What Future Medications May Be Available For Parkinsons
There are numerous studies investigating new treatments for Parkinsons disease.
There has been new information about the role of autoimmunity and T-cells in the development of Parkinsons disease, possibly opening the door to a role for biologics.
Stem cells are also being investigated as a treatment option for Parkinsons disease.
What New Treatments Are Being Developed
Thanks to the progress we’ve already made, new treatments are being tested in clinical trials that have the potential to slow, stop or even reverse Parkinson’s.
These include:
- stem cell therapies, which aim to use healthy, living cells to replace or repair the damage in the brains of people with Parkinson’s;
- gene therapies, which use the power of genetics to reprogramme cells and change their behaviour to help them stay healthy and work better for longer
- growth factors , which are naturally occurring molecules that support the growth, development and survival of brain cells.
And we’re developing treatments that aim to improve life with the condition, including new drugs that can reduce dyskinesia.
Functional Exercise For Chronic/persistent Pain
There are some simple exercises that you can try around the house to help:
- If you experience pain in your legs, keep them strong by practising standing up and sitting down in a chair.;
- If your shoulders are aching, start by loosening them with some shoulder rolling actions, then by lifting an object that is slightly weighty from a shelf, and then replacing it. This increases the range of movement in your back, shoulders and arms, and then your strength.
Don’t Miss: Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Id Like To See A Specialist Can You Recommend A Doctor Who Specialises In Parkinsons
If you would like to see a specialist or a nurse who specialises in Parkinsons, you should first talk with your doctor. Referral procedures depend;where you live and your doctor will be able to suggest who else you might be able to see.
Remember that a doctor with a special interest in Parkinsons may have a different name, again, depending on which country you live in, for example a;Neurologist, a Movement Disorder Specialist, or a Consultant in the Care of the Elderly with a special interest in Parkinsons.;;
See also: Creating your;healthcare team.
If I Am Unhappy With My Treatment Can I Seek A Second Opinion
Each country has its own agreed process to follow if you are unhappy with your treatment. Who you complain to will depend on which part of your treatment you are unhappy with. If it is not your own doctor you are unhappy with, then it is usually a good idea to talk to them first.
If you are unhappy with your own doctor you may find it helpful to contact a patient advice service or patient liaison organisation. The Parkinsons association in your country should be able to provide contacts and advice – this website contains the contact details for;Our members;and Other Parkinson’s organisations.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson Patient Life Span
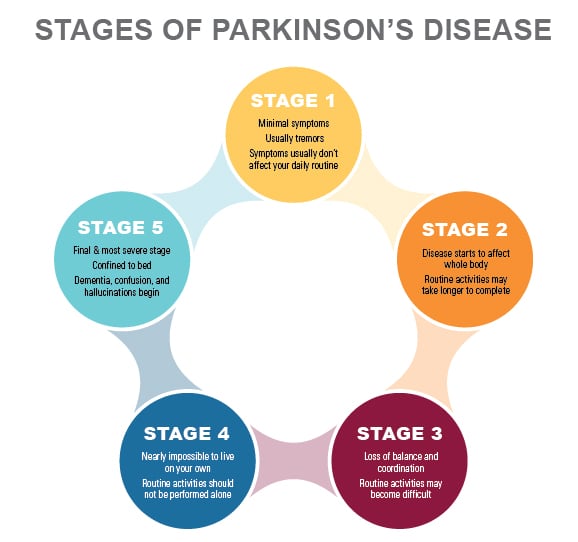
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms; others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes; difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking; urinary problems or constipation; skin problems; and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson’s as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. They may see that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Read Also: What Foods To Avoid With Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Why Isnt There A Greater Awareness Of Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
Its not uncommon for people with Parkinsons disease psychosis to remain silent about their experiences.2,4,9 In fact, only 10% to 20% actually report their symptoms to their physicians.4-9 Work continues to be done to raise awareness of this condition. You can find more information on the non-motor symptoms associated with Parkinsons disease here.
Also Check: What Are The Two Types Of Parkinson’s Disease
New Treatment For Parkinsons Disease
This fall, the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital expects to introduce a previously unavailable form of treatment for Parkinsons disease patients. Although the treatment will be limited to patients who fulfill specific criteria, the treatment has been shown to be effective in Europe, where it has been available for more than a decade.
The treatment involves administering the drug Duodopa directly into the patients small intestine via the stomach through a tube. The drugs dosage is controlled by a mini-pump weighing about half a kilogram that the patient wears at the waist. The body transforms levodopa to dopamine to increase the amount of dopamine in the brain. Parkinsons disease symptoms are linked to dopamine levels. Carbidopa helps to guide levodopa to the brain and also helps to avoid stomach upset and other undesirable side effects of levodopa.
The benefit of the Duodopa treatment is that the patient gets the drug continuously and so avoids the kinds of fluctuations that can come when drugs are taken orally at intervals during the day. Some patients have difficulty swallowing, and with this treatment, theres no need to swallow, says Dr. Anne-Louise Lafontaine, a neurologist and Director at The Neuros Movement Disorder Clinic.
Not all Parkinsons disease patients will qualify for the treatment.
This article was submitted by Neuro staff
- TAGS
When Getting Dressed
- Allow yourself plenty of time to get ready. Avoid rushing.
- Select clothes that are easy to put on and take off.
- Try using items with Velcro instead of buttons.
- Try wearing pants and skirts with elastic waist bands. These may be easier than buttons and zippers.
Yoga uses targeted muscle movement to build muscle, increase mobility, and improve flexibility. People with Parkinsons may notice yoga even helps manage tremors in some affected limbs. Try these 10 yoga poses to help ease symptoms of Parkinsons.
Also Check: Is Dementia Part Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Can I Get Help
First and most importantly, if you find yourself experiencing symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions, speak out. It is essential to talk about your full range of Parkinsons disease symptoms with your treatment team. A dialogue among patients, care partners, and physicians is a critical component of the effective management of your condition.
References: 1. Forsaa EB, Larsen JP, Wentzel-Larsen T, et al. A 12-year population-based study of psychosis in Parkinsons disease. Arch Neurol. 2010;67:996-1001. 2. Ravina B, Marder I Neural Neursurg Psychiatry. 2011;70:734-738. 4. Fenelon G, Mahieux F, Huon M, Ziegler M. Hallucinations in Parkinsons disease: prevalence, phenomenology and risk factors. Brain. 2000;123:733-745. 5. Wolters ECh. PD- related psychosis: pathophysiology with therapeutical strategies. J Neural Transm. 2006;71:31-37. 6. Goldman JG, Holden S. Treatment of psychosis and dementia in Parkinsons disease. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2014;16: 281. 7. Goldman JG, Vaughan C, Goetz CG. An update expert opinion on management and researcl, strategies in Parkinsons disease psychosis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011; 12:2009-2024. 8. Data on file, ACADIA Pharmaceuticals Inc. 9. Fenelon G, Alves G. Epidemiology of psychosis in Parkinsons disease. } Neurol Sci. 2010;289:12-17.
What Are The Side
Some of the patients who were treated with Kappikacchu have shown mild side effects, which include headache, dystonia , fatigue, tremors, syncope and thirst. Other drugs, such as Amantadine, which improves symptoms in about 50% of the patients may cause edema, confusion, and liver reticularis. Side effects of other drugs include confusion, delirium and psychosis.
Also Check: How Can You Prevent Parkinson’s
Natural Treatments For Parkinsons Disease: The Facts
It’s important to note that there is currently no cure for Parkinson’s disease, natural or otherwise. However, many patients find that medication combined with physical exercise and home remedies help them control their symptoms and live well with the condition. No treatment will stop your Parkinson’s disease from progressing. However, homeopathic treatments for Parkinson’s disease have been successful at controlling symptoms in many cases.
Here are the facts surrounding natural and homeopathic treatments for Parkinsons disease:
Natural Homeopathic Treatments For Parkinsons Disease Really
Many people find it hard to believe in natural treatments for Parkinsons disease, and with good reason. If you have been newly diagnosed, you will likely find information on natural, homeopathic treatment for Parkinsons disease all over the Internet. But do these treatments work or are they just a scam? Lets explore the more credible natural treatments for Parkinsons disease while dispelling some of the myths.
Read Also: What Is The Reason For Parkinson’s Disease
Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors
Other PD medications work by inhibiting the enzymes involved in dopamine metabolism, which preserves the levels of endogenous dopamine. One such class is the MAO-B inhibitors. As is discussed above, MAO-B is one of the main enzymes involved in the breakdown of dopamine, and reducing the activity of this enzyme therefore results in increased dopaminergic activity within the striatum, mediated by endogenous dopamine . Their use relieves motor symptoms in PD patients, and as with dopamine agonists they may be used as an initial treatment option, to delay the need for levodopa therapy, to reduce the risk of levodopa-induced motor complications . While they are sometimes sufficient for control of symptoms in early disease, most patients ultimately require levodopa-based treatment. MAO-B inhibitors may also be used in combination with levodopa-based preparations, to allow for a reduction in the levodopa dose.
How Do I Find Out More
Anyone who is considering taking part in research should speak to the professionals managing the project for more in-depth information. Contact details can be found on the project page.
If you have any queries, qualms or concerns please do ask the researchers, they should make your research visit as easy and enjoyable as possible.
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Tremors And Parkinson’s Disease
How Often Will I Be Seen And Will I Need More Tests
It is hard to say how often you should be seen as this will depend on the nature of your symptoms, the rate of their progression and the services available where you live.; If you are concerned about your symptoms, or if they are progressing quickly and you do not have a follow up appointment with another member of the multidisciplinary team for some time, speak with your doctor as they may be able to arrange an earlier appointment for you.
Your doctor will usually monitor the progression of your Parkinson’s by talking to you, observing your symptoms and by physical examination.; You will not usually need to have tests, although in certain circumstances, particularly if your Parkinson’s appears to be worsening quickly, your doctor may decide to run blood or urine tests. Brain scans, such as a;magnetic resonance imaging ;scan, are usually not necessary unless specific complications arise that;do not respond to medication, for example severe;freezing, balance problems or memory difficulties.
Lower Back Pain In People With Parkinsons
In a previous blog, we discussed pain and PD in general and highlighted different types of pain that a person with PD might experience.
PD contributes factors that can cause or worsen lower back pain, such as rigidity of the trunk muscles or dystonia of the trunk muscles. Both rigidity and dystonia can fluctuate with medication timing and correlate with ON and OFF time.
In addition, PD can be associated with central;pain, which is poorly understood and thought to be due to abnormalities in the brain itself. Some new research suggests that PD can change how the brain feels pain that the loss of dopamine can make pain feel worse or make a person more likely to feel pain.
We know that:
- there is a higher prevalence of lower back pain in people with PD vs aged-matched controls
- certain features of PD such as increased age, depression, rigidity, and stooped posture are associated with lower back pain
- lower back pain can make it harder to deal with the challenges of PD because it is associated with lower activity levels. This can breed a vicious cycle in which lower back pain leads to decreased activity levels and then lower activity levels conspire to make the lower back pain worse
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Speech
Q What Is The Pain Experience In Pd And Does It Differ Between Genders
Dr. Fleisher: As with almost everything else in PD, the pain experience is highly individualized, and no 2 people, regardless of gender, will have the same symptoms. Female gender appears to be an independent risk factor for chronic pain in PD, even though PD is more common in men than in women.2 Pain intensity also is higher in women than in men with PD.1
There is a lot of interesting research examining the contributions of hormones to the greater prevalence of PD in men or, conversely, the lower prevalence in women.3 Once we better understand the roles of sex hormones in the pathophysiology of PD, we may better understand whether hormones also play a role in the higher incidence of chronic pain in women with PD.
Read Also: Are There Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Psychosis

Two of the most prominent symptoms are hallucinations and delusions.7 Hallucinations involve seeing, hearing, experiencing or sensing things that are not really there. Delusions are false beliefs that are not based in reality. In describing symptoms of Parkinsons disease psychosis, patients may use such common terms as: seeing things, paranoia, flashbacks, nightmares, false beliefs, or not being in touch with reality.8
Recommended Reading: Why Do Parkinson’s Patients Have Trouble Sleeping
Foods High In Saturated Fat
The role that foods high in saturated fats play in Parkinsons progression is still under investigation and is often conflicting. We might eventually discover that there are certain types of saturated fats that actually help people with Parkinsons.
Some limited research does show that ketogenic, low-protein diets were beneficial for some with Parkinsons. Other research finds high saturated fat intake worsened risk.
But in general, foods that have been fried or heavily processed alter your metabolism, increase blood pressure, and impact your cholesterol. None of those things are good for your body, especially if youre trying to treat Parkinsons.
Medicines For Parkinson’s Disease
Medicines prescribed for Parkinson’s include:
- Drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain
- Drugs that affect other brain chemicals in the body
- Drugs that help control nonmotor symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapysuch as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessnessand reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People with Parkinson’s should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, such as being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
Other medicines used to treat Parkinsons symptoms include:
- Dopamine agonists to mimic the role of dopamine in the brain
- MAO-B inhibitors to slow down an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain
- COMT inhibitors to help break down dopamine
- Amantadine, an old antiviral drug, to reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Also Check: How Was Parkinson’s Disease Discovered
