What Are The Different Forms Of Parkinsonism
There are three main forms of parkinsonism, as well as other related conditions.
Most people with parkinsonism have idiopathic Parkinsons disease, also known as Parkinsons. Idiopathic means the cause is unknown.
The most common symptoms of idiopathic Parkinsons are tremor, rigidity and slowness of movement.
Vascular parkinsonism affects people with restricted blood supply to the brain. Sometimes people who have had a mild stroke may develop this form of parkinsonism.
Common symptoms include problems with memory, sleep, mood and movement.
Some drugs can cause parkinsonism.
Neuroleptic drugs , which block the action of the chemical dopamine in the brain, are thought to be the biggest cause of drug-induced parkinsonism.
The symptoms of drug-induced parkinsonism tend to stay the same only in rare cases do they progress in the way that Parkinsons symptoms do.
Drug-induced parkinsonism only affects a small number of people, and most will recover within months and often within days or weeks of stopping the drug thats causing it.
How Is Parkinson Disease Treated
Parkinson disease can’t be cured. But there are different therapies that can help control symptoms. Many of the medicines used to treat Parkinson disease help to offset the loss of the chemical dopamine in the brain. Most of these medicines help manage symptoms quite successfully.
A procedure called deep brain stimulation may also be used to treat Parkinson disease. It sends electrical impulses into the brain to help control tremors and twitching movements. Some people may need surgery to manage Parkinson disease symptoms. Surgery may involve destroying small areas of brain tissue responsible for the symptoms. However, these surgeries are rarely done since deep brain stimulation is now available.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect a condition that falls under parkinsonism, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
- Blood tests .
- Positron emission tomography scan.
New lab tests forthcoming
There are also new lab tests that, while still experimental or waiting for approval, might be able to help with diagnosing Parkinson’s disease or other conditions like it. These tests look for misfolded or malfunctioning alpha-synuclein proteins in your cerebrospinal fluid or nerves. But more research and testing are necessary before these tests are widely available.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Difference Between Parkinson’s Disease And Multiple Sclerosis
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Forgetfulness
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsonism
The key symptoms of parkinsonism are:
- Slowed movements *.
*This symptom always happens with parkinsonism.
Other possible symptoms include:
- Unstable posture or walking gait.
- Flexed, hunched or stooped posture.
- Freezing .
Condition-specific parkinsonian symptoms
Certain symptoms are more likely with a few conditions involving parkinsonism. Those conditions and the symptoms include:
- Parkinsons disease: In addition to motor symptoms, this condition tends to involve several non-motor symptoms also. Many of these affect the unconscious processes of your body. Examples of this include constipation, loss of sense of smell and sleep problems.
- Vascular parkinsonism: This condition tends to cause early balance and walking problems. It can also cause trouble speaking and swallowing . People with this also tend to have an unusual reflex when the bottom of their foot is touched a certain way .
- Drug-induced parkinsonism: People with this tend to have parkinsonism-type symptoms equally on both sides of their body. With Parkinsons disease, the effects usually are worse on one side.
- Toxin-induced parkinsonism: People with this have more severe “cogwheel rigidity,” which is a jerky pattern to their movements . Their muscles also are tense, causing slowed movements and trouble walking backward.
- Juvenile parkinsonism: Experts usually suspect this type of parkinsonism once they rule out other causes because it is rare for this condition to happen to those under age 45.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s
How Does Vascular Parkinsonism Differ From Parkinsons Disease
Several differences distinguish Parkinsons disease from vascular parkinsonism. Vascular parkinsonism occurs due to small strokes, affecting blood flow to the brain. In addition, Parkinsons disease is progressive, which means it gets worse as time passes. Vascular parkinsonism, however, is not a progressive disease.
Vascular parkinsons is not Parkinsons, one MyParkinsonsTeam member wrote. It only mimics and shows symptoms that are much like Parkinsons. Basically, it is caused by small strokes.
Vascular parkinsonism also differs from Parkinsons disease in the following ways:
- Vascular parkinsonism involves the lower body more often than Parkinsons disease does.
- People with vascular parkinsonism often have worse imbalance and more falls than those with Parkinsons disease.
- Vascular parkinsonism looks similar on both sides of the body more often than Parkinsons disease.
- Spasticity is more common in vascular parkinsonism than in Parkinsons disease.
- Pseudobulbar signs occur more often in vascular parkinsonism.
- People with vascular parkinsonism have bladder incontinence more commonly than those with Parkinsons disease.
- Cognitive impairment is more common in people with vascular parkinsonism.
- Levodopa is much less effective for vascular parkinsonism than for Parkinsons disease. Those with vascular parkinsonism have a positive response to levodopa only about 30 percent of the time.
It Mimics Parkinsons Disease But Is A Very Different Condition
Medically reviewed in November 2020
Former President George H.W. Bush went skydiving to celebrate his 85th birthday in 2009. Less than three years later, his son Jeb revealed that he was confined to a wheelchair .
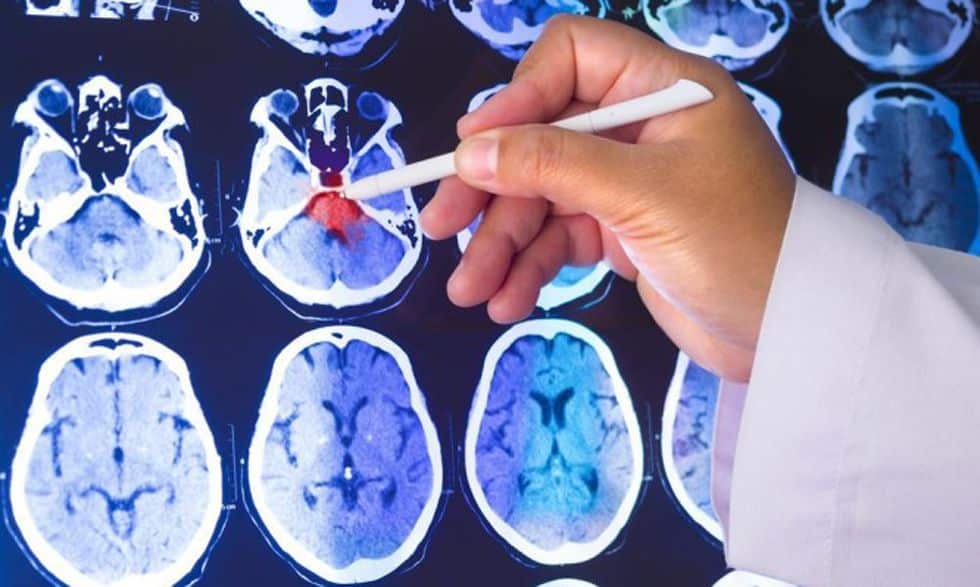
The reason? Aâ¯Parkinsons disease-like condition known as vascular parkinsonism . The movement issues from VP are caused by small strokes in a section of the brain called the basal ganglia, which controls movement, among other functions.â¯
VP versus Parkinsons While the two conditions share a number of symptoms, there are important differences. Parkinsons typically progresses gradually, but becauseâ¯strokes can happen suddenly, VP can appear or worsen suddenly. VP most often affects the lower body. There may be other signs of stroke with VP, such as slurred speech or cognitive impairment, and sometimes incontinence.
Risk factors Because VP is essentially a series of strokes, risk factors for VP are the same asâ¯risk factors for stroke. They include:
Diagnosis and treatment of VP Both Parkinsons and VP can be difficult to diagnose, as there areâ¯no blood testsâ¯for either. However, unlike Parkinsons, evidence of VP can often be detected by an imaging test like a CT scan or MRI. Abnormal brain scans are present in nearly all VP cases, and will often show evidence of multiple small strokes in the basal ganglia.â¯
Image credit: Ytoyoda, Wikimedia Commons
brain-health-nervous-system
article
article
article
article
article
©2022 Sharecare, Inc.
Don’t Miss: What Drugs Can Cause Parkinson’s Symptoms
What Are The Symptoms
VP is often called ‘lower body parkinsonism’ because it affects the legs more than the upper body. People living with VP may experience:4
- Bradykinesia, or slow muscle movements
- Rigid muscles
- Incontinence
Muscle tremors can also occur but these are not as common. While the symptoms usually affect the legs, some people living with VP may also experience these symptoms in their upper body.2
These symptoms may come on suddenly or may take weeks to months to develop. VP is not as progressive as PD but symptoms may also worsen over time in some people with VP.3,4
Whats The Difference Between Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Parkinsons
People with PSP generally progress more rapidly than people with Parkinsons. A person with Parkinsons tends to lean forward while a person with PSP tends to lean backward. Tremors are common in people with Parkinsons and rare in people with PSP. Speech and swallowing abnormalities are more severe and show up sooner in those living with PSP.
For more information on progressive supranuclear palsy, read this fact sheet and insights from the CurePSP organization website.
You May Like: Is There A Test To Diagnose Parkinson’s
Who Does It Affect
Parkinsonism overall is usually an age-related disease. Its slightly more common in people assigned male at birth than in those assigned female at birth. The most common forms of parkinsonism are more likely to happen after age 60.
But some forms can happen at a much earlier age. The average age when juvenile parkinsonism starts is 17. That form of parkinsonism is also four times more common in assigned males than assigned females.
What Are The Symptoms Of Vascular Parkinsonism
Most of the well-known symptoms of PD are also present in vascular Parkinsonism. With vascular Parkinsonism, muscle control challenges are more concentrated in the lower body, whereas with PD, they tend to affect the entire body.
While tremors are common in people with PD, it isnt a key symptom of vascular Parkinsonism. Some people with the vascular condition experience a resting tremor, but this usually occurs later in the course of disease.
The main symptoms of vascular Parkinsonism include:
Don’t Miss: What Are The Early Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Is The Difference Between Parkinsons Disease And Parkinsonism
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that leads to movement symptoms and non-movement symptoms. It is sometimes called idiopathic , but the cause is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Parkinsonism is a more general term that encompasses the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. A variety of disorders or syndromes can lead to Parkinsonism, and these syndromes can lead to faster progression of symptoms, increased falling, presence of hallucinations, and can be non-responsive to levodopa .
The majority of people with the symptoms of Parkinsons disease will be diagnosed with idiopathic Parkinsons disease. Between 10% to 15% of these people will be diagnosed with Parkinsonism that is caused by something else.
Living With Parkinson Disease
![Neural Stem Cell Therapy for Parkinsonâs Disease [PD]](https://www.parkinsonsinfoclub.com/wp-content/uploads/neural-stem-cell-therapy-for-parkinsonatms-disease-pd.jpeg)
These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
- An exercise routine can help keep muscles flexible and mobile. Exercise also releases natural brain chemicals that can improve emotional well-being.
- High protein meals can benefit your brain chemistry
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help your ability to care for yourself and communicate with others
- If you or your family has questions about Parkinson disease, want information about treatment, or need to find support, you can contact the American Parkinson Disease Association.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Side Effects Of Parkinson’s Medication
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
If you have parkinsonism, it’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance on caring for yourself and managing this condition. They are the best source of information about how your specific condition will affect you and what you can do to help yourself.
In general, you should do the following:
- Take your medication as prescribed. Taking your medications if your provider prescribes any can make a huge difference in the symptoms of parkinsonism. You should also talk to your provider if you notice side effects or start to feel like your medications aren’t as effective.
- See your provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help manage your conditions, find the right medications and dosages, and minimize any side effects.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Parkinsonism can cause a wide range of symptoms, many of which are treatable by treating the condition or the symptoms themselves. It’s also important to tell your provider about symptoms, even minor ones. Many parkinsonism conditions are easily mistaken for others, so telling your provider about all your symptoms can sometimes help avoid an incorrect diagnosis.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease symptoms usually start out mild, and then progressively get much worse. The first signs are often so subtle that many people don’t seek medical attention at first. These are common symptoms of Parkinson disease:
- Tremors that affect the face and jaw, legs, arms, and hands
- Slow, stiff walking
Don’t Miss: Can Drugs Cause Parkinson’s Disease
Multiple System Atrophy Formerly Called Shy
As predicted by the name of this parkinsonism, multiple system atrophy affects multiple systems of the body. It affects both the motor skills movement system and the involuntary system of the body. Though the symptoms can often be treated with medications, there is no cure. In addition, there are no drugs that are able to slow the progress of MSA.
Imaging Of Striatal Dopamine Transporters In Vp
Several studies looked at dopamine transporters in VP using -CIT single-photon emission computed tomography and FP-CIT SPECT. Gerschlager et al. reported preserved or mild reduction in the striatal -CIT and putamen/caudate ratio in 13 patients with VP when compared to 20 PD cases. On the other hand, Zijlmans et al. found that the mean striatal FP-CIT uptake was significantly lower in 13 VP patients than in healthy controls. When compared with the PD group, only the mean asymmetry index was significantly lower in VP patients. They suggested that in the majority of VP patients, the pre-synaptic dopaminergic function is reduced and they proposed using the asymmetry index as a criterion for the clinical diagnosis of VP.
Lorberboym et al. studied 20 patients who developed VP in the course of cerebrovascular disease with FP-CIT SPECT and 20 healthy controls. Nine patients had normal striatal FP-CIT binding similar to that of controls. In contrast, 11 patients had significantly diminished striatal binding when compared with controls.
It is therefore difficult to reach any firm conclusion from available studies about the role of dopamine transporter imaging in VP. The lack of uniform clinical diagnostic criteria clearly contributes to difficulties of interpretation of the results, some of which are conflicting. Further research is needed.
Read Also: Can Antidepressants Cause Parkinson’s
How Can I Prevent This Condition Or Reduce My Risk Of Developing It
Parkinsonism happens unpredictably in most cases, so it’s usually impossible to prevent it or reduce your risk of developing it. However, there are specific types of secondary parkinsonism that you can reduce the risk of developing. These are:
- Toxin-induced parkinsonism. Its possible to reduce your risk of developing this type of parkinsonism by avoiding toxins or substances that can cause it or by using safety equipment to reduce your exposure to these substances when you cant avoid them.
- Post-traumatic parkinsonism. You can reduce your risk of developing this by using safety equipment to protect yourself from head injuries.
- Vascular parkinsonism. Reducing your risk of developing this involves taking care of your circulatory health, especially the circulation in your brain. Managing this involves maintaining a weight that’s healthy for you, eating a balanced diet and staying physically active.
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing vascular Parkinsonism starts with a thorough review of your current symptoms and medical history, including your family medical history. A physical examination and a review of your current medications are also necessary.
To make sure your doctor gets an accurate diagnosis, brain imaging is critical. A 2019 scholarly review article suggests that an MRI of the brain can help determine whether your symptoms are caused by vascular Parkinsonism or PD. An accurate diagnosis is an important step in getting the most effective treatment.
Other brain imaging, such as a CT scan, can also be helpful for detecting signs of small strokes in the regions of the brain responsible for movement and muscle control.
Read Also: Does Alan Alda Have Parkinson’s
What Are The Imaging Findings In Vascular Parkinsonism
The literature in neuroimaging in VP is scarce. Computer tomography, magnetic resonance imaging , and cerebral angiography can be performed to delineate lesions. Even though imaging findings in VP are nonspecific and poorly defined, there are certain findings that would suggest VP over idiopathic PD. Ischemic changes in multiple vascular territories, periventricular white matter ischemia, global subcortical ischemic white matter involvement, ischemia in the basal ganglia and brain stem, and cortical atrophy are significant and more commonly seen in patients with VP
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
You should see your healthcare provider as recommended or if you notice changes in your symptoms, especially if the symptoms start to interfere with your life and routine. You should also see your provider if you notice any changes in the effectiveness of your medication.
When should I go to ER?
Your healthcare provider can give you guidance and information on signs or symptoms that mean you need to go to the hospital or get medical attention. In general, you should get medical attention if you fall, especially when you lose consciousness or might have an injury to your head, neck, chest, back or abdomen.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Parkinsonism is a term that covers a wide range of conditions that affect your ability to move and live independently. While these conditions all share certain similarities, they also can have major differences from each other. If youre diagnosed with parkinsonism, its important to talk to your healthcare provider about what condition you have , and what that diagnosis means for you. Not all parkinsonism conditions are the same, so understanding your specific case can make a big difference in managing it and how it affects your life.
Read Also: What Tests Diagnose Parkinson’s Disease
