Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Via Datscan And Clinical Exam Are Similarly Accurate
Despite the DaTscan being available to help diagnose Parkinsons, in most clinical situations, a DaTscan will not add information to what can be gleaned from the clinical exam. One study actually demonstrated that the accuracy of diagnosis in early PD was the same whether the diagnosis was reached using clinical exam or using DaTscan.
Whats Hot In Pd An Update On Dat Scanning For Parkinsons Disease Diagnosis
In 2011, the FDA approved a diagnostic test for Parkinsons disease. The DaTscan is a radiopharmaceutical agent which is injected into a patients veins in a procedure referred to as SPECT imaging. DaTscan, when it was approved, was considered an important addition to the armamentarium of the bedside clinician. In 2011 I wrote a Whats Hot column on DAT scanning, and this month I will update that posting and bring everyone up to date on the impact of this test.
The new DaT scans use a substance that tags a part of a neuron in the brain where dopamine attaches to it, thus showing the density of healthy dopamine neurons. Thus, the more of the picture that lights up, the more surviving brain cells. Dark areas could mean either Parkinsons disease or parkinsonism.
Selected References
What Is Essential Tremor And How Is It Different To A Parkinsons Tremor
A tremor is a rhythmical, involuntary movement that affects a part of the body, such as the hand.
Differences Between Parkinsons Disease And Atypical Parkinsonism
Other Tests Used To Diagnose Parkinsons Disease
Diagnosis of PD is generally made using a medical history and a physical exam. In addition to these tests, the patient presenting with Parkinsonian symptoms is usually given treatment with the medication levodopa. The relief of symptoms with levodopa is a sign that symptoms are caused by PD.6
An active area of research is discovering biomarkers, which are molecules in the blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid that can reliably diagnose Parkinsons disease.
There Is No Test To Diagnose Parkinsons Disease
Although Parkinsons disease is a specific, well defined disease that can be reliably diagnosed at autopsy, it is defined in life by clinical criteria. This means that the diagnosis rests entirely on the information that the patient provides plus the physical examination. There is no test to diagnose PD. When a doctor orders a test when evaluating a patient who he thinks has PD, the test is really being obtained to make sure that there isnt some other disorder that might look like PD. When I am convinced that a patient has Parkinsons Disease I order no tests at all. No CAT scan, no MRI, no EEG, no spinal tap, no blood tests. Nothing. The reason is that if any of these tests was to show an abnormality, it would mean to me that the patient had Parkinsons Disease plus some other disorder that has nothing to do with why the patient was seeing me in the first place. Generally Id rather not know.
Why Is A Pet Scan Used In Parkinsons Disease
Mri Brain Scans Detect People With Early Parkinson’s
Oxford University researchers have developed a simple and quick MRI technique that offers promise for early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.
The new MRI approach can detect people who have early-stage Parkinson’s disease with 85% accuracy, according to research published in Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
‘At the moment we have no way to predict who is at risk of Parkinson’s disease in the vast majority of cases,’ says Dr Clare Mackay of the Department of Psychiatry at Oxford University, one of the joint lead researchers. ‘We are excited that this MRI technique might prove to be a good marker for the earliest signs of Parkinson’s. The results are very promising.’
Claire Bale, research communications manager at Parkinson’s UK, which funded the work, explains: ‘This new research takes us one step closer to diagnosing Parkinson’s at a much earlier stage one of the biggest challenges facing research into the condition. By using a new, simple scanning technique the team at Oxford University have been able to study levels of activity in the brain which may suggest that Parkinson’s is present. One person every hour is diagnosed with Parkinson’s in the UK, and we hope that the researchers are able to continue to refine their test so that it can one day be part of clinical practice.’
We think that our MRI test will be relevant for diagnosis of Parkinson’s
Dr Michele Hu
You May Like: Parkinsons Double Vision
Imaging And Differential Diagnosis
The core clinical signs of PD include resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Most patients also experience nonmotor symptoms such as cognitive and emotional changes , dysautonomia, sleep disorders, and sensory disturbances. Many experience prodromal nonmotor symptoms such as anosmia, depression, constipation, and REM sleep behavior. Clinical subtypes of the disease have been identified, including tremor dominant and postural instability gait difficulty . Atypical features may be clues that there are other etiologies that can be differentiated with imaging studies.1 Structural brain imaging is frequently ordered to investigate these cases. In addition, SPECT imaging with DaT may be useful to confirm central nervous system dopamine signaling deficiency in select cases . On DaT scans, normal radiotracer uptake in the striatum forms 2 crescent-shaped regions of activity, mirrored around the median plane. In contrast, in PD, there is asymmetrically decreased activity in the putamen, often with preserved uptake in the caudate nucleus.2,3 A DaT scan is FDA approved for differentiating essential tremor from PD, and is also frequently useful for differentiating drug-induced parkinsonism from PD.
Cerebrovascular Disease
Corticobasal Degeneration
Multiple System Atrophy
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Neoplasms
Neurotoxicity
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
How Can Magnetic Resonance Imaging Help
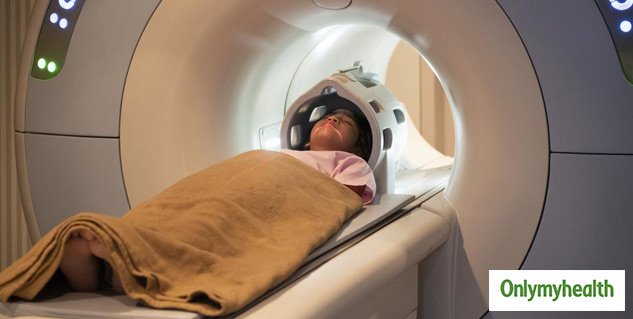
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to monitor a large variety of disorders and diseases throughout the body. the images produced during an MRI scan may show tissue structures and organs in excellent detail. Functional MRI is one technique that can provide information about the body during certain activities. Both conventional and functional MRI may help show the progress of diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, and may show the response to treatments.
Functional MRI may be used to image the brain during movement. Research for Parkinson’s disease has included fMRI to monitor what regions are activated during automatic motion.4 This study of 12 patients with Parkinson’s disease practiced sequences of finger movement until they were able to be done automatically. Then, they underwent fMRI to compare their scans before and after they had learned the sequences. The results showed that the most of the same areas of the brain were active while performing the sequences before or after they became automatic. Subjects without Parkinson’s had significantly reduced activity in the brain after automaticity. This means that patients with Parkinson’s disease had more trouble performing the actions than the people without.
Recommended Reading: End Stage Parkinsons Symptoms
New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.s Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But thats now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
What Tests Diagnose Parkinsons Disease
There currently are no tests that can definitively diagnose Parkinsons Disease. A diagnosis is based on the clinical findings of your physician in combination with your report on the symptoms you are experiencing.??
In situations where an older person presents with the typical features of Parkinsons and they are responsive to dopamine replacement therapy, there is unlikely to be any benefit to further investigation or imaging.
Computed Tomography Scan Ct Or Cat Scan
A diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of x-rays and computer technology to produce cross-sectional images , both horizontally and vertically, of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general x-rays.
Physical And Neurological Examination
These are some of the symptoms of Parkinsons your doctor can determine visually:
Can An Mri Detect Dementia
People who are suspected to have dementia will often ask can an MRI detect dementia.
This is because doctors often use brain scans to identify tumors, strokes, and other problems that might lead to dementia development.
MRI and CT scans are the most common types of brain scans that doctors use when they want to confirm whether a person has a neurodegenerative illness or not.
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication; in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Mri Scans Can Show Dementia
According to researchers from Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, the answer to can an MRI detect dementia is to some extent yes.
The scientists explained that doctors have an easier time telling whether a person has dementia through MRI scans.
This gets rid of the need to carry out invasive tests that people find unfriendly like the lumbar puncture where a doctor must stick a needle in the spine.
Additionally, it also helps to speed up the diagnosis process which is important seeing that dementia diagnosis for the longest time has been a struggle for medics often leading to delayed treatment.
In addition to telling whether a person has dementia, MRI scans may in the future help doctors determine whether an individual is at risk of dementia according to new research.
Research from the University of California San Francisco and the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis conducted a small study where MRI brain scans were able to predict with 89% accuracy the people who were going to develop dementia in three years.
The researchers presented their findings in Chicago during a Radiological Society of North America meeting.
It suggested that in a few years, physicians will be able to tell people their risk of developing dementia before they start to showcase any symptoms of the neurodegenerative illness.
Also Check: What Is Dbs Surgery For Parkinson’s Disease
Amyloid Scan To Detect Alzheimers Plaques
The Amyloid scan uses the tracer Amyvid to detect the brains level of amyloid plaque, an indicator of Alzheimers disease. A negative scan indicates that the symptoms of cognitive decline are caused by something other than Alzheimers, and is useful at ruling out the disease. A positive scan does not necessarily confirm an Alzheimers diagnosis, but it can be quite revealing and helpful in managing treatment.
What Can You Detect With A Parkinsons Mri
Generally, you can receive a Parkinsons diagnosis in a clinical setting, but an MRI can help to assess various aspects of the disease and its progress. In particular, a Parkinsons MRI can do the following for patients who have or are suspected to have Parkinsons disease:
- Evaluate tissue loss and how the brain is atrophying
- Check for changes to the basal ganglia region of the brain
- Find out if there are abnormal iron deposits in the basal ganglia or brainstem
- Look at changes to white matter
- Examine the diffusion of restricted tissues in acute infarction and neurodegenerative diseases
- Help to diagnose atypical parkinsonism
- Exclude treatable causes of parkinsonism such as normal pressure hydrocephalus
How Soon Will I Have My Pet Scan Results
PET scans are usually more extensive and detailed than similar tests that are available. Despite this, test results can usually be given within one to two days after the scan.
Radiology-Info.org: PET Scan and Parkinson Disease.
Neurological Imaging In Lakeland Florida
Brain Scan Can Spot Early Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Scientists at Oxford University have discovered that an MRI scan can pick up the very earliest signs of Parkinson’s disease, giving hope that it could be treated before the symptoms start
A brain-scanning technique that detects early signs of Parkinson’s holds out the hope of tackling the disease before it starts to cause symptoms.
Researchers identified patients with early-stage Parkinson’s disease with 85% accuracy using a special type of magnetic resonance imaging scan.
Conventional MRI scans cannot detect early Parkinson’s. The new approach, known as resting state fMRI, involves measuring the connectivity of neurons in the basal ganglia region of the brain.
Lead scientist Dr Clare Mackay, from the department of psychiatry at Oxford University, said: ”At the moment we have no way to predict who is at risk of Parkinson’s disease in the vast majority of cases.
”We are excited that this MRI technique might prove to be a good marker for the earliest signs of Parkinson’s. The results are very promising.”
Around 127,000 people in the UK are believed to have Parkinson’s, an incurable neurodegenerative disease that causes tremors, slow movements and muscle rigidity.
The progressive nerve cell damage produced by the condition is thought to begin long before symptoms appear.
Treatments that slow or halt the disease prior to it taking hold require better ways of identifying those affected.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Mri Test Used For
MRI scan helps to make a diagnosis for:
- most diseases of the brain
- sports injuries
- musculoskeletal problems
- ear, nose and throat conditions
- soft tissue and bone pathology/conditions
- spinal conditions such as tumours, spinal cord compression and herniated dics, fractures
- vascular abnormalities
- prostate problems
What Is Parkinson’s And How Can Mri Help

More than ten million people are living with Parkinson’s disease worldwide, with about one million cases expected to be in the United States by 2020.1 This is more than the number of people with multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy and Lou Gehrig’s disease combined.1 With the rising prevalence of Parkinson’s disease, its important to understand the signs and symptoms of the disease. Likewise, physicians and radiology departments may need to know what role magnetic resonance imaging may play.
You May Like: Parkinsons And Alzheimers Life Expectancy
Techniques For Visualization And Segmentation Of Brain Regions
MRI sequences for visualization of the basal ganglia and the cortex
The anatomy of the cortex is usually better depicted using conventional three-dimensional T1-weighted sequences which present high grey/white matter contrast.
Segmentation and volume calculation
Small structures such as the SN are usually outlined and segmented manually. Some cortical regions can be segmented manually, but automated techniques are preferred as exploratory tools to detect grey and white matters changes in the cortex . These techniques are designed for group studies, are automated, whole brain and rater independent. They include voxel-based, deformation-based and tensor-based morphometry, cortical thickness and sulci measurements. Voxel-based morphometry is now a standard technique, sensitive to differences in grey and white matter . VBM provides metrics such as the concentration, density and volume of grey matter. A major limitation of VBM is the nonspecificity with respect to the underlying tissue changes. Deformation-based and tensor-based morphometry provide information about global or local differences in shape, respectively . Other software allows measurements of topographic differences in thickness, surface area and curvature of the cortex .
Is The Imaging Metric Appropriate For The Question Being AskedNeuroanatomy Relevant to Parkinsons Disease
Brain Imaging And Other Tools To Aid Diagnosis Of Parkinsons
Helping diagnose Parkinsons with DaTscan and other tests
What Can I Expect On The Day Of The Ct Scan
Please allow at least one hour for your CT scan. Most scans take from 15 to 60 minutes.
Depending on the type of scan you need, a contrast material may be injected intravenously so the radiologist can see the body structures on the CT image.
After the contrast agent is injected, you may feel flushed, or you may have a metallic taste in your mouth. These are common reactions. If you experience shortness of breath or any unusual symptoms, please tell the technologist.
The technologist will help you lie in the correct position on the examining table. The table will then automatically move into place for imaging. It is very important that you lie as still as possible during the entire procedure. Movement could blur the images. You may be asked to hold your breath briefly at intervals when the X-ray images are taken.
After the test is performed the results are reviewed by a radiologist.
Also Check: Parkinsons Life Expectancy
Should I Be Afraid Of Mri Scan
Not at all.
Painless procedure
The MRI scan is a completely painless procedure.;When indicated by the;radiologist, the;operator;injects contrast material into the patients vein. This is also painless due to many years of experience of our technicians.
Patient with claustrophobia
Many patients get nervous and;anxious in the tunnel;during the scan. We would like to make them feel comfortable in our;MRI machine. At;our clinic, our scanner is closed but extremely short and it has a larger diameter than the average.
MRI operator provides you with detailed information
Our highly educated MRI operators always inform you about the whole examination process, including what to expect during the scan, and how long will the test last.
Thanks to our SIEMENS MRI scanner we can work fast and efficiently with the most advanced diagnostic technology.
What Are The Limitations Of The Test
Currently, DaTscan that is in clinical use is not quantitative, which means that the test is not designed to determine how impaired the dopamine system is just whether it is or not. This means that the test is not used to tell you whether the disease has progressed over time and is not used to follow a patients disease. It also is not used currently as a clinical test to screen for the disease before motor symptoms are evident. Because of these limitations, the search continues for additional measurable indicators, known as biomarkers, to help diagnosis and manage PD.
Tips and Takeaways
- DaTscan is a test that can help in the diagnosis of PD, although in most situations a clinical exam done by a neurologist offers the same information.
- Neurologists are skilled to diagnose PD through a clinical exam. While the exam to some may seem very basic and thus a PD diagnosis subjective or questionable, neurologists are well-trained to assess and diagnose with confidence.
- DaTscan may be useful in distinguishing PD from certain conditions, but not from others, so talk with your neurologist about whether DaTscan would be useful in your specific situation.
- DaTscan is not a test used for monitoring PD progression. It can be used to help clarify a PD diagnosis, but it is not a test you would undergo multiple times during the course of your disease.
Do you have a question or issue that you would like Dr. Gilbert to explore?
Dr. Rebecca Gilbert
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Tests
You May Like: Can A Person Die From Parkinson’s Disease
