Deadlines Associated With Paraquat Lawsuits
Each state has a different statute of limitations to bring a paraquat lawsuit. If you fail to file a lawsuit within the statute of limitations, you are unlikely to be able to recover any compensation, no matter how strong your case is. And bringing a paraquat lawsuit is not the kind of thing you do at the last minute.
A good paraquat lawsuit attorney needs as much time in advance of filing as possible to build the foundation of their clients case. Proving that paraquat led to your Parkinsons disease requires lengthy investigations, medical documentation, lab tests, expert analysis, expert testimony, and more.
It is best to contact a lawyer as soon as possible after your Parkinsons diagnosis. The sooner they can begin working on your case, conducting an investigation, and building the link between your exposure to paraquat and your Parkinsons disease, the better chance you have of receiving compensation.
Family History & Genetics
Researchers have been able to identify certain genetic mutations that can increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
These are the two types of Parkinsons disease, from a genetic standpoint:
- Hereditary Parkinsons disease: Roughly 15% of all cases of Parkinsons disease are inherited. In these cases, mutations in certain genes are passed down through families and increase the individuals risk of developing this condition.
- Sporadic Parkinsons disease: On the other hand, cases in which people dont have a family history of Parkinsons disease are referred to as sporadic cases. These cases are in fact the majority. Scientists have found that alterations in certain genes may also play a role in sporadic cases, in addition to other environmental and lifestyle-related factors.
However, the role that these genetic mutations play in the development of the condition hasnt been fully understood yet.
Lewy Bodies And Alpha
In addition to the dopamine deficiency and neuronal loss, PD is also associated with a buildup of intracellular inclusions inside the neurons, called Lewy bodies. Studies have shown that the Lewy bodies are made mainly of a protein called alpha-synuclein.
They are not seen in brain imaging studies but have been detected in research studies that examine the brains of people who had PD and donated their own brains to science for the purpose of research. There is no known treatment or method of removing the Lewy bodies at this time.
In PD, Lewy bodies are found in the substantia nigra as well as other areas, including the amygdala and locus coeruleus , the raphe nucleus , and the olfactory nerve . The functions controlled by these regions can be impaired in PD, although the symptoms arent as noticeable as the tremors and muscle stiffness.
Lewy bodies are also present in the brains of people who have Alzheimers disease and other types of dementia, and they are considered a sign of neurodegeneration.
Read Also: Can Adderall Cause Parkinson’s
How Can We Manage Hallucinations
It may not be necessary to treat all hallucinations of a person with PDD. Hallucinations are often harmless, and it is okay to allow them to happen, as long as they are not disruptive or upsetting to the person or surroundings. Sometimes, recognizing the hallucination and then switching the topic might be an efficient way of handling frustrations that occur because of a hallucination. If hallucinations need medical treatment, your provider may be able to discuss and suggest some options. However, many of the medications used to treat hallucinations may make movement symptoms worse.
Molecular Mechanisms Of Autophagy
The molecular understanding of autophagy was initiated by pioneering work in yeast utilizing genetic screens that led to the discovery of autophagy-related genes, followed by the identification of homologs in higher eukaryotes. The corresponding Atg proteins can be divided into four major groups: the Atg1/unc-51-like kinase complex, two ubiquitin-like protein conjugation systems, the class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase /Vps34 complex I, and the Atg9/mATG9 transmembrane protein system . The target of rapamycin , a master regulator of nutrient and growth factor signaling, is one of the critical components involved in controlling the induction of autophagy . In most cell types, TOR activity is necessary and sufficient to suppress autophagy under favorable growth conditions, primarily in response to nitrogen. Other kinases, including protein kinase A, AMPK/Snf1, and Pho85, modulate autophagy in response to various types of stress.
The main product of the ubiquitin-like conjugation systems is the covalent attachment of Atg8 to phosphatidylethanolamine . Atg8PE becomes associated with both the inner and outer membrane of the phagophore. Once the autophagosome is complete, Atg8 is cleaved off of PE from the outer membrane, whereas the Atg8 on the inner membrane remains associated with PE and is degraded in the vacuole. Atg8 controls the size of the forming autophagosome , and is also involved in cargo recognition during selective autophagy .
Read Also: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
The Role Of P62 In Parkin
p62 connects ubiquitinated proteins to LC3 for autophagic degradation . As accumulation of p62 is strikingly elevated when autophagy is blocked, it is widely used as an autophagy marker. The loss of mitochondrial membrane potential promotes the accumulation of p62 on clustered mitochondria in a PARKIN-dependent manner. Whether p62 is required for mitophagy, however, is controversial and further studies are needed to determine its role .
Not Quite Ready For Humans
While the treatment is promising for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases in humans, it still needs to go through more rigorous testing before being ready for human trials. In the next steps, the researchers plan to test the method with other mouse models of Parkinsons disease. These models involve genetic changes rather than chemical destruction of dopamine neurons.
The researchers have also patented their treatment in hopes of moving it forward to testing in humans.
Its my dream to see this through to clinical trials, to test this approach as a treatment for Parkinsons disease, but also many other diseases where neurons are lost, such as Alzheimers and Huntingtons diseases and stroke, Fu says. And dreaming even bigger what if we could target PTB to correct defects in other parts of the brain, to treat things like inherited brain defects?
I intend to spend the rest of my career answering these questions, he says.
The study is published in Nature.
Also Check: When Was Muhammad Ali Diagnosed With Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Niehs Doing
NIEHS supports diverse research, involving experts from many disciplines, to uncover what may cause or help prevent Parkinsons disease. Varied methods are important because no one can predict which paths of study will provide major breakthroughs. Basic research on Parkinson’s will continue to help us advance our understanding of the disease. Highlights from NIEHS research are described below, grouped by environmental factors that may affect Parkinsons and by research approaches.
Pesticides
Mounting evidence, from animal and human studies, suggests that exposure to certain types of pesticides can increase a persons risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
Some people are more vulnerable to the harmful effects of pesticides because of their age or genetic makeup.
- Many studies identified genetic variations that provide insight into why certain people appear to be at higher risk of developing Parkinsons.
- Using data from the NIEHS-conducted Agricultural Health Study, researchers found that Parkinson’s risk from paraquat use was particularly high in people with a particular variant of a gene known as GSTT1.5
- Similarly, other research has indicated that people with lower levels of the PON1 gene, which is important for the metabolism of organophosphate pesticides, showed faster progression of the disease.6
Trichloroethylene
Head Injuries
Air Pollution
Diet and Lifestyle
Predicting Disease
Some of the risk factors and premotor symptoms that may be involved in Parkinson’s.
The Hypothesis: Mitochondria Dysfunction In Pd
Mitochondria are essential organelles that provide > 90% of the energy in all eukaryotic cells through oxidative phosphorylation . Mitochondria are also involved in various other processes such as calcium homeostasis and regulation of apoptosis . However, mitochondria are also the major source of cellular reactive oxygen species . Normal levels of ROS can be tolerated because of cellular antioxidants, whereas in pathological situations of mitochondrial respiratory defect, dramatic ROS production exceeds the capability of antioxidant protection and causes severe damage to a wide range of cellular components including mitochondria. Accumulation of this damage is related to aging, cancer, and recently to neurodegenerative diseases such as PD .
Familial variants of PD account for up to 10% of all cases . In familial PD, several genes have been linked to autosomal recessive or dominant Parkinson . These genes have been linked to mitochondrial function and several very recent studies have demonstrated that the corresponding gene products are involved in the selective removal of damaged mitochondria through autophagy . Thus, these proteins may provide a link between mitophagy and PD.
You May Like: Parkinsonian Syndrome Life Expectancy
Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
Mitophagy: Autophagic Mitochondrial Removal
As discussed above, autophagy can be highly specific. During autophagy, the phagophore gradually expands and engulfs a portion of the cytoplasm, or specific cargos, to form the double-membrane autophagosome . The diameter of a typical autophagosome is approximately 500 nm however, the mechanism of autophagosome formation, involving the sequential expansion of the phagophore, provides autophagy with the capacity to sequester essentially any cellular components, including entire organelles, and deliver them into the lysosome for degradation.
In higher eukaryotes, autophagy also plays a critical role in degrading mitochondria. In fact, mitochondria were first detected inside an autophagosome in the 1950s however, a molecular understanding of this process is occurring only now. Studies suggest that the selective removal of mitochondria, especially damaged mitochondria, is part of an important homeostatic pathway for organelle quality control. Since mitochondria function is compromised in some PD models, a defect in mitochondria quality control may play a critical role in the pathogenesis of PD.
Recommended Reading: Freddie Roach Illness
How Can We Support The Sleep/wake Cycle Of Pdd
For people with PDD who are confused about the day-night cycle, some daily strategies can be helpful. At night, starting a lights out routine that happens at the same hour every day, where all curtains are closed and lights are turned off, can help the person understand that it is sleep time. During the day, opening the curtains, allowing the person with PDD to spend as much time in the daylight as possible, avoiding naps, and organizing stimulating activities, can be helpful. Having lots of calendars and clocks in every room might also help a person with PDD be less confused about the time of day.
Physiological Functions And Connections To Pd
Although autophagy is primarily a starvation response in yeast, in higher eukaryotic organisms, autophagy is involved in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes, including responses to nutrient deprivation, development, intracellular clearance, suppression of tumor formation, aging, cell death and survival, and immunity . As a primary protective mechanism that maintains nutrient and energy homeostasis in response to stress, dysregulation of autophagy underlies the pathophysiologies of many diseases. Increasing evidence suggests that dysregulation of autophagy results in the accumulation of abnormal proteins and/or damaged organelles, which is commonly observed in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer, Huntingtons, and Parkinsons diseases . Of note, autophagy is the only known mechanism that eukaryotic cells possess to degrade protein aggregates and damaged organelles that cannot be processed by the proteasome. Recent studies from transgenic mice, animal, and cell models of PD suggest the involvement of proteins genetically linked to autosomal dominant PD, particularly -synuclein and LRRK2, in the autophagy pathway . In addition, proteins related to recessive PD, such as PINK1 and PARKIN, have an important role in the process of mitophagy.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson Disease Life Expectancy
Scientists Have Made A Breakthrough In The Development Of A Nasal Spray For Parkinsons Disease Treatment
Researchers from the University of York have developed a new gel that can adhere to tissue inside the nose alongside the drug levodopa, helping deliver Parkinsons disease treatment directly to the brain.
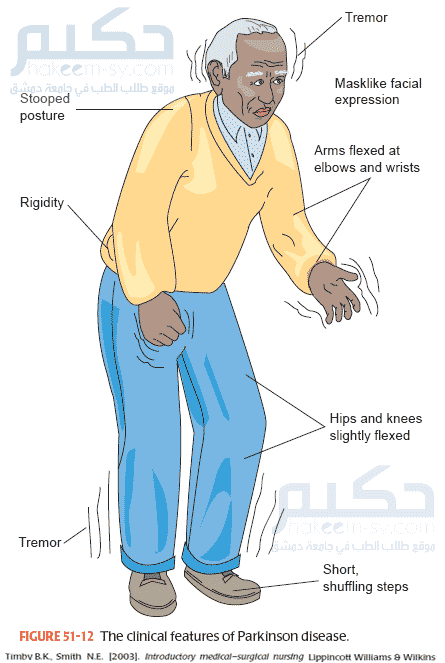
Parkinsons disease is a condition in which parts of the brain become progressively damaged over many years. This leads to a reduction in dopamine in the brain, which plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. The main symptoms include involuntary shaking, slow movement, and stiff and inflexible muscles.
Scientifically Backed Ways To Prevent Parkinsons Disease
Dopamine plays a major role in a variety of mental and physical functions, including:
- Voluntary movement
- Memory
- General behavior
Parkinsons now afflicts roughly 1.5 million people in the United States alone, with primary symptoms being body tremors, slow movement, rigid limbs, reduced memory, a shuffling gait and speech impairment. So we have to ask:
1.) What causes it?
2.) How do we prevent it?
Currently there isnt a known cure, and its not fully understood what causes the dip in dopamine however, we know that aging is the single most important risk factor for PD, with inflammation and stress contributing to cell damage. And we now know enough about the disease to understand the preventative measures that counter the aging and death of the neurons under attack.
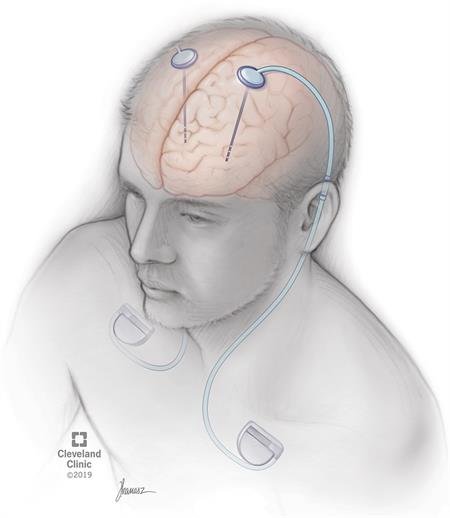
Because there is no known cure, its critical that we prevent the disease before symptoms arise. Granted, thanks to recent advancements in modern surgical procedures, there are some safe surgeries that can mitigate some of the more severe symptoms associated with PD. The most common one now is deep brain stimulation, in which they implant an electrode into the brain that can stop some of the more severe symptoms of Parkinsons.
But this article will try to keep it from getting to that point. The less drugs and surgery we can have in our lives, the better.
Recommended Reading: What Do Parkinson’s Patients Usually Die From
How To Diagnose Parkinson’s
Screening for mental health issues in the first visit to the neurologist is a must. In the busy clinics, the caretaker must proactively bring up issues pertaining to mental health so that they could be addressed. Usually, a multidisciplinary approach is needed to tackle mental health issues.
“An exercise program for victims of Parkinson’s disease helps boost their motivation and support groups help them overcome the depression. Appropriate medicines are added as per the need. Psychosis wherein Parkinson’s disease individuals lose touch with reality has to be dealt with sensitively. Caregivers and society need to be told that it is their faulty mind and not the original person that is behaving abnormally. Psychology, therapy, and drugs form the core of therapy,” addedAbhinay Huchche.
What If I Carry The Gene
There are ongoing clinical trials testing therapies to treat people who have Parkinson’s and carry certain gene mutations. Proving that it can be important to know which gene mutation you carry. Consult with your doctor when considering a genetic test to determine if you are eligible to participate in gene-based clinical trials.
The Parkinsons Foundation study, PD GENEration: Mapping the Future of Parkinsons Disease, is the first national study to offer genetic testing and counseling at no cost for those with a confirmed Parkinsons diagnosis. Learn more and enroll at Parkinson.org/PDGENEration.
*Please note that not all content is available in both languages. If you are interested in receiving Spanish communications, we recommend selecting both” to stay best informed on the Foundation’s work and the latest in PD news.
Read Also: Can Parkinson’s Run In The Family
How Is Age Related To Pdd
Both PD and PDD are more common with increasing age. Most people with PD start having movement symptoms between ages 50 and 85, although some people have shown signs earlier. Up to 80% of people with PD eventually develop dementia. The average time from onset of movement problems to the development of dementia is about 10 years.
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinson’s disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
You May Like: Parkinsons Disease Hereditory
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in deep parts of the brain called the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and are responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement. For reasons not yet understood, the dopamine-producing nerve cells of the substantia nigra begin to die off in some individuals. When 80 percent of dopamine is lost, PD symptoms such as tremor, slowness of movement, stiffness, and balance problems occur.
Body movement is controlled by a complex chain of decisions involving inter-connected groups of nerve cells called ganglia. Information comes to a central area of the brain called the striatum, which works with the substantia nigra to send impulses back and forth from the spinal cord to the brain. The basal ganglia and cerebellum are responsible for ensuring that movement is carried out in a smooth, fluid manner .
The action of dopamine is opposed by another neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. In PD the nerve cells that produce dopamine are dying. The PD symptoms of tremor and stiffness occur when the nerve cells fire and there isn’t enough dopamine to transmit messages. High levels of glutamate, another neurotransmitter, also appear in PD as the body tries to compensate for the lack of dopamine.
Living With Parkinson Disease

These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
- An exercise routine can help keep muscles flexible and mobile. Exercise also releases natural brain chemicals that can improve emotional well-being.
- High protein meals can benefit your brain chemistry
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help your ability to care for yourself and communicate with others
- If you or your family has questions about Parkinson disease, want information about treatment, or need to find support, you can contact the American Parkinson Disease Association.
You May Like: What Are The Four Cardinal Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease