Dopamine Agonist Withdrawal Syndrome
If you suddenly stop taking dopamine agonists, this can lead to dopamine agonist withdrawal syndrome, which can cause symptoms such as depression, anxiety or pain.
Any withdrawal from Parkinsons drugs needs to be done in a tapered way, under the supervision of a health professional.
Speak to your specialist for advice.
Its Not Just One Condition There Are Multiple Types Of Parkinsons
Like cancer, we are starting to understand the importance of subtyping Parkinsons and developing tailored treatments that will be more successful than a one size fits all approach. Better understanding is coming from large scale studies that follow vast numbers of people with the condition over time. And we are starting to see how the subtypes of Parkinsons have different symptoms, progression rates and even different responses to medication.
To effectively treat Parkinsons, we probably need to tackle each of these subtypes differently, providing the right treatments and support to suit the individual and their form of Parkinsons. And this starts with understanding more about how we classify and identify these different types.
You can read more about research into personalised treatments in our recent blog Precision medicine for Parkinsons, how close are we?
How Far Have We Come
There are only a few examples in history where a single approach has provided a cure for everyone with a condition, and Parkinsons will be no different. It will involve different treatments and therapies at different times for different people. But the multiple pieces of this puzzle are starting to come together, and we are starting to make breakthroughs that could relieve symptoms for the rest of life.
Parkinsons is a progressive neurological condition that affects about 145,000 people in the UK and an estimated 714 million people worldwide. There is currently no cure, and we desperately need better treatments.
You can help us speed up the development of new and better treatments, and a cure for Parkinsons by donating to groundbreaking research today.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Ribbon Color
What Would Happen If I Try To Manage Without Medication For Some Time
Any change to your medication regime must be discussed with your doctor so that you understand how this might affect you.
Parkinsons medication should never be stopped abruptly as this can be dangerous. If both you and your doctor agree to stop any medication, it will be necessary to do so by very gradually reducing the medication dose.
If you agree to do so, it would be useful if you kept a diary to monitor how this was affecting your symptoms. This can help to highlight any changes in symptom pattern, or in your emotions or behaviour that may be related to medication.;
Writing down your own individual experiences on a day-to-day basis can also help you to talk about any changes in your symptoms and your feelings with your doctor. This can be very useful, particularly as appointments are often too short for doctors to ask lots of questions, and your visit may be on a day when your symptoms do not follow their general pattern.
See also;Keeping a diary.
Speech And Occupational Therapy
Parkinsons disease can lead to slurred speech and difficulty swallowing. A speech and language therapist can provide muscle training techniques that may help overcome some of these problems.
An occupational therapist can help identify everyday tasks that can be challenging and work with the person to find practical solutions.
This may include new strategies for dressing, preparing meals, performing household chores, and shopping. Adaptations to the home environment can also make daily living easier.
For people with Parkinsons disease, deep brain stimulation may help manage:
- tremor
- an electrode inside the part of the brain that controls movement
- a pacemaker-like device, or neurostimulator, under the skin in the upper chest
- a wire under the skin connecting the neurostimulator to the electrode
The neurostimulator sends electrical impulses along the wire and into the brain via the electrode. These impulses can prevent symptoms by interfering with the electrical signals that cause them.
There is a small risk of brain hemorrhage, infection, and headaches. Some people may see no improvement, or their symptoms may worsen. There may also be discomfort during stimulation.
Nevertheless, the AAN considers this treatment safe and effective for specific people and say any adverse effects are usually mild and reversible. Anyone considering this treatment should discuss the pros and cons with a healthcare professional.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Awareness Color
Existing Parkinson’s Disease Treatments That Are Effective At Reducing The Disabling Symptoms
By;;|;;Submitted On November 09, 2006
Many researchers have been working hard of finding a cure for Parkinson’s, but despite the best efforts of scientists from around the world, the search still continues. The good news is, however, that there are treatments available that can do a great deal to relieve the pain experienced by many Parkinson’s patients. Not all patients will need drugs or medication for their condition, and generally these are only recommended if the condition is having a detrimental effect on the patient’s lifestyle. Treatment is based on the amount of disruption caused by the patient’s symptoms, how advanced that patient’s condition is, and how severe the condition has become. There’s no guarantee that medication will help reduce the symptoms, although treatment usually does help to make life more comfortable for the patient.
Levodopa is definitely one of the most effective treatments for Parkinson’s disease symptoms. One of the triggers for Parkinson’s is believed to be a substantial reduction in the production of dopamine in the body. Levodopa is obtained from a natural chemical that occurs in animals and plant matter, and it helps the nerve cells to produce more dopamine in the body. This drug is very effective at extending the period for which sufferers can lead normal lives, and in effect stalls the progress of Parkinson’s disease.
An Approach To The Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
No treatment can arrest or slow neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. The aim is to relieve symptoms and avoid the complications of therapy.
Early Parkinson’s disease
Many studies have shown that early treatment with dopamine agonists reduces the incidence of dyskinesia.1Fewer motor fluctuations were shown in some but not all of the studies. We recommend a dopamine agonist as the first treatment in younger patients who have mild disease and no cognitive deficit. It is necessary to add levodopa within 1-5 years in most patients. In more severe disease, treatment begins with levodopa but a dopamine agonist may be added to keep the daily dose of levodopa in the lower range if there is no cognitive deficit. Dopamine agonists are used infrequently and with caution in patients more than 70 years old because of the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse effects and postural hypotension. They are contraindicated in the presence of dementia.
Isolated resting tremor is rarely disabling, but if it interferes with function it can usually be managed with levodopa. When this is ineffective at low to moderate doses, the addition of an anticholinergic can sometimes be useful.
Patients with motor fluctuations
Role of physical therapy and surgery
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Disease Be Fatal
When Is It Best To Start The Parkinsons Drug Levodopa
Earlier treatment with levodopa provides symptomatic relief to those with symptoms but does not appear to slow Parkinsons disease from progressing. Therefore, timing is best determined by symptoms.
The treatment of Parkinsons disease is complex. Levodopa is the main drug used to reduce tremors and muscle stiffness. Whether it modifies the course of the disease or becomes less effective over time is debated, and it can have side effects, so patients and clinicians sometimes prefer to delay starting treatment.
This Dutch trial involved 445 participants with a recent diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, enrolled over five years. About half took levodopa for 80 weeks, and half placebo for the first 40 weeks and levodopa for the last 40 weeks. There was no difference in symptoms between the groups at the end of the study.
This evidence supports current guidance to start levodopa when symptoms begin to affect the quality of life and confirm that it has insufficient impact on disease progression to justify earlier treatment.
What Side Effects Does The Medication Have
The risk of side effects generally depends on the following:
- which medication is being taken
- the dose
- the person’s age and whether they have other diseases
- which other medication the person is on
Dopamine agonists are generally less well tolerated than levodopa. They are more likely to cause side effects such as fluid retention , sleepiness, constipation, dizziness, hallucinations and nausea. People who take dopamine agonists are therefore more likely to stop treatment or not take their medication regularly.
The possible side effects of levodopa include nausea, loss of appetite, dizziness, strong urges, and confusion. At high doses it can also lead to movement problems. Levodopa is usually well tolerated when taken in low doses.
Older people in particular can react to both medications with hallucinations and confusion. Parkinson’s medication can also lead to impulsive, obsessive behavior such as a shopping or gambling addiction, an insatiable hunger or sexual desire, or constantly repeating aimless tasks such as putting objects into a certain order.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Memory Loss With Parkinson’s Disease
What Side Effects Should I Be Aware Of And What Can I Do To Reduce Them
As with any medication, there can be side effects and these may differ from one medication to another. Each persons reaction to a medication is individual and many experience little or no side effects.
Each prescribed medication has an information leaflet that outlines possible side effects and it is very important that this leaflet is read prior to taking the medication. If you have any concerns, please ensure that you discuss these with your doctor, health professional or;pharmacist;as soon as possible so that they can advise or change the medication if necessary.
It is important to follow the instructions you are given for taking each individual medication, as some should be taken in a different way or at a different time of day to another. By following this advice you can minimise side effects. Taking the correct dose, on time, is also very important.
See also Managing medication.
How Does It Work
In people with Parkinsons disease, the brain doesnt produce enough of a neurotransmitter called dopamine. The cells that produce dopamine either die or become impaired. Dopamine is necessary for proper motor control and movement.
Specifically, dopamine transmits signals in the brain that are involved in smooth, purposeful movements like eating, writing, and typing. Like selegeline and rasagaline, safinamide is a type of MAO-B inhibitor, which prevents the;breakdown of dopamine and thus increases its levels in the brain.
Of note, safinamide also modulates glutamate release; however, the specific effect of this action on the drugs therapeutic actions is unknown.
Unlike other MAO-B inhibitors, which can be prescribed alone for those with early-stage Parkinsons disease, safinamide is intended to be used in conjunction with other types of antiparkinson drugs for the later-stage disease, most notably levodopa as well as dopamine agonists.
When people first start treatment for Parkinsons symptoms, drugs tend to work pretty well and symptoms are controlled throughout the day. Between five and 10 years, however, the efficacy of conventional Parkinsons drugs wanes in many people, and symptom control becomes more difficult to alleviate.
Specifically, in people with mid- to late-stage Parkinsons disease, motor fluctuations or involuntary muscle movements begin to crop up.
Read Also: Is Protein Bad For Parkinson’s Disease
Do I Need To Take Medication How And When Should I Take It
In the beginning, a single medication or a combination of different medications can be used with medical treatment being started in low doses and increased gradually. Medication is always individual and can vary greatly between people. Therefore, medical treatment requires follow-up by a physician with a good knowledge of the condition.
Your doctor will be on hand to advise when to take your medication so that it works best for you, for example before, with or after eating, whether you should take with or without protein etc. By working closely with your doctor, you will be able to find the right balance and combination of medications to suit you. It is important that you monitor your response to the medication regularly so that medicine remains as effective as possible;in managing your symptoms. Again, if you are unsure or do not understand everything the doctor has told you, please ask him or her to explain again as it is important for you to follow the advice you are given accurately.
Some people find that combining medication with conventional therapies such as;physiotherapy,;occupational therapy;and;speech and language therapy, as well as surgical treatments or complementary therapies;such as;aromatherapy,;reflexology,;yoga,;tai chi is helpful. But if you are considering these therapies it is always advisable to discuss with your doctor first.;
See also:;
See also Treatments;and Therapies.
Impulsive And Compulsive Behavior
Some people taking dopamine agonists may experience problems with impulsive or compulsive behaviours. For example an increased desire to gamble or engage in sexual activity. These behaviours often develop slowly so may not seem to be a problem immediately. It is important for both the person living with Parkinsons and their family to be aware of this side effect. If affected by this side effect, a reduction in dose or stopping the medication will stop the behaviour.
You May Like: What Disease Is Similar To Parkinson’s Disease
Keep A Medicine And Symptoms Diary
Keeping a diary is a helpful way of monitoring your condition and keeping track of your medicines. A diary can be a useful way of letting your doctor know what problems youre experiencing, any changes in your condition from day to day or over a period of time, and how well your medicine is controlling your symptoms. It can also help remind you of things you want to discuss during your appointment that you may otherwise forget. You can also use it to record any embarrassing issues that you want help with but find difficult to ask about.;Examples of diaries:
Medication Guidelines For Parkinson’s Disease
There is no one best mix of Parkinsonâs medicines. You and your doctor will have to try a few treatment approaches to figure out the best one for you.
But there are some general guidelines for taking your medication. Be sure to ask your doctor or pharmacist for any specific tips for your treatment.
Also Check: What’s The First Sign Of Parkinson’s Disease
Advantages Of Comt Inhibitors
When used with levodopa, COMT inhibitors can reduce the daily off time and increase the on time.
In many cases, the dose and frequency of levodopa can also be reduced.
The terms on/off or motor fluctuations refer to the period when people can no longer rely on the smooth and even symptom control that their drugs once gave them.
Why Was This Study Needed
Approximately 127,000 people in the UK have Parkinsons disease, around two people in every 1,000. It mostly affects adults over the age of 50.
Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurological condition that causes increasing disability. People experience, amongst other problems, muscle stiffness, slow movements and tremors.
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease, but treatment can control symptoms. Levodopa is the main drug used to improve movement. It can cause side effects, such as jerky movements, and might become less effective. Therefore, treatment is sometimes delayed to avoid side effects.
Earlier research has suggested that levodopa might slow down the worsening of the disease itself, as well as relieving symptoms. This study aimed to demonstrate whether this was the case and chart the development of any symptoms over almost 18 months.
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Lead To Dementia
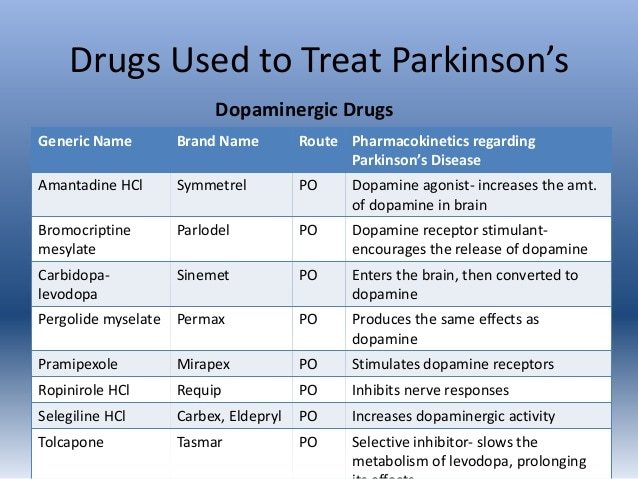
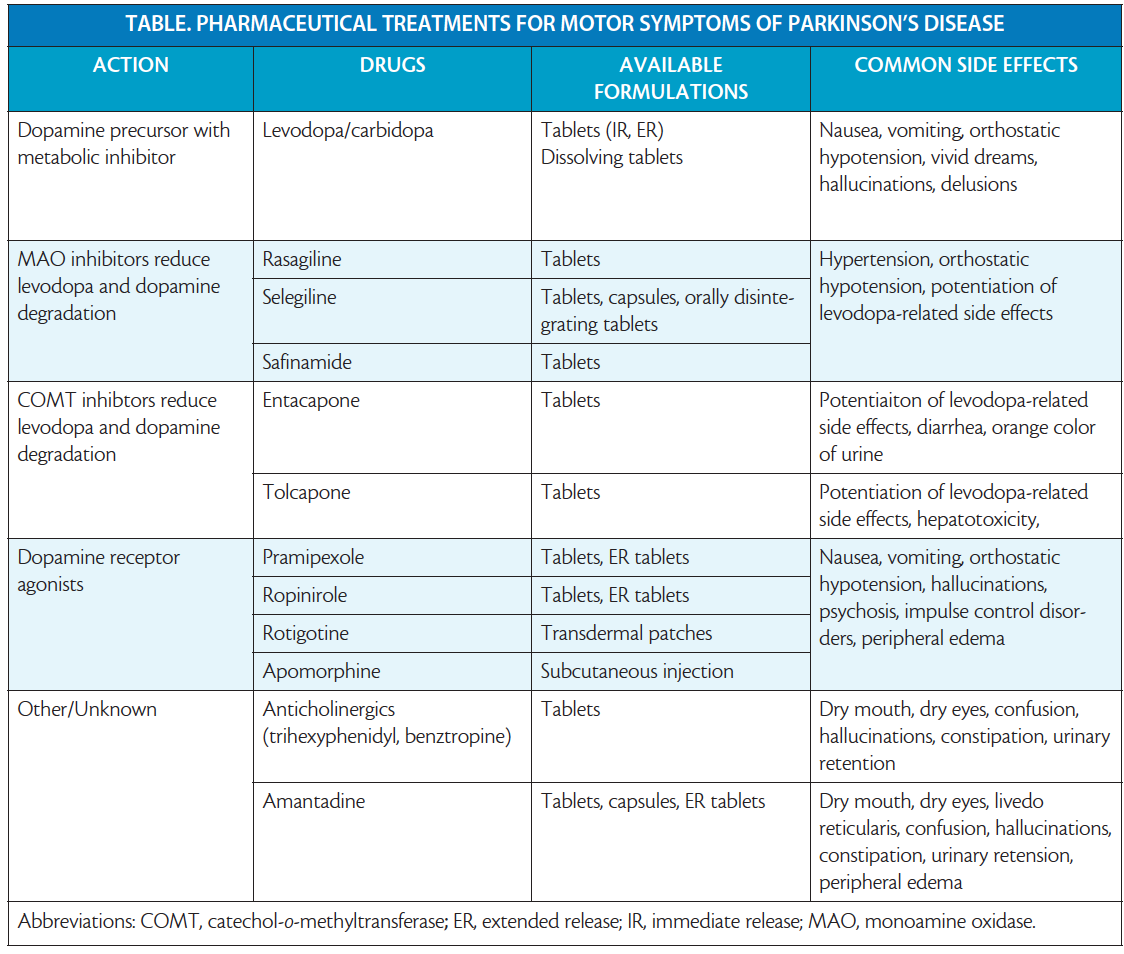
Mechanism Of Action Of Available Drugs
The major classes of drugs currently available for the treatment of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease are shown in Table 1. Many aim to increase dopamine in the brain, by increasing its production or altering its metabolism .
|
Table 1 |
Drugs with alter metabolism in boxed red italics
Levodopa
Levodopa is absorbed from the small intestine and transported into the brain where it is converted to dopamine. Levodopa has a short plasma half-life of about one hour. Early in Parkinson’s disease, levodopa has a long duration of action which is independent of plasma concentration, but as the disease progresses, the duration of the effect reduces. The short-duration effect is strongly linked to plasma concentration and lasts, at most, hours.
Slow-release preparations are gradually absorbed, resulting in more sustained plasma concentrations. They have reduced bioavailability; higher doses are required to match the benefit of an equivalent strength of a standard preparation. Rapid release preparations are taken in liquid form to enhance passage through the stomach and absorption from the small intestine.
Dopamine agonists
Apomorphine is a potent emetic so patients must be pre-treated with domperidone 20 mg three times daily orally for at least 48 hours before the first injection. Domperidone should be continued for at least a few weeks once regular intermittent treatment has commenced. The dose can then be tapered slowly as tolerance to the emetic effects of apomorphine usually develops.
Common Drugs For Parkinson’s Disease
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Diet For Parkinson Disease
