.
While increasing your natural dopamine wont prevent or stop the progression of Parkinsons disease, it might help stave off early symptoms of the disorder. For some people, natural dopamine boosts may be helpful alongside other treatments.
Read Also: Young Onset Parkinson’s Disease Life Expectancy
How Is Parkinsons Disease Dementia Diagnosed
No single test can diagnose Parkinsons disease dementia. Instead, doctors rely on a series or combination of tests and indicators.
Your neurologist will likely diagnose you with Parkinsons and then track your progression. They may monitor you for signs of dementia. As you get older, your risk for Parkinsons dementia increases.
Your doctor is more likely to conduct regular testing to monitor your cognitive functions, memory recall, and mental health.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
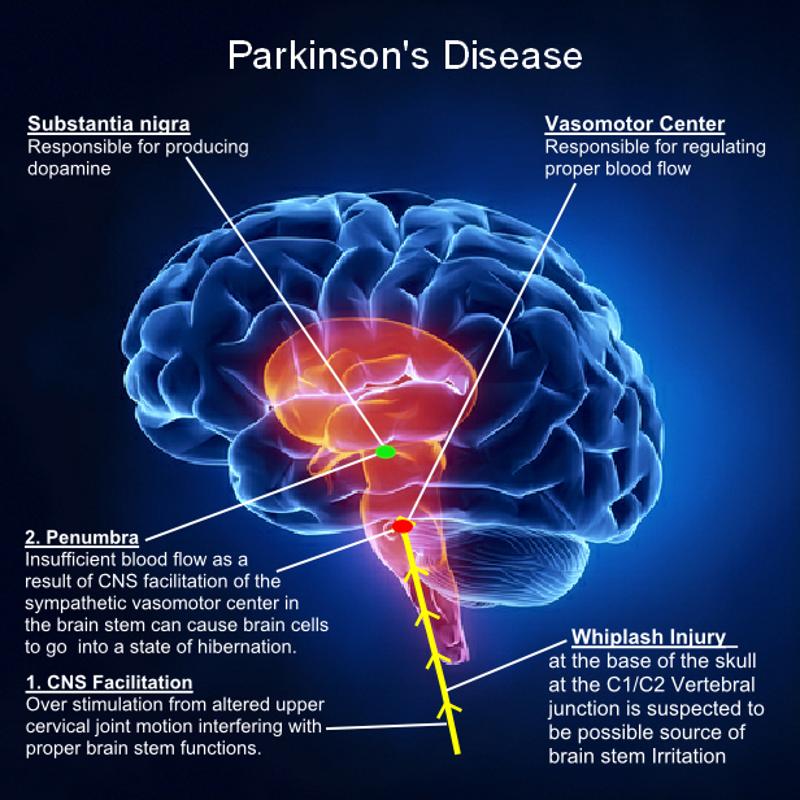
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in deep parts of the brain called the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and are responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement. For reasons not yet understood, the dopamine-producing nerve cells of the substantia nigra begin to die off in some individuals. When 80 percent of dopamine is lost, PD symptoms such as tremor, slowness of movement, stiffness, and balance problems occur.
Body movement is controlled by a complex chain of decisions involving inter-connected groups of nerve cells called ganglia. Information comes to a central area of the brain called the striatum, which works with the substantia nigra to send impulses back and forth from the spinal cord to the brain. The basal ganglia and cerebellum are responsible for ensuring that movement is carried out in a smooth, fluid manner .
The action of dopamine is opposed by another neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. In PD the nerve cells that produce dopamine are dying. The PD symptoms of tremor and stiffness occur when the nerve cells fire and there isn’t enough dopamine to transmit messages. High levels of glutamate, another neurotransmitter, also appear in PD as the body tries to compensate for the lack of dopamine.
Read Also: Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Further Information And Support
- Building 21, Macquarie Hospital, 120 Coxs Road , North Ryde;NSW 2133Freecall 1800 644 189
- 20 Kingston Road, Cheltenham VIC 3192Ph 9551 1122
- PO Box 1684, Springwood QLD 4127Ph 3209 1588
- 23A King William Road, Unley SA 5061Ph 8357 8909
- Centre for Neurological Support, The Niche Suite B, 11 Aberdare Road, Nedlands WA 6009Ph 9346 7373
- PO Box 222, Calwell ACT 2905Ph 6278 8916
- Locked bag 4, Sandy Bay TAS 7005Ph 6229 2509
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in deep parts of the brain called the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and are responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement. For reasons not yet understood, the dopamine-producing nerve cells of the substantia nigra begin to die off in some individuals. When 80 percent of dopamine is lost, PD symptoms such as tremor, slowness of movement, stiffness, and balance problems occur.
Body movement is controlled by a complex chain of decisions involving inter-connected groups of nerve cells called ganglia. Information comes to a central area of the brain called the striatum, which works with the substantia nigra to send impulses back and forth from the spinal cord to the brain. The basal ganglia and cerebellum are responsible for ensuring that movement is carried out in a smooth, fluid manner .
The action of dopamine is opposed by another neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. In PD the nerve cells that produce dopamine are dying. The PD symptoms of tremor and stiffness occur when the nerve cells fire and there isnt enough dopamine to transmit messages. High levels of glutamate, another neurotransmitter, also appear in PD as the body tries to compensate for the lack of dopamine.
You May Like: What Gene Mutation Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosis And Management Of Parkinsons Disease
There are no diagnostic tests for Parkinsons. X-rays, scans and blood tests may be used to rule out other conditions. For this reason, getting a diagnosis of Parkinsons may take some time.;;
No two people with Parkinsons disease will have exactly the same symptoms or treatment. Your doctor or neurologist can help you decide which treatments to use.
People can manage their Parkinsons disease symptoms through:;
- seeing a Doctor who specialises in Parkinsons
- medication
- multidisciplinary therapy provided for example, by nurses, allied health professionals and counsellors
- deep brain stimulation surgery .
Ways To Decrease The Risk Of Parkinsons And Alzheimers
There is currently no cure for either disease. Parkinsons is considered a more treatable condition, however, especially in the early stages of the disease. Treatments include medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes. Research continues to suggest that a brain-healthy lifestyle can help prevent both Alzheimers and Parkinsons. Here are some basic guidelines:
You May Like: What Is The Pathophysiology Of Parkinson’s Disease
The Substantia Nigra And Movement
The reason that Parkinsons causes movement symptoms is that the substantia nigra makes up part of the circuitry, called the basal ganglia, that the brain uses to turn thought about movement into action.
The structures of the basal ganglia.
The substantia nigra is the master regulator of the circuit, it mainly communicates using the chemical dopamine, but other chemical transmitters are also used to communicate between other areas of the basal ganglia.
The balance of signals being sent between these structures allows us to control movement. But as Parkinsons progresses, and the dopamine-producing brain cells in the substantia nigra are lost, movement symptoms appear. Without enough dopamine, it becomes harder to start and maintain movements, which leads to symptoms such as slowness of movement, rigidity and freezing. And an imbalance of signals in the basal ganglia means people with Parkinsons can experience what is known as a resting tremor.
But while this is the description of Parkinsons you may find in most textbooks, it is now recognised that changes are not limited to the substantia nigra and basal ganglia.
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This;leads to a reduction;in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Four Cardinal Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Support For People With Parkinsons Disease
Early access to a multidisciplinary support team is important. These teams may include doctors, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, dietitians, social workers and specialist nurses.;Members of the team assess the person with Parkinsons disease and identify potential difficulties and possible solutions.There are a limited number of multidisciplinary teams in Victoria that specialise in Parkinsons disease management. But generalist teams are becoming more aware of how to help people with Parkinsons disease.;;
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Forgetfulness
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
Don’t Miss: Can Antipsychotics Cause Parkinson’s
Related Diagnosis: Lewy Body Dementia
Current research is helping to differentiate dementia related conditions in relationship to Parkinsonâs disease. Doctorâs use a 12-month arbitrary rule to aid in diagnosis. When dementia is present before or within 1 year of Parkinsonâs motor symptoms developing, an individual is diagnosed with DLB. Those who have an existing diagnosis of Parkinsonâs for more than a year, and later develop dementia, are diagnosed with PDD.
In the simplest terms, Lewy bodies are abnormal clumps of proteins that develop in nerve cells. Cholinesterase inhibitors, medications originally developed for Alzheimerâs disease, are the standard treatment today for cognitive DLB and PDD symptoms. Early diagnosis is important, as DLB patients may respond differently than Alzheimerâs disease patients to certain drug, behavioral, and dementia care treatments.
This challenging, multi-system disorder involving movement, cognition, behavior, sleep, and autonomic function requires a comprehensive treatment approach to maximize the quality of life for both the care recipient and their caregiver. It is very important to pay attention to symptoms of dementia and to search for an expert clinician who can diagnose the condition accurately.
Slice Title3 Things We Know About Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s develops when cells in the brain stop working properly and are lost over time.;These brain cells produce a chemical called dopamine.
Symptoms start to appear when the brain cant make enough dopamine to control movement properly.
There are 3 main symptoms – tremor , slowness of movement and rigidity – but there are many other symptoms too.
Don’t Miss: Does Diet Soda Cause Parkinson’s
Other Causes Of Parkinsonism
“Parkinsonism” is the umbrella term used to describe the symptoms of tremors, muscle rigidity and slowness of movement.
Parkinson’s disease is the most common type of parkinsonism, but there are also some rarer types where a specific cause can be identified.
These include parkinsonism caused by:
- medication where symptoms develop after taking certain medications, such as some types of antipsychotic medication, and usually improve once the medication is stopped
- other progressive brain conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple systems atrophy, and;corticobasal degeneration
- cerebrovascular disease where a series of small strokes cause several parts of the brain to die
You can read more about parkinsonism on the Parkinson’s UK website.
Does Parkinsons Affect Voice
The voice is affected too, because the voice box is ultimately controlled by the basal ganglia as well. Thus the voice becomes soft, slurred and hushed. Others may comment that the patient is mumbling. The mumbling goes away temporarily once the patient becomes aware of it but soon returns to the soft, slurred state.;
This temporary improvement when attention is paid is true of many of the motor symptoms of PD because the condition primarily affects subconscious movements, and does not directly affect nerve or muscle control at the most basic level. Thus, conscious awareness can override the slowness to a certain extent. This fact is one reason why physical therapy and physical activity are so useful and necessary in treating PD.
- Slowness of walking and other movements
- Trouble with dexterity
- Reduced arm swing or stride length
- Delayed reactions physically
- Reduced facial reactions
- Softer or slurred speech
- Tremor in one or both limbs with the limb at rest
- Sometimes also tremor with holding a posture or with actions
- Usually asymmetric
Imbalance, loss of balance reflexes
- May fall backwards
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Disease Cause Back Pain
Parkinsons Dementia Vs Alzheimers Dementia
According to experts, Parkinsons dementia can cause impaired physical activity and impacts motor skills. Two neurotransmitters called dopamine and serotonin tend to be damaged by Parkinsons.
In addition to causing issues with movement and coordination, this form of dementia can also cause a slower thought process and memory problems. This is usually less pronounced however, until the later stages of the disease.
With Alzheimers, two types of proteins in the brain, tangles and plaques , accumulate and kill brain cells. This Alzheimers-induced dementia affects memory, clear thinking, language skills, and orientation. It reduces comprehension, learning capacity, and judgement. Storing new information and memory retrieval are impacted more than motor skills.
Distinguishing between these neurodegenerative conditions is important to determine the best treatment approach. Medications for one of condition might create problems when given to a patient with the other condition.
Medicines For Parkinson’s Disease
Medicines prescribed for Parkinson’s include:
- Drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain
- Drugs that affect other brain chemicals in the body
- Drugs that help control nonmotor symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapysuch as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessnessand reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People with Parkinson’s should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, such as being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
Other medicines used to treat Parkinsons symptoms include:
- Dopamine agonists to mimic the role of dopamine in the brain
- MAO-B inhibitors to slow down an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain
- COMT inhibitors to help break down dopamine
- Amantadine, an old antiviral drug, to reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Also Check: What Can You Do To Help Parkinson’s Disease
Surgical Treatment For Parkinsons
This is advised when the disease progresses and the medications are no longer controlling the symptoms of PD adequately.
- As the disease progresses, Levodopa still works, but the brains response to the medication becomes less predictable. Levodopa may take longer to kick in and may wear off earlier, requiring patients to take medication more frequently during the day. Higher doses of levodopa are associated with abnormal involuntary movements, known as dyskinesias . Unpredictable medication effect results in OFF time when patients feel stiff, rigid, stuck, frozen, slow, or fatigued, compared to ON time when movements are smooth and closer to normal.
- Treatment options as the disease progresses include taking levodopa more frequently; making the medication last longer by adding medications to reduce the metabolism of levodopa, or dopamine adding or changing to long-acting forms of levodopa , or adding or changing to long-acting forms of dopamine agonist . Amantadine can be added to reduce dyskinesia. As these options are being considered and implemented, its time to consider deep brain stimulation surgery .
- Deep brain stimulation surgery is FDA-approved for the treatment of motor complications in Parkinsons disease and is not experimental. DBS is not a last-resort treatment. It has been shown that DBS is more beneficial when performed earlier in the course of the disease compared to waiting for disability.
How Does Parkinsons Affect The Face
Everyday tasks such as getting dressed, writing, picking something up off the floor take twice as long as they used to. Some people describe the feeling of slowness and stiffness as walking through molasses or moving in slow-motion.;Because subconscious muscle movements of the face are responsible for ones facial expressions and others interpretation of our mood, patients can be thought to be upset or depressed when they are not. This is known as having a masked face.
Read Also: How To Tell Difference Between Parkinsons And Essential Tremor
Also Check: Can Stress Cause Parkinson’s
