Risk Factor Assessment For Large And Small Fiber Neuropathy
Patients with EMG abnormalities were older: 65.5±3.8 vs. 53±3 years , but abnormalities on SWT scores were not associated with age. In addition, patients with either SWT or EMG abnormalities were not more likely to be older than normal patients. Patients with EMG abnormalities were more likely to be older at the disease onset but there was no significant relationship between EMG abnormalities and disease duration. In addition, there wasnt any significant relationship between the age of disease onset or disease duration and SWT scores .
Regression analysis of tibial and peroneal CMAP amplitudes and conduction velocities or sural SNAP and conduction velocities versus the presence of DM or B12 levels was not significant. In addition, regression analysis also did not disclose any significant relationship between SWT scores and electrodiagnostic parameters, i.e. tibial and peroneal CMAP amplitudes and conduction velocities or between sural SNAP and conduction velocities.
Stooping Or Hunched Posture
People who have Parkinsons disease may notice changes in their posture due to other symptoms of the disease, such as muscle rigidity.
People naturally stand so that their weight is evenly distributed over their feet. However, people who have Parkinsons disease may start bending forward, making them appear hunched or stooped over.
You May Like: Weighted Silverware
Metabolic Pathways May Be Linked To Peripheral Neuropathy Onset In Parkinsons
This short article summarizes the study, Peripheral Neuropathy in de novo Patients with Parkinsons Disease, published in the Yonsei Medical Journal. Study results demonstrated a potential role of homocysteine and uric acid on peripheral neuropathy in unmedicated patients with Parkinsons. However, further long-term studies with a larger sample size will be needed to confirm the findings.
Don’t Miss: Does Anesthesia Affect Parkinson’s Disease
Median And Ulnar Neuropathy Assessment In Parkinsons Disease Regarding Symptom Severity And Asymmetry
Nilgul Yardimci
1Neurology Department, Minasera Aldan Hospital, Ahmet Taner Kislali Mah. 2741, Street No. 2 Cayyolu, Ankara, Turkey
2Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department, Medical Park Ankara Hospital, Kentkoop Mah., Kentkoop Parkici Yolu, Yenimahalle, Ankara, Turkey
3Biostatistics Department, Medicine Faculty, Hacettepe University, Hacettepe Mah., 06230 Ankara, Turkey
4Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department, Medicine Faculty, Turgut Ozal University, Alparslan Turkes Cad. No. 57, Emek, 06510 Ankara, Turkey
5Neurology Department, Medicine Faculty, Turgut Ozal University, Alparslan Turkes Cad. No. 57, Emek, 06510 Ankara, Turkey
6Neurology Department, Medicine Faculty, Gazi University, Emniyet, Yenimahalle, 06560 Ankara, Turkey
Abstract
1. Introduction
Parkinsons disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, characterised by tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability associated with degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta and the presence of eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions .
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Parkinsons Disease Group
Firstly, the patients were examined for existence of any median or ulnar neuropathy according to the electrophysiologically diagnostic criteria based on control data performed in our laboratory.
2.2. Comparison Group
Read Also: Judy Woodruff Parkinsons
Autonomic Dysfunction And Parkinsons
Autonomic dysfunction often occurs in Parkinsons due to the loss of dopamine-producing cells and the presence of microscopic protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain. As a result, a number of non-motor symptoms may be experienced. Research suggests that the peripheral nervous system may be affected long before such symptoms appear.
If autonomic dysfunction is severe, atypical parkinsonism, such as multiple system atrophy , should be suspected.
Please click on the links below for information on individual symptoms related to ANS dysfunction:
- bladder problems including urgency, frequency, incontinence and night time urination
- constipation and weight loss
- swallowing difficulties .
Scientists now recognise that many medications used to treat Parkinsons can affect the ANS and so make symptoms worse. It is important to monitor your medications and symptoms so that you can discuss these with your doctor. He or she may then be able to adjust medications to reduce the impact on the ANS and so improve symptom control. See Keeping a diary for more information on this and how it can help.
Research suggests that about 90% of people with Parkinsons experience autonomic dysfunction which may considerably reduce quality of life.
You May Like: Does Caffeine Make Parkinson’s Tremors Worse
Things That Really Bother Me About Life With Parkinsons
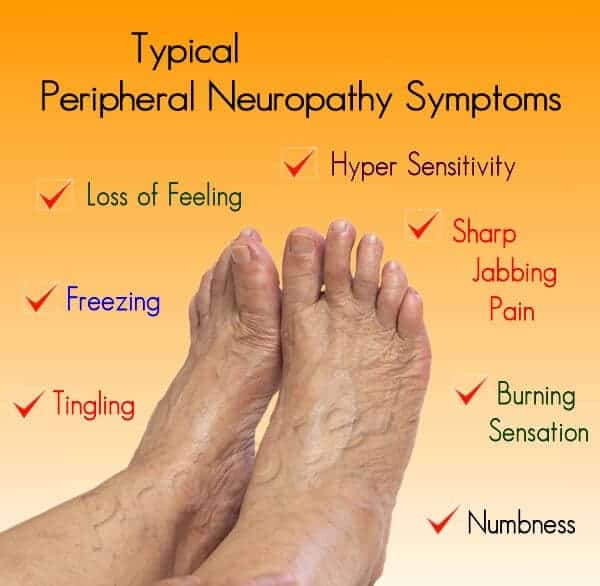
Peripheral neuropathy, or damage to the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, often leads to weakness, numbness, and pain, usually in the hands and feet, resulting in problems with balance and mobility.
While some studies suggest peripheral neuropathy is a feature of Parkinsons, others indicate that the use of levodopa could aggravate neuropathy.
Most of this research used traditional electrophysiological testing methods that can only measure damage to large nerve fibers responsible for detecting vibrations and sensing movement, but not damage to small nerve fibers, which relay information about pain and temperature.
The Neurometer is a more sensitive and non-invasive neurodiagnostic device that evaluates the function of more than 90% of sensory nerve fiber types, including large myelinated fibers, medium-size myelinated fibers, and small unmyelinated fibers. Of note, myelin is a fat-rich material that surrounds nerve fibers to increase the speed of electrical signals.
Researchers at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University in China applied the Neurometer to determine the functional status of each type of peripheral nerve fiber in a group of Parkinsons patients. They investigated both peripheral neuropathy and the potential the impact of levodopa therapy.
A group of 22 age-matched healthy adults was assessed as a control group for comparison. Blood levels of vitamin B12, folic acid, and homocysteine were measured in all participants.
Relation Between Corneal Nerve Parameters Intraepidermal Nerve Fibers And Clinical Features
CNFD correlated positively with IENFD in PD patients . Correlations between CCM parameters, IENFD and clinical data are summarized in Table 2. CNBD and CNFL but not CNFD correlated inversely with UPDRS-III. There was no correlation between any of the corneal nerves parameters and disease duration, cumulative Levodopa dose, non-motor symptoms, pain scales or sensory thresholds. However, there was an inverse correlation between heat-induced pain threshold and SFMPQ . A significant positive correlation was found between DB-HRV and all corneal nerve parameters, but not IENFD . However, IENFD correlated with disease duration, disease severity and cumulative Levodopa dose. Both CNFD and IENFD correlated with NDS. CNFD, IENFD and NDS were independent of vitamin B12, folate, methylmalonate and homocysteine levels.
Also Check: Is Gabapentin Used For Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment Options For Peripheral Neuropathy In Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease Patients
In our initial case series with IPD patients identified to have peripheral neuropathy , all patients identified to have one of cobalamin deficiency, methylmalonic acid elevation, or elevated homocystine levels were prescribed monthly intramuscular injections of 1000 µg of cobalamin . This was provided via intramuscular injections and not oral therapy due to concerns of potential inadequate absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. All patients initialized on therapy were subjected to repeated clinical examinations using the Toronto Clinical Scoring System and electrophysiological evaluations at 6, 12, and 24 months after diagnosis of the peripheral neuropathy when cobalamin therapy was initiated. Repeated blood tests for cobalamin, fasting methylmalonic acid and fasting homocysteine were concurrently performed.
Corneal And Intraepidermal Nerve Fibers
Twenty-six PD patients and 26 controls underwent CCM and 24 PD patients and 10 controls underwent skin biopsies. Both CNFD and IENFD were significantly lower in PD patients compared to controls . However, CNBD was significantly higher in PD patients compared to controls , P< 0.001). CNFL was also significantly higher in PD patients .
Mean ± SEM of corneal nerve fiber density , intraepidermal nerve fiber density , corneal nerve fiber branch density and fiber length in Parkinsons disease compared to controls with significance level and effect size.
Both IENFD and CCM parameters displayed asymmetry between sides in PD patients. However, when CCM measures and IENFD were separated according to the clinically more affected side and the clinically less affected side there was no significant difference in CCM measures or IENFD.
Also Check: Zhichan Capsule
You May Like: What Leads To Parkinson’s Disease
Tackling Neuropathy Fatigue And Gi Issues In Pd
While its known as a movement disorder, people who live with Parkinsons disease experience many non-movement, or non-motor, symptoms too though not all of them are related to the disease. Peripheral neuropathy, or nervous system damage, fatigue and GI issues are common PD challenges that can also stem from other causes. Working with your doctor to identify the source of your symptoms is key to effective treatment.
This article is based on the Parkinsons Foundation Expert Briefing series Symptom Management: Is it PD, Medication or Aging? Exploring Non-motor Symptoms: Neuropathy, Fatigue, GI Issues presented by Ellen Walter, Nurse Practitioner, Cleveland Clinic, and Steven Swank, Clinical Pharmacist, University of Kansas Medical Center. Both organizations are Parkinsons Foundation Centers of Excellence.
Causes of neuropathy, fatigue and impaired gastrointestinal function during the course of PD can be wide-ranging and include everything from normal aging to .
With any health challenge, its recommended to log symptoms. This can help your doctor rule out potential causes. When did symptoms start? Are there any patterns?
Peripheral Neuropathy And Parkinson’s: The Connection
This article briefly explains the peripheral nervous system, peripheral neuropathy , and the research into whether PN is a symptom of Parkinson’s Disease, related to treatment medications, or a combination of the two. References are provided by clicking on ‘View References’ at the end of the article.
Don’t Miss: Does Alcohol Affect Parkinson’s
Peripheral Neuropathy In Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease
| Cognitive dysfunction |
| Arrhythmias and other cardiovascular manifestationsOrthostatic hypotensionUrinary urgency, incontinence or nocturiaGastrointestinal manifestations including constipationThermoregulatory dysfunction including change in sweating function |
| Sleep disorders |
Read Also: Prayers For Parkinsons Disease
What Were The Results

There was a big difference between the groups. In the PD group, 37.8% had a polyneuropathy, compared to 8.1% in the comparison group. Another way of saying this is that if a person had PD, they were 7 times more likely to have a polyneuropathy than if they had another kind of neurologic illness. There was a big difference in the vitamin B12 levels in each group. In people with PD, the average B12 level was 286.8 ng/L compared to 413.2 ng/L in the comparison group.
You May Like: What Year Was Michael J Fox Diagnosed With Parkinson’s Disease
Small Fibre Neuropathy In Parkinsons Disease: Comparison Of Skin Biopsies From The More Affected And Less Affected Sides
Article type: Short Communication
Authors: Jeziorska, Mariaa | Atkinson, Andrewa | Kass-Iliyya, Lewisbc | Kobylecki, Christopherbc | Gosal, Davidb | a | Malik, Rayaz A.ad | Silverdale, Montybc*
Affiliations: Division of Cardiovascular Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK | Department of Neurology, Manchester Centre for Clinical Neurosciences, Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust, Salford, UK | Division of Neuroscience and Experimental Psychology, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK | Weill Cornell Medicine-Qatar, Doha, Qatar
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Monty A. Silverdale, PhD, Department of Neurology, Manchester Centre for Clinical Neurosciences, Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust, Salford, UK. Tel.: +44 1612062574 E-mail: .
Keywords: Parkinsons disease, peripheral neuropathy, intraepidermal nerve fibre
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-191697
Journal: Journal of Parkinsons Disease, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 761-765, 2019
Abstract
The study was approved by NRES committee/North West .
Thirty-three patients fulfilling the UK Brain Bank criteria for the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease were recruited from neurology clinics. Ten patients were excluded after screening for other causes of peripheral neuropathy . Unified Parkinsons disease Rating Scale-III was used to determine the more affected and the less affected side. Specifically, parts 38 and parts 1517 were compared.
Fig.1
What is Neuropathy?
Favorite Resource For Comorbidities
The HNF brings awareness not only to neuropathy but also Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and other inherited neuropathies. CMT is a genetic disorder caused by a gene mutation. The HNF is a great place for family members and caregivers to educate themselves. Check out the blog, newsletter, and webinar, or research upcoming events and clinical trials.
Neuropathy is a common complication of cancer, whether due to the location of your tumor or the treatment, such as chemotherapy, that youve undergone. On Cancer.Net, which is part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology , find essential 101 info on the cancer-related triggers and treatments for nerve damage.
For more on the connection between cancer and nerve damage, check out our article.
Don’t Miss: Vascular Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
Results Of Large Fiber Neuropathy Assessment
NCS/EMG was performed in 39 patients . 12 out of the 26 PD and 4 out of the 13 from the parkinsonism group had abnormal NCS/EMG results. As expected, patients with abnormalities suggestive of peripheral neuropathy on the screening neurological exam were more likely to have abnormal EMG . Neuropathy prevalence was similar in the groups with PD and parkinsonism , whether PN was assessed by SWT, NCS/EMG or clinically .
Fig. 1
Part a shows mean peroneal compound motor action potential amplitudes and mean sural sensory nerve action potential amplitudes in patients with Parkinsons disease . PD all patients refers to mean values from the whole group , PD no PN refers to mean values from PD patients without large fiber neuropathy, PD SFN refers to patients with PD and small fiber neuropathy and PD Neuropathy to mean values in patients with PD and large-fiber neuropathy. Part b shows mean values of peroneal motor and sural sensory conduction velocities in the same groups
Fig. 2
Nerve Conduction Studies Hrus And Diagnosis Criteria Of Pnp
All patients underwent electrophysiological examination performed by a board-certified neurologist with the use of a Medtronic four channel electroneurography device . Motor studies of tibial and median nerve as well as sensory studies of sural and median nerve were done bilaterally maintaining skin temperature at 36°C and were referenced to normal values. Nerve HRUS examination was performed with an Affinity®70G ultrasound system with an 18-MHz linear array transducer as described previously. It was performed bilaterally at entrapment and nonentrapment sites. The entrapment sites included the median nerve , the ulnar nerve , and fibular nerve . The nonentrapment sites contained the median nerve , the ulnar nerve , and the fibular nerve . In order to avert anisotropy, the transducer was kept perpendicular to the nerves and no additional force was applied while the extremities were kept in neutral position to avoid nerve deformation. The measurement of CSA was performed at the inner border of the thin hyperechoic epineural rim by a continuous tracing technique.
The diagnosis criteria for PNP were determined by nerve conduction studies. The lower value of bilateral conduction was regarded to detect early PNP. In order to include and analyze neuropathy groups with different severity in NCS we defined three PNP subgroups based on normal values .
Also Check: Does Dennis Quaid Have Parkinson’s
Clinical Neurophysiological Quantitative Sensory And Autonomic Measures Of Neuropathy
NDS, DB-HRV and sensory thresholds all showed impairment in PD compared to controls . Overall, there was no significant postural drop in blood pressure in PD . Three out of 27 PD patients had large fiber axonal neuropathy on nerve conduction studies and 2 of these patients had raised methylmalonate. However, methylmalonate was raised in a further 4 PD patients with normal nerve conduction studies. Homocysteine was raised in 5 patients all of whom had normal neurophysiology. All patients had normal vitamin B12 and folate levels. Protein electrophoresis was normal in patients with large fiber neuropathy.
Why Does Type 2 Diabetes Cause Your Feet To Go Numb
Neuropathy can lead to complications during surgery as well, explains Highlander. That is because of a condition called Charcot neuropathic osteoarthropathy , in which inflammation and unaddressed injuries subject bones, joints, and soft tissues to microfractures and deformity. This is not the same disorder as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, and it can have many causes, including diabetic neuropathy.
A neuropathic ankle fracture is much higher risk for complications, and so it should be treated differently. If a patient knows they have neuropathy, that should be brought up before surgery, says Highlander.
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Disease Cause Personality Changes
The Peripheral Nervous System And Parkinsons Disease
It is well-established that the autonomic nervous system can be significantly affected in PD causing symptoms such as constipation, urinary dysfunction and orthostatic hypotension. The autonomic nerves that bring signals to the gut for example, can be directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration.
What remains unclear is if motor and sensory nerves are also affected in PD.
The Use Of Levodopa And Peripheral Neuropathy
There are reports in the literature that levodopa use may increase the risk of peripheral neuropathy, although other studies suggest that this is not the case. There are studies that demonstrate for example, that cumulative Levodopa exposure correlates to prevalence of PN in people with PD. Other studies however, demonstrate no difference in the prevalence of PN whether the person was treated with Levodopa or not, suggesting that Levodopa treatment does not play a role in development of PN.
Another area of research that emerges from the literature is the potential role of Vitamin B12 deficiency in the development of PN in those with PD. Some studies suggest that Vitamin B12 deficiency is a more common cause of PN among those with PD than those with PN who do not have PD.
There is also research that suggests that levodopa treatment may contribute to PN through impairment of Vitamin B12 metabolism, leading to Vitamin B12 deficiency. Taking COMT inhibitors such as Entacapone may protect against this complication.
Regardless, if PN is diagnosed in anyone, whether they have PD or not, and whether they take Levodopa or not, Vitamin B12 and various other markers of Vitamin B12 metabolism should be tested. If Vitamin B12 levels are low or even low-normal, a person should take Vitamin B12 supplementation, which may help with the symptoms of PN. Other causes of PN, many of which can be checked with various blood tests, should be investigated as well.
Also Check: Does Restore Gold Work For Parkinson’s
