Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behaviour Disorder
REM sleep behaviour is associated with PD and is a prodromal symptom in many cases. Patients with REM sleep disorder often physically act out vivid dreams during REM sleep, which can affect their quality of life and that of their family and carers. NICE recommends the off-label use of clonazepam or melatonin . Benzodiazepines are cautioned in the elderly population therefore, this patient cohort must be monitored closely by their care team if started on clonazepam.
Parkinsons Disease: Management And Guidance
An overview of Parkinsons disease management, including discussion of the updated National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines.
Nervous system diseases
DR. MICHAEL SOUSSAN/ISM/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Parkinsons disease is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative condition resulting from the loss of the dopamine-containing cells of the substantia nigra, and its prevalence increases with age. Using primary care data from 2015, a Parkinsons UK report of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink found that the prevalence of PD is 45 per 100,000 people who are aged 3039 years, compared with 1,696 per 100,000 people who are aged 8084 years. Prevalence rates almost double at each five-year interval between the ages of 50 and 69 years for both men and women. The lifetime risk of being diagnosed with PD is 2.7% equating to 1 in every 37 people being diagnosed at some point in their lifetime. Owing to population growth and an increasing ageing population, the estimated prevalence of PD is expected to increase by 23.2% by 2025.
Levodopa Usually Is Best First Therapy For Motor Symptoms Neurology Group Says
byJudy George, Senior Staff Writer, MedPage Today November 15, 2021
Neurologists should counsel people with early Parkinson’s disease about the benefits and risks of starting treatment with levodopa, dopamine agonists, or monoamine oxidase B inhibitors for motor symptoms, new guidelines from the American Academy of Neurology stated.
If treatment is started, levodopa is the preferred initial therapy for most early Parkinson’s patients, wrote Tamara Pringsheim, MD, of the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada, and co-authors in Neurology.
“We carefully reviewed the available research on the effectiveness and possible risks of medications to treat motor symptoms in people with early Parkinson’s disease and found that levodopa is usually the best first treatment for these symptoms,” Pringsheim said in an AAN statement.
“Still, there are side effects with levodopa as well as other drugs, so it is important that a person newly diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease discusses all options with their neurologist before deciding on the best treatment plan for them,” she added.
The guidelines update AAN practice parameters from 2002. Since then, new medications and new formulations of older medications have become available, Pringsheim and colleagues noted.
The analysis showed:
- Levodopa was better at reducing motor symptoms than dopamine agonists, with most studies demonstrating significantly greater improvement in UPDRS part III scores for up to 5 years of follow-up
Read Also: What Is Parkinson’s Dementia
Management Of Competing Interests
All guideline panel members agreed to terms of reference that included disclosure of all perceived and actual competing interests to the entire panel at the beginning and end of the guideline development process. Panellists with competing interests were permitted to participate in panel discussions, and later in the voting matrix, without restriction.
Basics Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease , or paralysis agitans, is a common neurodegenerative condition, which typically develops between the ages of 55 and 65 years. This disease was first named and described by James Parkinson in 1817. The progression of this disease is gradual and prolonged. It has a plausible familial incidence, although the estimates of these occurrences are low and usually sporadic. This disease is organized into two classifications: genetic and sporadic. Genetic PD follows Mendelian inheritance. Sporadic PD, which accounts for about 90% of all Parkinsons cases, is a more complex category in which the pathogenic mechanisms that underlie it are not yet fully understood. Nonetheless, it is known that the byzantine interactions of genetic and environmental influences play roles in the determination of sporadic PD. Several subtypes of PD exist. Each has its own set of causative factors and susceptibilities, pathology, and treatment courses. General risk factors, symptoms, and pathology will be discussed first, before addressing some of the subtypes.
You May Like: What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Management Of Parkinsons Disease
Overall treatment is specific to the patient and the symptoms they experience. Symptoms can be variable from day to day or even hour to hour therefore, it is important that patients have a good understanding of their treatment, disease, coping mechanism, support system and regular reviews. Life expectancy can be normal however, more advanced symptoms can lead to increased disability and poor health, which may make someone more vulnerable to complications .
Fractioning The Total Dose Of Levodopa And Dietary Orientation
Due to levodopas short half-life, it is recommended to reduce the interval between levodopa doses, preferably without increasing the total daily dose3838. Freitas ME, Hess CW, Fox SH. Motor complications of dopaminergic medications in Parkinsons disease. Semin Neurol. 2017 Apr 37:147-57. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1602423 . It is also recommended that patients have an interval of at least one hour between the levodopa intake and a meal so that this kind of regimen overcomes the competition with dietary proteins3939. Contin M, Martinelli P. Pharmacokinetics of levodopa. J Neurol. 2010 Nov 257:S253-61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5728-8 ,4040. Barichella M, Marczewska A, De Notaris R, Vairo A, Baldo C, Mauri A, et al. Special low-protein foods ameliorate postprandial off in patients with advanced Parkinsons disease. Mov Disord. 2006 Oct 21:1682-7. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21003 .
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Parkinson’s
Pharmacological Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
There is currently no proven disease-modifying or neuroprotective therapy for PD. A summary of previous neuroprotection trials is given in a recent review article. Current evidence-based treatment for PD is symptomatic and mainly based around dopaminergic replacement or modulation . The evidence base is summarised in recent guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Levodopa, dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors are all licensed for use as initial therapy in PD. Anticholinergics are no longer routinely used due to the risk of cognitive decompensation.
Pharmacological therapies currently used for initial and adjunctive treatment of motor symptoms in Parkinsons disease
Also Check: Parkinsons Age Of Onset
Important Points About The New Medications
With multiple new medications available for the treatment of PD, there is more hope than ever that Parkinsons symptoms can be successfully managed for many years. A few things to consider:
- For people whose symptoms are difficult to control, these new treatments are welcome additions to what was previously available and many people with PD have been using these new medications with significant benefit.
- On the other hand, many of the newly-approved medications have the same mechanisms of action as older medications so they are not breaking new ground in treating symptoms.
- In addition, for some people, the effect on symptoms may be mild or not substantial.
These caveats may mean that your physician has not suggested a medication change for you. It is also important to note that despite all the new medications, carbidopa/levodopa remains the most potent medication to treat the motor symptoms of PD.
If your doctor does choose to try one of the new options, there may be multiple paths that your doctor can take when contemplating a medication adjustment. Often trial and error is the only way to determine the best medication regimen for you, so you may need to practice some patience as you work together with your doctor to determine what works or doesnt work.
Recommended Reading: Are Intention Tremors Common In Parkinson’s
Deep Brain Stimulation For The Treatment Of Pd Patients
Current surgical indications for PD include reducing motor fluctuations, off time, dyskinesias, tremor, and improvement of levodopa-responsive symptoms. Deep brain stimulation is probably the most critical advance in treatment of PD since the introduction of levodopa. The beneficial effects of DBS on motor symptoms and quality of life in advanced PD have been shown in randomized, controlled studies6666. Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Schäfer H, Bötzel K, et al. A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinsons disease. N Engl J Med. 2006 Aug 31 355:896-908. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa060281 ,6767. Williams A, Gill S, Varma T, Jenkinson C, Quinn N, Mitchell R, et al. Deep brain stimulation plus best medical therapy versus best medical therapy alone for advanced Parkinsons disease : a randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Neurol. 2010 Jun 1 9:P581-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-442270093-4 .
Systematic Review: Efficacy And Safety Of Medical Marijuana In Selected Neurologic Disorders
Current systematic review. Endorsed by the American Autonomic Society, the American Epilepsy Society, the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers, the International Organization of Multiple Sclerosis Nurses, and the International Rett Syndrome Foundation. Reaffirmed January 21, 2014, and January 11, 2020.
Also Check: Latest Cure For Parkinsons Disease
Also Check: What Is Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a progressive brain disorder that causes shaking and muscle stiffness, and slows movement. It develops when neurons in a particular part of the brain stop working properly and are lost over time. These neurons produce an important chemical called dopamine. Dopamine is used by the brain to send messages across brain areas to help control movement. Eventually, the brain cannot make enough dopamine to control the movement properly.1,2
Pharmacological Management Of Motor Symptoms
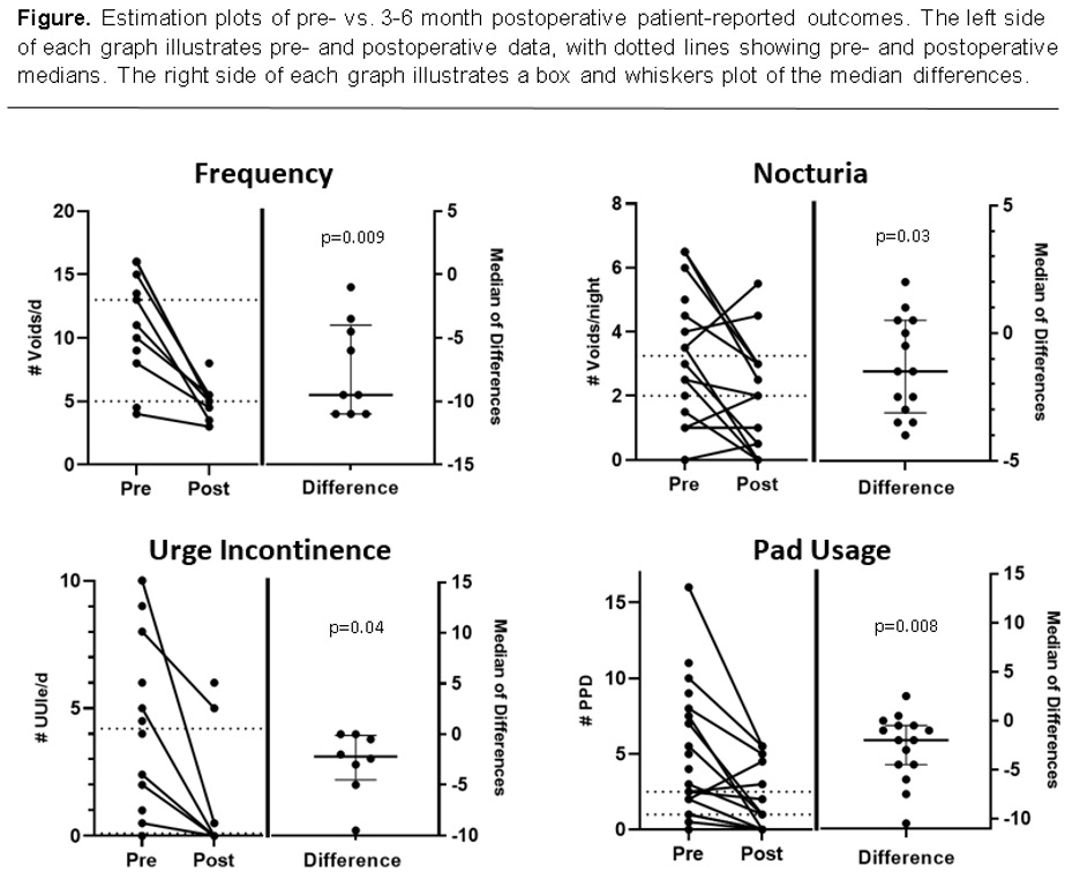
The Parkinsons UK audit identified medicines management as a main area for improvement in PD services, as a third of patients feel that they are not given enough information when starting a new medicine . People with PD have a higher rate of emergency hospital admission than the general population and are also twice as likely to stay in hospital studies suggest that medicines management plays a part in extended lengths of stay.
The inpatient management of PD was previously covered in the learning article Considerations for the inpatient management of Parkinsons disease.
There is no cure for PD and no drug treatments have been proven to impact disease progression. Management is therefore symptomatic. Treatments to manage motor symptoms work by increasing dopaminergic activity. This is broadly achieved by three mechanisms:
Anticholinergics, such as benztropine and trihexyphenidyl, are not routinely prescribed in idiopathic PD but may be introduced for the management of tremor when dopaminergic medications are not effective. However, they should be avoided in the elderly population as they can cause hallucinations and confusion.
Levodopa therapy
Catechol-O-methyl transferase inhibitors
Glutamate antagonists
Dopamine agonists
Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Patients Take Melatonin
Common Drugs For Parkinsons Disease
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
Canadian Guidelines On Pd
The Canadian Guidelines on PD were developed to address the need to provide health care providers who treat individuals with PD with a tool to guide the best management of the disease. The CGPD are the result of a joint effort by specialists in the treatment of movement disorders, family physicians, allied health professionals, individuals diagnosed with PD and patient advocacy groups such as Parkinson Society Canada. The aim of the CGPD is to improve the care for all Canadians who have been diagnosed with PD through the application of
-
best published evidence,
-
patient involvement in the choice of treatment and informed decision-making, and
-
relevance to the Canadian health care system.
A comprehensive description of the guideline development process is provided with the publication of the CGPD in the Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. Since there are other current, high-quality guidelines available for the management of PD, the goal of the CGPD was to review these guidelines to select the recommendations most relevant to the Canadian health care provider.
Recommended Reading: Can Epilepsy Cause Parkinson’s Disease
Occupational Therapy Practice Guidelines For People With Parkinsons Disease
Whitney Henderson, OTD, MOT, OTR/L,Erin R. Foster, PhD, OTD, OTR/L,
Julia Wood, Whitney Henderson, Erin R. Foster Occupational Therapy Practice Guidelines for People With Parkinsons Disease. Am J Occup Ther May/June 2022, Vol. 76, 7603397010. doi:
When To Start Treatment
Deciding when to start drug therapy for Parkinsons disease should be individually tailored to a patients symptoms, circumstances and comorbidities. Treatment is indicated when symptoms impact on quality of life. When treatment is needed there is no evidence to support undue delay because of concerns about levodopa toxicity or the development of treatment resistance.3 The aim is to control symptoms and maintain an on state.
Some drugs with good symptomatic benefit are speculated to have a role in neuroprotection and some specialists advocate their use from the time of diagnosis.4 Delayed start trials have been used to try and differentiate symptomatic from disease-modifying effects. A recent delayed start study of rasagiline, a monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, in treatment-naïve patients with mild Parkinsons disease showed a small benefit in the low-dose treatment group. This was not seen with the 2 mg dose and a clear explanation for this has not been established.5 Further studies are needed before such treatments are considered truly disease modifying. Until a drug is unequivocally proven to slow disease progression, the time to commence treatment will remain contentious.
Dont Miss: On Off Phenomenon In Parkinsons Disease
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Disease Cause Personality Changes
Canadian Guideline For Parkinson Disease
See related article at www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.191089
Parkinson disease is chronic and progressive in nature, decreasing the quality of life for both patients with the disease and their caregivers and placing an onerous economic burden on society.1
The first Canadian guideline on Parkinson disease was published in 2012.2 Since that guideline, there have been substantial advances in the literature on the disease, particularly with respect to diagnostic criteria and treatment options. Parkinson Canada undertook to update the existing guideline to reflect these advances, as well as to add information on palliative care.
Treating Motor Symptoms In Early Parkinson Disease: Aan Releases New Guidelines
The American Academy of Neurology released updated guidelines on the initiation of dopaminergic therapy for the treatment of motor symptoms in patients with early Parkinson disease . A summary of these guidelines was published in Neurology.
During early PD, patients can experience tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and gait and balance impairment. The treatment strategy for these symptoms is to enhance the dopaminergic tone by using dopamine agonists , monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors, and/or levodopa. There are no current disease-modifying pharmacologic treatment options, and these therapies solely aim at symptom management.
In 2002, the AAN released guidelines about treatment of early PD. Since that time, many new therapeutic options have become available, leading the AAN to release 6 updated recommendations. The neurology group reviewed peer-reviewed studies up until June 2020 that focused on patients with early PD and they also assessed the medications prescribed using the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale part III, which measures motor symptoms.
Like levodopa, DAs come in multiple formulations such as short-acting or long-acting and they are also available in various delivery methods, including oral and as transdermal injection. There was little evidence to support the use of a specific
Disclosure: Multiple authors declared affiliations with industry. Please refer to the original article for a full list of disclosures.
Reference
Read Also: What’s The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
Motor Fluctuations And Dyskinesia
For the treatment of motor features of tremor, bradykinesia, and rigidity associated with Parkinsons disease, dopaminergic therapies are initially effective however, motor fluctuations eventually complicate therapy and can cause significant disability and impair quality of life. Sustained-release carbidopa/levodopa and bromocriptine have not been found to reduce off time.
Risk factors for motor complications include disease severity, younger age at onset of Parkinsons disease, high levodopa dosage, and longer disease duration. The motor fluctuations usually are addressed with levodopa adjustments as well as adjunctive medications or surgery as discussed below.
Read Also: What Tests Are Done To Diagnose Parkinsons
