Simplifying Parkinsons Disease Medications
The first step in treating psychosis in Parkinsons disease is to cut out or decrease the dosage of certain medications. When I first started taking a new drug four times daily, the night hallucinations were dreadful, one MyParkinsonsTeam member shared. When I told my neurologist about these, she dropped the medication to three per day, and I have to take my last one no later than 5 p.m., otherwise I will hallucinate.
Health care providers usually remove PD drugs in the following order:
- Anticholinergics block the effect of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the brain, helping to offset lowered dopamine levels in the brain. Trihexyphenidyl and benztropine mesylate are examples of this class of drug.
- Amantadine sold as Gocovri and Symmetrel is used to increase the level of dopamine in the brain, which can help control movement difficulty in people with PD. One MyParkinsonsTeam member reported, I had hallucinations years ago with amantadine, but my doctor reduced the dosage and they stopped.
- Dopamine agonists imitate the effect of dopamine in the brain and can help manage the movement symptoms of PD. Pramipexole dihydrochloride, rotigotine transdermal system, bromocriptine mesylate , and ropinirole are all examples of dopamine agonists.
Some clinicians may also cut out the following types of medications:
Treatment For Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
Treating Parkinsons disease psychosis is a balancing act, and a holistic approach is important. You dont want your psychiatric symptoms to get better while your physical symptoms get worseor vice versa.
Antipsychotic medications tend to regulate one of two chemicals in the braindopamine or serotonin. Medications that target dopamine can help your mood but can harm your motor function, because dopamine influences both in different ways.
Other medications that target serotonin are considered safer for those with Parkinsons disease, improving mood without worsening motor function. One study of a treatment targeting serotonin receptors showed psychotic symptom improvement in as little as two weeks.
Keep in mind all treatments have benefits and risks, and each person reacts to treatment differently. Your healthcare team should help you weigh your options from both a neurological and psychiatric perspective. Youve done yourself a great service by going into the conversation better informed.
Medications Used For Treating Psychosis
Antipsychotic agents are designed to balance abnormal chemical levels in the brain. Up until the 1990s, the use of antipsychotics in PD was controversial because the drugs used until that time work by reducing excess dopamine. This alleviated psychosis but caused dramatic worsening of PD motor symptoms.Fortunately, medications that are better tolerated by people with PD are now available. Today, there are three antipsychotic medications considered relatively safe for people with PD. They cause limited worsening of PD while treating hallucinations and delusions.
Recommended Reading: How To Manage Parkinsons Symptoms
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Disease Treatment Exercise Program
Sleep Disorders Are Another Possible Pd Clue
One is called REM sleep behavior disorder . In normal REM sleep, your body is relaxed and your muscles dont move. With this disorder, a switch gets turned off, and people move in relation to their dream content. We call it dream enactment, explains Mya Schiess, M.D., a professor of neurology at McGovern Medical School at the University of Texas Health Science Center in Houston. You might kick your partner, or thrash around so much you fall out of bed, she says. RBD probably has the highest risk factor for the development of Parkinsons, Dr. Schiess adds, as well as Lewy Body dementia.
What Causes Psychosis In Parkinsons
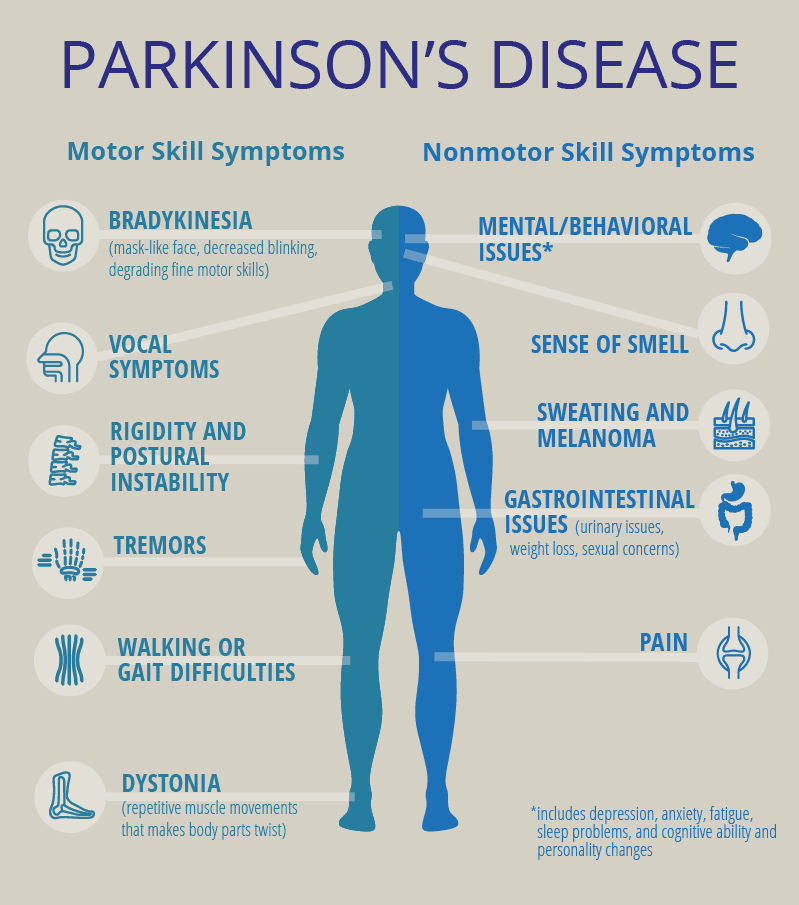
Currently, there is not a clear understanding of the exact cause of Parkinsons disease psychosis, although certain brain chemicals and receptors are believed to play a role. In general, the condition is believed to be caused by either one of the following:
Side effect of dopamine therapy:
Although an exact causal relationship has not been established, some believe that this condition may be a side effect of dopaminergic therapy .2Dopaminergic therapy increases dopamine levels, helping improve motor symptoms in patients with Parkinsons disease. However, increasing dopamine levels can also cause chemical and physical changes in the brain that inadvertently lead to symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions.
Natural outcome of the disease:
This condition can be triggered by changes in the brain that occur regardless of taking dopamine enhancing medication. Some of these changes occur naturally as Parkinsons disease progresses.2
Also Check: What’s New In Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Psychosis
Two of the most prominent symptoms are hallucinations and delusions.7 Hallucinations involve seeing, hearing, experiencing or sensing things that are not really there. Delusions are false beliefs that are not based in reality. In describing symptoms of Parkinsons disease psychosis, patients may use such common terms as: seeing things, paranoia, flashbacks, nightmares, false beliefs, or not being in touch with reality.8
Treatment Not A Must Early On
Typically, people with PD who develop psychosis dont do so until five to 10 years into their disease course, Dr. Hui says. For some, particularly early on, mild psychosis symptoms may be manageable without treatment. If the hallucinations are very mild and fleeting, we may not treat it if the patient is aware it is not real and can pretty much ignore them, she explains. We start treating when hallucinations become more severe or scary, like seeing attackers, or thinking someone is breaking in, and it interferes with activities of daily living or is emotionally distressing.
Read Also: What Is The Progression Of Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosing Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
To properly diagnose psychosis in Parkinsons, a health care provider will rule out other diseases and disorders that can also cause psychosis, such as dementia with Lewy bodies, schizophrenia, delirium, or major depression with psychosis.
PD psychosis can be a side effect of Parkinsons medicine. Psychosis can also emerge as part of the brain changes involved in Parkinsons as the disease progresses.
Once your health care provider has confirmed that the psychosis hasnt come from another disease or disorder, theyll also make sure of the following:
- The person with PD has, in fact, been experiencing hallucinations or delusions.
- Parkinsons symptoms began before any of the psychosis symptoms.
- The psychosis symptoms have been happening either continually or every now and then for at least one month.
Contraindicated Drugs For Parkinsons Patients
More than two dozen drugs should not be taken by Parkinsons patients because they alter the brains dopamine system. Always let your neurologist know before you have surgery, so he or she can work with your medical team to keep your Parkinsons in control. View a list of drugs that Parkinsons patients should not take.
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Be Detected By Mri
Psychosis And Dopamine Agonists
The majority of PDP symptoms are felt to be secondary to treatment with dopamine agonists, as the prevalence of psychotic symptoms dramatically rises with the addition of dopamine agonists. This is parsimonious and consistent with the general idea that psychosis is a consequence of increased dopaminergic transmission in the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway. In a cross-sectional retrospective study of PD patients with psychosis vs. age-matched controls without psychosis, there was a positive correlation found between psychosis and dementia, number of medications, and pergolide intake . In terms of medications, the adjusted odds ratio was calculated to be the highest with pergolide and the lowest with levodopa . This lack of association with levodopa is further supported by data showing that the relationship of PDP symptoms with mean levodopa and levodopa-equivalent may not be always established .
Another study using the administrative health care databases of Ontario, Canada, examined 10,347 individuals 66 years of age or older following recent initiation with dopaminergic therapy. The estimate for the cumulative probability of requiring an antipsychotic at 7 years was 35% 499 individuals were prescribed an antipsychotic within 1 year of starting dopaminergic therapy. This also suggests a role for dopaminergic treatment in the development of psychosis .
How Common Is Parkinson’s Disease Psychosis
Between 20-40% of people with Parkinsons report the experience of hallucinations or delusions.
When followed as the disease progresses over the years, this number increases. The increase does not mean that the hallucinations are persistent across the majority of people with PD. However, it is important to note that these statistics sometimes include delirium, in which the symptoms are temporary due to medication that needs to be adjusted or infection that needs to be treated, and isolated minor symptoms or minor hallucinations, including illusions, where instead of seeing things that are not there , people misinterpret things that are really there.
These are the most common types of psychosis in people with PD, with different studies placing the occurrence between 25-70% of people with Parkinsons. Typically, if the person with PD only has these minor hallucinations, their doctor will not prescribe an antipsychotic medication, though more significant psychosis that requires medication may develop over time. In one study, 10% of those with minor hallucinations had their symptoms resolved within a few years, while 52% saw their symptoms remain the same and 38% saw their psychosis symptoms get worse.
We recommend that people with Parkinsons not use a single percentage to represent the prevalence of hallucinations and PDP. Parkinsons is a complex disease and as it progresses the percentages and risk of symptoms will change.
Read Also: Michael J Fox Parkinson Diagnosis
Box 2 Treatment Strategy For Psychosis In Parkinsons Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
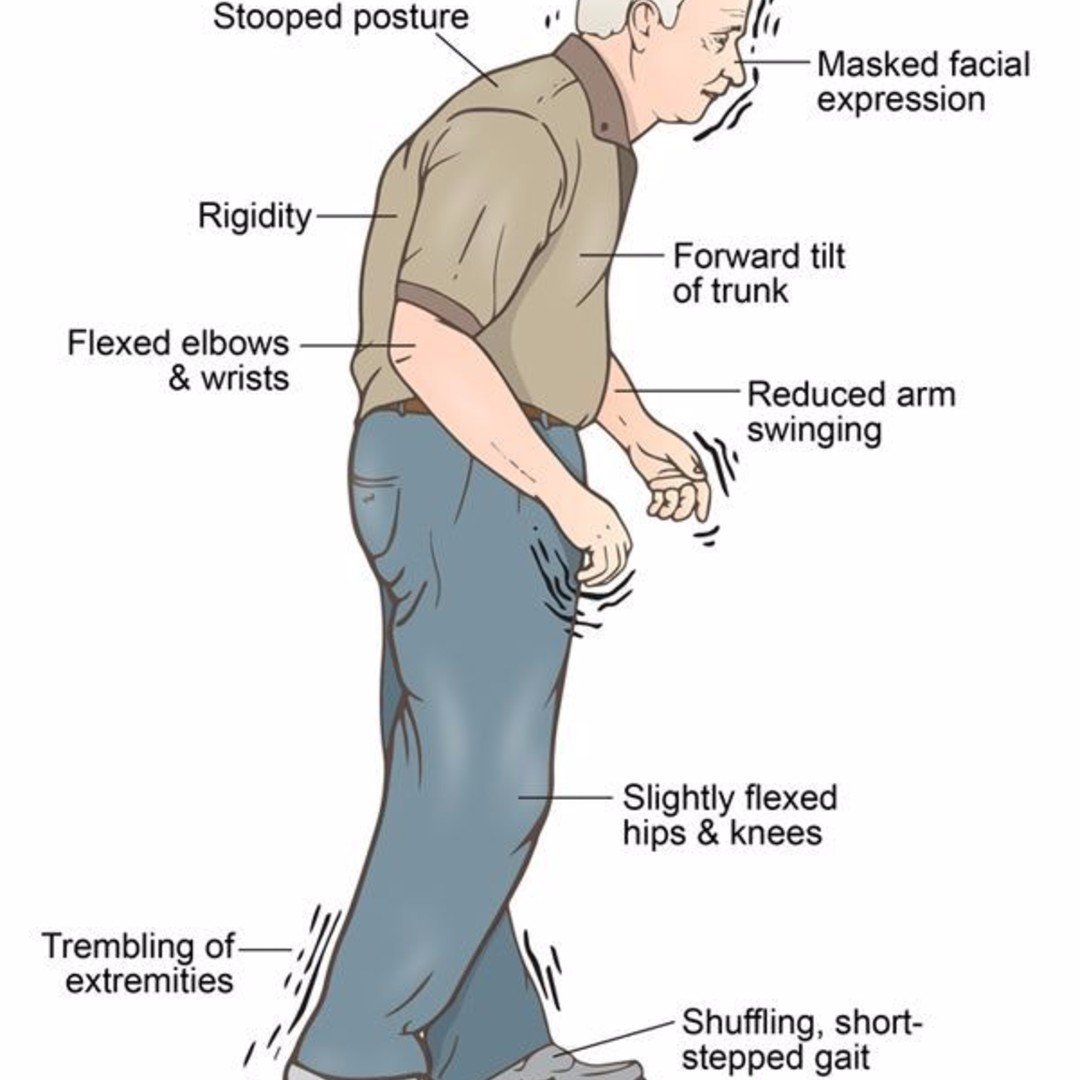
Parkinsons disease psychosis is a non-motor symptom of Parkinsons disease that causes patients to experience hallucinations and/or delusions.More than half of all patients with Parkinsons disease eventually develop symptoms over the course of their disease.1
Diagnosing and treating this condition can be complex. The condition relates to both neurology and psychiatry . For this reason, Parkinsons disease psychosis is considered a neuropsychiatric condition, since it deals with mental health symptoms caused by a disease of the nervous system .
Introducing an easier way to track your symptoms and manage your care.
Dont want to download the app? Use the non-mobile version here.
Also Check: How Prevalent Is Parkinson’s Disease
Motor And Nonmotor Symptoms Of Pd
At its core, PD is characterized by four cardinal symptoms: bradykinesia, rigidity, resting tremor, and postural instability.4 Along with these typical motor symptoms come many nonmotor symptoms with significant associated morbidity and mortality. These include autonomic dysfunction, disorders of sleep and wakefulness, cognitive dysfunction and dementia, mood disorders, and psychosis.5 These nonmotor symptoms of PD are responsible for a significant proportion of hospitalizations, with psychosis reportedly accounting for 24% of hospital admissions in patients with PD.6 This fact signifies the importance of properly managing patients with PD psychosis on both an inpatient and an outpatient basis.6
Drugs With Promise In The Treatment Of Parkinson Disease Psychosis
6.3.1. Quetiapine and Clozapine
Atypical antipsychotics can be used if, after other steps are taken, psychosis symptoms are still troubling and persistent. Clozapine is recommended and is the only antipsychotic with proven efficacy in PDP . Although in a randomized open-label trial of 45 patients with PDP, clozapine and quetiapine were shown to be equally effective in reducing psychotic symptoms, as measured by the BPRS, several subsequent randomized clinical trials demonstrated no change in psychotic outcomes with quetiapine . Neither worsened motor symptoms on the UPDRS.
In 2006, the American Academy of Neurology released guidelines for the treatment of PDP with atypical antipsychotics. These guidelines recommended the use of clozapine over quetiapine on the basis of a double-blind prospective cohort study because clozapine may improve both psychosis and motor function . Clozapine is considered the gold standard in the treatment of PDP. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence 2006 guidelines agree with the use of clozapine and quetiapine, and new guidelines are currently in draft form and are expected in 2017 .
6.3.2. Other Antipsychotics
6.3.3. Cholinesterase Inhibitors
6.3.4. Serotonin Agonists/Antagonists
6.3.5. Other Treatments
You May Like: What Does Azilect Do For Parkinson’s
Epidemiology And Risk Factors
Psychosis in PD generally occurs late in the disease, although there may be a bimodal onset, with early onset associated with motor fluctuations and large doses of drugs, and more commonly a late onset associated with cognitive impairment. Hospital based studies show prevalence rates of 8%40% for hallucinations in patients receiving long term treatment for PD.
Old age, cognitive impairment, history of depression, and sleep disorders are important risk factors for the development of psychosis in PD. Several drugs, including those used in treating PD can worsen or even precipitate psychosis in PD. The relation between the drug dose and psychosis in PD is complex. Underlying genetic susceptibility may be important. Interestingly, a recent study did not find antiparkinsonian drugs a risk factor for psychosis.
What Are The Types Of Parkinsons Hallucinations
Hallucinations can affect any of the five senses:
- Sight . Seeing something that isnt there, such as insects crawling on the walls or a deceased relative.
- Hearing . Hearing voices or sounds that arent real.
- Smell . Smelling an odor that isnt there, like cookies baking or a skunks spray.
- Feeling . Feeling imaginary things, like bugs crawling on your skin.
- Taste . Having a strange taste in your mouth that isnt from something youve eaten or a medical condition.
Some people sense the presence of a person or an animal nearby. Others see real objects transform into other things for example, a vase changes into a dog.
Its more common to have hallucinations at night, when the darkness creates shadows. Hallucinations can last anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes.
Early in the disease, most people with Parkinsons psychosis have insight, which means they understand that what theyre experiencing isnt real. Later in the disease, often people lose insight and believe that what they see, hear, or feel is real.
Don’t Miss: Is Double Vision A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Or Parkinsons Itself May Lead To Psychosis
In other cases, the disease’s progression, rather than its treatments, is likely at the root of psychosis, says Ling Pan, M.D., clinical assistant professor of neurology and neurosurgery at NYU Langone Health in New York City. Psychosis can be symptom of Parkinsons itself, so patients, for example, who have not been on medications you track the natural course of their disease may develop psychosis as part of the disease pathology. However, it appears PD medications do increase the risk, she adds.
What Causes Psychotic Symptoms
Psychotic symptoms in people with PD are usually caused as a side effect of medications used to treat PD.
All of the current PD medications can potentially cause psychotic symptoms. Hallucinations and delusions may also be caused by the chemical and physical changes that occur in the brain as a result of PD. 3
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Deep Brain Stimulation Success Rate
What Are Hallucinations
Hallucinations are seeing, hearing, or feeling something that is not actually there. Most hallucinations experienced in PD are visual, although some people experience auditory, tactile , or olfactory hallucinations.
Hallucinations occur when the person is awakenot sleeping or dreamingand can occur at any time of day or night. They can be frightening, for the patient experiencing them as well as their caregiver. Generally, hallucinations are repetitive and last for a short duration.1,3
How Can I Get Help

First and most importantly, if you find yourself experiencing symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions, speak out. It is essential to talk about your full range of Parkinsons disease symptoms with your treatment team. A dialogue among patients, care partners, and physicians is a critical component of the effective management of your condition.
References: 1. Forsaa EB, Larsen JP, Wentzel-Larsen T, et al. A 12-year population-based study of psychosis in Parkinsons disease. Arch Neurol. 2010 67:996-1001. 2. Ravina B, Marder I Neural Neursurg Psychiatry. 2011 70:734-738. 4. Fenelon G, Mahieux F, Huon M, Ziegler M. Hallucinations in Parkinsons disease: prevalence, phenomenology and risk factors. Brain. 2000 123:733-745. 5. Wolters ECh. PD- related psychosis: pathophysiology with therapeutical strategies. J Neural Transm. 2006 71:31-37. 6. Goldman JG, Holden S. Treatment of psychosis and dementia in Parkinsons disease. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2014 16: 281. 7. Goldman JG, Vaughan C, Goetz CG. An update expert opinion on management and researcl, strategies in Parkinsons disease psychosis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011 12:2009-2024. 8. Data on file, ACADIA Pharmaceuticals Inc. 9. Fenelon G, Alves G. Epidemiology of psychosis in Parkinsons disease. } Neurol Sci. 2010 289:12-17.
Don’t Miss: What Happens In Stage 5 Of Parkinson’s Disease
Adding Medication If Psychosis Symptoms Continue
Many people with Parkinsons psychosis will still have psychosis symptoms after making changes to their existing medication. These psychosis symptoms may be mild at this point, and the doctor may just want to monitor them for a while.
If hallucinations and delusions become serious, a health care provider may prescribe medications to manage these symptoms. Below are the primary drugs used to treat psychosis in people with Parkinsons:
- Pimavanserin is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of hallucination and delusions in Parkinsons psychosis. It is the first drug specifically approved to treat Parkinsons psychosis. Clinical trial results showed it was superior to a placebo for lessening hallucinations and delusions without increasing the motor symptoms of PD.
- Clozapine is an antipsychotic that usually does not significantly worsen the motor signs of PD. Two studies separately showed that clozapine works better than a placebo for psychosis in PD. Treatment with this drug requires frequent blood testing to monitor for serious side effects that may affect the bone marrow.
- Quetiapine is an antipsychotic approved by the FDA for schizophrenia, but it can be prescribed off-label to manage psychosis in PD. Doctors usually consider quetiapine when pimavanserin and clozapine are both ineffective in treating psychosis symptoms.
Another member shared, I am taking Seroquel for my hallucinations. No problems anymore.
