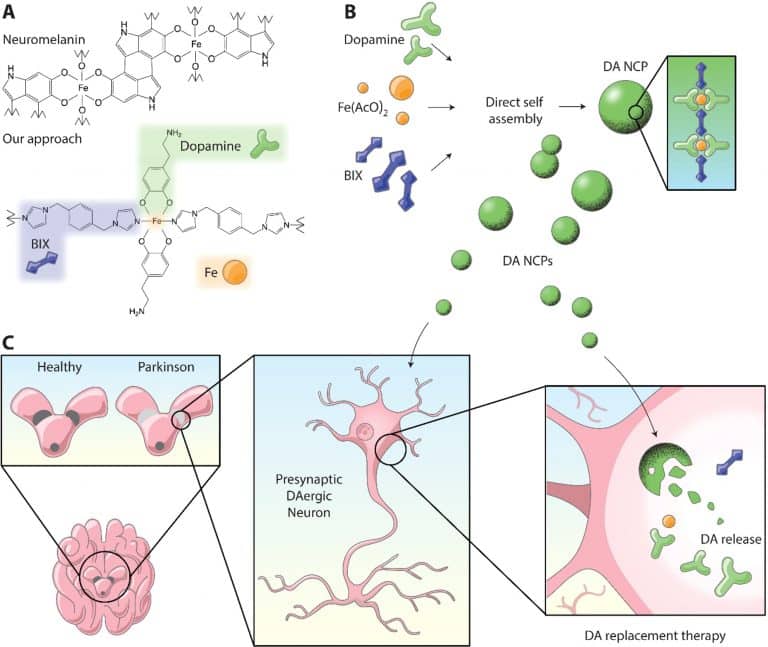
Synthesisand Characterization Of Da
Chemicaland morphological characterization of DA-NCPs. SEMimages of neuromelanin-inspired DA-NCPs. The inset shows a colloidaldispersion of the nanoparticles in ethanol. Scale bar, 200 nm. Particle size distribution of DA-NCPs determined by SEM and negative-staining transmission electron microscopy . TEM image and EDX profile of DA-NCPs along the dark red linemarked . UVvis absorbance spectra of the particles and the corresponding chemical precursors: DA, BIX , and Fe2 determined at a concentration of 100 g/mLin water.
Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease usually develop gradually and are mild at first.
There are many different symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease. Some of the more common symptoms are described below.
However, the order in which these develop and their severity is different for each individual. It’s unlikely that a person with Parkinson’s disease would experience all or most of these.
Can Dopamine Be Used To Treat Parkinsons
If Parkinsons disease is caused by a drop in dopamine, it might make sense that replacing that dopamine would stop the symptoms and halt the progression of the disorder. But its not that easy.
Dopamine from a medication or injection cant penetrate the blood-brain barrier. That makes it an ineffective treatment.
An amino acid called levodopa can help increase levels of dopamine in the brain. If given as a medication, it can cross the blood-brain barrier. Once in the brain, levodopa is converted to dopamine.
Levodopa wont replace all of the lost dopamine, but it can help to reduce symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Its particularly helpful with movement control.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
What Other Information Should I Know
Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory. Your doctor will order certain lab tests to check your response to levodopa and carbidopa.
Before having any laboratory test, tell your doctor and the laboratory personnel that you are taking levodopa and carbidopa.
Levodopa and carbidopa can lose its effect completely over time or only at certain times during the day. Call your doctor if your Parkinson’s disease symptoms worsen or vary in severity.
As your condition improves and it is easier for you to move, be careful not to overdo physical activities. Increase your activity gradually to avoid falls and injuries.
Levodopa and carbidopa can cause false results in urine tests for sugar and ketones .
Do not let anyone else take your medication. Ask your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription
It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you visit a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important information to carry with you in case of emergencies.
When To Start Treatment
Deciding when to start drug therapy for Parkinsons disease should be individually tailored to a patients symptoms, circumstances and comorbidities. Treatment is indicated when symptoms impact on quality of life. When treatment is needed there is no evidence to support undue delay because of concerns about levodopa toxicity or the development of treatment resistance.3 The aim is to control symptoms and maintain an on state.
Some drugs with good symptomatic benefit are speculated to have a role in neuroprotection and some specialists advocate their use from the time of diagnosis.4 Delayed start trials have been used to try and differentiate symptomatic from disease-modifying effects. A recent delayed start study of rasagiline, a monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, in treatment-naïve patients with mild Parkinsons disease showed a small benefit in the low-dose treatment group. This was not seen with the 2 mg dose and a clear explanation for this has not been established.5 Further studies are needed before such treatments are considered truly disease modifying. Until a drug is unequivocally proven to slow disease progression, the time to commence treatment will remain contentious.
Read Also: Can Spinal Stenosis Mimic Parkinson’s
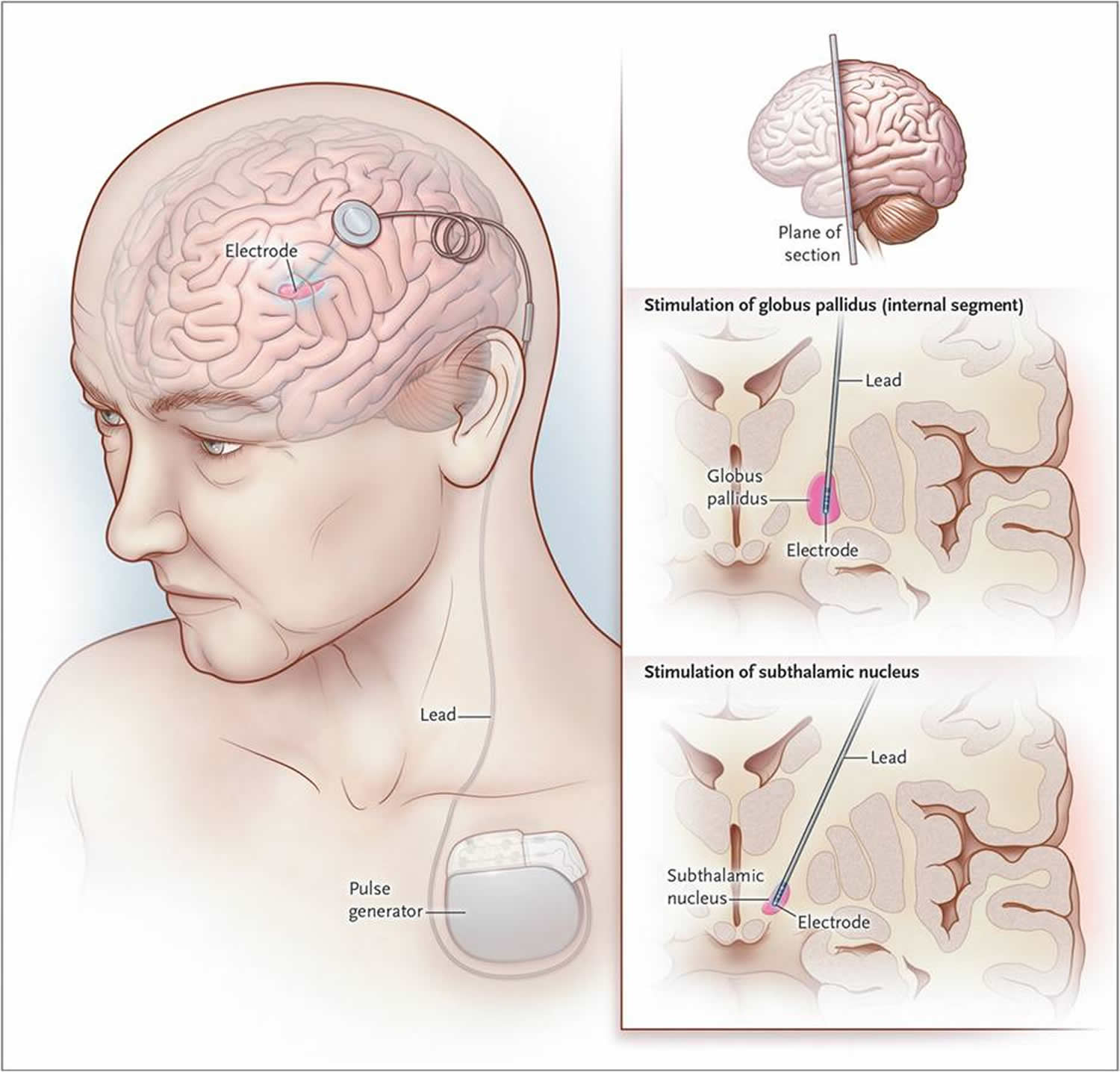
Mechanisms Of Dbs Action
Even though the exact underlying physiological mechanism of DBS remains unclear, the therapeutic benefits of DBS seem to be frequency-dependent and can modulate cortical activities. Several animal studies have shown support for the hypothesis of direct cortical activation during STN-DBS . These studies have provided evidence of the occurrence of antidromic spikes in M1 during the DBS paradigm which coincides with the optimal effect of STN-DBS. Whether a similar antidromic activation of the known cortex-GPi projection contributes to the therapeutic effect of GPi-DBS remains to be studied. Non-invasive brain stimulation studies using TMS have shown abnormal motor cortical plasticity in PD which has been investigated further for understanding the mechanism of DBS. It has been shown that paired associative cortical plasticity could be induced by repeated STN and M1 stimulations at specific intervals, signifying that STN-DBS can modulate cortical plasticity . Moreover, STN stimulation with clinical efficacy increased the excitability of the motor cortex at specific short and medium latencies, suggesting that cortical activation could be one of the mechanisms mediating the clinical effects of STN-DBS in PD . It has been further suggested that enhancement of inhibitory synaptic plasticity, non-specific synaptic depletion and frequency-dependent potentiation might be complementary mechanisms of DBS action .
Molecular Mechanisms Of L
Parkinsonian symptoms appear when brain levels of dopamine are reduced by 7080% . Dopamine itself has low bioavailability and does not cross the blood-brain barrier , hence its precursor L-DOPA is used clinically it is readily transported into the central nervous system and is converted into dopamine in the brain by the enzyme DOPA decarboxylase . Only a small quantity of systemically administered L-DOPA enters into the brain however, this quantity is enough to restore the nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurotransmission. Although conversion into dopamine is the basic mechanism of levodopas pharmacological effect, it also possesses a direct neuromodulatory action and contributes to the therapeutic efficiency.
Figure 1. Illustration of the molecular mechanism of L-DOPA.
Recommended Reading: Workup For Parkinson’s Disease
Types Of Dopamine Replacement Therapies
Dopamine replacement therapy comes in a variety of formulations and combinations. The more common preparations are as follows:
Levodopa/Carbidopa: This combination comes in a short-acting form as well as a long-acting one which only requires twice-daily dosing. levodopa/carbidopa also comes in an orally disintegrating tablet that doesnt require water to take and is helpful for those with swallowing difficulties.
Levodopa/Carbidopa/Entacapone: Stalevo is another brand name long-acting preparation of dopamine replacement that in addition to levodopa and carbidopa has the added medication entacapone, which further prolongs the effectiveness of this formulation allowing for longer dosing periods.
Currently only available in Canada and Europe, levodopa/carbidopa gel is a form of dopamine replacement that is delivered directly into the small intestine via a surgically placed tube. It is best used for those with advanced disease who are unable to gain control over their disabling motor symptoms with other available medications. By using a pump system similar to the insulin pump in diabetes, Duodopa is able to deliver the medication continuously throughout the day.
What Can I Expect If I Have This Condition
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative condition, meaning the effects on your brain get worse over time. However, this condition usually takes time to get worse. Most people have a normal life span with this condition.
You’ll need little to no help in the earlier stages and can keep living independently. As the effects worsen, youll need medication to limit how the symptoms affect you. Most medications, especially levodopa, are moderately or even very effective once your provider finds the minimum dose you need to treat your symptoms.
Most of the effects and symptoms are manageable with treatment, but the treatments become less effective and more complicated over time. Living independently will also become more and more difficult as the disease worsens.
How long does Parkinsons disease last?
Parkinsons disease isnt curable, which means its a permanent, life-long condition.
Whats the outlook for Parkinsons disease?
Parkinson’s disease isn’t fatal, but the symptoms and effects are often contributing factors to death. The average life expectancy for Parkinson’s disease in 1967 was a little under 10 years. Since then, the average life expectancy has increased by about 55%, rising to more than 14.5 years. That, combined with the fact that Parkinson’s diagnosis is much more likely after age 60, means this condition doesn’t often affect your life expectancy by more than a few years .
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Falls Risk
Green Tea And Coffee To Reduce The Risk Of Developing Pd
Green tea is prepared from the leaves of the Camellia Sinensis plant and contains phenolic compounds such as -Epigallocatechin-3-gallate a potent antioxidant and neuroprotective compound. Preclinical clinical and self-report studies suggest that green tea may prevent PD . However, the therapeutic mechanism of green teas potential protective actions in PD is unclear. It is feasible that green teas phenolic compounds are modulating critical neuroprotective signaling pathways in the brain . On the other hand, green tea could exert its effects via caffeine-induced inactivation of the adenosine receptor.
How Does This Condition Affect My Body
Parkinsons disease causes a specific area of your brain, the basal ganglia, to deteriorate. As this area deteriorates, you lose the abilities those areas once controlled. Researchers have uncovered that Parkinsons disease causes a major shift in your brain chemistry.
Under normal circumstances, your brain uses chemicals known as neurotransmitters to control how your brain cells communicate with each other. When you have Parkinsons disease, you dont have enough dopamine, one of the most important neurotransmitters.
When your brain sends activation signals that tell your muscles to move, it fine-tunes your movements using cells that require dopamine. Thats why lack of dopamine causes the slowed movements and tremors symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
As Parkinson’s disease progresses, the symptoms expand and intensify. Later stages of the disease often affect how your brain functions, causing dementia-like symptoms and depression.
Recommended Reading: Low Protein Diet For Parkinson’s Disease
Preventative Approaches: Targeting The Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
Unfortunately, although some therapies for PD produce a period of recovery for about 5 years, there is a sharp decrease in the beneficial effects of treatments thereafter . Indeed, the best approach would be to understand the relevant triggers of the disease in order to target the physiopathological mechanisms causing the death of dopaminergic neurons. Epidemiological studies have shown that less than 10% of PD cases have a strict familial etiology, while most of them are sporadic and appear to be caused by other factors associated with susceptibility genes . Although these factors are not fully understood, there is a consensus that PD is induced by a combination of age, gender, genetic background, and environmental factors. However, neither of these has, alone, been identified as a leading cause of PD . While the cellular and neurochemical mechanisms underlying PD have remained incompletely understood, what data have been collected point to heavily to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of both familial and sporadic cases of PD .
This evidence suggests that preventing mitochondrial dysfunction can be a key therapeutic goal to achieve as stand-alone or adjunctive therapy against PD.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect Parkinsons disease or need to rule out other conditions, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
New lab tests are possible
Researchers have found possible ways to test for possible indicators or Parkinsons disease. Both of these new tests involve the alpha-synuclein protein but test for it in new, unusual ways. While these tests cant tell you what conditions you have because of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, that information can still help your provider make a diagnosis.
The two tests use the following methods.
- Spinal tap. One of these tests looks for misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins in cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. This test involves a spinal tap , where a healthcare provider inserts a needle into your spinal canal to collect some cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
- Skin biopsy. Another possible test involves a biopsy of surface nerve tissue. A biopsy includes collecting a small sample of your skin, including the nerves in the skin. The samples come from a spot on your back and two spots on your leg. Analyzing the samples can help determine if your alpha-synuclein has a certain kind of malfunction that could increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Test For Parkinson’s Disease
Other Types Of Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
Some people with Parkinson’s have surgery called deep brain stimulation . In this procedure, doctors place a wire deep inside a specific spot in the brain, depending on the symptoms that need treatment. DBS can lead to dramatic improvements in many people.
Scientists are also exploring ways to place cells that make dopamine into the brain to help treat people with Parkinson’s, instead of taking medicine. Some experts are trying to see if stem cells can be used for this, but research is still in an early stage.
Some treatments focus on the effects of the disorder, rather than the causes. Your doctor might refer you to a physical therapist to improve your balance and your ability to move. A physical therapist may also teach muscle-strengthening exercises to help you speak or swallow.
It’s important to keep up a daily exercise program and to stay socially active. You can get information about support groups and exercise classes in your area by checking with the American Parkinson Disease Association.
Show Sources
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Muscle stiffness, where muscle remains contracted for a long time
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Early symptoms of this disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s disease often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward take small, quick steps and reduce swinging their arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Symptoms often begin on one side of the body or even in one limb on one side of the body. As the disease progresses, it eventually affects both sides. However, the symptoms may still be more severe on one side than on the other.
Read Also: Is Dementia Part Of Parkinson’s
Background Of The Disease
About 250,000 people suffer on Parkinsons disease in Germany. Another 100,000 can be assumed as not detected. Up to 180 patients per 100,000 habitants are estimated. About 1% of the 60-years old people and 3% of the 80-years old people have Parkinsons disease. 10% of the patients are younger than 40 years, 30% younger than 50 years. 40% get the disease between 50 and 60 years. Men have a double risk to get the disease then women. Incidence is increasing with age.
The clinical symptoms or Morbus Parkinson is mainly the bradykinesis, tremor , and rigor .
Nightshade Vegetables: Eggplants Tomatoes And Peppers
There is mounting evidence that eating nightshade vegetables, like tomatoes and peppers, can improve the symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Nightshades are a group of plants that include eggplant, potatoes, and chili peppers. They have been shown to contain dietary nicotine, which may slow the progression of Parkinsons disease.
These vegetables may also reduce inflammation and oxidative damage in the brain, which are thought to be responsible for some of the motor symptoms of this condition.
You May Like: What’s The Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
A Review On Parkinsons Disease Treatment
Tori K. LeeEva L. Yankee
Department of Biology, Angwin, CA 94508, USA .
Correspondence Address: Tori K. Lee, Department of Biology, Pacific Union College, 1 Angwin Ave, Angwin, CA 94508, USA. E-mail: tolee@puc.edu
Received:First Decision:Revised:Accepted:Available online:Academic Editors:Copy Editor:Production Editor:
© The Author 2021. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
How Does Pd Affect Dopamine
Doctors believe that PD affects the brains ability to create dopamine.7 Since the brain cannot produce the dopamine it needs, a persons movement begins to be affected. PD can also cause other symptoms as the brain begins to create less dopamine.8
People with PD can have issues with sleep, depression, and blood pressure. Younger people with PD can also have issues with impulse control.9 As you can see, these are all related to the parts of the brain that create dopamine. Doctors are not sure why this happens, or what causes PD.
PD causes the neuron cells in the substantia nigra to break down and die. People with PD have 80 percent fewer dopamine-producing cells in their substantia nigra than people without PD have.7
Doctors are not sure why this happens. If doctors can figure out why PD causes the brain to stop producing dopamine, they think they may be able to find a better treatment for PD.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Signs Of Parkinson’s
Data Synthesis And Confidence In Evidence Statements For Levodopa Vs Das
-
1. In people with early PD, what is the comparative efficacy of levodopa vs DAs vs MAO-B inhibitors for motor symptoms?
-
2. In people with early PD, what is the comparative risk of adverse effects of levodopa vs DAs vs MAO-B inhibitors?
UPDRS Part III Score
The change in the UPDRS part III score from baseline to endpoint was extracted from studies comparing levodopa to DAs and the RMD between treatments was calculated . Negative values favored levodopa. Where possible, estimates were combined using meta-analysis at specific time points. The minimal clinically important difference in the UPDRS part III score was determined by consensus to be 3 points changes of 1 point or less were considered unimportant.
Long-Acting vs Immediate-Release Levodopa: Change in Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale Part III Score From Baseline to Endpoint, Risk of Dyskinesia, Hallucinations, and Adverse EventRelated Discontinuation
The available evidence is insufficient to make conclusions regarding the relative efficacy of long-acting vs IR levodopa for improvement in motor function or the risk of hallucinations. There do not appear to be major differences between long-acting and IR levodopa in the risk of dyskinesia or AE-related discontinuation.
