Can Antipsychotics Cause Parkinsons Disease
Antipsychotics are mainly useful in the management of psychosis, such as disordered thoughts, paranoia, hallucinations, delusions, principally in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Doctors usually call them as neuroleptics or major tranquilizers and recommend them to manage various conditions. In addition, such medicines relieve psychosis symptoms on a short-term basis.
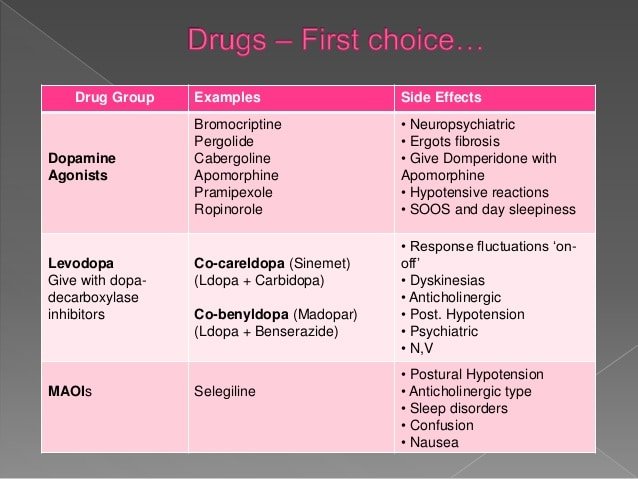
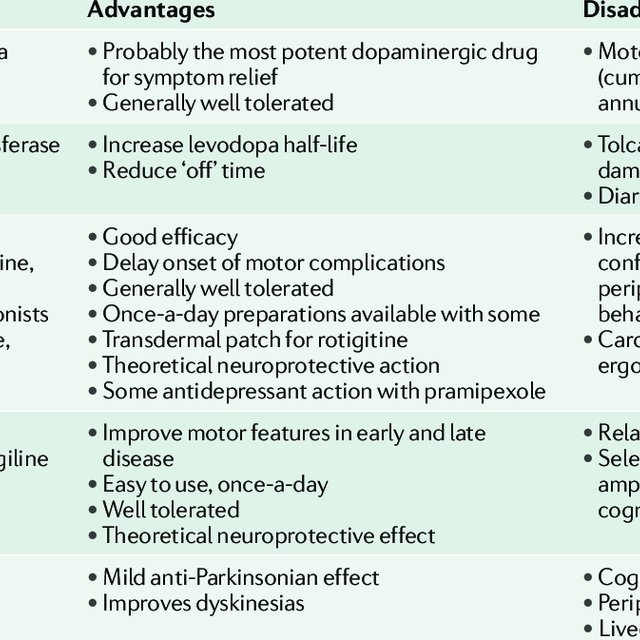
Key Aspects Of Drug Induced Parkinsonism
- Drug induced Parkinsonism is relatively less likely to produce the problem of tremor than its counterpart idiopathic Parkinsons disease.
- DIP is highly symmetric, but doctors usually fail to distinguish the 2 syndromes in case of an individual therapy.
- The problem of DIP persists in patients for a few weeks to up to many months even when a patient stops the consumption of respective offending drug.
- Drug induced Parkinsonism has a longstanding and a significant effect on the daily lives of a patient. Hence, doctors should essentially stay cautious while prescribing the drugs of depaminergic receptor blockers to their patients.
Also Read:
A Critical Reappraisal Of The Worst Drugs In Parkinsons Disease
What are the worst drugs for Parkinsons disease patients? Couldnt a simple list be assembled and disseminated to the Parkinson community? Recently Ed Steinmetz, an experienced neurologist in Ft. Meyers, FL pointed out to me, a list approach published in the Public Citizen Newsletter . The approach was to list every drug associated with a single confirmed or unconfirmed symptom of Parkinsons disease or parkinsonism. Parkinsons disease is defined as a neurodegenerative syndrome , whereas parkinsonism encompasses a wider net of drug induced and other potential causes. In parkinsonism symptoms are similar to Parkinsons disease, but patients do not have Parkinsons disease. Patients and family members confronted with a simple drug list approach may falsely conclude that most medicines are bad for Parkinsons disease, and that any medicine may cause parkinsonism. This concept is in general, incorrect. Although the approach is well-meaning, it is in need of a major revision, as Parkinsons disease and parkinsonism are too complex to summarize by simple lists. In this months column I will try to summarize the key information that patients and family members need to know about the worst pills, for Parkinsons disease and parkinsonism.
A Florida Parkinsons Treatment Blog by Michael S. Okun, M.D.
UF Center for Movement Disorders & Neurorestoration, Gainesville FL
Antipsychotics Are Dopamine Blocking Drugs
A few people develop Parkinsons disease like symptoms after they undergo treatment with specific type of medicines. This type of medicine refers to drug-induced Parkinsonism or DIP i.e. secondary type of Parkinsonism. Specific medicines, including antipsychotics may make the symptoms worse in patients, who already suffer from Parkinsons disease.
Almost every medicine responsible to create blockage of dopamine in humans may create symptoms related to Parkinsons disease. Dopamine refers to a brain chemical that mainly controls body movements. Antipsychotics are common types of dopamine blocking drugs, which are useful in the treatment of specific mental illnesses or nausea in its severe form. In less common cases, calcium channel blockers medicines may result in drug induced Parkinsonism. These drugs are helpful in the treatment of high blood pressure, chest pain as well as irregular heart beat rate.
What Are The Causes
Drug-induced parkinsonism is caused by medications that reduce dopamine levels in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that works to control bodily movements.
Dopamine is also part of the brains reward system. It helps you feel pleasure and enjoyment, and it supports your ability to learn and focus.
Medications that bind to and block dopamine receptors are called dopamine antagonists. These medications arent used to treat Parkinsons disease. Rather, theyre used to treat other conditions that might seriously impact your quality of life.
Some medications that cause drug-induced parkinsonism include:
Top Medicines That Worsen Parkinsons Disease Or Cause Secondary Parkinsonism
Medications to avoid
Some medications can worsen movement symptoms of PD, including slowness, stiffness, tremor and dyskinesia. These drugs, listed below, are used to treat psychiatric problems such as hallucinations, confusion or gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea. The stress of your illness, hospital stay or new medicines can increase your risk of hallucinations while hospitalized. Common anti-hallucination medicines to be avoided are listed by generic or chemical name followed by the trade name.
Anti-hallucination medicines to avoid
Note: the anti-hallucination medicines Quetiapine or Clozapine can be used. The following should be avoided:
- aripiprazole , chlorpromazine , flufenazine , haloperidol , molindone , perphenazine , perphenazine and amitriptyline , risperidone , thioridazine , thiothixene
Anti-nausea medicines to avoid
- metoclopramide , phenothiazine , promethazine
Medicines to avoid if you are on Rasagiline or Selegiline
- Pain medicines Meperidine , Tramadol ,Antispasmodic medicine Flexeril , Dextromthorphan and St Johns Wort.
- This is not a complete list of medicines to avoid. If you have questions about other medications, ask your pharmacist or doctor.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as or scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Parkinsonism Falls And Fracture Risk
All forms of parkinsonism, both PD and DIP, have implications for bone health. A 2014 meta-analysis on PD and fracture risk concludes that PD increases the risk of fracture.4
Given that the symptoms of parkinsonism affect balance, motor skills, gait, and the bodys ability to control movement, it is no surprise that people with PD are more likely to experience a fall than people without PD. Here is an excerpt from a 2016 study comparing the incidence of falls and fracture in PD patients:
It is estimated that 60.5% of patients with PD experience at least one fall and 39% have recurrent falls. The high frequency of falls consequently contributes to the increased risk for fractures in PD patients, which has been estimated to be approximately two times the risk in healthy controls. It has been estimated that 76% of falls in PD patients require health care services and 33% result in fractures. Falls and fractures may result in a series of unfavorable outcomes, such as disabilities and death. Furthermore, among PD patients with fractures, the mortality rate is approximately 10.6%.5
All too often, doctors prescribe these drugs without appropriate consideration of this risk. This excerpt from a study on DIP clarifies the danger of accepting a prescription of an unnecessary or inappropriate prescription drug:
Shockingly, the drugs that cause DIP are still being prescribed. This yet one more example further proving that the FDAs drug approval process is useless.
Synopsis
Update On Parkinson’s Disease
ROSABEL YOUNG, M.D., M.S., King-Drew Medical Center, Los Angeles, California
Am Fam Physician. 1999 Apr 15;59:2155-2167.
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive degenerative disorder of the central nervous system. The hallmark physical signs are tremor, rigidity and bradykinesia. Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease is caused by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and nigrostriatal pathway of the midbrain. Secondary parkinsonism may be caused by certain drugs or by cerebrovascular disease . The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the history and physical findings. Dopamine replacement is still considered the most efficacious treatment for Parkinson’s disease, but dopamine agonists, formerly prescribed only as adjunctive therapy, are emerging as useful initial therapy. Other pharmacologic treatments include drugs that inhibit dopamine-metabolizing enzymes . Injections of botulinum toxin can be helpful in patients with associated dystonia or blepharospasm. Surgery may be indicated for certain patients or when symptoms do not respond to medical therapy. Additional adjunctive therapies include physical therapy, nutritional counseling and techniques to help patients manage emotional and cognitive changes related to the disease.
FIGURE 1.
FIGURE 1.
Which Test Can Be Done When The Diagnosis Is In Doubt
I request a small set of tests on almost all patients I diagnose with Parkinsons. These detect some mimics of Parkinsons disease.
Some doctors dont request all these tests. And for a good reason.
The diagnosis of Parkinsons mimics is primarily based on a careful history and examination. Even in my practice, these tests change the diagnosis only in a minority of patients.
I like the additional confirmation provided by these tests. They also have other benefits. For example, they help me determine the proper dosages of medications like Amantadine.
| Simple tests to detect Parkinsons Mimics |
|---|
| 1. MRI-Brain with size measurements of brain parts called the midbrain and pons. I usually also request a unique picture called SWI, which shows iron inside the brain.
2. Blood tests: |
But when the diagnosis s really in doubt, there is another brain scan that can be done.
A Trodat scan. Or even better an F-DOPA scan. Both these scans measure dopamine activity inside the brain.
You can read more about Trodat & F-DOPA scans by clicking here.
These scans are not perfect. Let me tell you why very quickly:
In Parkinsons disease, dopamine activity inside the brain is deficient. This deficiency produces an abnormal scan. If the Trodat/F-DOPA scan is normal, it is unlikely that you have Parkinsons disease.
Can Drug Induced Parkinsonism Be Prevented
Although there is no surety in the prevention of drug-induced parkinsons disease, but efforts may be made to check the dosage of drugs so prescribed-
Be Cautious with Antipsychotics: The patient or in some cases the caregiver should make sure that antipsychotic drugs are given at their least effective dosage.
Inform the Doctor: The doctor should be informed well before in case the patient already has symptoms of Parkinsons disease so that they do not appear to get worse with the starting of some prescribed drugs.
Abrupt Stoppage of Medicine: It is never a wise decision to stop taking a medicine by oneself. It is important to talk to the doctor in case of any concerns.
Antipsychotics To Deal With Psychotic Symptoms
Psychotic symptoms remain present in approximately half of the patients dealing with Parkinsons disease. These symptoms create detrimental effects on the quality of life lead by patients and their caregivers, while result in mortality in some cases. Pathogenesis associated with psychotic symptoms in Parkinsons disease is complicated and usage of antipsychotics i.e. dopaminergic medications involve many risk factors. Treatment for psychotic symptoms in patients dealing with Parkinsons disease is complicated because of the property of any antipsychotic medicine to make motor symptoms worse.
What To Do To Prevent Drug
The most common drugs linked to this condition are two used to treat schizophrenia or psychotic symptoms of dementia. They are haloperidol and perphenazine . Ask your doctor about parkinsonism if you or a loved one is concerned about a drug, especially these two drugs.
In general:
* Make sure you or a loved one are on the lowest effective dose.* If you already have Parkinsons disease, then tell your doctor if the symptoms appear to be getting worse since starting the drug.* Never stop taking a drug on your own. Talk to your doctor about any concerns.
* Parkinsons Disease Society. Drug-induced parkinsonism.* Albin RL. Parkinsons disease: background, diagnosis, and initial management. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine. 2006;22:735-751.* Alvarez MV, Evidente VG. Understanding drug-induced parkinsonism Separating pearls from oysters. Neurology. 2008;70:e32-e34.
Connies notes: Neuro meds common side effects include dizziness,nausea,headache,vomitting and sleep disorders
Prescription Medications To Avoid If You Have Parkinsons
There are many drugs to be avoided in PD because they block dopamine receptors and can increase the slowness, stiffness and balance problems of PD. There are also drugs that interact with particular PD medications, specifically monoamine oxidase B inhibitors and need to be avoided by people taking those particular medications. Both of these groups of medications are listed in APDAs Medications to Avoid educational supplement.
In addition to these two groups of medications, many medications have side effects that need to be considered in the context of PD. Because people with PD may be particularly prone to certain non-motor symptoms, they may be more sensitive to particular medication side effects such as fatigue, confusion, low blood pressure or constipation, among others. For example, particular medications for anxiety or sleep could potentially cause gait unsteadiness and would need to be used with caution in those with balance and gait difficulties. For all of these reasons, it is important to periodically review all of your medications with your doctor.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
How Is A Diagnosis Made
Because other conditions and medications mimic the symptoms of PD, getting an accurate diagnosis from a physician is important. No single test can confirm a diagnosis of PD, because the symptoms vary from person to person. A thorough history and physical exam should be enough for a diagnosis to be made. Other conditions that have Parkinsons-like symptoms include Parkinsons plus, essential tremor, progressive supranuclear palsy, multi-system atrophy, dystonia, and normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Not All Drugs In These Classes Will Cause Symptoms Of Parkinsonism
Whats the difference?
Drug-induced parkinsonism usually develops on both sides of the body, while typical Parkinsons disease does not. Also, drug-induced parkinsonism usually does not progress like typical Parkinsons.
Unlike Parkinsons, drug-induced symptoms usually go away after the drug is stopped. It may take several months, though, for the symptoms to completely stop. If the symptoms remain, then it is possible that the drug may have unmaskedunderlying Parkinsons disease.
Who is at risk?
- Female: Women are twice as much at risk as men.
- Elderly: Older people are more likely to be on multiple medications or to have underlying Parkinsons disease.
- Those with a family history of Parkinsons disease.
- People with AIDS.
What Is The Difference Between Drug Induced Parkinsons Disease And Typically Occurring Parkinsons Disease
It has been seen that drug-induced Parkinsonism usually occur on both sides of your body while usual Parkinsons starts from one side of the body. Apart from this, the medication-induced signs generally are seen to go away after the medicine is finished. However, it may take few months to stop, but is does stop eventually. On the contrary, the typically occurring Parkinsons disease cannot be reversed. Another thing to be kept in mind is that medication-induced Parkinsons disease is not progressive, unlike the typical Parkinsons disease.
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinson’s may experience some of these more common “hallmark” symptoms:
- Bradykinesia – slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest – involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity – stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability – sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
What To Do If Your Senior Has Parkinsons

If you notice Parkinsons-like symptoms in your older adult, the first thing to do is talk with their doctor. The doctor should review their complete medication history and you should let them know about any other symptoms or changes.
Important: Dont make any changes to medications without doctor approval that could cause serious problems.
Serotonin Reuptake Blocking Antidepressants Fluoxetine Sertraline And Paroxetine
Several other medications have been reported to cause drug-induced parkinsonism and to worsen parkinsonism in people with Parkinson disease, including the serotonin reuptake blocking antidepressants fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine. Two calcium channel blockers available in Europe and South America , which are piperazine derivatives, are thought to cause drug-induced parkinsonism by blocking dopamine receptors. Reports of parkinsonism induced by other drugs, such as lithium and amiodarone, are so rare that only after parkinsonism has developed should the possible drug effect be taken into account. Because lithium is not known to block dopamine receptors, another mechanism is likely. Some animal data implicate an effect of lithium on intercellular signalling via G-protein coupled receptors . One antidepressant, amoxapine, has dopamine receptor-blocking properties and, therefore, may induce parkinsonism. Parkinsonism as a transient side effect of alcohol withdrawal has been reported without later development of Parkinson disease, but it is unknown how common this is .
Environmental Toxins And Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is said to be because of the loss of dopamine-releasing nerve cells in a small, central part of the brain called the substantia nigra. The substantia nigra produces dopamine, which helps coordinate movement in our body.
But when nigral nerve cells are impaired, less dopamine is released and motor function is affected. And thats when hallmark Parkinsons symptoms including tremors, difficulty balancing, and slowed movement start to set in.
Several studies have suggested that environmental toxicants including pesticides, herbicides, and other pollutants are linked to an increased risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
Heres how these chemicals are said to play a role in the development of the neurological disorder:
Looking Out For Side Effects If You’re A Carer
If youre a carer of someone with Parkinsons, medication side effects can be difficult and tiring to cope with.
It may be that the person having side effects such as hallucinations and delusions or impulsive and compulsive behaviour does not realise they are experiencing them.
Its important to seek help from your specialist as soon as you can.
When To Be Suspicious Of Medications
In many cases, symptoms of Parkinsons could be caused by a new medication that was started a few days or a few months ago.
In other cases, it could be caused by medications that start out at one dose and are increased to higher doses. If the dose increases move too quickly, that can also cause these symptoms.
Other factors also make it more likely that someone will develop Parkinsons symptoms from medications. These include having a history of:
- Dementia
- Strokes or transient ischemic attacks
- Parkinsons in the family
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Surgery For Parkinson’s Disease
At one time, surgery was reserved for use in patients with early-onset Parkinson’s disease who became disabled in their prime working years. However, techniques have advanced so rapidly that surgery is now considered an option even in elderly patients as long as they meet medical screening criteria, including failure to respond to available medications and absence of cardiopulmonary risk factors for surgery. It is essential to select a neurosurgeon who is part of a movement disorders team with considerable experience in performing the surgical procedures used to treat Parkinson’s disease.
Diagnosis Of Dip And The Role Of Dat Imaging
The clinical diagnostic criteria for DIP are defined as 1) the presence of parkinsonism, 2) no history of parkinsonism before the use of the offending drug, and 3) onset of parkinsonian symptoms during use of the offending drug. Since asymmetrical rest tremors are common in many DIP patients and symptoms persist or progress after cessation of the offending drug, patients clinically diagnosed with DIP may include individuals in the preclinical stage of PD whose symptoms were unmasked by the drug.,,,
DATs are presynaptic proteins in the membrane on terminals of dopaminergic neurons. They take up dopamine from the synaptic cleft projections that extend from the substantia nigra to the striatum. These transporters control dopaminergic transmission by spatial and temporal buffering, rendering the molecule an imaging target in diseases affecting the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway. Single-photon-emission computed tomography and positron-emission tomography scans are available using several DAT ligands., SPECT radioligands include 123I-N-3-fluoropropyl-2-carbomethoxy-3-nortropane , 123I-ioflupane, DaTSCAN, and 123I-2-carbomethoxy-3-tropane . PET scans may be superior to SPECT for imaging DATs, in that the lower energy of positrons provides higher resolution, resulting in better image quality with widespread clinical applications. However, most DAT imaging studies, including those in patients with DIP, have utilized SPECT.,-
Tremors Caused By Medications

In addition to drug-induced parkinsonism, which includes rest tremor and is caused by medications that block the dopamine receptor, there are also a wide variety of medications that do not block the dopamine receptor, but can cause other types of tremors, such as postural and action tremors. So if you have these types of tremors, but without the slowness, stiffness and other PD-like symptoms, you could have drug-induced tremor .
A postural tremor occurs when a body part is held against gravity. Postural tremors occur for example, when the arms are extended, such as when holding a tray. An action tremor occurs when a body part is moving. Action tremors occur for example, when the arm is moving toward the mouth to eat.
Drug-induced tremors typically are symmetric or equal on both sides of the body. The medications that can cause tremor include, but are not limited to, lithium, valproic acid, amiodarone, beta-adrenergic agonists, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors . Be attentive to whether a tremor starts after any new medication is started. If it does, discuss this with your doctor.
