Parkinsons Doesnt Always Cause Dementia
While cognitive decline is common in both Alzheimers and Parkinsons, it is less likely to occur in Parkinsons patients. According to studies, only half of those with Parkinsons develop cognitive difficulties. This can range from mild forgetfulness to full-blown dementia.
When dementia does manifest itself with Parkinson, it occurs in the subcortical area of the brain. Alzheimers dementia occurs in the cortical area of the brain. As a result of this, the clinical symptoms of these two dementias can be somewhat different.
Movement Problems And Lewy Body Dementia
Some people with LBD may not experience significant movement problems for several years. Others may have them early on. At first, movement symptoms, such as a change in handwriting, may be very mild and easily overlooked. Movement problems may include:
- Muscle rigidity or stiffness
What Are The Causes Of Lewy Body Dementia
The precise cause of LBD is unknown, but scientists are learning more about its biology and genetics. For example, we know that an accumulation of Lewy bodies is associated with a loss of certain neurons in the brain that produce two important chemicals that act as messengers between brain cells . One of these messengers, acetylcholine, is important for memory and learning. The other, dopamine, plays an important role in behavior, cognition, movement, motivation, sleep, and mood.
Scientists are also learning about risk factors for LBD. A risk factor is something that may increase the chance of developing a disease. Some risk factors can be controlled while others cannot. Age is considered the greatest risk factor. No specific lifestyle factor has been proven to increase one’s risk for LBD.
Other known risk factors for LBD include certain diseases and health conditions, particularly Parkinson’s disease and REM sleep behavior disorder, which have been linked to a higher risk of LBD.
Having a family member with LBD also may increase a person’s risk, though LBD is not considered a genetic disease. Variants in three genes APOE, SNCA, and GBA have been associated with an increased risk, but in most cases, the cause is unknown.
Recommended Reading: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
If You Live In South Jersey And Have Questions About The Final Stages Of Parkinsons Disease Or Hospice Care For Your Loved One Please Call Samaritan At 229
Samaritan is a member of the National Partnership for Healthcare and Hospice Innovation, a network of not-for-profit hospice and palliative providers across the country. If you know someone outside of our service area who is living with advanced illness and can benefit from hospice or palliative care, please call 1 -GET-NPHI for a referral to a not-for-profit provider in your area.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
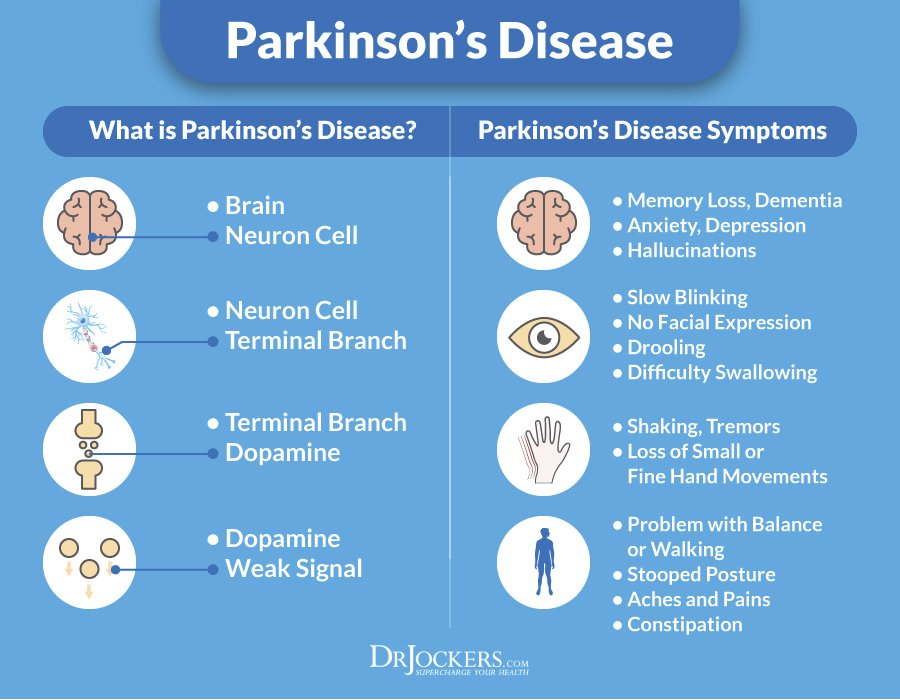
Parkinson disease symptoms usually start out mild, and then progressively get much worse. The first signs are often so subtle that many people don’t seek medical attention at first. These are common symptoms of Parkinson disease:
- Tremors that affect the face and jaw, legs, arms, and hands
- Slow, stiff walking
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Tips For Caring For Someone With Brain Disorder
- Join a community of caregivers to help cope with caregiver burnoutcaregivers
- Personal care: bathing, eating, dressing, toileting, grooming
- Household care: cooking, cleaning, laundry, shopping, finances
- Health care: medication management, physicians appointments, physical therapy
- Emotional care: companionship, meaningful activities, conversation
- Supervision: oversight for safety at home and to prevent wandering
- Make sure the person always carries ID
- Dress your loved one in bright clothing
- Use radio tracking devices
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Dementia And Senility
What Is Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease , the most common form of dementia among older adults, is an irreversible degeneration of the brain that causes disruptions in memory, cognition, personality, and other functions that eventually lead to death from complete brain failure. Genetic and environmental factors including diet, activity, smoking, traumatic brain injury, diabetes, and other medical diseases contribute to the risk of developing this form of the disease. The hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease are the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques between nerve cells in the brain and neurofibrillary tangles, which are twisted fibers found inside the brain’s cells). These tangles consist primarily of a protein called tau.
You May Like: What Color Represents Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment And Care For Lewy Body Dementia
While LBD currently cannot be prevented or cured, some symptoms may respond to treatment for a period of time. An LBD treatment plan may involve medications, physical and other types of therapy, and counseling. A plan to make any home safety updates and identify any equipment can make everyday tasks easier.
A skilled care team often can suggest ways to improve quality of life for both people with LBD and their caregivers.
Severity Of Motor Symptoms
Compared to those without dementia, PDD patients had more severe motor features with a greater impairment in balance. Of the 36 participants, 13 were characterised H & Y stage IV and V, whereas the others were between stages IIII. In particular, of the seven PDD participants, six were characterised by having H & Y stages IV and V.
You May Like: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Living With Parkinson Disease
These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
- An exercise routine can help keep muscles flexible and mobile. Exercise also releases natural brain chemicals that can improve emotional well-being.
- High protein meals can benefit your brain chemistry
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help your ability to care for yourself and communicate with others
- If you or your family has questions about Parkinson disease, want information about treatment, or need to find support, you can contact the American Parkinson Disease Association.
How Parkinsons And Alzheimers Affect The Body And Brain Differently
Alzheimers and Parkinsons are both neurological illnesses. Both diseases are caused by damaged brain cells. Both conditions can involve dementia, as well as depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. Both conditions can lead to psychotic symptoms such as delusions and hallucinations.
While Alzheimers and Parkinsons share certain causes and effects, the two diseases are different. They impact the brain and progress in different ways. Both disorders affect people differently, manifest themselves differently, and progress at different rates.
I had a father with Parkinsons and a mother with dementia. My experience was that the Parkinsons progressed at a slower rate and was more motor-related than mental.
My father experienced tremors, as well as changes in his walking and facial expressions. But his cognitive ability was relatively intact up to the very last stages of the disease. My mothers dementia made her feeble and uncertain on her feet, but she remained active and mobile, even as her cognitive ability declined.
Also Check: Alzheimers Color Ribbon
Read Also: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Coping With Dietary Problems
Many people with Parkinsons experience various eating and dietary problems, such as constipation, chewing and swallowing difficulties, and upset stomach. The following tips can help you minimize the symptoms.
If you suffer from constipation Drink lots of water and eat fiber-rich foods, including beans, brown rice, whole grains, and fruit.
If you have trouble chewing or swallowing food Cut foods into smaller portions to avoid choking and to encourage digestion, and remain upright for 30 minutes after eating.
If youre struggling with fatigueLimit the amount of sugar youre eating. Also avoid alcohol and caffeine, especially before bed, as they can reduce the quality of your sleep.
If you take levodopa Dont eat meat or other protein-rich foods for at least 30-60 minutes after taking levodopa, as protein blocks your bodys ability to absorb the medication.
If your medication gives you an upset stomach Take your medication with a full glass of water and a small non-protein based snack, such as a piece of toast or fruit.
Some Parkinsons disease medications need to be taken promptly at specified times before or after eating, so it can also help to establish a regular routine for meal and medication times.
Signs And Symptoms Of Pdd

Common signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease dementia include:
- Poor memory and concentration
- Depression
- Visual hallucinations
If youve noticed some of the above signs and symptoms in yourself or a loved one, its important to get them checked out. But dont jump to conclusions. People with Parkinsons often experience cognitive changes such as anxiety, lack of motivation, and slowed thinking. These symptoms do not automatically mean dementia.
You May Like: Parkinson Dementia Life Expectancy
Typical Timescale For Pdd
According to the Parkinsons Foundation, PDD is typically diagnosed when a person living with Parkinsons disease experiences cognitive decline after a year or more of motor symptoms. But in most cases, people experience many years of tremors, slowness of movement, and muscle cramps before showing signs of significant cognitive decline. The Weill Institute for Neurosciences estimates the average time from onset of movement problems to developing dementia is 10 years. An estimated 50% to 80% of people with Parkinsons will eventually experience Parkinsons disease dementia, says the Alzheimers Association.
Is There A Test To Diagnose Pd Dementia
There is no single test for PDD. The diagnosis is made clinically. If you or someone you spend time with notices cognitive changes, it is important to discuss them with your care team. If you dont have a care team in place, its important to find a specialist or physician familiar with dementia or geriatric medicine. Call the Parkinson’s Foundation Helpline 1-800-4PD-INFO for a referral.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Happens In Pdd
People with PDD may have trouble focusing, remembering things or making sound judgments. They may develop depression, anxiety or irritability. They may also hallucinate and see people, objects or animals that are not there. Sleep disturbances are common in PDD and can include difficulties with sleep/wake cycle or REM behavior disorder, which involves acting out dreams.
PDD is a disease that changes with time. A person with PDD can live many years with the disease. Research suggests that a person with PDD may live an average of 57 years with the disease, although this can vary from person to person.
What Will Participants Learn
Using a case study example from Cardiff and Vale Health Board’s Parkinson’s dementia service, this course focuses on:
- managing Parkinson’s services, and what that entails
- why set up a new service? Focusing specifically on the reasons why Cardiff and Vale Health board set up a Parkinson’s dementia clinic
- the process of setting up Parkinson’s services – discussions of what needs to change in your practice, focus groups, required resources and planning ahead
- evaluating the success of your new service – has there been an improvement?
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Patient Life Span
Cognitive Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
LBD causes changes in thinking abilities. These changes may include:
- Visual hallucinations, or seeing things that are not present. Visual hallucinations occur in up to 80 percent of people with LBD, often early on. Nonvisual hallucinations, such as hearing or smelling things that are not present, are less common than visual ones but may also occur.
- Unpredictable changes in concentration, attention, alertness, and wakefulness from day to day and sometimes throughout the day. Ideas may be disorganized, unclear, or illogical. These kinds of changes are common in LBD and may help distinguish it from Alzheimer’s disease.
- Severe loss of thinking abilities that interfere with daily activities. Unlike in Alzheimer’s dementia, memory problems may not be evident at first but often arise as LBD progresses. Other changes related to thinking may include poor judgment, confusion about time and place, and difficulty with language and numbers.
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease Dementia
Diagnosis of PDD typically requires the initial diagnosis of PD, with the signs of Parkinsons disease of rest tremor, bradykinesia , rigidity , and postural instability.
At Pacific Movement Disorders Center we regularly monitor patients for cognitive changes which could signal the beginning of dementia, utilizing evidence-based screening tests. If concern arises, detailed neuropsychological evaluation with clear delineation of cognitive strengths and weakness can be obtained. On occasion, volumetric MRI scanning or PET scanning may play a role.
Differentiating between PDD and Dementia with Lewy Bodies can be challenging, given both conditions pertain to dementia and parkinsonism .
Lewy Bodies in PD patients predominate in the deep part of the brain called the substantia nigra, whereas in DLB they are widespread from onset.
The main differentiating factor is the clinical history:
In PDD, parkinsonism comes first, typically years prior to onset of dementia, whereas in DLB, cognitive changes either precede or coincide with onset of parkinsonism.In PDD, there tends to be clear improvement with levodopa for the motor symptoms at least.
For more on differentiating between PDD and DLB, see this comparison table.
Don’t Miss: Hemp Oil And Parkinson’s
What Are Pd Dementia Safety Concerns
Safety issues should be considered and monitored from the time of diagnosis. As PDD progresses, ensure that your loved one is not left alone.
- Evaluate driving privileges before safety is a concern. Your doctor can make a driving evaluation referral.
- Work out legal and financial issues and safeguard finances. People with dementia are at greater risk of falling victim to scams and fraud.
- Minimize prescription risks. Confirm with the doctor the medication names and doses of the person with PD. If the person is in dementias early stages and capable, fill up their weekly pill box together and monitor use.
- Medical alert systems can be critical in case your loved one falls or wanders outside of the home. Many types of systems are available, from bracelets and pendants to smart watches with fall detection and one-button connections to 911.
- Evaluate gun safety. If your loved one owns a firearm or has one in the home, consider speaking with their doctor about the subject and taking appropriate safety precautions.
What Is Parkinsons Disease Dementia

Parkinsons disease dementia is a brain disorder that occurs in somebut not allpeople living with Parkinsons disease. The brain cell damage caused by the disease can lead to a loss of memory and other cognitive functions such as problem solving and speed of thinking. These changes in thinking and behavior can impact your daily living, independence, and relationships.
In those who do develop Parkinsons disease dementia, there is at least one yearand usually 10 to 15 yearsbetween the Parkinsons diagnosis and the onset of dementia. According to estimates by the Alzheimers Association, 50% or more of people with Parkinsons disease eventually experience dementia, although there are a number of risk factors that impact the likelihood of developing symptoms:
- Parkinsons patients who experience hallucinations, excessive daytime sleepiness, and more severe motor control problems are at higher risk for dementia.
- Dementia is more common in people who are older at onset of Parkinsons.
- Dementia is a bigger risk factor in non-tremor predominant Parkinsons.
- Overwhelming stress, cardiovascular disease, and adverse reactions to the Parkinsons disease drug levodopa can also indicate an increased risk for developing dementia.
- Dementia is relatively rare in people who develop Parkinsons before age 50, no matter how long they have had the disease.
Also Check: What Color Represents Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinson’s disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
Differences Between Pdd And Dlb
So, how are PDD and DLB different from each other? That depends on whom you ask. Some clinicians feel that these two conditions are simply different versions of the same disorder. In fact, some professionals use the terms interchangeably. Yet, according to currently agreed-upon diagnostic guidelines, there are some differences.
Also Check: What Color Ribbon Is Alzheimers
You May Like: How Long Can A Person Live With End Stage Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease Dementia
Doctors don’t yet know the exact cause of Parkinson’s disease dementia, but they think it has to do with an accumulation of a protein called alpha-synuclein. When it builds up in the brain, it can create clumps called “Lewy bodies” in nerve cells, causing them to die.
The death of those cells usually results in the motor symptoms typically associated with Parkinson’s disease. As Parkinson’s disease progresses, those Lewy bodies may eventually damage the brain and cause problems with memory and thinking.
While many people with Parkinson’s disease experience cognitive changes, not all of them will go on to develop dementia. It’s estimated that between 50% and 80% of individuals with the disease eventually develop Parkinson’s disease dementia, usually in the later stages of the disease.
What Is Parkinsons
Parkinsons affects brain cells that produce dopamine, an important brain chemical involving nerve cell communication. Dopamine lives in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra, a structure in the middle of the brain that plays a role in reward in movement.
While there can be cognitive issues associated with Parkinsons, there are usually more physical issues. These can include tremors, changes in posture, as well as changes in walking patterns and facial expressions.
Parkinsons disease causes problems with motor coordination, especially initiating movement, consecutive movement, and slowness of movement. The brain circuit controlling rhythm and movement gets derailed by Parkinsons.
Parkinsons symptoms tend to develop slowly over the years. There are five stages of Parkinsons, ranging from mild to more pronounced. Stage One does not interfere dramatically with a persons daily life. In Stage Two, tremors and movement issues become more pronounced.
In Stage Three,or the mid-stage, balance becomes an issue, falls are common, and getting dressed may be a challenge. A person with Stage Four Parkinsons should probably not be living alone, as it becomes difficult to stand and live a fully independent life.
While there is no cure for Parkinsons, it is considered a highly treatable condition. With proper diagnosis early on, many Parkinsons patients continue to lead productive, self-sufficient lives for many years.
Read Also: Sudden Onset Sleep Parkinson’s
