What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Wolff
Individuals affected by Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome can experience palpitations, rapid heart rates, difficulty breathing, and lightheadedness as well as near loss of consciousness and complete loss of consciousness. For the most part, these symptoms occur all of a sudden and are not associated with warning signs. Usually, there are no dramatic triggers, however, caffeine, alcohol, and exercise can cause the heart to start racing.
Figure 1Open in new tab
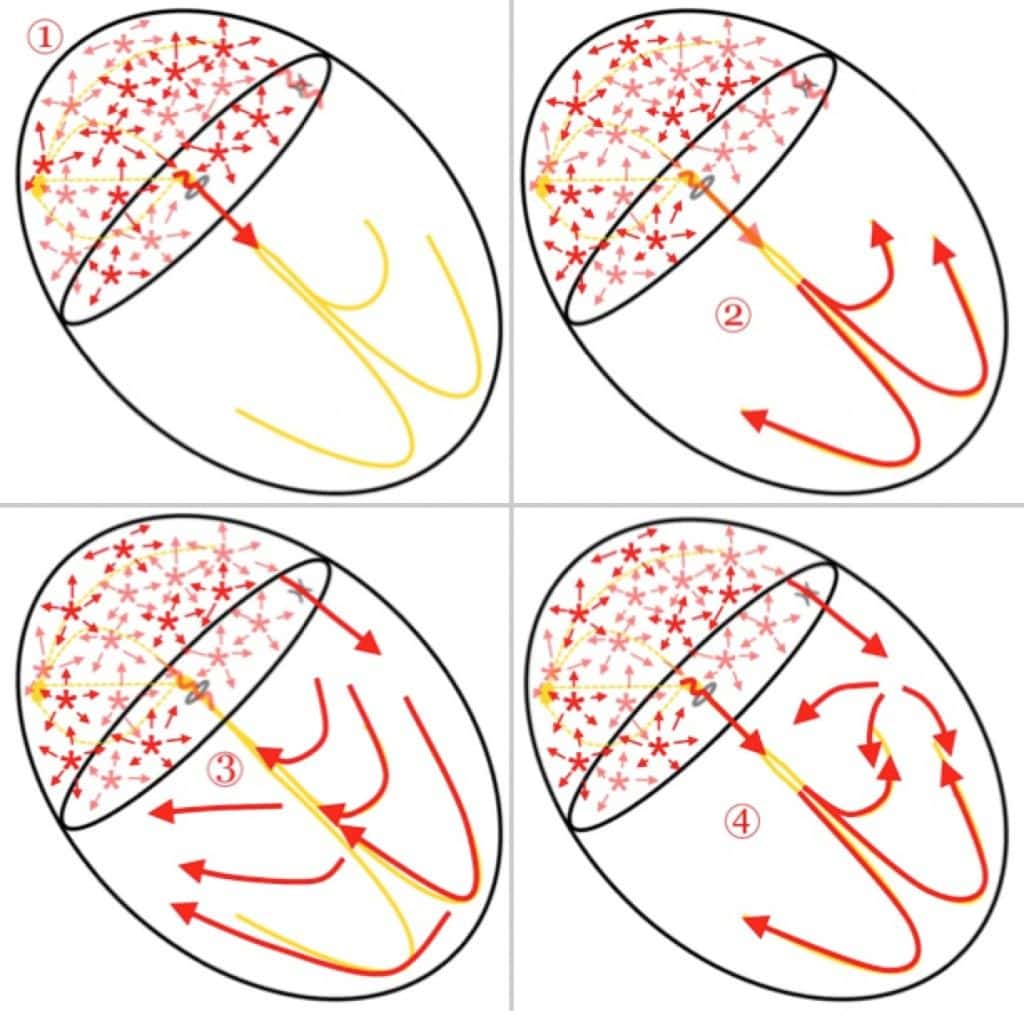
Atrial endocardial mapping sites. The upper part of the figure shows 12 endocardial mapping sites in the right atrium. The atrial endocardial electrograms were recorded in each patient from the anterior, lateral, posterior, and medial aspects of the high right atrium , mid right atrium , and low right atrium . SVC, superior vena cava IVC, inferior vena cava Ao, aorta PA, pulmonary artery LA, left atrium RV, right ventricle LV, left ventricle. The lower part of the figure shows two atrial endocardial electrograms to distinguish an abnormal atrial electrogram with 10 fragmented deflections and 130 ms in duration, from a normal atrial electrogram with two deflections and 80 ms in duration. Reprinted with permission from Centurion et al .
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you keep getting a fast or noticeable heartbeat . It’s important to get it checked out in case it could be something serious.
Dial 999 for an ambulance if:
- your heartbeat doesn’t go back to normal in a few minutes
- you have chest pain that lasts more than 15 minutes you may also have pain in your arms, back or jaw
- you have chest pain and other symptoms like feeling sick, being sick , shortness of breath or sweating
- someone passes out and doesn’t regain consciousness
If you’ve been diagnosed with WPW syndrome and you experience an episode, first try the techniques you’ve been taught or take any medication you’ve been given.
Dial 999 or go to your nearest accident and emergency department if these measures don’t stop the episode within a few minutes, or if someone you know has WPW syndrome and collapses or faints.
Understanding The Neurologic Control Of The Cardiac System
Before we explore this issue, lets first learn a bit about the autonomic nervous system and about the cardiac systems place within it. The ANS is part of the peripheral nervous system, a network of nerves throughout the body. The ANS exerts control over functions that are not under conscious direction such as respiration, heart function, blood pressure, digestion, urination, sexual function, pupillary response, and much more. The ANS is further subdivided into the parasympathetic nervous system and the sympathetic nervous system. Both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems regulate most major organs. Often, they have opposite effects, with the sympathetic nervous system activating a system and the parasympathetic system calming it down.
One of the systems controlled by the ANS is cardiac regulation. Blood pressure sensors, known as baroreceptors, reside in the heart as well as in the carotid artery, the major artery in the neck. If the baroreceptors sense a change in the blood pressure, a signal is sent to particular areas in the brain. From there, the autonomic nervous system sends signals to the heart to control heart rate and cardiac output. Signals are also sent to the blood vessels to change the size of their diameter, thereby regulating blood pressure.
Also Check: Is Peripheral Neuropathy A Symptom Of Parkinson’s Disease
Different Anatomical Sites Of The Accessory Pathway
The location of the AP was also related to the induction of AF. It was shown that patients with an anteroseptal AP had a high rate of inducible arrhythmia . Patients with a right free wall AP had a rather low rate of inducible arrhythmia . Patients with left free wall and posteroseptal AP had a 44 and 36% rate of induction, respectively. Patients with a right-sided AP had a lower inducibility of AVRT and a relatively long retrograde ERP over the AP. This allowed only relatively late PVCs to be conducted retrogradely over the AP to the atria, which might explain the lower rate of inducibility of AF in these patients.
Pearls And Other Issues
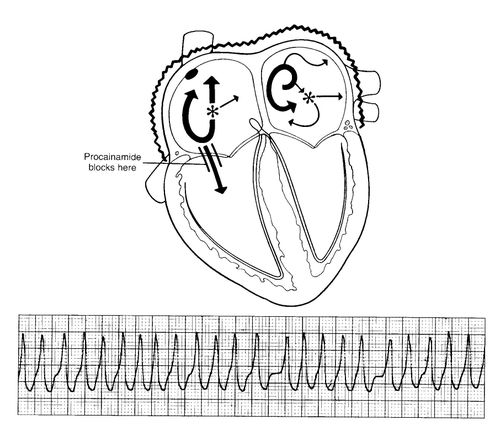
Patients with atrial fibrillation and rapid ventricular response are often treated with amiodarone or procainamide. Procainamide and cardioversion are accepted treatments for conversion of tachycardia associated with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In acute AF associated with WPW syndrome, the use of IV amiodarone may potentially lead to ventricular fibrillation in some reports and thus should be avoided.
AV node blockers should be avoided in atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In particular, avoid adenosine, diltiazem, verapamil, and other calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers. They can exacerbate the syndrome by blocking the hearts normal electrical pathway and facilitating antegrade conduction via the accessory pathway.
An acutely presenting wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be ventricular tachycardia if doubt remains about the etiology.
Don’t Miss: Is Parkinson’s A Fatal Disease
Treatment Of Atrial Fibrillation And Wpw Syndrome
-
Direct-current cardioversion
The treatment of choice for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is direct-current cardioversion Direct-Current Cardioversion-Defibrillation The need for treatment of arrhythmias depends on the symptoms and the seriousness of the arrhythmia. Treatment is directed at causes. If necessary, direct antiarrhythmic therapy, including antiarrhythmic… read more . The usual rate-slowing drugs used in atrial fibrillation are not effective, and digoxin and the nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers are contraindicated because they may increase the ventricular rate and cause ventricular fibrillation. If cardioversion is impossible, drugs that prolong the refractory period of the accessory connection should be used. IV procainamide or amiodarone is preferred, but any class Ia, class Ic, or class III antiarrhythmic drug Drugs for Arrhythmias The need for treatment of arrhythmias depends on the symptoms and the seriousness of the arrhythmia. Treatment is directed at causes. If necessary, direct antiarrhythmic therapy, including antiarrhythmic… read more can be used.
Bmi Affects Young Men’s Risk Of Early Atrial Fibrillation And Subsequent Health Outcomes After Diagnosis
by Wiley
A recent analysis published in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that rising body mass index in adolescent men is strongly associated with developing early atrial fibrillation, or an irregular heart rate, as well as with subsequent worse clinical outcomes after being diagnosed with atrial fibrillation.
The study included 1,704,467 young men enrolled in compulsory military service in Sweden from 1969 through 2005. During a median follow-up of 32 years, 36,693 cases of atrial fibrillation were recorded, at an average age of 52.4 years at diagnosis. Compared with men with a baseline BMI of 18.5< 20.0 kg/m2, men with a BMI of 20.0< 22.5 kg/ m2 had a 1.06-times higher risk of developing atrial fibrillation and those with a BMI of 40.050.0 kg/ m2 had a 3.72-times higher risk.
In men diagnosed with atrial fibrillation who were followed for a median of approximately 6 years, investigators identified 3,767 deaths, 3,251 cases of heart failure, and 921 cases of ischemic stroke. Compared with those with a baseline BMI of < 20 kg/ m2, those with a baseline BMI of > 30 kg/ m2 had 2.86-times, 3.42-times, and 2.34-times higher risks of these outcomes, respectively.
Explore further
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease Fatal
Assessment Of Atrial Conduction Times In Patients With Newly Diagnosed Parkinsons Disease
Yiit Çanga
Abstract
1. Introduction
Parkinsons disease has been associated with an increased risk of ischemic stroke and stroke-related mortality . A recent population-based, propensity score-matched longitudinal follow-up study demonstrated that newly diagnosed PD was related with an increased risk of developing ischemic stroke . Patients with atrial fibrillation have about 3- to 5-fold higher risk of stroke even after adjustment for risk factors . Atrial fibrillation has been associated with stroke in different patient populations . Prediction of atrial fibrillation may be crucial for risk stratification of PD patients with regard to ischemic stroke.
Prolonged atrial conduction times have been related to both onset and recurrence of atrial fibrillation . Tissue Doppler Echocardiography has been used to determine atrial electromechanical coupling and electromechanical delay intervals between different regions as indicators of electrical and/or structural remodeling of atria and as predictors of atrial fibrillation . Regional changes in atrial conduction times might have a different influence on surface p waves leading to an interlead variation in p-wave duration called p-wave dispersion . In the present study, we investigated atrial conduction parameters in patients with newly diagnosed PD and also evaluated their relationship with the severity of PD.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Echocardiography
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Disclosure
How Is Wpw Treated
Treatment depends on the type and frequency of arrhythmias, associated symptoms such as syncope, and presence of structural heart disease. Typically a physician will recommend an ablation procedure to further define the characteristics of the accessory pathway, and ultimately, to eliminate the pathway entirely.
- Observation If you have no symptoms, you may not require treatment. Your doctor may choose to have regular follow-up without treatment.
- Medications A variety of drugs are available to treat arrhythmias. Because everyone is different, it may take trials of several medications and doses to find the one that works best for you. It is important to know:
- The names of your medications
- What they are for
- How often and at what times to take them
Dont Miss: Foods Not To Eat With Parkinsons Disease
Read Also: What Are The Stages Of Parkinsons
Atrial Electrophysiological Responses Induced By Programmed Stimulation
AF can also be initiated by ectopic beats originating from the pulmonary veins and elsewhere. The pulmonary veins are well established as the dominant sources of triggers in PAF, in addition to their contribution to maintenance of AF. However, there is no available data suggesting that firing from the pulmonary veins is the main source of recurrent AF in WPW patients that had their AP ablated. The elimination of triggers of AF requires spontaneous firing to be readily identifiable during an ablation procedure. Ablation targeting the pulmonary veinleft atrial junction is effective in isolating the left atrium from proarrhythmic pulmonary vein activity. Despite the latest progress in AF ablation, there is limited knowledge of how to identify, map, and ablate the culprit atrial substrate in an individual patient, because AF is generally associated with locally complex electrograms of indefinable timing and sequence. This heterogeneity of substrate may explain why no single predetermined ablation technique is effective for all patients across the entire spectrum of AF. To the best of our knowledge, there is no detailed study addressing ablation of the pulmonary veins to suppress recurrent AF in WPW patients that had already undergone successful AP ablation.
Prevention Of Thromboembolism During Rhythm Control
Patients, particularly those in whom the current episode of atrial fibrillation has been present > 48 hours, have a high risk of thromboembolism for several weeks after pharmacologic or direct current cardioversion. If the onset of the current episode of atrial fibrillation is not clearly within 48 hours, the patient should be anticoagulated for 3 weeks before and at least 4 weeks after cardioversion regardless of the patients predicted risk of a thromboembolic event .
Alternatively, therapeutic anticoagulation is started, transesophageal echocardiography is done, and, if no left atrial or left atrial appendage clot is seen, cardioversion may be done, followed by at least 4 weeks of anticoagulation therapy.
If urgent cardioversion is required because of hemodynamic compromise, cardioversion is done and anticoagulation is started as soon as is practical and continued for at least 4 weeks.
If the onset of the current episode of atrial fibrillation is clearly within 48 hours, cardioversion may be done without prior anticoagulation if the patient has nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and is not at high risk of a thromboembolic event. After cardioversion, therapeutic anticoagulation is given for 4 weeks however, anticoagulation may not be necessary in patients at low risk of a thromboembolic event.
After 4 weeks of postconversion anticoagulation therapy, some patients require long-term anticoagulation .
Also Check: How Does Parkinson’s Affect The Mind
Data Source And Study Design
This study was conducted using the NHIRD data files maintained by the Health and Welfare Data Science Center . The NHIRD is a claims-based database managed by the National Health Insurance Administration of Taiwan Taiwan’s NHI provides coverage for 99% of its residents. The NHIRD files include inpatient, outpatient, and pharmaceutical claims and disease diagnoses coded according to the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification . In addition, the enrollment files of beneficiaries and providers were also included. The data in this study were from 2000 to 2015. Additionally, we linked the collected data with the national death registry to obtain death records. The two data sets can be linked according to the regulations of the HWDC. Both case-control and cohort studies were applied to examine the temporal relationship between PD and AF.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
AF is a huge financial burden on health care. Therefore, managing AF requires an interprofessional approach with close involvement of various health care professionals such as primary care physicians, cardiologists, electrophysiologists, neurologists, surgeons, pharmacists, and nursing staff.
Ensuring guideline-directed treatment of AF is pivotal in improving overall outcomes and reducing health care costs. Nurse-led, guideline-based clinics supported by appropriate software and cardiologists have shown superior results in cardiovascular mortality and hospitalizations. . Outpatient specialty AF clinics have shown better outcomes in AF-related hospitalizations and quality of life compared to usual care clinics. . Similar results have been seen with pharmacist-managed anticoagulation compared to telephone/usual care clinics. AF management guidelines published by the European Society of Cardiology have stressed the importance of integrated management in coordinating care and improving outcomes.
Also Check: How Do You Get Parkinsons
You May Like: What Is Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
Warning Disclaimer Use For Publication
WARNING: Please DO NOT STOP MEDICATIONS without first consulting a physician since doing so could be hazardous to your health.
DISCLAIMER: All material available on eHealthMe.com is for informational purposes only, and is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment provided by a qualified healthcare provider. All information is observation-only. Our phase IV clinical studies alone cannot establish cause-effect relationship. Different individuals may respond to medication in different ways. Every effort has been made to ensure that all information is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. The use of the eHealthMe site and its content is at your own risk.
If you use this eHealthMe study on publication, please acknowledge it with a citation: study title, URL, accessed date.
Read Also: Parkinsons Dbs Side Effects
Research Is Underway To Further Understand The Cardiac Effects Of Parkinsons
It is possible to image the sympathetic nervous system of the human heart by injecting a radioactive tracer, meta-iodo-benzyl-guanidine, . Development of this technique, known as MIBG cardiac imaging, holds much promise as a test to confirm the diagnosis of PD , to identify those who are at risk of developing PD in the future, and to distinguish PD from related disorders. MIBG cardiac imaging is still considered an experimental procedure for detection of PD and is not yet in use as a clinical tool for this purpose.
A recent research study was conducted in monkeys in which the destruction of the sympathetic nerves of the heart was chemically induced to mimic the changes that are seen in PD. The cardiac system was then imaged using a number of new-generation radioactive tracers, which bind to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. This model system may help to shed light on the molecular changes that accompany the loss of the sympathetic nerves of the heart and can also be used to track the response of the cardiac system to therapeutic agents.
Recommended Reading: What Happens In Stage 5 Of Parkinson’s Disease
Baseline Characteristics Of The Cohort
Study participants were followed up until December 31, 2017, and the mean follow-up duration was 3.35 ± 1.8 years. The baseline characteristics of the study population are summarized in Table . The mean age of all the participants was approximately 70 years and 40.2% of them were men. The proportion of patients with low income was higher in the PD group than in the control group . Compared with patients without PD, the patients with PD had greater number of comorbidities, including hypertension, DM, dyslipidemia, CHF, previous MI, stroke, PAD, COPD, and ESRD.
| Parkinsonâs disease |
|---|
You May Like: Motor And Non Motor Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Autonomic Nervous System And The Heart
In PD, there are two major reasons why the automatic control of the cardiac system is impaired. First, areas of the brain that control this system often contain Lewy bodies and have undergone neurodegeneration. In addition, the autonomic nervous system itself is directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration. This means, when the baroreceptors in the heart and carotid artery sense a drop in blood pressure and try to generate a signal to the heart and blood vessels to increase the blood pressure, the message may not get through. This results in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension , or drops in blood pressure upon standing due to autonomic nervous system dysfunction. There are no medications that can cure nOH by restoring the autonomic nervous system in PD. nOH however, can be treated. Read more about nOH and its treatments here.
Structural problems of the heart such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy are not thought to be part of the pathology of PD, although of course, could co-exist with PD.
Also Check: What Kind Of Medical Marijuana For Parkinson’s Disease
