What Is Parkinson’s And How Can Mri Help
More than ten million people are living with Parkinson’s disease worldwide, with about one million cases expected to be in the United States by 2020.1 This is more than the number of people with multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy and Lou Gehrig’s disease combined.1 With the rising prevalence of Parkinson’s disease, its important to understand the signs and symptoms of the disease. Likewise, physicians and radiology departments may need to know what role magnetic resonance imaging may play.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
We do not know what causes Parkinsons disease. There is some evidence to suggest that there is a genetic factor which increases the risk of Parkinsons disease within some families. Also, there might be an increased risk if people have come into contact with a particular toxin or toxins found in the environment via pesticides and other chemicals used in agriculture. The specific toxin or toxins have not yet been identified but there is ongoing research into this possible cause.
Brain Mri Advances For Parkinsons Disease
In Parkinsons disease, the damage to brain cells begins long before any symptoms develop. Therefore, at-risk patients can benefit from early diagnosis, and efforts to slow the progression of the disease can start early.
Researchers are working on newer MRI approaches to precisely detect Parkinsons disease-related structural and metabolic activity in the brain and correlate it to the function of the organ. For example, scientists from Oxford University used a technique called the resting-state functional MRI to assess the strength of nerve cells in the a region of the brain called the basal ganglia to send and receive information. Because the physical signs of brain cell damage in Parkinsons disease are not recognizable by conventional MRI, this approach may help visualize the impact of the damage on the activity of brain cells and aid in early diagnosis.
Similarly, MRI is used to identify Parkinsons disease-specific biomarkers. Tracking the biomarkers using high-field and ultra-high field MRI can identify Parkinsons disease patients and help follow the progression of the condition.
Although many of these advancements are yet to be implemented in the clinical setting, such; adaptations may help better understand the disease and develop new treatments.
Don’t Miss: Bryant Gumbel Health Parkinson
Brain Imaging And Other Tools To Aid Diagnosis Of Parkinsons
In addition to taking a history and performing a detailed neurologic examination, physicians sometimes use brain imaging to help support a particular diagnosis. However, these studies have their limitations in the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease and are typically used only in select patients. Brain imaging is not routinely performed by neurologists or movement disorder specialists when they are considering a diagnosis, especially if the persons symptoms strongly suggest to the physician that idiopathic Parkinsons disease is the correct diagnosis.
Helping diagnose Parkinsons with DaTscan and other tests
Rather, use of imaging is most helpful when the diagnosis is uncertain, or when physicians are looking for changes in the brain that are more typical of one of several Parkinsonian syndromes and other conditions that can mimic Parkinsons. Imaging studies to evaluate Parkinsons disease and Parkinsonian syndromes include magnetic resonance imaging , which examines the structure of the brain, and DaTscan, an imaging test approved by the Food and Drug Administration to detect the dopamine function in the brain. A DaTscan may help differentiate idiopathic Parkinsons disease from certain other neurologic disorders. Most physicians offices will have access to MRI; however, DaTscan imaging may only be available at larger hospitals or medical centers.
What Are The Symptoms
Each person is affected differently by Parkinsons disease and no two people will experience exactly the same symptoms. The impact of Parkinsons disease can be unpredictable and it is common for people to have good days and bad days.
The main symptoms of Parkinsons disease are:
- tremor
- rigidity
- balance problems
- problems with posture
Other possible symptoms include difficulty initiating movement , a shuffling gait when walking, and freezing when trying to move . People might experience a loss of facial expression, speech problems , swallowing problems, bowel and bladder problems, difficulties at night and tiredness during the day. Skin can become greasy and people might experience excessive sweating. Sexual problems are common. People often experience depression and anxiety. Another common symptom is small handwriting .
Other less common symptoms can include pain and memory problems.
Also Check: What Are The Four Cardinal Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Brain Scan Can Spot Early Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
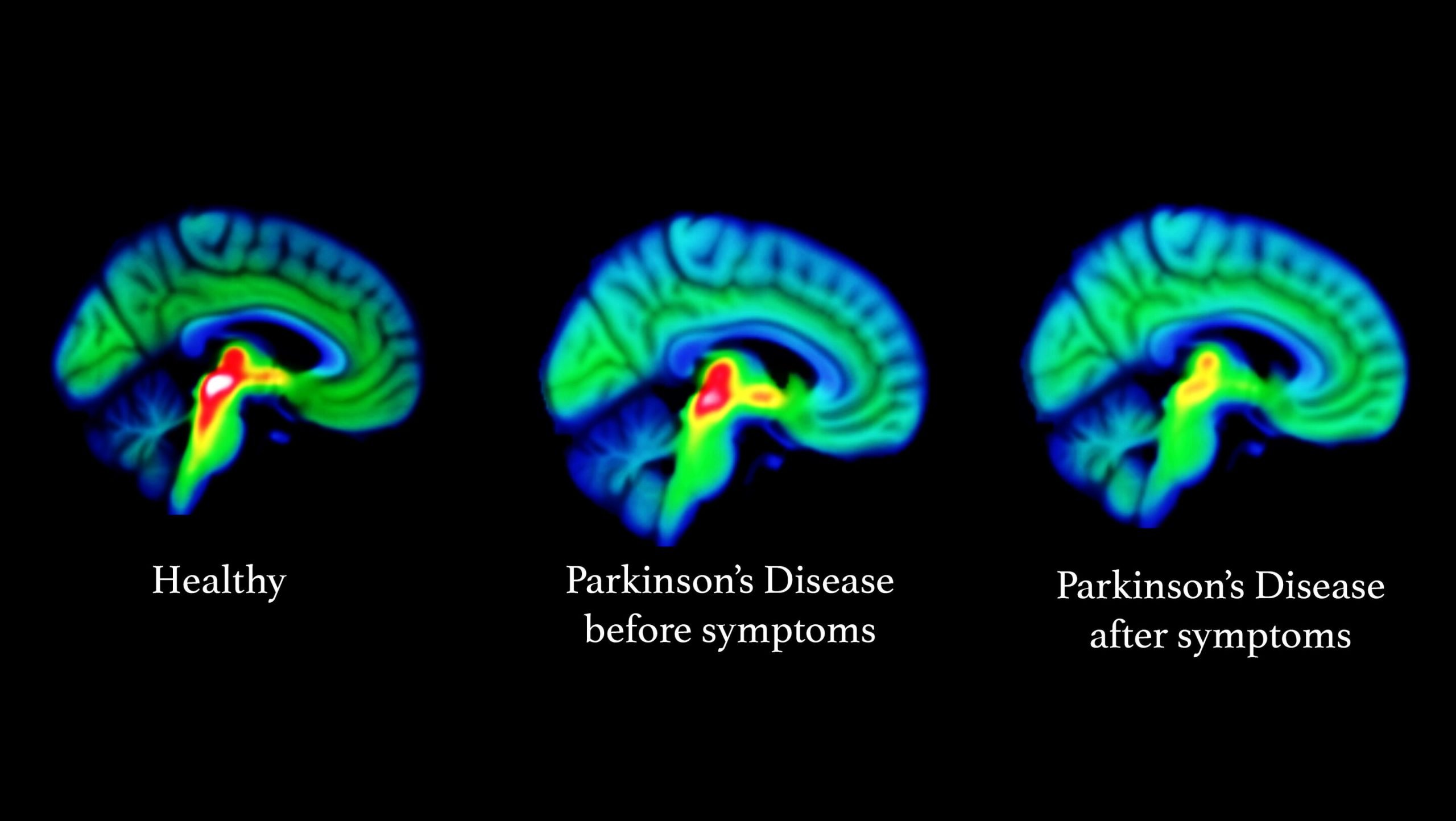
Scientists at Oxford University have discovered that an MRI scan can pick up the very earliest signs of Parkinson’s disease, giving hope that it could be treated before the symptoms start
A brain-scanning technique that detects early signs of Parkinson’s holds out the hope of tackling the disease before it starts to cause symptoms.
Researchers identified patients with early-stage Parkinson’s disease with 85% accuracy using a special type of magnetic resonance imaging scan.
Conventional MRI scans cannot detect early Parkinson’s. The new approach, known as resting state fMRI, involves measuring the connectivity of neurons in the basal ganglia region of the brain.
Lead scientist Dr Clare Mackay, from the department of psychiatry at Oxford University, said: ”At the moment we have no way to predict who is at risk of Parkinson’s disease in the vast majority of cases.
”We are excited that this MRI technique might prove to be a good marker for the earliest signs of Parkinson’s. The results are very promising.”
Around 127,000 people in the UK are believed to have Parkinson’s, an incurable neurodegenerative disease that causes tremors, slow movements and muscle rigidity.
The progressive nerve cell damage produced by the condition is thought to begin long before symptoms appear.
Treatments that slow or halt the disease prior to it taking hold require better ways of identifying those affected.
How A Diagnosis Is Made
The bedside examination by a neurologist remains the first and most important diagnostic tool for Parkinsons disease . Researchers are working to develop a standard biological marker such as a blood test or an imaging scan that is sensitive and specific for Parkinsons disease.
A neurologist will make the diagnosis based on:
- A detailed history of symptoms, medical problems, current and past medications. Certain medical conditions, as well as some medications, can cause symptoms similar to Parkinsons.
- A detailed neurological examination during which a neurologist will ask you to perform tasks to assess the agility of arms and legs, muscle tone, gait and balance, to see if:
- Expression and speech are animated.
- Tremor can be observed in your extremities at rest or in action.
- There is stiffness in extremities or neck.
- You can maintain your balance and examine your posture.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Exclusion Of Alternative Diagnoses
Structural MRI with conventional MR sequences is usually normal in early PD patients limiting its application in clinical routine for the detection of early PD. Recent studies, however, identified imaging correlates of underlying neuropathology in PD patients through advanced MRI techniques. These imaging abnormalities will be discussed in detail later in this review. Nevertheless, cMRI was repetitively shown to be useful in discriminating PD from APDs such as MSA and PSP. Latter are characterized by disease-specific atrophy patterns and signal intensity changes. In addition, current operational diagnostic criteria require the exclusion of symptomatic causes of parkinsonism in the work-up of patients with PD .
Further Testing In Parkinson’s
In other situations, where perhaps the diagnosis is not as clear, younger individuals are affected, or there are atypical symptoms such as tremor affecting both hands or perhaps no tremor at all, further testing may help. For example, imaging can play a role in differentiating between essential tremor and Parkinsons. It can also be important to confirm what is initially a clinical diagnosis of Parkinsons prior to an invasive treatment procedure such as surgical DBS
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Looking For Signs Of Parkinsons
Your specialist will examine you to look for common signs of Parkinsons. You may be asked to:
- write or draw to see if your writing is small or gradually fades
- walk to see whether theres a reduction in the natural swing of your arm or in your stride length and speed
- speak to see if your voice is soft or lacks volume
The specialist will also look at and ask you;about your:
- face to see if there is a masked look or if you have difficulty with facial expressions
- limbs to see if you have a tremor, any stiffness or slowness of movement
As well as examining you for any of the typical signs of Parkinsons, the specialist will also look for signs that may suggest a different diagnosis.
It may be helpful to take someone with you for support when seeing a specialist. Taking a list of questions you want to ask can also be useful so you dont forget to mention something you want to know about. If a healthcare professional says something you dont understand, dont be afraid to ask them to explain what they mean.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
You May Like: Yopd Life Expectancy
Advanced Mri Studies Provide New Insight On Early Parkinson’s Disease
- Date:
- University at Buffalo
- Summary:
- Parkinson’s disease is a degenerative disorder of the brain affecting movement, speech, mood, behavior, thinking and sensation for which there is no known cause or cure. Two new studies shed new light on very early development of the disease.
Parkinson’s disease is a degenerative disorder of the brain affecting movement, speech, mood, behavior, thinking and sensation for which there is no known cause or cure.
Two studies from the University at Buffalo being presented at the 2008 American Academy of Neurology meeting in Chicago shed new light on very early development of the disease.
The work is the result of a joint project by neurology and imaging specialists from UB, Stavanger University Hospital and University of Bergen, both in Norway.
Turi O. Dalaker, M.D., a doctoral fellow from Stavanger University Hospital who conducted the research in the Buffalo Neuroimaging Analysis Center , is first author on both studies. The BNAC, housed in Kaleida Health’s Buffalo General Hospital, is part of the Jacobs Neurological Institute, the Department of Neurology in the UB School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences.
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease result from disintegration of the brain’s white matter, the network of nerves that transport messages to the various brain regions, and grey matter, the brain regions where those messages are received, interpreted and acted upon.
Story Source:
Imaging And Differential Diagnosis

The core clinical signs of PD include resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Most patients also experience nonmotor symptoms such as cognitive and emotional changes , dysautonomia, sleep disorders, and sensory disturbances. Many experience prodromal nonmotor symptoms such as anosmia, depression, constipation, and REM sleep behavior. Clinical subtypes of the disease have been identified, including tremor dominant and postural instability gait difficulty . Atypical features may be clues that there are other etiologies that can be differentiated with imaging studies.1 Structural brain imaging is frequently ordered to investigate these cases. In addition, SPECT imaging with DaT may be useful to confirm central nervous system dopamine signaling deficiency in select cases . On DaT scans, normal radiotracer uptake in the striatum forms 2 crescent-shaped regions of activity, mirrored around the median plane. In contrast, in PD, there is asymmetrically decreased activity in the putamen, often with preserved uptake in the caudate nucleus.2,3 A DaT scan is FDA approved for differentiating essential tremor from PD, and is also frequently useful for differentiating drug-induced parkinsonism from PD.
Cerebrovascular Disease
Corticobasal Degeneration
Multiple System Atrophy
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Neoplasms
Neurotoxicity
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Don’t Miss: Parkinson Disease Dementia Life Expectancy
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a chronic neurological condition. It is progressive and symptoms worsen over time. It is named after Dr James Parkinson who first described the condition in 1817.
People with Parkinsons disease experience a loss of nerve cells in the part of their brains responsible for controlling voluntary movements. This part of the brain is called the substantia nigra . The nerve cells in the substantia nigra usually produce a chemical called dopamine which helps transmit messages from the brain to the rest of the body via the central nervous system . As these cells are lost, people with Parkinsons disease experience a loss of dopamine and the messages controlling movement stop being transmitted efficiently.
Parkinsons disease is more common as people get older but it can affect younger adults. Men tend to be affected in slightly higher numbers than women.
Brain Mri Tracks Parkinsons Progression
All Science News articles summarize a research study and are not an official opinion, endorsement or position of the Parkinsons Foundations.
Researchers at a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence;have found that a brain MRI that uses a special protocol can track changes that occur as Parkinsons disease progresses. This biomarker could be used in clinical trials, as an objective way to monitor whether the therapies being tested are effective. The study appears in the August 2017 issue of;Brain.
Doctors currently diagnose PD based on a persons symptoms slowness, stiffness, tremor and balance difficulties. But these symptoms, and the rate at which they progress, differ from person to person. And there is no blood test, or biomarker, to definitively diagnose PD or objectively monitor underlying biological changes as PD progresses. Currently, a brain MRI may be ordered to rule out other conditions, but cannot diagnose PD or monitor its progression.
In earlier research, scientists led by David Vaillancourt, Ph.D., at the University of Florida in Gainesville a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence, used a brain scanning technique called diffusion MRI to detect changes that happen only in the brains of people with PD. The scans showed an increase in free water water outside of brain cells in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra.
Results
What Does It Mean?
Exclusion Of Symptomatic Parkinsonism
Physical And Neurological Examination
Also Check: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
Mri In Parkinson’s Testing
One of the more common tests done during a neurologic workup is an MRI scan and one may think that in the investigation of a disease that affects the brain such as Parkinsons, this imaging test would be a necessity. In the context of Parkinsons disease, however, an MRI is not particularly helpful. It looks at the structure of the brain which, for all intents and purposes, appears normal in this disease. An MRI may, however, be indicated when symptoms appear in younger people or if the clinical picture or the progression of symptoms is not typical for Parkinsons. In these situations, MRI can be used to rule out other disorders such as;stroke, tumors,;hydrocephalus;, and Wilsons Disease .
Is Early Diagnosis Possible
Experts are becoming more aware of symptoms of Parkinsons that precede physical manifestations. Clues to the disease that sometimes show up before motor symptoms and before a formal diagnosis are called prodromal symptoms. These include the loss of sense of smell, a sleep disturbance called REM behavior disorder, ongoing constipation thats not otherwise explained and mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression.
Research into these and other early symptoms holds promise for even more sensitive testing and diagnosis.
For example, biomarker research is trying to answer the question of who gets Parkinsons disease. Researchers hope that once doctors can predict that a person with very early symptoms will eventually get Parkinsons disease, those patients can be appropriately treated. At the very least, these advances could greatly delay progression.
Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center
Our center provides compassionate and timely treatment to patients with movement disorders, such as dystonia, ataxia, essential tremor and similar conditions. But our mission goes beyond patient care excellence. By offering educational events and support groups, we empower patients and caregivers to become better partners in their health.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
How Parkinsons Disease Is Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease can be complicated because there isnt a specific blood test or screening test that can determine whether or not you have it.
Instead, Parkinsons is diagnosed clinically, which means a doctor will examine you, review your symptoms and medical history, and diagnose accordingly.;
Parkinsons disease is a neurological condition that can make movement difficult. If your general practitioner thinks you might have Parkinsons, they may refer you to a neurologist who specializes in movement disorders for a diagnosis.;
It can be challenging to catch Parkinsons in the early stages because the symptoms may be too mild to notice or meet the diagnostic criteria. Also, early Parkinsons symptoms are often mistaken for typical signs of aging.
The symptoms of Parkinsons disease are also similar to those of other health conditions, which may be misdiagnosed as Parkinsons at first. Your doctor may suggest specific tests and scans to help eliminate other conditions that can mimic the symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Also Check: What Makes Parkinsons Disease Worse
