Living With Parkinsons Disease
Depending on severity, life can look very different for a person coping with Parkinsons Disease. As a loved one, your top priority will be their comfort, peace of mind and safety. Dr. Shprecher offered some advice, regardless of the diseases progression. Besides movement issues Parkinsons Disease can cause a wide variety of symptoms including drooling, constipation, low blood pressure when standing up, voice problems, depression, anxiety, sleep problems, hallucinations and dementia. Therefore, regular visits with a neurologist experienced with Parkinsons are important to make sure the diagnosis is on target, and the symptoms are monitored and addressed. Because changes in your other medications can affect your Parkinsons symptoms, you should remind each member of your healthcare team to send a copy of your clinic note after every appointment.
Dr. Shprecher also added that maintaining a healthy diet and getting regular exercise can help improve quality of life. Physical and speech therapists are welcome additions to any caregiving team.
Why Is Dementia Progressive
Dementia is not a single condition. It is caused by different physical diseases of the brain, for example Alzheimers disease, vascular dementia, DLB and FTD.
In the early stage of all types of dementia only a small part of the brain is damaged. In this stage, a person has fewer symptoms as only the abilities that depend on the damaged part of the brain are affected. These early symptoms are usually relatively minor. This is why mild dementia is used as an alternative term for the early stage.
Each type of dementia affects a different area of the brain in the early stages. This is why symptoms vary between the different types. For example, memory loss is common in early-stage Alzheimers but is very uncommon in early-stage FTD. As dementia progresses into the middle and later stages, the symptoms of the different dementia types tend to become more similar. This is because more of the brain is affected as dementia progresses.
Over time, the disease causing the dementia spreads to other parts of the brain. This leads to more symptoms because more of the brain is unable to work properly. At the same time, already-damaged areas of the brain become even more affected, causing symptoms the person already has to get worse. Eventually most parts of the brain are badly damaged by the disease. This causes major changes in all aspects of memory, thinking, language, emotions and behaviour, as well as physical problems.
Apda In Your Community
APDAUncategorizedUnderstanding Weakness in Parkinsons disease
It is common for Parkinsons Disease patients to feel weak. They frequently describe their legs as feeling, like theyre made out of lead,like theyre in concrete. But they will also feel weak all over, or describe weakness in their hands or arms. In fact, when Parkinsons Disease patients are tested for strength they are normal but they do fatigue easier. That is, with repeated muscle contractions they do lose force, so it is more difficult for a Parkinsons Disease patient to do repetitive tasks.
When patients think about weakness in Parkinsons Disease they should recall that the original name for this disease was, The Shaking Palsy.Shaking refers to the tremor, of course, but palsy means weakness. James Parkinson called his monograph on the disease, The Shaking Palsy. Thus Parkinson, himself, called this disorder weakness and tremor, but substituted the technical terminology of his day. The coding book used for billing insurance companies calls Parkinsons Disease Paralysis agitans, meaning paralysis with tremor .
Although patients feel the weakness in their limbs, the problem is in the brain. Studies have shown that the actual, objectively measurable muscle weakness that occurs with repeated tasks improves with treatment of the dopamine deficit in the brain with Parkinsons Disease medications.
Don’t Miss: Life Expectancy For Parkinson’s
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Body
Life with Parkinsons is challenging, to say the least. This progressive disease starts slowly, and because theres currently no cure, it gradually worsens how you think and feel.
Giving up may seem like the only solution, but it certainly isnt. Thanks to advanced treatments, many people are able to continue living healthy, productive lives with Parkinsons.
Take a glance at this infographic to get a visual picture of how Parkinsons can affect everything from your memory to your movement.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson Fatal
Who Gets Parkinsons Disease
Estimates vary, but about 1 million people are living with Parkinsons disease in the U.S. Doctors diagnose about 60,000 cases a year, most in people over age 60. Younger people can also get Parkinsons. About 5-10% of patients have young-onset Parkinsons disease, diagnosed before age 50.
About 15% of patients have Parkinsons-plus syndromes, also known as atypical Parkinsons. Medications may be less effective for these syndromes, which can lead to disability sooner.
Risk factors for Parkinsons disease include:
- Age: Risk increases with age. Average age at diagnosis is 65.
- Gender: Men are at higher risk.
- Environmental exposure: Lifetime exposure to well water, which may contain pesticide runoff, can increase risk. So can exposure to air particles containing heavy metals, such as in industrial areas.
- Family history: Having a close relative with the disease could increase your risk. Researchers have identified a dozen genes that may be linked to Parkinsons disease.
- Sleep disorder: People who act out their dreams are up to 12 times more likely to develop Parkinsons disease. Its not clear whether this condition, called REM sleep behavior disorder or RBD, is a cause or symptom of Parkinsons disease.
- Head trauma: Traumatic brain injury increases risk of Parkinsons, even years later.
Precautionary Measures With Parkinson’s Disease
Many people 50-60 years of age experience slight tremors, especially in the hands. This is not Parkinson’s disease. If you are experiencing other symptoms, or shake movements getting worse, you should consult a doctor.
It should be noted that some Parkinson’s patients will suffer from depression, and it is important that both doctor and family are aware of this possibility, since the treatment of depression will give more energy and capacity to cope with the other effects of the disease.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
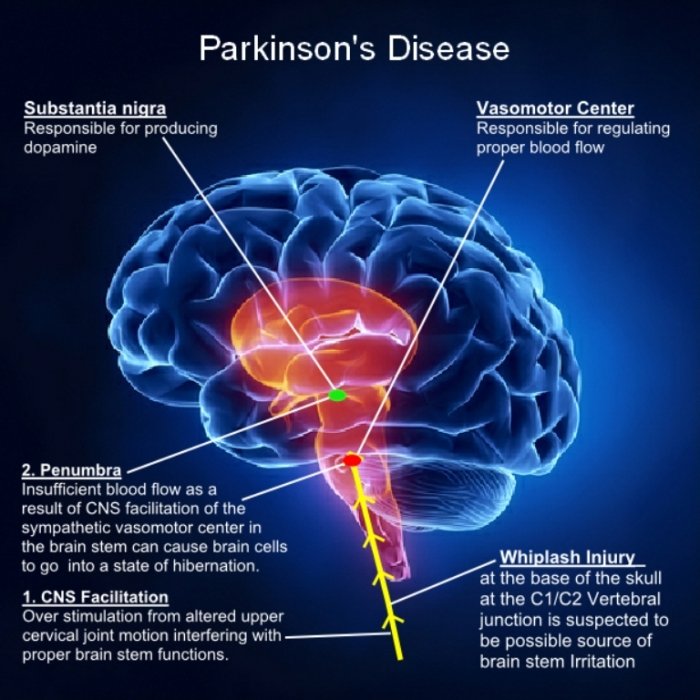
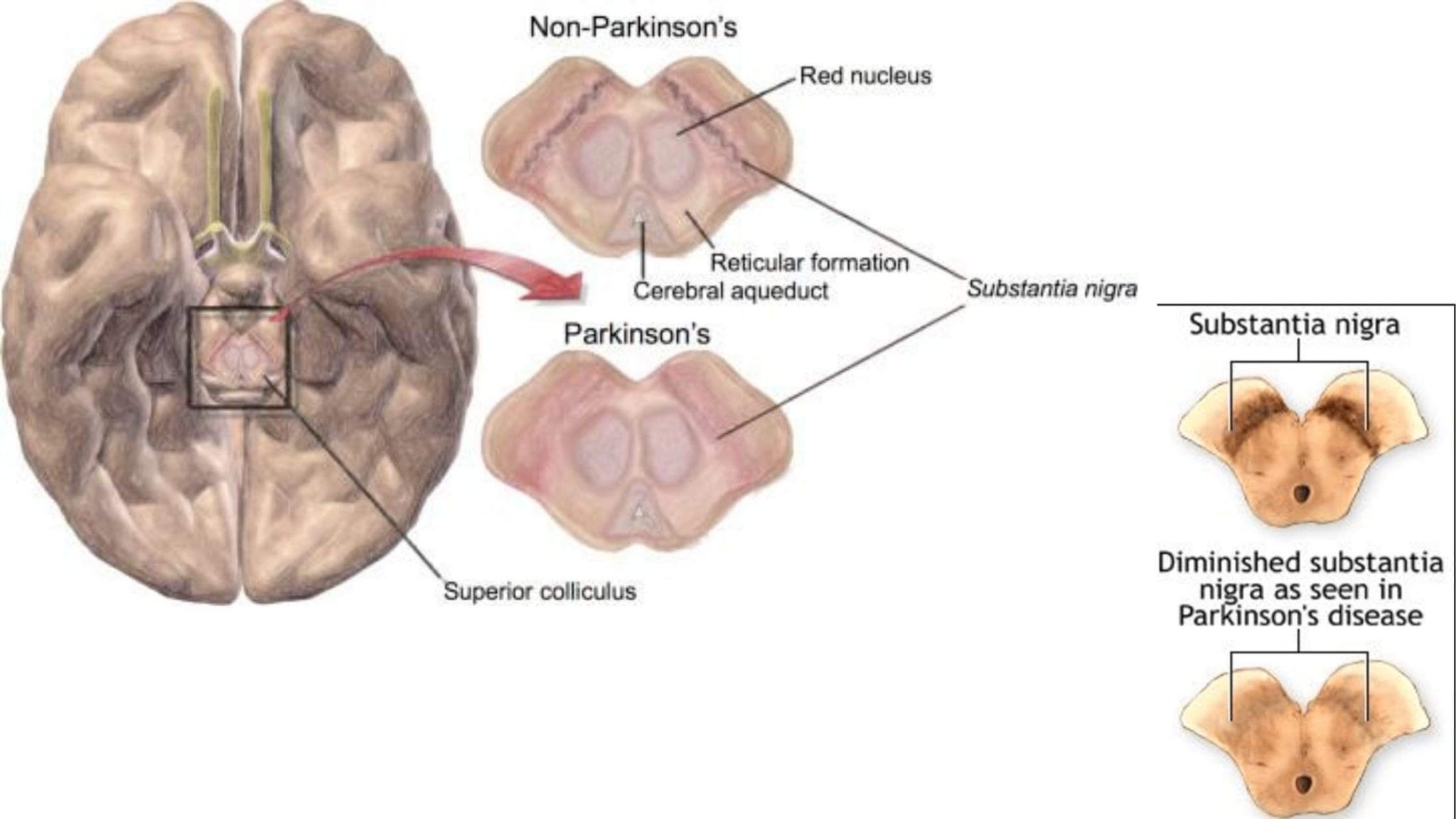
Beyond The Substantia Nigra
In Parkinsons, other areas of the brain beyond the substantia nigra are involved as the condition progresses. Changes in higher brain areas are linked to non-motor symptoms that can affect people with Parkinsons later on in the condition, and often have a significant impact on quality of life.
For instance, symptoms that affect memory and thinking can be linked to the presence of Lewy bodies in the largest area of the brain the cerebral cortex as well as the limbic system. The limbic system is also believed to be involved in symptoms involving mood and pain, and similar changes in the inferior temporal gyrus, an area of the brain involved in processing what we see, are thought to be the reason for hallucinations.
But research into the spread of Parkinsons through these areas, and how we can stop it , is just one side of the story. There is also ongoing research into where Parkinsons starts, and the effects it is having before it reaches these areas.
The presence of non-motor symptoms many months and maybe even years before the physical symptoms, such as tremor and slowness of movement, points towards the presence of other changes in the body long before the loss of dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra. These early symptoms could even help researchers predict those who will go on to be diagnosed with Parkinsons, which would help in the development of new and better treatments.
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Life Span
Incidence Of Parkinsons Disease
Its estimated that approximately four people per 1,000 in Australia have Parkinsons disease, with the incidence increasing to one in 100 over the age of 60. In Australia, there are approximately 80,000 people living with Parkinsons disease, with one in five of these people being diagnosed before the age of 50. In Victoria, more than 2,225 people are newly diagnosed with Parkinsons every year.
How Does Parkinson’s Affect The Body
The telltale symptoms all have to do with the way you move. You usually notice problems like:
Rigid muscles. It can happen on just about any part of your body. Doctors sometimes mistake early Parkinson’s for arthritis.
Slow movements. You may find that even simple acts, like buttoning a shirt, take much longer than usual.
Tremors. Your hands, arms, legs, lips, jaw, or tongue are shaky when you’re not using them.
Walking and balance problems. You may notice your arms aren’t swinging as freely when you walk. Or you can’t take long steps, so you have to shuffle instead.
Parkinson’s can also cause a range of other issues, from depression to bladder problems to acting out dreams. It may be a while before abnormal movements start.
Read Also: How To Donate To Parkinson’s Research
Which Medicines Are Used To Treat Parkinson’s Disease
Guidelines released by the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network recommend starting with a dopamine agonist, levodopa with a dopa-decarboxylase inhibitor or a monoamine-oxidase inhibitor. Other medicines are also sometimes used, usually in addition to one of these three main types of medication.
What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinson’s is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
You May Like: Sleep And Parkinson’s
The Importance Of Self
your
Self-care is so important. I am the only person with the whole picture. To me, self-care is everything I do to stay as healthy as possible with a disease that is a difficult life companion. It entails everything from making sure I take my medication in the optimal way, to eating healthily, getting enough sleep, to making sure I stay physically active.
How Parkinson’s Affects The Nervous System
Parkinson’saffects nerveNerve
It has long been understood that Parkinson’s disease does not just cause movement symptoms, but also causes a litany of non-motor symptoms with effects throughout the body. One of the organ systems that is affected is the cardiac system, encompassing the heart, as well as the major and minor blood vessels.
Secondly, what are the changes to the brain caused by Parkinson’s disease? The brain changes caused by Parkinson’s disease begin in a region that plays a key role in movement, leading to early symptoms that include tremors and shakiness, muscle stiffness, a shuffling step, stooped posture, difficulty initiating movement and lack of facial expression.
Similarly one may ask, does Parkinson’s affect your spine?
Low back pain and back of the neck pain are probably the most common pain conditions in PD. The reason Parkinson’s Disease patients have so many problems with their low back and their neck is their posture. Because of the stooped posture, the muscles in the lower back have to pull much harder to keep the spine upright.
Does stress cause Parkinson’s?
Research suggests that stressful life events may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease. In addition, animal studies indicate that stress damages dopamine cells, resulting in more severe parkinsonian symptoms. In humans, acute stress can worsen motor symptoms, including bradykinesia, freezing, and tremor.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons And Difficulty Eating
In the later stages of the disease, the muscles in your throat and mouth may work less efficiently. This can make chewing and swallowing difficult. It can also increase the likelihood of drooling or choking while eating.
Fear of choking and other eating problems may affect your nutrition. However, working with an occupational therapist or speech-language therapist may help you regain some control of your facial muscles.
Who Is Affected By Lewy Body Dementia
LBD is a disease associated with abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. These deposits, called Lewy bodies, affect chemicals in the brain whose changes, in turn, can lead to problems with thinking, movement, behavior, and mood. LBD is one of the most common causes of dementia, after Alzheimers disease and vascular disease.
Dementia is a severe loss of thinking abilities that interferes with a persons capacity to perform daily activities such as household tasks, personal care, and handling finances. Dementia has many possible causes, including stroke, tumor, depression, and vitamin deficiency, as well as disorders such as LBD, Parkinsons, and Alzheimers.
Diagnosing LBD can be challenging for a number of reasons. Early LBD symptoms are often confused with similar symptoms found in brain diseases like Alzheimers. Also, LBD can occur alone or along with Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease.
There are two types of LBD dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. The earliest signs of these two diseases differ but reflect the same biological changes in the brain. Over time, people with dementia with Lewy bodies or Parkinsons disease dementia may develop similar symptoms.
Recommended Reading: What Essential Oils Are Good For Parkinson’s Disease
Living With Parkinson Disease
These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
- An exercise routine can help keep muscles flexible and mobile. Exercise also releases natural brain chemicals that can improve emotional well-being.
- High protein meals can benefit your brain chemistry
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help your ability to care for yourself and communicate with others
- If you or your family has questions about Parkinson disease, want information about treatment, or need to find support, you can contact the American Parkinson Disease Association.
Role Of Pet Scans In Diagnosis
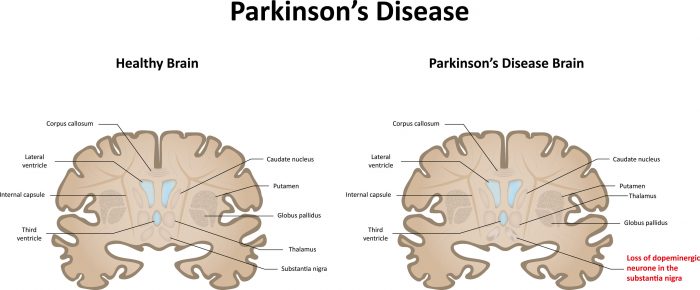
Scanning for loss of dopamine, the major chemical responsible for some symptoms of Parkinsons, permits comparison against scans of people who have no dopamine deficiency. By itself, a scan does not make the diagnosis of Parkinson’s but identifies the decline in dopaminergic neurones. It is used by experienced neurologists in cases where the diagnosis of Parkinsons is uncertain.Scans include radionuclide positron emission tomography or by injecting radiopharmaceutical agent in the brain) into a patients veins in a procedure referred to single photon emission computed tomography imaging.
PET scans typically focus on glucose metabolism, and DaT/SPECT scans focus on the activity of the dopamine transporter. Unfortunately, this decline is seen in conditions other than Parkinsons such as Multiple Systems Atrophy and Progressive supranuclear palsy .
Don’t Miss: Stages Of Parkinson’s Disease Life Expectancy
In The Loop: Staying Ahead Of Parkinsons Disease One Ping Pong Game At A Time
Since being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, Steve Grinnell has worked hard to stay active, stepping up his table tennis game and, thanks to co-workers, testing his skills outside his home.
Four years ago, Steve Grinnell’s life was forever changed when doctors at Mayo Clinic in Rochester diagnosed him with early-onset Parkinson’s disease. Since that time, the progressive nervous system disorder has begun to take a toll on Steve and his family, just as it does on the millions of other Americans living with the disease. “It has greatly diminished his quality of life, leaving him with tremors, physical exhaustion, impaired balance, troubled grasping things with his right hand, slow right-arm movement and problems sleeping,” the Rochester Post-Bulletin recently reported. “That’s to name just a few of his symptoms.”
Reading that, one might assume the disorder is winning. And to Steve, sometimes it feels like it is. But much of the time, he tells us he also feels like he’s staying one step ahead of the disease by staying as physically active as possible. “Parkinson’s presents such a conundrum because it wears you down physically, and yet exercise is so valuable,” Steve says. “My legs, feet and right arm are always cramping, so it takes mental effort to get moving.”
Increased Falls And Loss Of Balance
Parkinsons disease can alter your sense of balance and make simple tasks like walking seem more dangerous. When youre walking, be sure to move slowly so your body can rebalance itself. Here are some other tips to avoid losing your balance:
- Dont try to turn around by pivoting on your foot. Instead, turn yourself around by walking in a U-turn pattern.
- Avoid carrying things while walking. Your hands help your body balance.
- Prepare your home and remove any fall hazards by arranging furniture with wide spaces between each piece. The wide spaces will give you ample room to walk. Position furniture and lighting so that no extension cords are needed and install handrails in hallways, entryways, stairwells, and along walls.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
