What Is The Difference Between Tardive Dyskinesia And Dystonia
Tardive dyskinesia refers to uncontrollable mouthing and lip-smacking grimaces that develop following the long-term use of neuroleptics. Dystonia refers to abnormal muscle tone resulting in muscle spasms or abnormal postures.
Tardive dyskinesia is always caused by the long-term use of neuroleptics. However, various factors such as different drugs, neurodegenerative diseases and traumatic damages to central nervous system can cause dystonia. Moreover, dystonias include a variety of movement disorders that occur due to various reasons while tardive dyskinesia is only a subgroup of primary dystonias.
What Is Parkinsonian Tremor
Like dyskinesia, a parkinsonian tremor involves involuntary muscle movements. Unlike dyskinesia, however, a tremor is characterized by regular, rhythmic movements.
A tremor can affect one or more parts of the body, with the most common being a persons hands. In the early stages of Parkinsons, tremor is typically seen on one side of the body often starting in a hand however, as Parkinsons progresses, tremor may impact both sides and affect more body regions.
Typically, Parkinsons tremors, often referred to as a rest tremor, occur when the person is at rest or under emotional or physical stress. During sleep and other relaxed states, and when the affected part of the body is actively moving, tremors often subside.
Regardless of the body parts they affect, tremors can interfere with routine activities such as writing, shaving, getting dressed, tying shoelaces, cutting, and other tasks that require fine motor coordination.
Take Additional Medication For Your Parkinsons Disease
Taking a medication called a dopamine agonist can allow your doctor to reduce your levodopa dosage, which may help ease the symptoms of dyskinesia. However, according to the 2016 review, these drugs can cause similar side effects as those of levodopa for some people and may require you to adjust your dose of levodopa.
Adding amantadine to your treatment regimen may also provide relief of dyskinesia symptoms.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Guidelines 2021
How Is Tardive Dyskinesia Diagnosed
If youre taking a medication that can cause tardive dyskinesia, your healthcare provider will watch for problems.
If symptoms develop, your healthcare provider may recommend certain tests. These tests can rule out other movement disorders like Parkinsons disease.
These tests include:
- Physical exam to assess nervous system functions.
- Blood tests and urinalysis to check for infections, illnesses and other problems.
- Electroencephalogram to measure electrical activity in your brain.
- Electromyography to measure communication between muscles and nerves.
Medications And Supplements Used To Treat Tardive Dyskinesia
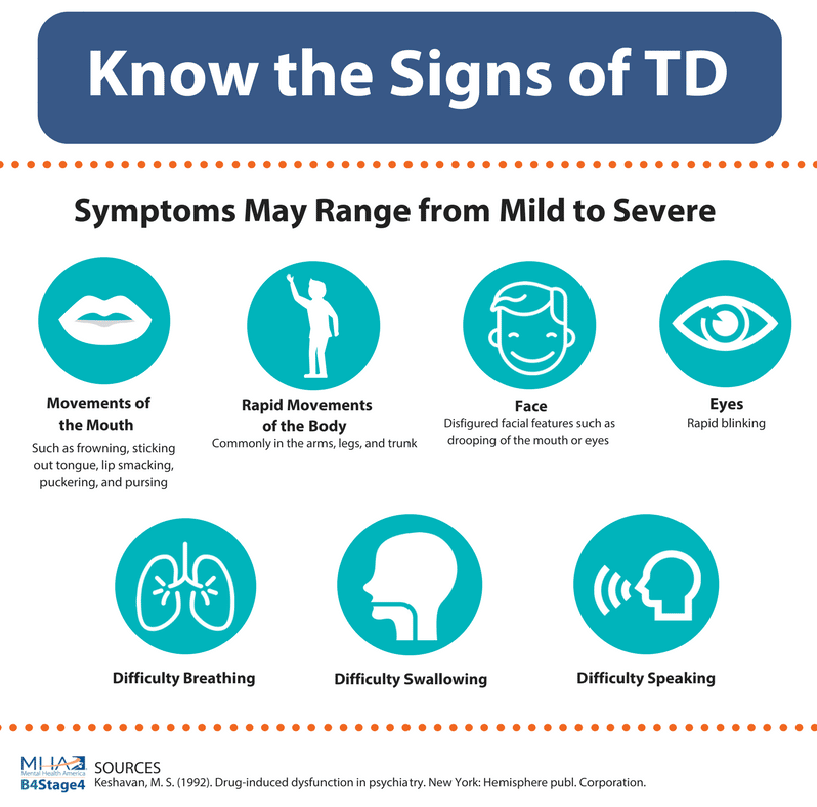
A number of medications and supplements have been identified that ameliorate TD symptoms.
Cholingergic Agents.
Cholinergic agents are used as muscle stimulants to diagnose myasthenia gravis and to treat glaucoma. These agents can also improve the Parkinsonian features of TD. Donepezil, a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, is currently the only cholinergic medication that has shown benefit against TD. Overall, however, cholinergic agents are not a widely accepted treatment for TD as sufficient evidence is lacking to suggest they are more helpful than other treatments.
Clozapine, Quetiapine, Olanzapine, and Apomorphine.
Clozapine, a serotonin and dopamine receptor antagonist, is an atypical APD used to treat schizophrenia. Clozapine is the best current medication recommended for patients who require antipsychotics and simultaneously have TD, as clozapine has been reported to reverse TD symptoms., Clozapine has been linked to TD however, the incidence is much lower compared to other atypical APDs. Drugs with similar mechanisms of action such as quetiapine, a weak striatal dopamine antagonist, and olanzapine, a dopamine and serotonin receptor antagonist, have also been shown to be effective in ameliorating TD symptoms. Apomorphine, a dopamine receptor antagonist, can be given in conjunction with L-DOPA to decrease dyskinesias.
Tetrabenazine Analogs.
Dont Miss: What Age Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Don’t Miss: Meds For Parkinson’s Tremors
Beyond Dopamine: The Role Of Other Neurotransmitters In Parkinsonism And Psychosis
Other neurotransmitter systems are also implicated in PD motor symptoms and drug-induced parkinsonism and may help explain why DIP may occur with medications that do not have direct effects on dopamine levels or receptors. For example, due to the interrelationship between dopaminergic and cholinergic pathways, parkinsonism has been conceptualised as resulting from relative dopamine deficiency and relative acetylcholine excess. This hypothesis is supported by observations that parkinsonism is aggravated by centrally acting cholinergic medications and improved by anticholinergic medications. Gait impairment in PD is pathophysiologically complex and freezing of gait, specifically, may be associated with dysfunction in the noradrenergic and cholinergic systems.
Whats The Main Difference Between Tremor And Dyskinesia
Tremor seen in Parkinsons disease is one of the hallmark features of the condition. Its one of the motor symptoms of Parkinsons that shows improvement with medication.
On the other hand, dyskinesia tends to show up later in the course of the disease as a long-term side effect of medications used to treat Parkinsons. Sometimes it can be a bit hard to tell whether the abnormal movements are tremor or dyskinesia.
Read Also: How Do I Know If I Have Parkinson’s Disease
How Can I Manage Or Stop Drug
Managing drug-induced dyskinesia can be challenging. One effective method is to reduce the dose of medication, particularly levodopa. However, this may cause some of the motor symptoms related to Parkinsons to return.
Newer formulations and methods of delivering medications provide a more sustained release of the drug and help reduce the symptoms of dyskinesia. Sustained release formulations and direct intestinal infusions are examples of such methods.
Newer generations of non-levodopa medications, such as safinamide , a monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, and opicapone , a catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor, have also shown promise in reducing dyskinesia.
Surgery for Parkinsons, such as deep brain stimulation , also results in a reduction of dyskinesia symptoms. This may be because DBS frequently helps to lessen the amount of medication needed for Parkinsons.
You May Like: Is Dizziness A Symptom Of Parkinsons
What Causes Dyskinesia And Dystonia
Dyskinesia is a common side effect of the Parkinsons drug levodopa. This drug is used to help increase the level of dopamine in the brain, alleviating symptoms of the disease. However, levodopa is taken intermittently throughout the day, causing dopamine levels to rise and fall over time. These fluctuations are thought to be the cause of dyskinesia. There are two types of dyskinesia:
- Peak-dose dyskinesia, which occurs when the level of levodopa is at its highest
- Diphasic dyskinesia, which occurs when levels of levodopa are rising or falling
While dystonia can be a symptom of Parkinsons disease itself, it can also be caused by levodopa treatment, similar to dyskinesia. Dystonia symptoms occur when there is a decrease in brain dopamine levels, which can occur before medication is taken in the mornings or as it is wearing off during the day. This off and on dystonia can be addressed by taking an extended-release form of levodopa or by increasing the number of doses taken per day.
Dystonic dyskinesia can occur when the movements caused by levodopa are more sustained and twisting than in typical dyskinesia. When this occurs, it is important to determine the cause whether the movement occurs at peak-dose levels of dopamine or it is off and on dystonia.
Recommended Reading: Spinal Stenosis And Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: When To Start Parkinson’s Medication
Talk To Your Doctor About Continuous Drug Infusion
One way to potentially avoid fluctuations in medication delivery and dopamine levels is through a continuous drug delivery system such as duodenal infusion, in which the medication travels through a tube directly into the intestine. Another option is continuous subcutaneous apomorphine infusion, in which a small device similar to an insulin pump is clipped to the clothing, according to the Parkinsons Foundation. A wire then enters the skin to deliver a steady dose of the medication apomorphine , a dopamine agonist, which may reduce the off periods, when levodopa stops working, and may minimize dyskinesia symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Support Group For Caregivers
What Is Dyskinesia In Parkinsons Disease
Dyskinesia is predominately a side effect of a medication called levodopa thats used to treat Parkinsons disease.
To the trained eye, dyskinesias look quite different , says Herrington. Dyskinesias are not rhythmic they have a more writhing quality.
Herrington points out that you can see an example of dyskinesia if you look at videos of Michael J. Fox. Usually, he says, when is on camera, he has some dyskinesia, or extra movements that are involuntary.
Also Check: Dbs Device For Parkinsons
Read Also: How Many People Have Parkinson’s
How Is Dyskinesia Diagnosed
Parkinsons dyskinesia is most often diagnosed via a physical examination and clinical history review. Movement disorder specialists and neurologists are best equipped to make this diagnosis. To help confirm the diagnosis more objectively, your doctor may also suggest that you video yourself when youre at home or use a wearable device that can detect movements over time.
Impact Of Td In Older People
The impact of TD on an individuals physical, mental, and economic health may intensify with age.3,22 The social and emotional effects of symptoms are highly debilitating for people with TD of all ages, but feelings of isolation and depression may be especially profound for older people.3,16 Older individuals are also uniquely vulnerable to the physical consequences of TD, such as impaired gait and balance, which can lead to falls.16,26 TD in older patients often presents as oro-bucco-lingual dyskinesia, and these movements can interfere with eating and swallowing incidents of choking resulting from respiratory TD have been reported.7,19,46 Further, oro-bucco-lingual TD can cause loosening of natural and artificial teeth and be augmented by edentulousness and denture use edentulousness itself can cause abnormal movements of the mouth in the absence of neurological disorders such as TD.26,46,47 Older patients may also be affected by dyskinesias of the limbs, trunk, and respiratory system, with symptoms such as grunting.7,26,48
You May Like: What Causes Stooped Posture In Parkinson’s
Key Differences Between Tardive Dyskinesia And Parkinson’s Disease
ByJason Bacot | Submitted On April 05, 2011
Tardive dyskinesia and Parkinson’s disease are both movement disorders, and both have causes related to the neurotransmitter chemical called dopamine. Dopamine takes signals from the brain to certain parts of the body, regulating their function. Both diseases can be the result of medication side effects. Though Parkinson’s disease may be congenital , only in extremely rare cases is tardive dyskinesia congenital. Tardive dyskinesia is usually caused by certain drugs.
In the human brain, dopamine works on five types of dopamine receptors. It is produced in several parts of the brain. Though dopamine is available as an intravenous medication, it only acts on the sympathetic nervous system when given as a drug, producing a higher heart rate and increased blood pressure. Dopamine given as a drug, however, cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, and so cannot affect the central nervous system.
Inside the brain, dopamine is associated with the brain’s “reward” system, causing a feeling of enjoyment and increasing motivation. It is released by rewarding experiences like sexual activity, food, drugs, and even normally neutral stimuli that become associated with activation of the brain’s reward system. Drugs like cocaine, amphetamines, and nicotine directly or indirectly cause an increase of dopamine levels in one of the brain’s reward pathways, and this may help explain the addictive nature of these drugs.
Mechanism Of Adverse Medication Reactions
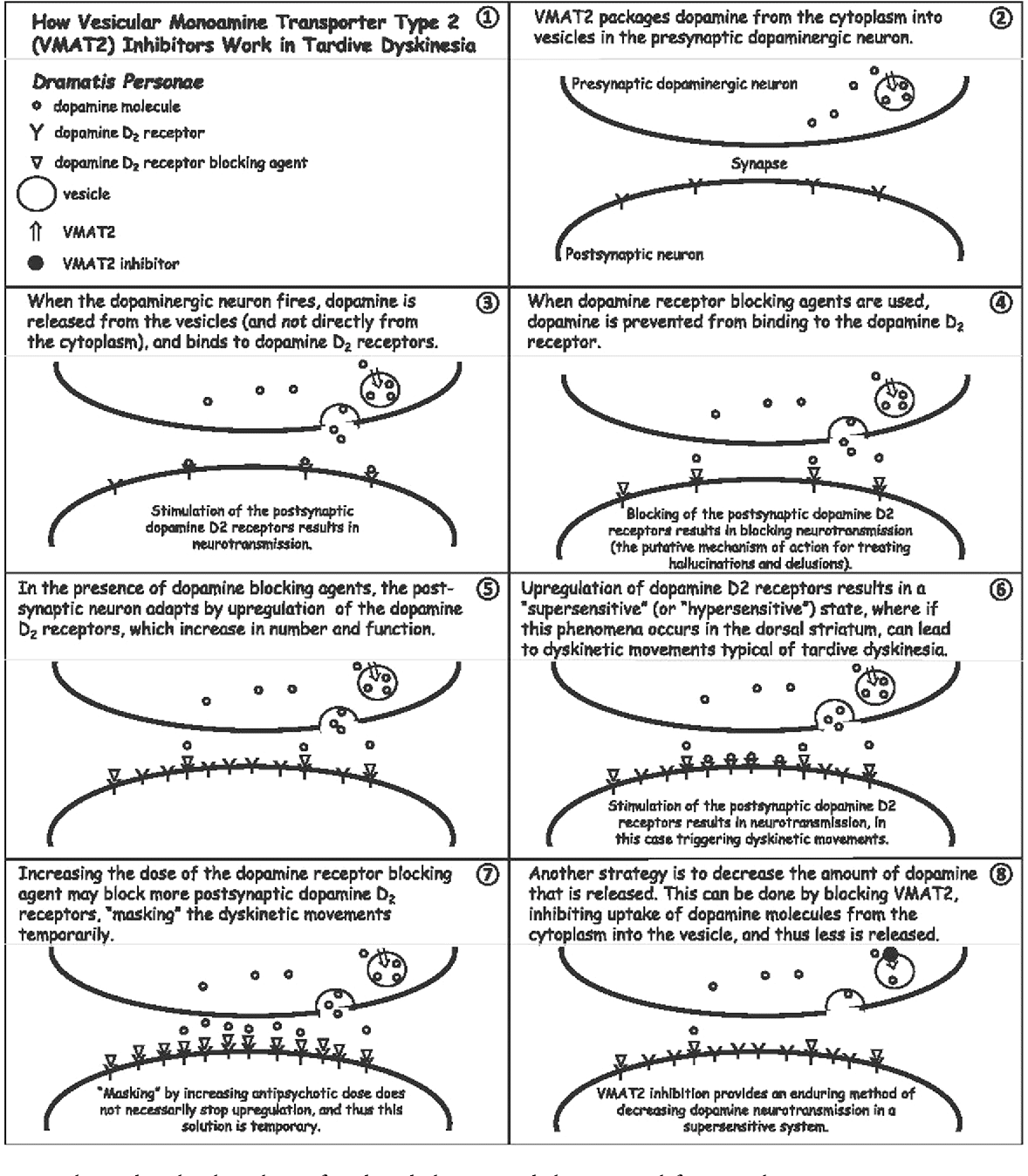
The exact mechanisms of adverse medication reactions that cause TD are not well defined. However, the blockade of dopamine receptors by dopamine antagonists is the most widely accepted theory. Chronic dopamine blockade caused by dopamine D2 receptor antagonists or APDs could result in an upregulation of dopamine receptor responsiveness, resulting in a compensatory supersensitivity of the receptors, especially in the basal ganglia. However, some studies suggest that D3, D4, and D5 receptors are also involved in the pathogenesis of TD., D3 and D5 receptors have a consistent positive correlation with TD, but evaluations of D4 yield inconsistent results.,
Anticholinergic agents are also linked to TD, and taken together with the dopamine receptor supersensitivity hypothesis, an imbalance of dopamine and acetylcholine is likely involved in TD pathogenesis. Evidence also suggests an imbalance of serotonin. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors such as fluoxetine inhibit dopamine neurons in the nigrostriatal pathway by increasing serotonin in the raphe nucleus. SSRIs act by potentiating the inhibitory effects of serotonin on dopamine production in the basal ganglia. This decrease in dopamine production by serotonin could contribute to the pathogenesis of TD.
You May Like: How Did Surgeons Deliver The Stem Cells To Parkinson’s Patients
Subclinical Dopaminergic Deficits In The Ns And Aip Risk Variants
Turning back to schizophrenia patients, an alternative functional explanation for the role of AIP genetic risk variants may be their influence on NS pathway integrity . Dopaminergic deficits in the NS pathway may thus be a predisposing factor for AIP since schizophrenia patients with latent subclinical deficits in NS function would be more susceptible to external blockade of dopaminergic receptor, as happens in AIP . Thus, among AIP patients carrying the risk allele, administration of antipsychotic drugs that block DRD2s might aggravate preexisting, subclinical, pre-synaptic dopaminergic changes.
Integrity of NS tract can be evaluated by neuroimaging methods, including FP-CIT SPECT. The cocaine derivate -FP-CIT is a sensitive marker for degeneration of the NS pathway, due to its binding to the dopamine transporter , a protein localized to pre-synaptic dopaminergic terminals . By implementing this neuroimaging technique to quantify dopaminergic deficits, it is possible to study the effects of AIP risk variants on NS integrity among healthy individuals and PD or schizophrenia patients and thereby link genetic variants to pre-synaptic dopaminergic changes. There is evidence that 3344% of variability in pre-synaptic dopamine uptake in the striatum is influenced by genetic factors .
Dyskinesia Vs Dystonia: Understanding The Difference
- Dyskinesia and dystonia are common motor symptoms that may develop in people with Parkinsons disease and other movement disorders.
- Dyskinesia is a side effect of levodopa, a medication used to treat Parkinsons. Dystonia can be caused by medication, or it may be a symptom of the disease itself.
- Dyskinesia and dystonia can be treated similarly through deep brain stimulation or modifications to medication.
Parkinsons medications like levodopa can cause motor symptoms known as dyskinesia. Another set of motor symptoms, dystonia, can also develop as a side effect of Parkinsons medications, or as a direct symptom of Parkinsons or another movement disorder.
Parkinsons disease is a neurological disorder characterized by a lack of dopamine in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, or chemical messenger, responsible for controlling muscle movements. When dopamine levels are low, signaling is disrupted, leading to the development of movement disorders. Dopaminergic treatments can increase dopamine levels or mimic the chemical to improve symptoms.
Parkinsons disease and other forms of parkinsonism are characterized by abnormal movements, bradykinesia , and myoclonus .
Read Also: Holistic Chiropractic And Parkinsons
Recommended Reading: What Treatment Is There For Parkinson’s Disease
How Are Tremors And Dyskinesia Experienced By Caregivers
People with Parkinsons disease can experience their condition much differently than do their caregivers or spouses. Sometimes being in the off state looks more comfortable to the caregiver because the person is still, and can even seem kind of calm, says Herrington. But for the person with Parkinsons, they experience that off state as very uncomfortable. They may describe it as feeling trapped because they want to move but and they cant.
In this case, he continues, the person might say, Look, I know I have dyskinesia, but I prefer being free to move than feeling stuck and trapped. The caregiver, however, may feel bothered by the increased movement, he says, and think that the person is taking too much medication.
There can be a real disconnect there between what the patient would want and what the caregiver might think is best, says Herrington. Its not always the best thing to try to get rid of every last bit of dyskinesia, because the person might be less comfortable in that state.
Continuous Delivery Of Levodopa
Continuous intraduodenal infusion of the levodopa/carbidopa enteral gel has been used successfully in treating patients with advanced Parkinson disease and shows no increase in dyskinesia as compared to oral polypharmacy. Subcutaneous or intramuscular injections of levodopa methyl ester and intravenous infusion of levodopa have also given similar results., However, limitations of such strategies in clinical practice are obvious.
Read Also: How To Treat Parkinson’s Tremor
Are Tremors Or Dyskinesias Painful
Tremors are almost never painful, says Herrington. And unless the dyskinesias are very severe, they also hardly ever cause pain.
However, Herrington says that when a persons medication wears off, the person can experience a condition called dystonia, which is related to dyskinesia. Dystonia is a potentially painful, cramping condition that can occur in the face, arms, or legs and can be very uncomfortable.
How Can People Manage Parkinsons

When it comes to managing dyskinesia and tremors, its important to strike a balance between too much medication and too little. You can have too much dopamine medication , which can make dyskinesias occur earlier and can make them worse once they start, says Herrington. Then theres the effect of not enough dopamine medication, which can leave people with this off, slow, stiff feeling.
The person and the caregiver and loved ones need to be aware of the necessary trade-offs that are involved, he continues. Only then can you make an informed decision on how best to move forward.
The more people know about the treatment options for Parkinsons, the better off they tend to feel. There may be a situation where a patient feels very uncomfortable in the off state but the spouse is bothered by dyskinesias, Herrington says. I share with that we cant necessarily find the perfect dose that gives your partner relief from the slow, stiff, off symptoms and causes no dyskinesias. For some patients, finding that middle ground is very difficult.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Clinical Trials

